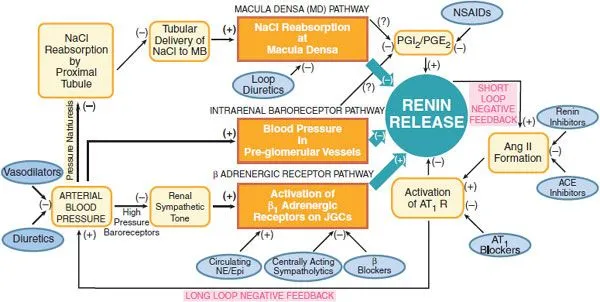
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Renin production and regulation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 1: A 60-year-old man presents to the office for a scheduled follow-up visit. He has had hypertension for the past 30 years and his current anti-hypertensive medications include lisinopril (40 mg/day) and hydrochlorothiazide (50 mg/day). He follows most of the lifestyle modifications recommended by his physician, but is concerned about his occasional occipital headaches in the morning. His blood pressure is 160/98 mm Hg. The physician adds another drug to his regimen that acts centrally as an α2-adrenergic agonist. Which of the following second messengers is involved in the mechanism of action of this new drug?
- A. Calcium ions
- B. Inositol triphosphate
- C. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- D. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (Correct Answer)
- E. Diacylglycerol
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Cyclic adenosine monophosphate***
- The physician likely added **clonidine or methyldopa**, both of which are **central α2-adrenergic agonists** used to treat hypertension.
- Activation of **α2-adrenergic receptors** leads to the **inhibition of adenylyl cyclase** and a decrease in **intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels**, which is the second messenger.
*Calcium ions*
- While calcium ions are crucial second messengers in many cellular processes, they are primarily involved in the mechanism of action of **α1-adrenergic receptors** and **voltage-gated calcium channels**, not directly inhibited by α2-agonists.
- **α2-adrenergic agonism** primarily acts to *reduce* neuronal excitability, which can indirectly affect calcium flux but does not directly involve calcium as the primary second messenger.
*Inositol triphosphate*
- **Inositol triphosphate (IP3)** is a second messenger primarily associated with the activation of **Gq protein-coupled receptors**, leading to the release of intracellular calcium.
- This pathway is characteristic of **α1-adrenergic receptors**, which cause vasoconstriction, and is antagonistic to the α2-agonist mechanism.
*Cyclic guanosine monophosphate*
- **Cyclic GMP (cGMP)** is a key second messenger in processes such as **vasodilation mediated by nitric oxide** and the action of ANP/BNP.
- **α2-adrenergic agonists** do not directly modulate cGMP levels as their primary mechanism of action.
*Diacylglycerol*
- **Diacylglycerol (DAG)** is a second messenger, along with IP3, produced from the hydrolysis of **PIP2** by phospholipase C, following activation of **Gq protein-coupled receptors**.
- This pathway is associated with **α1-adrenergic receptor activation**, not the inhibitory pathway initiated by central α2-adrenergic agonists.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 2: A 64-year-old African American female comes to the physician's office for a routine check-up. The patient's past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes, and osteoarthritis in her right knee. Her medications include metformin, glimepiride, lisinopril, metoprolol, hydrochlorothiazide, and ibuprofen as needed. Her only complaint is an unremitting cough that started about 3 weeks ago and she has noticed some swelling around her mouth. The drug most likely responsible for her recent symptoms causes its primary renal hemodynamic effect on which part of the kidney?
- A. Collecting duct
- B. Distal convoluted tubule
- C. Juxtaglomerular cells
- D. Efferent arteriole (Correct Answer)
- E. Afferent arteriole
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Efferent arteriole***
- The patient's symptoms of an **unremitting cough** and **angioedema** (swelling around her mouth) are classic side effects of **ACE inhibitors**, such as **lisinopril**.
- ACE inhibitors primarily exert their renal hemodynamic effects by **dilating the efferent arteriole**, leading to a decrease in intraglomerular pressure and glomerular filtration rate.
*Collecting duct*
- The collecting duct is the primary site of action for **vasopressin (ADH)** and **aldosterone**, regulating water and sodium reabsorption, respectively.
- While other medications like **thiazides** (used by the patient) affect distal tubules and collecting ducts indirectly, their direct impact on the collecting duct is not the cause of angioedema or cough.
*Distal convoluted tubule*
- The distal convoluted tubule is the main site of action for **thiazide diuretics** (e.g., hydrochlorothiazide), which inhibit the Na-Cl cotransporter.
- This tubule segment is not directly involved in the mechanism leading to angioedema or cough caused by ACE inhibitors.
*Juxtaglomerular cells*
- Juxtaglomerular cells are responsible for producing **renin**, which is the initial step in the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)**.
- While ACE inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, they do not directly act on the juxtaglomerular cells themselves to cause their side effects.
*Afferent arteriole*
- The afferent arteriole is primarily regulated by **sympathetic tone** and local factors, and is the main site of action for medications like **NSAIDs** (e.g., ibuprofen, which the patient takes as needed).
- While NSAIDs cause **afferent arteriole constriction** and can impair renal function, they do not cause angioedema or a chronic cough.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 3: A 42-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of confusion. His wife says he has been urinating more frequently than usual for the past 3 days. He has not had fever or dysuria. He has bipolar disorder, for which he takes lithium. His pulse is 105/min, and respirations are 14/min. He is lethargic and oriented only to person. Physical examination shows dry mucous membranes and increased capillary refill time. Laboratory studies show a serum sodium concentration of 158 mEq/L and an antidiuretic hormone (ADH) concentration of 8 pg/mL (N = 1–5). Which of the following is the most likely site of dysfunction in this patient?
- A. Hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus
- B. Descending loop of Henle
- C. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
- D. Collecting duct (Correct Answer)
- E. Posterior pituitary gland
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Collecting duct***
- The patient presents with **hypernatremia** (Na 158 mEq/L), **polyuria**, and **dehydration** (dry mucous membranes, increased capillary refill time, confusion), indicative of **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus**.
- His ADH level is **elevated** (8 pg/mL), suggesting that the kidneys are not responding to ADH; the **collecting ducts** are the primary site where ADH exerts its effect via aquaporin-2 channels to reabsorb water.
- **Lithium**, which this patient is taking for bipolar disorder, is a well-known cause of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by interfering with ADH action at the collecting duct level.
*Hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus*
- This nucleus is responsible for synthesizing **ADH**. Dysfunction here would lead to **decreased ADH production** (central diabetes insipidus), but the patient's ADH level is elevated.
- A lack of ADH from this area would not explain the kidney's unresponsiveness to the high ADH levels observed.
*Descending loop of Henle*
- The descending loop of Henle is permeable to water but not directly responsible for ADH-mediated water reabsorption that is impaired in diabetes insipidus.
- Its primary role is to concentrate the filtrate as it descends into the hypertonic medulla.
*Juxtaglomerular apparatus*
- The juxtaglomerular apparatus regulates **blood pressure** and **glomerular filtration rate** through the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system**.
- While important for kidney function, it's not directly involved in the ADH-mediated water reabsorption whose impairment leads to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
*Posterior pituitary gland*
- This gland stores and releases ADH, which is synthesized in the hypothalamus.
- If the posterior pituitary were dysfunctional, it would lead to **decreased ADH release** (central diabetes insipidus), contradicting the patient's **elevated ADH level**.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 4: A new drug has been shown to block epithelial sodium channels in the cortical collecting duct. Which of the following is most likely to be decreased upon drug administration?
- A. Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules
- B. Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules
- C. Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules (Correct Answer)
- D. Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules
- E. Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules***
- Blocking **epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)** in the cortical collecting duct reduces sodium reabsorption, which in turn diminishes the electrochemical gradient driving **potassium secretion** into the lumen.
- This is because sodium reabsorption creates a more negative luminal charge, attracting potassium ions to move from the cell into the tubule.
- This is the mechanism of **potassium-sparing diuretics** like amiloride and triamterene.
*Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules*
- Urea **reabsorption** primarily occurs in the **medullary collecting duct** via urea transporters (UT-A1, UT-A3) and is influenced by the inner medullary osmolarity and ADH.
- Blocking ENaC would primarily affect sodium flux and potassium secretion, with minimal direct impact on urea reabsorption in the collecting duct.
*Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules*
- **Hydrogen ion (H+) secretion** occurs in the collecting tubules via intercalated cells (α-intercalated cells), which is important for acid-base balance.
- While blocking ENaC can indirectly reduce H+ secretion (by decreasing the lumen-negative potential), the primary and most significant effect is on **potassium secretion**, making this a less likely answer.
*Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules*
- The primary function of ENaC is to **reabsorb sodium** from the tubular lumen back into the blood, not to secrete it.
- Sodium is not normally secreted in the collecting tubules; blocking ENaC would decrease sodium **reabsorption**, not affect sodium secretion.
*Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule*
- **Sodium chloride reabsorption** in the distal convoluted tubule is mainly mediated by the **thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl co-transporter (NCC)**.
- ENaC are predominantly located in the cortical collecting duct (downstream from the DCT), so blocking them would not directly impact NaCl reabsorption in the distal tubule.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 5: A new drug X is being tested for its effect on renal function. During the experiments, the researchers found that in patients taking substance X, the urinary concentration of sodium decreases while urine potassium concentration increase. Which of the following affects the kidneys in the same way as does substance X?
- A. Aldosterone (Correct Answer)
- B. Furosemide
- C. Spironolactone
- D. Atrial natriuretic peptide
- E. Hydrochlorothiazide
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Aldosterone***
- **Aldosterone** acts on the **principal cells** of the **collecting duct** to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
- This action leads to a decrease in urinary sodium concentration and an increase in urinary potassium concentration, matching the effects of drug X.
*Furosemide*
- **Furosemide** is a **loop diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-K-2Cl cotransporter** in the **thick ascending limb** of the loop of Henle.
- This inhibition leads to increased excretion of sodium, potassium, and water, resulting in higher urinary sodium concentration.
*Spironolactone*
- **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that blocks aldosterone's effects on the collecting duct.
- This leads to increased sodium excretion and decreased potassium excretion (potassium-sparing effect), which is the opposite of drug X.
*Atrial natriuretic peptide*
- **Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** is released in response to atrial stretch and causes **natriuresis** (increased sodium excretion) and **diuresis**.
- It works by dilating afferent arterioles and constricting efferent arterioles, increasing GFR, and inhibiting sodium reabsorption, thus increasing urinary sodium concentration.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- **Hydrochlorothiazide** is a **thiazide diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-Cl cotransporter** in the **distal convoluted tubule**.
- This leads to increased sodium and chloride excretion but typically causes potassium wasting (hypokalemia), which differs from the increased urinary potassium concentration seen with drug X.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 6: A 60-year-old male presents to the emergency room complaining of substernal chest pain. He reports a three-hour history of dull substernal chest pain that radiates into his left arm and jaw. He had a similar incident two months ago after walking one mile, but this pain is more severe. His past medical history is notable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. An EKG demonstrates non-specific changes. Serum troponins are normal. In addition to aspirin, oxygen, and morphine, he is started on a medication that releases nitric oxide. Which of the following is a downstream effect of this molecule?
- A. Guanylyl cyclase activation (Correct Answer)
- B. cAMP production
- C. L-type calcium channel inhibition
- D. ß1-adrenergic antagonism
- E. Prostaglandin synthesis inhibition
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Guanylyl cyclase activation***
- The medication releasing **nitric oxide (NO)** is **nitroglycerin**, an organic nitrate that undergoes bioconversion to release NO.
- **Nitric oxide** activates **soluble guanylyl cyclase** in vascular smooth muscle, leading to increased production of **cGMP (cyclic guanosine monophosphate)**.
- Increased cGMP causes **vascular smooth muscle relaxation**, resulting in **venodilation** (reducing preload) and **coronary vasodilation** (improving myocardial oxygen supply).
*cAMP production*
- **cAMP production** is mediated by **adenylyl cyclase**, typically activated by **beta-adrenergic receptors** or other G-protein coupled receptors.
- This is not the primary mechanism of nitric oxide signaling, which works through the cGMP pathway.
*L-type calcium channel inhibition*
- **L-type calcium channel inhibition** is the mechanism of action for **calcium channel blockers** (e.g., amlodipine, diltiazem, verapamil).
- These drugs directly block calcium channels, reducing cardiac contractility and vascular tone through a mechanism distinct from nitric oxide signaling.
*ß1-adrenergic antagonism*
- **ß1-adrenergic antagonism** is the primary mechanism of **beta-blockers** (e.g., metoprolol, atenolol), which reduce heart rate and myocardial contractility.
- This is a distinct pharmacological action unrelated to nitric oxide's downstream effects.
*Prostaglandin synthesis inhibition*
- **Prostaglandin synthesis inhibition** is the mechanism of action for **NSAIDs** including **aspirin**, which irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes.
- While aspirin is given to this patient for antiplatelet effects, it is not related to the nitric oxide-releasing medication.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 7: A physician is choosing whether to prescribe losartan or lisinopril to treat hypertension in a 56-year-old male. Relative to losartan, one would expect treatment with lisinopril to produce which of the following changes in the circulating levels of these peptides?
- A. Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease
- B. Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease
- C. Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase
- D. Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease (Correct Answer)
- E. Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease***
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor**, which directly blocks the conversion of **angiotensin I** to **angiotensin II**, leading to a decrease in circulating **angiotensin II** levels.
- ACE is also responsible for the breakdown of **bradykinin**, so inhibiting ACE with lisinopril will lead to an **increase in bradykinin** levels, contributing to vasodilation but also the characteristic cough.
*Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** (an ACE inhibitor) decreases **angiotensin II**, which in turn leads to a **decrease in aldosterone** synthesis and release, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase due to ACE inhibition, as ACE is involved in its degradation.
*Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** directly inhibits the enzyme responsible for producing **angiotensin II**, thus leading to its **decrease**, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase because its degradation pathway (via ACE) is blocked, not decrease.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase*
- **Lisinopril** reduces the negative feedback on **renin** release, leading to an **increase in renin** levels, not a decrease.
- While ACE is inhibited by lisinopril, this leads to an accumulation of its substrate, **angiotensin I**, resulting in an increase of angiotensin I.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase*
- As an ACE inhibitor, lisinopril would lead to an **increase in renin** due to reduced negative feedback from angiotensin II, not a decrease.
- **Angiotensin II** levels would **decrease** because its production from angiotensin I is directly inhibited by lisinopril.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is studying receptors that respond to epinephrine in the body and discovers a particular subset that is expressed in presynaptic adrenergic nerve terminals. She discovers that upon activation, these receptors will lead to decreased sympathetic nervous system activity. She then studies the intracellular second messenger changes that occur when this receptor is activated. She records these changes and begins searching for analogous receptor pathways. Which of the following receptors would cause the most similar set of intracellular second messenger changes?
- A. Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract
- B. Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system
- C. Vasopressin receptors in the kidney
- D. Dopamine receptors in the brain (Correct Answer)
- E. Aldosterone receptors in the kidney
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Dopamine receptors in the brain***
- The described presynaptic receptors for epinephrine that decrease sympathetic activity are **alpha-2 adrenergic receptors**, which are **G inhibitory protein (Gi)-coupled receptors**.
- Gi-coupled receptors **inhibit adenylyl cyclase**, leading to a **decrease in intracellular cAMP**, a signaling pathway shared by **D2 dopamine receptors**.
*Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract*
- Most muscarinic receptors (M1 and M3) in the GI tract are **Gq-coupled**, leading to an **increase in phospholipase C (PLC) activity**, ultimately increasing intracellular **IP3 and DAG** and promoting smooth muscle contraction.
- This mechanism is distinct from the **Gi-mediated inhibition of cAMP** described for the presynaptic adrenergic receptor.
*Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system*
- Growth hormone receptors are **tyrosine kinase-associated receptors** (specifically, they are linked to **JAK/STAT pathways**), not G protein-coupled receptors.
- Their intracellular signaling involves **protein phosphorylation cascades**, which are fundamentally different from second messenger changes involving cAMP.
*Vasopressin receptors in the kidney*
- Vasopressin (ADH) acts on **V2 receptors** in the kidney, which are **G stimulatory protein (Gs)-coupled receptors**.
- Activation of V2 receptors leads to an **increase in adenylyl cyclase activity** and thus an **increase in intracellular cAMP**, the opposite effect of the described Gi-coupled receptor.
*Aldosterone receptors in the kidney*
- Aldosterone receptors are **intracellular steroid hormone receptors** that directly bind to DNA and regulate gene transcription.
- They do not engage in rapid intracellular second messenger changes like G protein-coupled receptors, but rather alter **protein synthesis** over hours to days.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 9: Which mechanism primarily regulates sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct?
- A. Glomerulotubular balance
- B. Atrial natriuretic peptide
- C. Antidiuretic hormone
- D. Aldosterone (Correct Answer)
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Aldosterone***
- **Aldosterone** is the primary hormone that stimulates **sodium reabsorption** and **potassium secretion** in the principal cells of the collecting duct.
- It acts by increasing the synthesis and activity of **ENaC channels** on the apical membrane and **Na+/K+-ATPase pumps** on the basolateral membrane.
*Glomerulotubular balance*
- **Glomerulotubular balance** refers to the mechanism by which the **proximal tubule** reabsorbs a constant fraction of the filtered load, regardless of changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- This mechanism maintains a relatively constant delivery of fluid and solutes to downstream segments but does not primarily regulate sodium in the collecting duct.
*Atrial natriuretic peptide*
- **Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** primarily **inhibits sodium reabsorption** in the collecting duct, leading to **natriuresis** and **diuresis**, which is the opposite of sodium reabsorption.
- ANP is released in response to atrial stretch, indicating increased blood volume.
*Antidiuretic hormone*
- **Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)** primarily regulates **water reabsorption** in the collecting duct by increasing the insertion of **aquaporin-2 channels** into the apical membrane, making the collecting duct permeable to water.
- While ADH can indirectly affect sodium concentration by influencing water movement, it does not directly regulate sodium transport to the same extent as aldosterone.
Renin production and regulation US Medical PG Question 10: A 52-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after a motor vehicle accident. He was an unrestrained passenger who was ejected from the vehicle. On presentation, he is found to be actively bleeding from numerous wounds. His blood pressure is 76/42 mmHg and pulse is 152/min. Attempts at resuscitation fail, and he dies 25 minutes later. Autopsy shows blood in the peritoneal cavity, and histology of the kidney reveals swelling of the proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cells. Which of the following is most likely the mechanism underlying the renal cell findings?
- A. Decreased activity of caspase 7
- B. Increased activity of caspase 9
- C. Increased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase
- D. Increased activity of caspase 8
- E. Decreased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase (Correct Answer)
Renin production and regulation Explanation: ***Decreased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase***
- The patient experienced **hypovolemic shock** due to severe blood loss, leading to a significant drop in blood pressure and organ perfusion. This results in **ischemia** of the renal cells.
- **Ischemic injury** impairs ATP production, which is essential for the function of the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump**. Failure of this pump leads to intracellular accumulation of sodium and water, causing **cellular swelling**, particularly noticeable in the proximal convoluted tubules.
*Decreased activity of caspase 7*
- **Caspases**, including caspase 7, are involved in **apoptosis** (programmed cell death), which involves cell shrinkage and fragmentation, not the swelling observed here.
- Decreased caspase activity would generally *reduce* apoptosis, which is not the primary mechanism of acute cell injury in shock.
*Increased activity of caspase 9*
- Increased activity of **caspase 9** is indicative of the **intrinsic apoptotic pathway**, typically initiated by mitochondrial damage.
- While prolonged ischemia can eventually lead to apoptotic changes, the acute finding of **cellular swelling** points more directly to immediate membrane pump dysfunction due to ATP depletion.
*Increased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase*
- **Increased function** of the Na+/K+-ATPase would actively pump sodium out of the cell and potassium in, *preventing* intracellular swelling.
- This option contradicts the observed finding of proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cell swelling, which is characteristic of acute cellular injury due to pump failure.
*Increased activity of caspase 8*
- **Caspase 8** is a key initiator caspase in the **extrinsic apoptotic pathway**, often triggered by death receptor signaling.
- Similar to caspase 9, increased caspase 8 activity would lead to apoptosis, characterized by cell shrinkage, not the **cellular swelling** seen in acute ischemic injury.
More Renin production and regulation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.