Reproductive physiology (menstrual cycle, pregnancy)

On this page
🌙 The Menstrual Symphony: Orchestrating Life's Greatest Performance
The menstrual cycle is not merely a monthly event but a precisely timed cascade of hormonal signals, cellular transformations, and organ-level coordination that prepares the body for potential pregnancy while revealing fundamental principles of endocrine feedback and tissue remodeling. You'll trace how the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovaries, and endometrium communicate through shifting hormone levels to orchestrate follicle maturation, ovulation, and either menstruation or the dramatic physiological pivot into pregnancy. Mastering these interconnected phases equips you to interpret fertility patterns, diagnose menstrual disorders, manage contraception, and understand the profound maternal adaptations that sustain new life.
📌 Remember: HOPE for menstrual phases - Hypothalamic (GnRH), Ovarian (E2/P4), Pituitary (FSH/LH), Endometrial (proliferative/secretory). Each component must synchronize perfectly for reproductive success.
The cycle's 28-day average conceals remarkable individual variation, with normal cycles ranging 21-35 days. This variability reflects the complex interplay between genetic programming, environmental factors, and metabolic status. Women experience approximately 400 cycles during their reproductive lifetime, making cycle mastery essential for clinical practice.
| Cycle Phase | Duration (Days) | Dominant Hormone | FSH Level (mIU/mL) | LH Level (mIU/mL) | Estradiol (pg/mL) | Progesterone (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Menstrual | 1-5 | None | 3-12 | 2-10 | 25-75 | <1 |
| Follicular | 1-14 | Estradiol | 3-12 | 2-10 | 25-400 | <1 |
| Ovulatory | 13-15 | LH | 4-25 | 25-40 | 200-600 | 1-5 |
| Luteal | 15-28 | Progesterone | 1-9 | 1-12 | 75-300 | 2-25 |
| Pregnancy | Variable | hCG/Progesterone | <1 | <1 | 200-4000 | 10-90 |
-
Hypothalamic Control Center
- GnRH neurons fire in 90-minute pulses during follicular phase
- Pulse frequency increases to 60 minutes approaching ovulation
- Kisspeptin neurons integrate metabolic and circadian signals
- Body fat below 17% disrupts GnRH pulsatility
- Leptin levels must exceed 4 ng/mL for normal cycling
-
Pituitary Response Amplification
- FSH stimulates follicular development and aromatase activity
- LH surge reaches 25-40 mIU/mL triggering ovulation within 36 hours
- Gonadotroph sensitivity varies 10-fold across cycle phases
💡 Master This: Estradiol creates its own LH surge through positive feedback when levels exceed 200 pg/mL for 48+ hours. This self-triggering mechanism ensures ovulation occurs at peak fertility, demonstrating the cycle's elegant self-regulation.
Understanding menstrual cycle mechanics provides the foundation for mastering ovarian pathophysiology and hormonal contraception principles that follow.
🌙 The Menstrual Symphony: Orchestrating Life's Greatest Performance
⚡ Follicular Dynamics: The Ovarian Power Grid
📌 Remember: FADS for follicular stages - First (primordial), Activated (primary), Antral (secondary), Dominant (graafian), Surge responsive. Each stage requires specific hormonal signals and growth factors for progression.
The dominant follicle emerges through superior FSH sensitivity and enhanced aromatase activity. By cycle day 8-10, the leading follicle reaches 10-12 mm diameter and begins producing significant estradiol (>100 pg/mL). This estradiol surge suppresses FSH through negative feedback, starving competing follicles and ensuring single ovulation.
| Follicle Stage | Size (mm) | Duration (Days) | FSH Requirement | Key Features | Atresia Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primordial | 0.03 | Dormant | None | Single oocyte layer | 99.9 |
| Primary | 0.04-0.2 | 85 | Low | Cuboidal granulosa | 95 |
| Secondary | 0.2-2 | 70 | Moderate | Antral formation | 90 |
| Early Antral | 2-5 | 25 | High | Multiple antra | 85 |
| Dominant | 5-20 | 14 | Variable | LH receptors | 0-20 |
-
Follicular Recruitment Mechanisms
- 15-20 follicles begin development each cycle regardless of FSH levels
- Growth factors (IGF-1, activin, inhibin) modulate FSH sensitivity
- Apoptosis eliminates 99.9% of follicles through atresia
- Bcl-2 family proteins regulate follicular survival
- Oxidative stress accelerates age-related follicle loss
-
Dominant Follicle Selection
- Occurs when leading follicle reaches 8-10 mm diameter
- Enhanced aromatase converts androgens to estradiol efficiently
- LH receptor acquisition enables luteinization capacity
- Granulosa cells express 1000x more LH receptors
- Theca cells maintain androgen production throughout
💡 Master This: The "two-cell, two-gonadotropin" model explains ovarian steroidogenesis - theca cells respond to LH producing androgens, while granulosa cells respond to FSH converting androgens to estradiol via aromatase. This cooperation enables the 100-fold estradiol increase during follicular phase.
Follicular dynamics mastery enables understanding of ovulation mechanisms and the precise hormonal triggers that coordinate reproductive timing.
⚡ Follicular Dynamics: The Ovarian Power Grid
🎯 Ovulation Precision: The Cellular Breakout Protocol
📌 Remember: SURGE for LH effects - Steroidogenesis shift, Ultimate maturation, Rupture preparation, Granulosa luteinization, Enzymatic activation. Each process must complete within 36 hours for successful ovulation.
Ovulation involves coordinated proteolytic breakdown of follicular wall components. The LH surge activates matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), particularly MMP-1 and MMP-13, which degrade collagen fibers. Simultaneously, prostaglandin E2 and F2α levels increase 5-10 fold, promoting smooth muscle contractions and inflammatory responses essential for follicle rupture.
| Ovulation Timeline | Hours Post-LH Peak | Key Events | Hormone Levels | Clinical Markers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-surge | -12 to 0 | Estradiol peak | E2: 200-600 pg/mL | Cervical mucus changes |
| Early surge | 0-12 | LH rise begins | LH: 10-25 mIU/mL | Mittelschmerz onset |
| Peak surge | 12-24 | Maximum LH | LH: 25-40 mIU/mL | BBT nadir |
| Ovulation | 24-36 | Follicle rupture | LH declining | Progesterone rise |
| Post-ovulation | 36-48 | Corpus luteum formation | P4: 1-5 ng/mL | BBT elevation |
-
Enzymatic Ovulation Cascade
- Collagenase activation weakens follicular wall structural integrity
- Hyaluronidase release dissolves cumulus-oocyte complex connections
- Plasminogen activator converts plasminogen to plasmin for fibrinolysis
- Plasmin activity increases 20-fold during ovulation
- Tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) prevent excessive proteolysis
-
Inflammatory Ovulation Response
- Prostaglandin synthesis increases 500% in pre-ovulatory follicles
- Complement activation promotes inflammatory cell recruitment
- Cytokine release (IL-1β, TNF-α) coordinates rupture timing
- COX-2 expression increases 100-fold in granulosa cells
- NSAIDs can inhibit ovulation when used during surge
💡 Master This: The cumulus-oocyte complex undergoes dramatic expansion during ovulation, increasing 10-fold in volume through hyaluronic acid accumulation. This expansion enables oocyte pickup by fallopian tube fimbriae and provides the first 6-8 hours of oocyte protection post-ovulation.
Understanding ovulation mechanics provides essential foundation for corpus luteum physiology and the progesterone-dominated luteal phase that determines pregnancy potential.
🎯 Ovulation Precision: The Cellular Breakout Protocol
🏗️ Luteal Architecture: The Progesterone Powerhouse
📌 Remember: LUTEAL for corpus luteum functions - Luteinization, Uterine preparation, Temperature elevation, Estrogen production, Angiogenesis, Lifespan determination. Each function requires precise hormonal coordination for reproductive success.
The corpus luteum develops the richest blood supply per gram of any tissue, with capillary density reaching 2,000 vessels/mm³. This vascularization enables massive steroid production but also creates vulnerability to ischemic regression. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression increases 50-fold during luteinization, promoting angiogenesis essential for progesterone synthesis.
| Luteal Phase Day | Progesterone (ng/mL) | Estradiol (pg/mL) | LH (mIU/mL) | Key Events | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 1-5 | 100-200 | 5-15 | Early luteinization | Implantation window opens |
| 4-6 | 5-15 | 150-250 | 2-8 | Peak angiogenesis | Endometrial receptivity |
| 7-9 | 15-25 | 200-300 | 1-5 | Maximum function | hCG rescue window |
| 10-12 | 10-20 | 150-250 | 1-5 | Functional plateau | Pregnancy detection |
| 13-14 | 2-5 | 75-150 | 2-10 | Luteolysis begins | Menstruation trigger |
-
Steroidogenic Luteal Machinery
- Cholesterol uptake increases 10-fold through LDL receptor upregulation
- Mitochondrial biogenesis expands steroid synthesis capacity
- Enzyme cascade converts cholesterol to progesterone via pregnenolone
- StAR protein facilitates rate-limiting cholesterol transport
- P450scc cleaves cholesterol side chain in 2-step process
-
Luteal Regression Mechanisms
- Prostaglandin F2α from endometrium triggers luteolysis
- Apoptosis activation through Fas/FasL pathway
- Vascular regression reduces blood flow by 80% within 24 hours
- Endothelin-1 causes vasoconstriction and ischemia
- Matrix metalloproteinases degrade vascular basement membrane
💡 Master This: Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) rescues the corpus luteum by mimicking LH action, maintaining progesterone production above 20 ng/mL through the first 8-10 weeks of pregnancy. Without hCG rescue by day 11-12 post-ovulation, prostaglandin F2α triggers irreversible luteolysis within 48 hours.
Luteal phase mastery enables understanding of pregnancy establishment and the critical hormonal transitions that determine reproductive outcomes.
🏗️ Luteal Architecture: The Progesterone Powerhouse
🔄 Endometrial Synchronization: The Uterine Calendar System
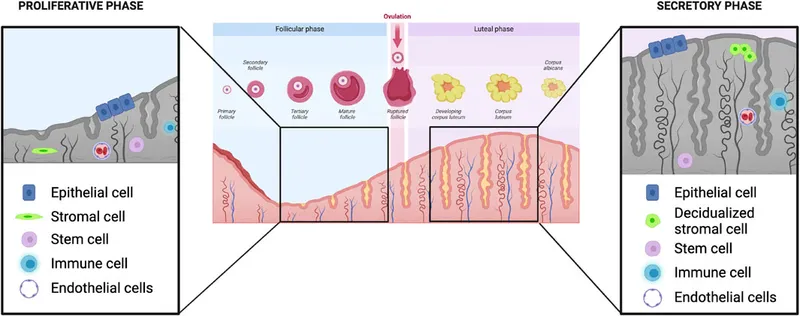
📌 Remember: PHASES for endometrial cycle - Proliferative (estrogen), Hyperplastic (peak estrogen), Active secretory (progesterone), Stable secretory (peak progesterone), Early breakdown, Shedding (menstruation). Each phase has distinct histological and molecular signatures.
The implantation window occurs during luteal days 6-10 when endometrial receptivity peaks. This window is characterized by pinopode formation, integrin expression changes, and cytokine secretion patterns that enable blastocyst attachment. Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) expression increases 20-fold during this period, serving as a critical implantation mediator.
| Endometrial Phase | Days | Thickness (mm) | Dominant Hormone | Key Features | Molecular Markers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Menstrual | 1-5 | 2-3 | None | Tissue breakdown | MMP-1, MMP-3 ↑ |
| Early Proliferative | 6-9 | 3-5 | Estradiol | Gland elongation | Ki-67 ↑, ER ↑ |
| Late Proliferative | 10-14 | 6-8 | Peak Estradiol | Mitotic activity | PCNA ↑, VEGF ↑ |
| Early Secretory | 15-19 | 8-10 | Progesterone | Gland coiling | PR ↑, IGFBP-1 ↑ |
| Mid Secretory | 20-24 | 10-12 | Peak Progesterone | Implantation window | LIF ↑, Integrin αvβ3 ↑ |
-
Proliferative Phase Mechanisms
- Estrogen receptor α activation drives DNA synthesis and mitosis
- Growth factors (IGF-1, EGF, FGF) amplify proliferative signals
- Angiogenesis increases vascular density 3-fold through VEGF
- Spiral arteriole development begins in basal layer
- Capillary sprouting extends into functional layer
-
Secretory Phase Transformation
- Progesterone receptor activation shifts metabolism to secretory
- Glycogen accumulation in glandular epithelium increases 10-fold
- Decidualization prepares stromal cells for potential pregnancy
- cAMP-dependent protein kinase activates decidual markers
- Prolactin and IGFBP-1 secretion increases 100-fold
💡 Master This: The "window of implantation" requires precise molecular synchronization between embryonic development and endometrial receptivity. Integrin αvβ3 expression peaks during luteal days 6-8, serving as a biomarker for endometrial receptivity and predicting IVF success rates with 85% accuracy.
Endometrial cycle mastery provides the foundation for understanding pregnancy physiology and the remarkable maternal adaptations that support fetal development.
🔄 Endometrial Synchronization: The Uterine Calendar System
🤰 Pregnancy Transformation: The Maternal Metamorphosis Engine
📌 Remember: PREGNANT for major adaptations - Plasma volume ↑50%, Respiratory rate ↑15%, EGFR ↑50%, Glucose tolerance ↓, Nausea (hCG), Aldosterone ↑, Nipple changes, Thyroid binding ↑. Each adaptation serves specific maternal-fetal needs.
Cardiovascular adaptations begin by week 6, with cardiac output increasing 30-50% through combined heart rate elevation (+15 bpm) and stroke volume increase (+30%). Blood volume expands 40-50% (1,500-2,000 mL increase), while systemic vascular resistance decreases 25% due to progesterone-mediated smooth muscle relaxation and placental arteriovenous shunting.
| System | Parameter | Non-Pregnant | Pregnant (Term) | Change (%) | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Cardiac Output (L/min) | 4.5-5.0 | 6.0-7.5 | +40-50% | Supports placental flow |
| Respiratory | Tidal Volume (mL) | 500 | 700 | +40% | Compensates for O2 demand |
| Renal | GFR (mL/min) | 120 | 180 | +50% | Handles increased waste |
| Hematologic | Plasma Volume (mL) | 2,600 | 3,800 | +45% | Dilutional anemia |
| Metabolic | Insulin Resistance | Baseline | 2-3x baseline | +200% | Diabetogenic effect |
-
Respiratory System Adaptations
- Diaphragmatic elevation (4 cm) reduces functional residual capacity 20%
- Minute ventilation increases 40% through tidal volume expansion
- Arterial PCO2 decreases to 27-32 mmHg creating respiratory alkalosis
- Compensatory bicarbonate reduction maintains pH 7.40-7.45
- Oxygen consumption increases 20% by term
-
Renal and Metabolic Changes
- Glomerular filtration rate increases 50% by second trimester
- Glucose threshold decreases causing physiological glucosuria
- Insulin resistance develops progressively, peaking in third trimester
- Placental hormones (hPL, cortisol) antagonize insulin action
- Maternal glucose sparing ensures fetal energy supply
💡 Master This: The 50% increase in maternal blood volume serves multiple functions: maintains perfusion pressure for 600-800 mL/min uteroplacental flow, provides reserve for delivery blood loss (500-1000 mL), and supports increased metabolic demands. This expansion begins by week 6 and plateaus by week 32-34.
Understanding pregnancy physiology provides essential foundation for recognizing normal versus pathological adaptations and managing maternal-fetal complications throughout gestation.
🤰 Pregnancy Transformation: The Maternal Metamorphosis Engine
🎯 Reproductive Mastery: The Clinical Command Center
📌 Remember: MASTER reproductive essentials - Menstrual timing (14-day luteal), AMH levels (ovarian reserve), Surge detection (LH peak), Temperature patterns (BBT), Estradiol thresholds (>200 pg/mL), Receptivity window (luteal days 6-10). These parameters guide 90% of reproductive interventions.
| Clinical Parameter | Normal Range | Clinical Significance | Diagnostic Use | Treatment Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle Length | 21-35 days | Ovulatory function | Regularity assessment | <21 or >35 days |
| AMH Level | 1.5-4.0 ng/mL | Ovarian reserve | IVF protocol selection | <1.0 ng/mL |
| LH Surge | 25-40 mIU/mL | Ovulation prediction | Fertility timing | Absent surge |
| Luteal Progesterone | >10 ng/mL | Corpus luteum function | Ovulation confirmation | <10 ng/mL |
| Endometrial Thickness | >7 mm | Implantation potential | IVF readiness | <7 mm |
-
Rapid Assessment Framework
- Day 3 FSH/LH ratio evaluates ovarian reserve and function
- Mid-luteal progesterone confirms ovulation and corpus luteum adequacy
- Thyroid function affects cycle regularity and fertility outcomes
- TSH should remain <2.5 mIU/L for optimal reproductive function
- Subclinical hypothyroidism reduces pregnancy rates 15-20%
-
Treatment Decision Matrix
- Ovulation induction for anovulatory cycles with clomiphene or letrozole
- Luteal support with progesterone for luteal phase defects
- Assisted reproduction for tubal factors, male factors, or unexplained infertility
- IVF success rates correlate with AMH levels and antral follicle counts
- Fresh transfer success: 35-40% under age 35, 15-20% over age 40
💡 Master This: Reproductive success depends on temporal precision - the 36-hour ovulation window, 6-day fertility period, 14-day luteal phase, and 6-day implantation window must align perfectly. Clinical interventions that optimize this timing improve pregnancy rates by 25-40% in fertility treatments.
Understanding reproductive physiology transforms complex hormonal interactions into practical clinical tools that optimize fertility outcomes and guide evidence-based reproductive interventions.
🎯 Reproductive Mastery: The Clinical Command Center
Practice Questions: Reproductive physiology (menstrual cycle, pregnancy)
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 26-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting. Her last menstrual period was 9 weeks ago. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine pregnancy consistent in size with a 7-week gestation. The hormone that was measured in this patient's urine to detect the pregnancy is also directly responsible for which of the following processes?










