RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for RAAS in blood pressure control. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 1: Which region of the nephron reabsorbs the highest percentage of filtered bicarbonate?
- A. Collecting duct
- B. Thick ascending limb
- C. Distal tubule
- D. Proximal tubule (Correct Answer)
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Proximal tubule***
- The **proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)** reabsorbs approximately 80-90% of the **filtered bicarbonate** through a process involving **carbonic anhydrase** and the **Na+/H+ exchanger**.
- This vital function ensures that the majority of bicarbonate, a key buffer, is returned to the blood to maintain **acid-base balance**.
*Collecting duct*
- While the collecting duct does have the ability to reabsorb and secrete bicarbonate, its contribution is minor compared to the PCT, primarily for fine-tuning acid-base balance.
- Cells in the collecting duct, particularly **Type A intercalated cells**, are important for secreting acid (H+) in acidosis and therefore reabsorbing bicarbonate, but not the bulk of it.
*Thick ascending limb*
- The primary role of the **thick ascending limb** is the reabsorption of **sodium**, **potassium**, and **chloride** to create a concentrated interstitium, not significant bicarbonate reabsorption.
- It is largely impermeable to water and is relatively impermeable to bicarbonate.
*Distal tubule*
- The **distal convoluted tubule (DCT)** reabsorbs a small percentage of filtered bicarbonate, but its main role is regulated reabsorption of **sodium** and **calcium**, and secretion of **potassium** and **hydrogen ions**.
- Its contribution to bicarbonate reabsorption is much less significant than that of the proximal tubule.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 2: A patient presents with periods of severe headaches and flushing however every time they have come to the physician they have not experienced any symptoms. The only abnormal finding is a blood pressure of 175 mmHg/100 mmHg. It is determined that the optimal treatment for this patient is surgical. Prior to surgery which of the following noncompetitive inhibitors should be administered?
- A. Phentolamine
- B. Isoproterenol
- C. Atropine
- D. Propranolol
- E. Phenoxybenzamine (Correct Answer)
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Phenoxybenzamine***
- This patient likely has a **pheochromocytoma**, which explains the episodic headaches, flushing, and hypertension. **Phenoxybenzamine** is a **non-competitive, irreversible alpha-adrenergic blocker** that is crucial for preoperative preparation to prevent a **hypertensive crisis** during surgery.
- Its **irreversible binding** provides sustained alpha blockade, essential to control blood pressure and avoid catecholamine-induced surges during tumor manipulation.
*Phentolamine*
- **Phentolamine** is a **competitive alpha-adrenergic blocker** used to manage acute hypertensive episodes, but it has a shorter duration of action.
- It is not preferred for sustained preoperative alpha blockade due to its **reversible nature** and potential for drug washout during surgery, which could lead to catecholamine surges.
*Isoproterenol*
- **Isoproterenol** is a **beta-adrenergic agonist** that increases heart rate and contractility, and causes bronchodilation.
- It would be contraindicated in a patient with pheochromocytoma as it could worsen hypertension and cardiac symptoms by stimulating beta receptors that are already overly sensitive to endogenous catecholamines.
*Atropine*
- **Atropine** is a **muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist** that blocks parasympathetic effects, like bradycardia and salivation.
- It has no role in managing hypertension or the catecholamine excess seen in pheochromocytoma.
*Propranolol*
- **Propranolol** is a **non-selective beta-adrenergic blocker** that can be used to control tachycardia and arrhythmias in pheochromocytoma, but only *after* adequate alpha-blockade has been established.
- Using **propranolol alone** or before alpha-blockade can lead to **unopposed alpha-adrenergic stimulation**, resulting in a severe, life-threatening hypertensive crisis.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 3: A 47-year-old man with bipolar I disorder and hypertension comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of increased thirst, urinary frequency, and sleep disturbance. He says that he now drinks up to 30 cups of water daily. He has smoked 2 packs of cigarettes daily for the past 20 years. Examination shows decreased skin turgor. Serum studies show a sodium concentration of 149 mEq/L, a potassium concentration of 4.1 mEq/L, and an elevated antidiuretic hormone concentration. His urine osmolality is 121 mOsm/kg H2O. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
- A. Tumor in the adrenal cortex
- B. Adverse effect of a medication (Correct Answer)
- C. Paraneoplastic production of a hormone
- D. Polydipsia caused by acute psychosis
- E. Tumor of the pituitary gland
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Adverse effect of a medication***
- The patient's presentation of **polyuria**, **polydipsia**, **hypernatremia**, and **elevated ADH** with **low urine osmolality** is consistent with **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus**.
- **Lithium**, a common treatment for bipolar I disorder, is a well-known cause of **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus** by interfering with the renal collecting duct's response to ADH.
*Tumor in the adrenal cortex*
- An adrenal cortical tumor would typically lead to conditions like **Cushing's syndrome** ( excess cortisol) or **Conn's syndrome** (excess aldosterone), causing **hypokalemia** and **hypertension**, but not primarily hypernatremia with low urine osmolality.
- While it can affect fluid balance, it does not directly cause the classic presentation of **diabetes insipidus** with elevated ADH and low urine osmolality.
*Paraneoplastic production of a hormone*
- Paraneoplastic syndromes can cause various endocrine abnormalities, but paraneoplastic production of a hormone leading to **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus** with high ADH and low urine osmolality is highly unlikely.
- More common paraneoplastic syndromes affecting water balance involve inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH), leading to **hyponatremia**, not hypernatremia.
*Polydipsia caused by acute psychosis*
- Primary polydipsia typically results in **hyponatremia** due to excessive water intake diluting serum sodium, especially if renal concentrating mechanisms are intact. The patient has **hypernatremia**.
- While patients with psychiatric conditions can exhibit **primary polydipsia**, the body usually compensates by suppressing ADH and excreting dilute urine; an **elevated ADH** makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Tumor of the pituitary gland*
- A pituitary tumor could cause **central diabetes insipidus** if it interfered with ADH production or release, but this would lead to a *low* or *inappropriately normal* ADH level, not an **elevated ADH** level.
- An elevated ADH with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus indicates the kidneys are not responding to ADH, rather than a problem with ADH production.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 4: A new drug has been shown to block epithelial sodium channels in the cortical collecting duct. Which of the following is most likely to be decreased upon drug administration?
- A. Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules
- B. Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules
- C. Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules (Correct Answer)
- D. Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules
- E. Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules***
- Blocking **epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)** in the cortical collecting duct reduces sodium reabsorption, which in turn diminishes the electrochemical gradient driving **potassium secretion** into the lumen.
- This is because sodium reabsorption creates a more negative luminal charge, attracting potassium ions to move from the cell into the tubule.
- This is the mechanism of **potassium-sparing diuretics** like amiloride and triamterene.
*Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules*
- Urea **reabsorption** primarily occurs in the **medullary collecting duct** via urea transporters (UT-A1, UT-A3) and is influenced by the inner medullary osmolarity and ADH.
- Blocking ENaC would primarily affect sodium flux and potassium secretion, with minimal direct impact on urea reabsorption in the collecting duct.
*Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules*
- **Hydrogen ion (H+) secretion** occurs in the collecting tubules via intercalated cells (α-intercalated cells), which is important for acid-base balance.
- While blocking ENaC can indirectly reduce H+ secretion (by decreasing the lumen-negative potential), the primary and most significant effect is on **potassium secretion**, making this a less likely answer.
*Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules*
- The primary function of ENaC is to **reabsorb sodium** from the tubular lumen back into the blood, not to secrete it.
- Sodium is not normally secreted in the collecting tubules; blocking ENaC would decrease sodium **reabsorption**, not affect sodium secretion.
*Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule*
- **Sodium chloride reabsorption** in the distal convoluted tubule is mainly mediated by the **thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl co-transporter (NCC)**.
- ENaC are predominantly located in the cortical collecting duct (downstream from the DCT), so blocking them would not directly impact NaCl reabsorption in the distal tubule.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 5: A 69-year-old man with hypertension and congestive heart failure is brought to the emergency department because of a 9-day history of worsening shortness of breath and swelling of his legs. His respirations are 25/min, and blood pressure is 160/98 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on 5 L O2 via nasal cannula shows an oxygen saturation of 92%. Examination shows 2+ pretibial edema bilaterally. Crackles are heard at both lung bases. ACE inhibitors are being considered for this patient's treatment. The enzyme that these medications inhibit, which is responsible for bradykinin breakdown, is primarily produced in which of the following?
- A. Pulmonary endothelium (Correct Answer)
- B. Atria
- C. Juxtaglomerular cells
- D. Zona glomerulosa
- E. Liver
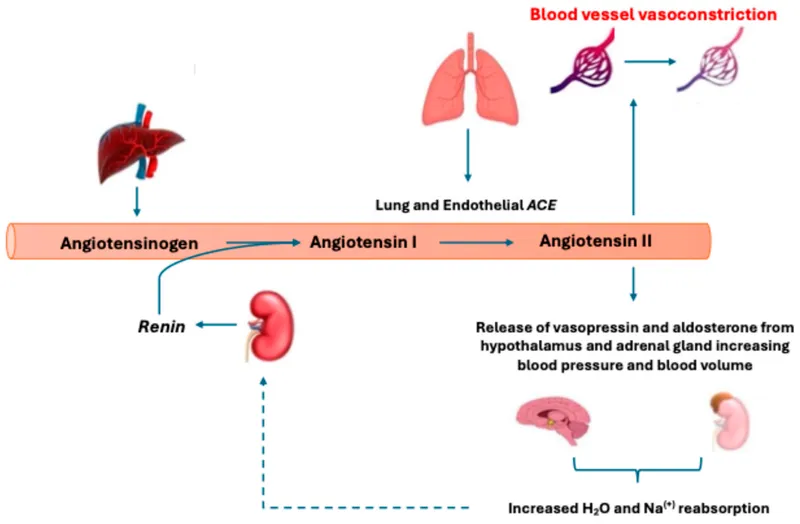
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Pulmonary endothelium***
- The **pulmonary endothelium** is rich in **angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)**, which is responsible for the breakdown of **bradykinin**.
- Medications like **ACE inhibitors** block this enzyme, leading to increased bradykinin levels, which can cause side effects like **cough** and **angioedema**.
*Atria*
- The **atria** produce **atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** in response to stretch, which plays a role in fluid and electrolyte balance but not directly in bradykinin breakdown.
- ANP promotes **vasodilation** and **natriuresis**, contributing to blood pressure regulation.
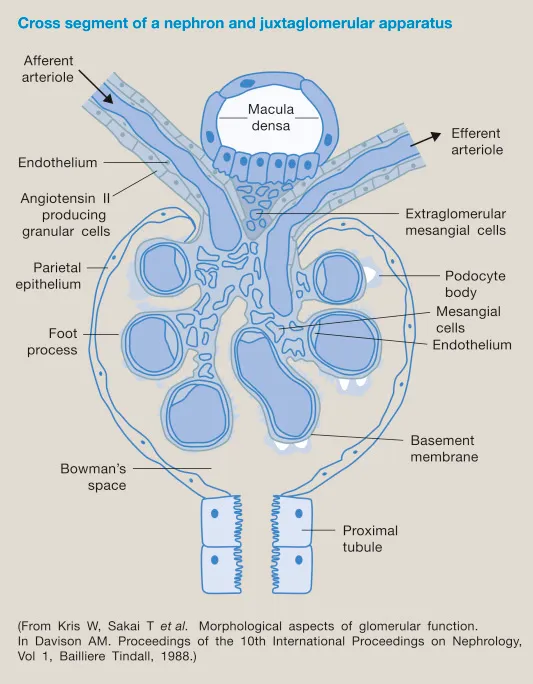
*Juxtaglomerular cells*
- **Juxtaglomerular cells** in the kidney produce **renin**, an enzyme that initiates the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system** by converting angiotensinogen to angiotensin I.
- Renin production is stimulated by reduced renal perfusion pressure, sympathetic activity, and decreased sodium delivery to the macula densa.
*Zona glomerulosa*
- The **zona glomerulosa** of the adrenal cortex produces **aldosterone**, a mineralocorticoid that regulates sodium and potassium balance.
- Aldosterone's primary role is in salt and water retention, and it does not directly participate in bradykinin metabolism.
*Liver*
- The **liver** is involved in the synthesis of many plasma proteins, clotting factors, and detoxification processes, but it is not the primary site for bradykinin breakdown.
- While the liver metabolizes many substances, **ACE activity** for bradykinin degradation is concentrated in the pulmonary endothelium.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 6: A 57-year-old otherwise healthy male presents to his primary care physician for a check-up. He has no complaints. His blood pressure at the previous visit was 160/95. The patient did not wish to be on any medications and at the time attempted to manage his blood pressure with diet and exercise. On repeat measurement of blood pressure today, the reading is 163/92. His physician decides to prescribe a medication which the patient agrees to take. The patient calls his physician 6 days later complaining of a persistent cough, but otherwise states that his BP was measured as 145/85 at a local pharmacy. Which of the following is a contraindication to this medication?
- A. Congestive heart failure
- B. Black race
- C. Bilateral renal artery stenosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- E. Gout
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Bilateral renal artery stenosis***
- The patient's developing **cough** after starting a new antihypertensive suggests he was likely prescribed an **ACE inhibitor**.
- **Bilateral renal artery stenosis** is a strong contraindication for ACE inhibitors due to the risk of precipitating **acute kidney injury**, as these medications rely on efferent arteriolar vasodilation to maintain renal perfusion when there's reduced afferent flow.
*Congestive heart failure*
- **ACE inhibitors** are often a **first-line treatment** for heart failure due to their ability to improve cardiac remodeling and reduce mortality.
- They are used to prevent ventricular remodeling and reduce afterload, making this an indication, not a contraindication.
*Black race*
- While ACE inhibitors may be **less effective as monotherapy** in black patients, they are not contraindicated and can be effectively used in combination with other antihypertensives, such as **thiazide diuretics** or **calcium channel blockers**.
- **African Americans** often respond better to calcium channel blockers and diuretics for hypertension but ACE inhibitors are not absolutely contraindicated.
*Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease*
- **ACE inhibitors** are **not contraindicated** in COPD, as they do not affect bronchial smooth muscle tone.
- **Beta-blockers**, not ACE inhibitors, are typically avoided or used with caution in patients with reactive airway diseases like asthma or severe COPD.
*Gout*
- **ACE inhibitors** do not significantly impact **uric acid levels** and are generally safe for use in patients with gout.
- In contrast, **thiazide diuretics** can increase uric acid levels and worsen gout, but this is not the medication indicated by the patient's cough.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 7: A physician is choosing whether to prescribe losartan or lisinopril to treat hypertension in a 56-year-old male. Relative to losartan, one would expect treatment with lisinopril to produce which of the following changes in the circulating levels of these peptides?
- A. Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease
- B. Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease
- C. Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase
- D. Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease (Correct Answer)
- E. Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease***
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor**, which directly blocks the conversion of **angiotensin I** to **angiotensin II**, leading to a decrease in circulating **angiotensin II** levels.
- ACE is also responsible for the breakdown of **bradykinin**, so inhibiting ACE with lisinopril will lead to an **increase in bradykinin** levels, contributing to vasodilation but also the characteristic cough.
*Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** (an ACE inhibitor) decreases **angiotensin II**, which in turn leads to a **decrease in aldosterone** synthesis and release, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase due to ACE inhibition, as ACE is involved in its degradation.
*Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** directly inhibits the enzyme responsible for producing **angiotensin II**, thus leading to its **decrease**, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase because its degradation pathway (via ACE) is blocked, not decrease.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase*
- **Lisinopril** reduces the negative feedback on **renin** release, leading to an **increase in renin** levels, not a decrease.
- While ACE is inhibited by lisinopril, this leads to an accumulation of its substrate, **angiotensin I**, resulting in an increase of angiotensin I.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase*
- As an ACE inhibitor, lisinopril would lead to an **increase in renin** due to reduced negative feedback from angiotensin II, not a decrease.
- **Angiotensin II** levels would **decrease** because its production from angiotensin I is directly inhibited by lisinopril.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 8: A 71-year-old African American man diagnosed with high blood pressure presents to the outpatient clinic. In the clinic, his blood pressure is 161/88 mm Hg with a pulse of 88/min. He has had similar blood pressure measurements in the past, and you initiate captopril. He presents back shortly after initiation with extremely swollen lips, tongue, and face. After captopril is discontinued, what is the most appropriate step for the management of his high blood pressure?
- A. Initiate a beta-blocker
- B. Switch to ramipril
- C. Initiate a thiazide diuretic (Correct Answer)
- D. Reinitiate captopril
- E. Initiate an ARB
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Initiate a thiazide diuretic***
- The patient experienced **angioedema** after taking **captopril**, which is an **ACE inhibitor**. This is a life-threatening adverse effect, and it indicates that all **ACE inhibitors** should be avoided in the future.
- Due to the risk of angioedema, a different class of antihypertensive should be used. Given his African American ethnicity, a **thiazide diuretic** or **calcium channel blocker** would be an appropriate initial choice for monotherapy if hypertension is stage 1, or combination therapy if stage 2 hypertension, otherwise, a second agent, such as a **calcium channel blocker**, can be added.
*Initiate a beta-blocker*
- While beta-blockers are a class of antihypertensive drugs, they are generally not preferred as **first-line monotherapy** for **hypertension**, especially in older African American patients, unless there are specific comorbidities like heart failure or coronary artery disease.
- The most appropriate first-line choice after **ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema** would be a thiazide diuretic or calcium channel blocker, as per ACC/AHA guidelines for primary hypertension.
*Switch to ramipril*
- **Ramipril** is also an **ACE inhibitor**, and the patient experienced **angioedema** with **captopril** (another ACE inhibitor).
- Cross-reactivity and recurrence of angioedema are high with other ACE inhibitors, making this choice extremely dangerous and contraindicated.
*Reinitiate captopril*
- The patient developed **angioedema**, a severe and potentially fatal hypersensitivity reaction, to **captopril**.
- Reinitiating the same drug could lead to recurrent, and potentially more severe, angioedema and is therefore absolutely contraindicated.
*Initiate an ARB*
- **Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)**, while a different class from ACE inhibitors, act on the renin-angiotensin system and carry a **small but significant risk of cross-reactivity** leading to angioedema, especially in patients who have experienced it with an ACE inhibitor.
- Given the life-threatening nature of angioedema, it is generally recommended to avoid ARBs if a patient has a history of ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 9: A 48-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. At her visit 1 month ago, her glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was 100 mL/min/1.73 m2 and her renal plasma flow (RPF) was 588 mL/min. Today, her RPF is 540 mL/min and her filtration fraction (FF) is 0.2. After her previous appointment, this patient was most likely started on a drug that has which of the following effects?
- A. Inhibition of the renal Na-K-Cl cotransporter
- B. Constriction of the afferent arteriole
- C. Relaxation of urinary smooth muscle
- D. Constriction of the efferent arteriole (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibition of vasopressin
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***Constriction of the efferent arteriole***
- The previous GFR was 100 mL/min and RPF was 588 mL/min. For the follow-up, RPF is 540 mL/min and FF is 0.2. The new GFR can be calculated as FF × RPF = 0.2 × 540 = **108 mL/min**.
- The patient shows **increased GFR** (100→108 mL/min) with **decreased RPF** (588→540 mL/min), resulting in an **increased filtration fraction**.
- Medications that **constrict the efferent arteriole**, such as **NSAIDs**, produce this pattern by blocking prostaglandin synthesis. Prostaglandins normally cause vasodilation (predominantly of the afferent arteriole). When blocked, there is relatively more **efferent arteriolar constriction**, which increases glomerular hydrostatic pressure, thereby **increasing GFR while reducing overall RPF**.
*Inhibition of the renal Na-K-Cl cotransporter*
- This effect describes **loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide), which increase sodium excretion and water diuresis.
- Loop diuretics typically cause a **decrease in GFR** due to reduced fluid volume and lower filtration pressure, which contradicts the slight increase in GFR observed.
*Constriction of the afferent arteriole*
- **Afferent arteriole constriction** (e.g., by NSAIDs in high doses or norepinephrine) would decrease blood flow into the glomerulus, leading to a **decrease in both RPF and GFR**.
- While RPF decreased in this case, GFR actually increased, making this option incorrect.
*Relaxation of urinary smooth muscle*
- Relaxation of urinary smooth muscle is characteristic of drugs like **alpha-blockers** (e.g., tamsulosin) or antimuscarinics used for conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia or overactive bladder.
- This effect primarily impacts urine flow out of the bladder and does **not directly affect GFR or RPF** in the way described.
*Inhibition of vasopressin*
- Vasopressin (ADH) inhibition leads to **increased water excretion** and is seen with drugs like **vasopressin receptor antagonists** (vaptans) or ethanol.
- While it affects fluid balance, it typically causes a **decrease in GFR** due to hypovolemia and has no direct mechanism to increase GFR with decreased RPF as observed.
RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG Question 10: Two days after vaginal delivery of a healthy newborn at term, a 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, is unable to breastfeed. Her labor was complicated by antepartum hemorrhage and she received two units of packed red blood cells. Her pulse is 99/min and blood pressure is 90/55 mm Hg. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following sets of serum findings?
$$$ ACTH %%% Aldosterone %%% Cortisol $$$
- A. ↑ ↓ ↓
- B. ↓ ↑ ↓
- C. ↑ normal ↑
- D. ↓ normal ↑
- E. ↓ normal ↓ (Correct Answer)
RAAS in blood pressure control Explanation: ***↓ normal ↓***
- This scenario describes **Sheehan's syndrome**, caused by **postpartum pituitary necrosis** due to severe hemorrhage and hypotension during delivery.
- Decreased **ACTH** (adrenocorticotropic hormone) leads to secondary **adrenal insufficiency**, causing decreased **cortisol**. **Aldosterone** secretion, primarily regulated by the **renin-angiotensin system**, remains largely normal because only the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, which produces aldosterone, is regulated directly by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), whereas the pituitary regulates the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis.
*↑ ↓ ↓*
- This pattern (high ACTH, low aldosterone, low cortisol) suggests **primary adrenal insufficiency** (Addison's disease), where the adrenal glands themselves are failing, leading to a compensatory increase in ACTH. However, this patient's condition is due to pituitary damage.
- In primary adrenal insufficiency, both **cortisol** and **aldosterone** would be low, and **ACTH** would be elevated due to a lack of negative feedback.
*↓ ↑ ↓*
- This pattern (low ACTH, high aldosterone, low cortisol) is inconsistent with most common adrenal or pituitary pathologies. Low ACTH and low cortisol would suggest secondary adrenal insufficiency, but high aldosterone does not fit.
- **Hyperaldosteronism** with secondary adrenal insufficiency is rare and not indicated by the patient's presentation.
*↑ normal ↑*
- This pattern (high ACTH, normal aldosterone, high cortisol) suggests **Cushing's disease** (pituitary adenoma secreting ACTH), or an ectopic ACTH tumor, or a state of acute stress.
- The patient's **hypotension** and inability to breastfeed point away from Cushing's and towards hypopituitarism.
*↓ normal ↑*
- This pattern (low ACTH, normal aldosterone, high cortisol) could be seen in states of iatrogenic **exogenous corticosteroid use**, leading to suppressed ACTH and endogenous cortisol, or in an adrenal tumor producing cortisol independent of ACTH.
- This is inconsistent with the symptoms of postpartum hemorrhage and inability to lactate, which indicate a **deficit** rather than an excess of pituitary hormones.
More RAAS in blood pressure control US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.