Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 1: A 37-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He is being evaluated for high blood pressure readings that were incidentally recorded at a routine health maintenance examination 1 month ago. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. His pulse is 88/min and blood pressure is 165/98 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Serum studies show:
Na+ 146 mEq/L
K+ 3.0 mEq/L
Cl- 98 mEq/L
Glucose 77 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
His plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) to plasma renin activity (PRA) ratio is 36 (N = < 10). A saline infusion test fails to suppress aldosterone secretion. A CT scan of the adrenal glands shows bilateral adrenal abnormalities. An adrenal venous sampling shows elevated PACs from bilateral adrenal veins. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Propranolol therapy
- B. Unilateral adrenalectomy
- C. Amiloride therapy
- D. Bilateral adrenalectomy
- E. Eplerenone therapy (Correct Answer)
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Eplerenone therapy***
- The patient's presentation is consistent with **primary hyperaldosteronism** (resistant hypertension, hypokalemia, elevated PAC/PRA ratio, and non-suppression with saline infusion). The bilateral adrenal abnormalities on CT and elevated PACs from bilateral adrenal veins indicate **bilateral adrenal hyperplasia**.
- **Eplerenone** is a selective **aldosterone antagonist** that blocks the effects of aldosterone, making it the most appropriate medical therapy for bilateral adrenal hyperplasia.
*Propranolol therapy*
- **Propranolol** is a **beta-blocker** primarily used for hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias, but it does not specifically address the underlying pathology of primary hyperaldosteronism, which is excessive aldosterone production.
- While it can lower blood pressure, it would not correct the **hypokalemia** or the fundamental hormonal imbalance.
*Unilateral adrenalectomy*
- **Unilateral adrenalectomy** is the treatment of choice for **unilateral adrenal adenoma** (Conn's syndrome) causing primary hyperaldosteronism.
- In this case, the patient has **bilateral adrenal abnormalities** and elevated PACs from **bilateral adrenal veins**, indicating bilateral hyperplasia, which is not amenable to unilateral surgery.
*Amiloride therapy*
- **Amiloride** is a **potassium-sparing diuretic** that directly inhibits sodium channels in the collecting duct, thereby reducing potassium excretion.
- While it can help with **hypokalemia**, it is less effective than aldosterone antagonists like eplerenone in blocking the full spectrum of aldosterone's effects and is not the first-line pharmacologic treatment for bilateral adrenal hyperplasia.
*Bilateral adrenalectomy*
- **Bilateral adrenalectomy** would cure the hyperaldosteronism but would lead to **adrenal insufficiency**, requiring lifelong glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement.
- This invasive procedure is generally reserved for cases where medical management fails or specific genetic syndromes, and is not the first-line approach for bilateral adrenal hyperplasia given the availability of effective pharmacotherapy.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is studying patients with acute decompensated congestive heart failure. He takes measurements of a hormone released from atrial myocytes, as well as serial measurements of left atrial and left ventricular pressures. The investigator observes a positive correlation between left atrial pressures and the serum level of this hormone. Which of the following is most likely the mechanism of action of this hormone?
- A. Increases potassium excretion at the collecting ducts
- B. Constricts afferent renal arteriole
- C. Decreases sodium reabsorption at the collecting tubules (Correct Answer)
- D. Decreases reabsorption of bicarbonate in the proximal convoluted tubules
- E. Increases free water reabsorption from the distal tubules
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Decreases sodium reabsorption at the collecting tubules***
- The hormone described, exhibiting a positive correlation with left atrial pressure and released from atrial myocytes, is **Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)**.
- ANP promotes **natriuresis** (sodium excretion) and **diuresis** by directly inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubules, thereby reducing blood volume and cardiac preload.
*Increases potassium excretion at the collecting ducts*
- While ANP does promote fluid and electrolyte excretion, its primary effect is on sodium and water, not a direct increase in **potassium excretion**. **Aldosterone**, not ANP, primarily increases potassium secretion in the collecting ducts.
- This option describes a mechanism more consistent with **mineralocorticoid activity**, which is counteracted by ANP.
*Constricts afferent renal arteriole*
- ANP generally causes **vasodilation** of the afferent arteriole and constriction of the efferent arteriole, increasing glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- **Angiotensin II** is a primary constrictor of the afferent and efferent renal arterioles, which is the opposite effect of ANP.
*Decreases reabsorption of bicarbonate in the proximal convoluted tubules*
- This mechanism is primarily involved in **acid-base balance** and is influenced by factors like parathyroid hormone or respiratory/metabolic acidosis/alkalosis.
- ANP's main action is on **sodium and water balance**, not directly on bicarbonate reabsorption.
*Increases free water reabsorption from the distal tubules*
- **Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone, ADH)** is responsible for increasing free water reabsorption in the distal tubules and collecting ducts.
- ANP's action is to *increase* water excretion, working in opposition to ADH to reduce circulating fluid volume.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 3: A 64-year-old African American female comes to the physician's office for a routine check-up. The patient's past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes, and osteoarthritis in her right knee. Her medications include metformin, glimepiride, lisinopril, metoprolol, hydrochlorothiazide, and ibuprofen as needed. Her only complaint is an unremitting cough that started about 3 weeks ago and she has noticed some swelling around her mouth. The drug most likely responsible for her recent symptoms causes its primary renal hemodynamic effect on which part of the kidney?
- A. Collecting duct
- B. Distal convoluted tubule
- C. Juxtaglomerular cells
- D. Efferent arteriole (Correct Answer)
- E. Afferent arteriole
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Efferent arteriole***
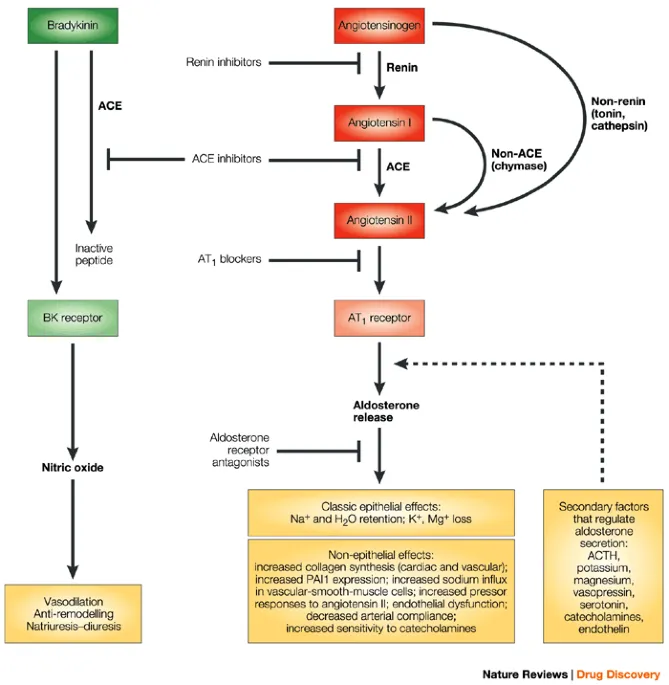
- The patient's symptoms of an **unremitting cough** and **angioedema** (swelling around her mouth) are classic side effects of **ACE inhibitors**, such as **lisinopril**.
- ACE inhibitors primarily exert their renal hemodynamic effects by **dilating the efferent arteriole**, leading to a decrease in intraglomerular pressure and glomerular filtration rate.
*Collecting duct*
- The collecting duct is the primary site of action for **vasopressin (ADH)** and **aldosterone**, regulating water and sodium reabsorption, respectively.
- While other medications like **thiazides** (used by the patient) affect distal tubules and collecting ducts indirectly, their direct impact on the collecting duct is not the cause of angioedema or cough.
*Distal convoluted tubule*
- The distal convoluted tubule is the main site of action for **thiazide diuretics** (e.g., hydrochlorothiazide), which inhibit the Na-Cl cotransporter.
- This tubule segment is not directly involved in the mechanism leading to angioedema or cough caused by ACE inhibitors.
*Juxtaglomerular cells*
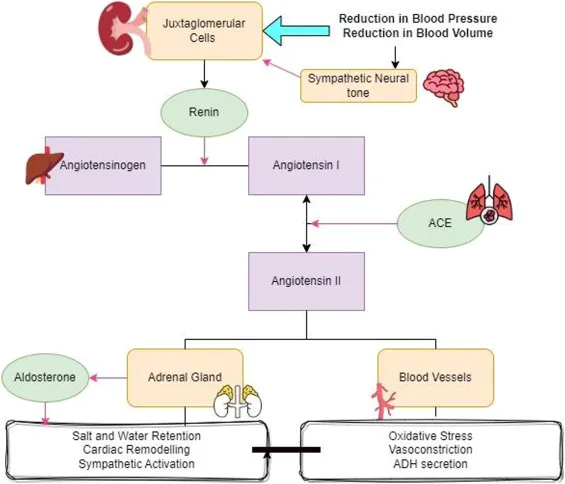
- Juxtaglomerular cells are responsible for producing **renin**, which is the initial step in the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)**.
- While ACE inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, they do not directly act on the juxtaglomerular cells themselves to cause their side effects.
*Afferent arteriole*
- The afferent arteriole is primarily regulated by **sympathetic tone** and local factors, and is the main site of action for medications like **NSAIDs** (e.g., ibuprofen, which the patient takes as needed).
- While NSAIDs cause **afferent arteriole constriction** and can impair renal function, they do not cause angioedema or a chronic cough.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 4: A 33-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for a wellness check-up. She states that recently she has been feeling well other than headaches that occur occasionally, which improve with ibuprofen and rest. She has a past medical history of hypertension and headaches and is currently taking hydrochlorothiazide. Her temperature is 99.2°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 157/108 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam reveals a young woman who appears healthy. A normal S1 and S2 are auscultated on cardiac exam, and her lungs are clear with good air movement bilaterally. From her previous visit, it was determined that she has an elevated aldosterone and low renin level. Laboratory values are ordered as seen below.
Serum:
Na+: 139 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 3.7 mEq/L
HCO3-: 29 mEq/L
BUN: 20 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.1 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Benign essential hypertension
- B. Pheochromocytoma
- C. Cushing syndrome
- D. Narrowing of the renal arteries
- E. Primary hyperaldosteronism (Correct Answer)
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Primary hyperaldosteronism***
- The patient presents with **hypertension**, **mild hypokalemia (K+ of 3.7 mEq/L)**, and **metabolic alkalosis (HCO3- of 29 mEq/L)**, which are classic signs of primary hyperaldosteronism.
- The elevated aldosterone and low renin levels, as noted from her previous visit, are diagnostic for primary hyperaldosteronism.
*Benign essential hypertension*
- While essential hypertension is common, the presence of **hypokalemia**, **metabolic alkalosis**, and particularly the **elevated aldosterone with low renin** points away from benign essential hypertension, which typically has normal renin-aldosterone ratios.
- This patient's hypertension is likely **secondary** due to a specific endocrine imbalance.
*Pheochromocytoma*
- This condition presents with **episodic or paroxysmal hypertension**, **tachycardia**, **sweating**, and headaches, often in a more dramatic fashion.
- The patient's blood pressure is consistently elevated, and she lacks the typical paroxysmal symptoms and signs of catecholamine excess.
*Cushing syndrome*
- Cushing syndrome is characterized by **hypertension**, central obesity, moon facies, buffalo hump, and striae, none of which are described.
- While it can cause hypertension, it is due to cortisol excess and does not typically present with the specific aldosterone-renin profile seen in this patient.
*Narrowing of the renal arteries*
- **Renal artery stenosis** causes **renovascular hypertension** and is associated with **elevated renin levels** as the kidney perceives hypoperfusion and activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
- This patient presents with **low renin levels**, which directly contradicts the pathophysiology of renal artery stenosis.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 5: A 42-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of confusion. His wife says he has been urinating more frequently than usual for the past 3 days. He has not had fever or dysuria. He has bipolar disorder, for which he takes lithium. His pulse is 105/min, and respirations are 14/min. He is lethargic and oriented only to person. Physical examination shows dry mucous membranes and increased capillary refill time. Laboratory studies show a serum sodium concentration of 158 mEq/L and an antidiuretic hormone (ADH) concentration of 8 pg/mL (N = 1–5). Which of the following is the most likely site of dysfunction in this patient?
- A. Hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus
- B. Descending loop of Henle
- C. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
- D. Collecting duct (Correct Answer)
- E. Posterior pituitary gland
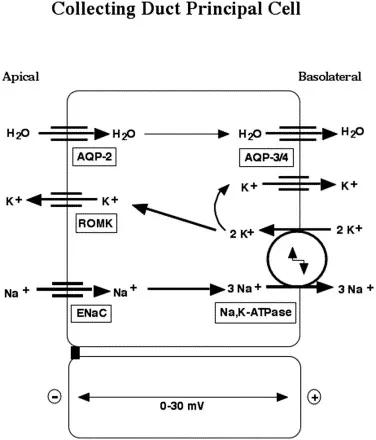
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Collecting duct***
- The patient presents with **hypernatremia** (Na 158 mEq/L), **polyuria**, and **dehydration** (dry mucous membranes, increased capillary refill time, confusion), indicative of **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus**.
- His ADH level is **elevated** (8 pg/mL), suggesting that the kidneys are not responding to ADH; the **collecting ducts** are the primary site where ADH exerts its effect via aquaporin-2 channels to reabsorb water.
- **Lithium**, which this patient is taking for bipolar disorder, is a well-known cause of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by interfering with ADH action at the collecting duct level.
*Hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus*
- This nucleus is responsible for synthesizing **ADH**. Dysfunction here would lead to **decreased ADH production** (central diabetes insipidus), but the patient's ADH level is elevated.
- A lack of ADH from this area would not explain the kidney's unresponsiveness to the high ADH levels observed.
*Descending loop of Henle*
- The descending loop of Henle is permeable to water but not directly responsible for ADH-mediated water reabsorption that is impaired in diabetes insipidus.
- Its primary role is to concentrate the filtrate as it descends into the hypertonic medulla.
*Juxtaglomerular apparatus*
- The juxtaglomerular apparatus regulates **blood pressure** and **glomerular filtration rate** through the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system**.
- While important for kidney function, it's not directly involved in the ADH-mediated water reabsorption whose impairment leads to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
*Posterior pituitary gland*
- This gland stores and releases ADH, which is synthesized in the hypothalamus.
- If the posterior pituitary were dysfunctional, it would lead to **decreased ADH release** (central diabetes insipidus), contradicting the patient's **elevated ADH level**.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 6: A new drug has been shown to block epithelial sodium channels in the cortical collecting duct. Which of the following is most likely to be decreased upon drug administration?
- A. Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules
- B. Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules
- C. Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules (Correct Answer)
- D. Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules
- E. Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules***
- Blocking **epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)** in the cortical collecting duct reduces sodium reabsorption, which in turn diminishes the electrochemical gradient driving **potassium secretion** into the lumen.
- This is because sodium reabsorption creates a more negative luminal charge, attracting potassium ions to move from the cell into the tubule.
- This is the mechanism of **potassium-sparing diuretics** like amiloride and triamterene.
*Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules*
- Urea **reabsorption** primarily occurs in the **medullary collecting duct** via urea transporters (UT-A1, UT-A3) and is influenced by the inner medullary osmolarity and ADH.
- Blocking ENaC would primarily affect sodium flux and potassium secretion, with minimal direct impact on urea reabsorption in the collecting duct.
*Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules*
- **Hydrogen ion (H+) secretion** occurs in the collecting tubules via intercalated cells (α-intercalated cells), which is important for acid-base balance.
- While blocking ENaC can indirectly reduce H+ secretion (by decreasing the lumen-negative potential), the primary and most significant effect is on **potassium secretion**, making this a less likely answer.
*Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules*
- The primary function of ENaC is to **reabsorb sodium** from the tubular lumen back into the blood, not to secrete it.
- Sodium is not normally secreted in the collecting tubules; blocking ENaC would decrease sodium **reabsorption**, not affect sodium secretion.
*Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule*
- **Sodium chloride reabsorption** in the distal convoluted tubule is mainly mediated by the **thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl co-transporter (NCC)**.
- ENaC are predominantly located in the cortical collecting duct (downstream from the DCT), so blocking them would not directly impact NaCl reabsorption in the distal tubule.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 7: A 63-year-old woman presents to your outpatient clinic complaining of headaches, blurred vision, and fatigue. She has a blood pressure of 171/91 mm Hg and heart rate of 84/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Her lab results include K+ of 3.1mEq/L and a serum pH of 7.51. Of the following, which is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Pheochromocytoma
- B. Renal artery stenosis
- C. Cushing’s syndrome
- D. Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn’s syndrome) (Correct Answer)
- E. Addison’s disease
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn’s syndrome)***
- The combination of **hypertension**, **hypokalemia (K+ 3.1 mEq/L)**, and **metabolic alkalosis (pH 7.51)** is highly characteristic of primary hyperaldosteronism.
- Excess aldosterone leads to increased sodium reabsorption and potassium/hydrogen ion excretion, causing these electrolyte imbalances.
*Pheochromocytoma*
- This condition involves episodic **hypertension**, palpitations, sweating, and anxiety due to catecholamine excess.
- While hypertension is present, the absence of paroxysmal symptoms and the specific electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia, alkalosis) make it less likely.
*Renal artery stenosis*
- This can cause **secondary hypertension** and occasionally hypokalemia, but it typically presents with **renal bruits**, and the metabolic alkalosis is not a direct or prominent feature.
- The elevated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis would lead to secondary hyperaldosteronism, but primary hyperaldosteronism is suggested by the overall clinical picture.
*Cushing’s syndrome*
- Cushing's syndrome is characterized by **central obesity**, striae, moon facies, and **hyperglycemia**, among other symptoms.
- While hypertension and hypokalemia can occur in severe cases, the predominant clinical features are not aligned with this patient's presentation.
*Addison’s disease*
- This condition is characterized by **adrenal insufficiency**, leading to hypoglycemia, **hyponatremia**, **hyperkalemia**, and **hypotension**.
- The patient's hypertension and hypokalemia directly contradict the typical presentation of Addison’s disease.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 8: Which mechanism primarily regulates sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct?
- A. Glomerulotubular balance
- B. Atrial natriuretic peptide
- C. Antidiuretic hormone
- D. Aldosterone (Correct Answer)
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Aldosterone***
- **Aldosterone** is the primary hormone that stimulates **sodium reabsorption** and **potassium secretion** in the principal cells of the collecting duct.
- It acts by increasing the synthesis and activity of **ENaC channels** on the apical membrane and **Na+/K+-ATPase pumps** on the basolateral membrane.
*Glomerulotubular balance*
- **Glomerulotubular balance** refers to the mechanism by which the **proximal tubule** reabsorbs a constant fraction of the filtered load, regardless of changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- This mechanism maintains a relatively constant delivery of fluid and solutes to downstream segments but does not primarily regulate sodium in the collecting duct.
*Atrial natriuretic peptide*
- **Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** primarily **inhibits sodium reabsorption** in the collecting duct, leading to **natriuresis** and **diuresis**, which is the opposite of sodium reabsorption.
- ANP is released in response to atrial stretch, indicating increased blood volume.
*Antidiuretic hormone*
- **Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)** primarily regulates **water reabsorption** in the collecting duct by increasing the insertion of **aquaporin-2 channels** into the apical membrane, making the collecting duct permeable to water.
- While ADH can indirectly affect sodium concentration by influencing water movement, it does not directly regulate sodium transport to the same extent as aldosterone.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 9: A previously healthy 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency room by his mother 5 hours after the onset of abdominal pain and nausea. Over the past 2 weeks, he has also had progressive abdominal pain and a 4-kg (8.8-lb) weight loss. The mother reports that her son has been drinking more water than usual during this period. Last week he wet his bed three times despite being completely toilet-trained since 3 years of age. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), pulse is 128/min, respirations are 35/min, and blood pressure is 95/55 mm Hg. He appears lethargic. Physical examination shows deep and labored breathing and dry mucous membranes. The abdomen is soft, and there is diffuse tenderness to palpation with no guarding or rebound. Serum laboratory studies show:
Na+ 133 mEq/L
K+ 5.9 mEq/L
Cl- 95 mEq/L
HCO3- 13 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 25 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
Urine dipstick is positive for ketones and glucose. Further evaluation is most likely to reveal which of the following?
- A. Serum glucose concentration > 600 mg/dL
- B. Increased total body sodium
- C. Increased arterial pCO2
- D. Hypervolemia
- E. Decreased total body potassium (Correct Answer)
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: **Decreased total body potassium**
- Despite **hyperkalemia** on serum labs, patients with **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** often have a **total body potassium deficit** due to increased renal losses and intracellular-to-extracellular shifts.
- The combination of polyuria, vomiting, and acidemia all contribute to significant potassium disturbances.
*Serum glucose concentration > 600 mg/dL*
- A glucose level of **over 600 mg/dL** is more characteristic of **hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS)**, not typically seen in pediatric DKA.
- While DKA involves hyperglycemia, severe dehydration and altered mentation typically occur at lower glucose thresholds in DKA.
*Increased total body sodium*
- Patients with DKA are typically **hypovolemic and hyponatremic** (even if serum sodium appears normal due to pseudohyponatremia) due to osmotic diuresis caused by hyperglycemia.
- There is no mechanism in DKA that would lead to an increase in total body sodium.
*Increased arterial pCO2*
- The patient's **deep and labored breathing (Kussmaul respirations)** is a compensatory mechanism to **blow off CO2** and correct the metabolic acidosis.
- Therefore, arterial pCO2 would be **decreased**, not increased.
*Hypervolemia*
- **Polyuria** (increased urination) due to osmotic diuresis and poor oral intake typically leads to **hypovolemia and dehydration** in DKA patients.
- The patient exhibits signs of dehydration such as dry mucous membranes, increased pulse, and low blood pressure.
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Department after 2 days of shortness of breath, orthopnea, and lower limb edema. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and a myocardial infarction 3 years ago that required a coronary arterial bypass graft. He has not been able to take prescribed medicine in several months due to recent unemployment and issues with insurance. On admission, his blood pressure is 155/92 mmHg, heart rate is 102/min, respiratory rate is 24/min, and temperature is 36.4°C (97.5°F). On physical examination there are fine rales in both lungs, regular and rhythmic cardiac sounds with an S3 gallop and a grade II/VI holosystolic murmur. Initial laboratory tests are shown below:
Na+ 140 mEq/L
K+ 4.2 mEq/L
Cl- 105 mEq/L
BUN 20 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
The patient is stabilized and admitted to the hospital. The next day his blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg, heart rate is 110/min, respiratory rate is 18/min, and temperature is 36.4°C (97.5°F). This morning's laboratory tests are shown below:
Na+ 135 mEq/L
K+ 3.2 mEq/L
Cl- 102 mEq/L
BUN 45 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.7 mg/dL
Which of the following best explains the changes seen in this patient?
- A. Urinary tract obstruction
- B. Diuretic therapy (Correct Answer)
- C. Chronic renal failure
- D. Glomerular basement membrane damage
- E. Cholesterol emboli
Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS Explanation: ***Diuretic therapy***
- The patient's initial presentation is consistent with **acute decompensated heart failure**, characterized by shortness of breath, orthopnea, lower limb edema, rales, S3 gallop, and a holosystolic murmur (likely mitral regurgitation due to ventricle dilation). The initial normal kidney function (BUN 20, creatinine 0.8) and electrolyte values support acute heart failure.
- The subsequent drop in blood pressure (155/92 to 110/60 mmHg), increase in heart rate (102 to 110/min), and significant rises in BUN (20 to 45 mg/dL) and creatinine (0.8 to 1.7 mg/dL) with a decrease in potassium (4.2 to 3.2 mEq/L) strongly suggest **diuretic-induced volume depletion** leading to worsened renal function (prerenal azotemia) and hypokalemia.
*Urinary tract obstruction*
- This would typically present with symptoms like **dysuria**, frequency, or hesitancy, and acute kidney injury with a more prominent rise in creatinine relative to BUN, none of which are described.
- Obstruction would be less likely to cause a significant drop in blood pressure and hypokalemia, as seen in this patient.
*Chronic renal failure*
- While kidney function has worsened, the initial labs showed normal kidney function, ruling out **chronic disease** as the cause of the acute deterioration.
- Chronic renal failure would typically present with elevated BUN and creatinine for an extended period, which is not the case here.
*Glomerular basement membrane damage*
- Conditions involving **glomerular damage**, such as glomerulonephritis, typically present with proteinuria, hematuria, and often hypertension, which are not detailed in this scenario.
- The acute changes in electrolytes and BUN/creatinine are more indicative of a **hemodynamic issue** rather than a primary glomerular pathology.
*Cholesterol emboli*
- While a patient with a history of CABG is at risk for **cholesterol emboli**, this condition typically causes acute kidney injury, livedo reticularis, eosinophilia, and digital ischemia, which are not described.
- It would not explain the rapid electrolyte shifts and clear signs of volume depletion seen in this patient.
More Sodium and potassium handling in RAAS US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.