Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pharmacological targeting of RAAS. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 1: A 78-year-old Caucasian male actor presents to your office complaining of a dry, non-productive cough. He has a history of hypertension, diabetes, and coronary artery disease and he follows a complicated regimen of medications to treat his multiple co-morbidities. Which of the following medications is most likely to be associated with his chief complaint?
- A. Aspirin
- B. Lisinopril (Correct Answer)
- C. Hydrochlorothiazide
- D. Metoprolol
- E. Nifedipine
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Lisinopril***
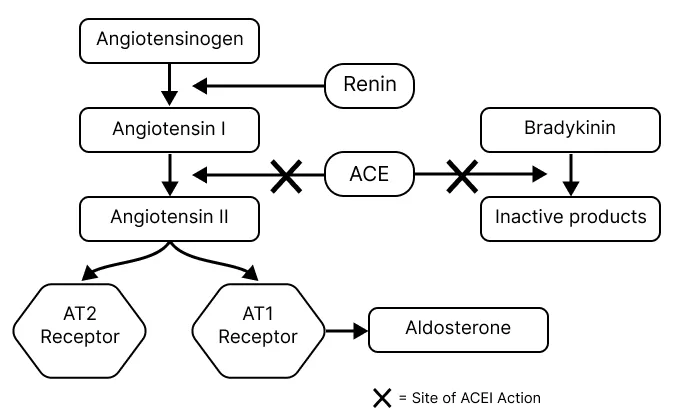
- **Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors** like lisinopril are well-known to cause a **persistent dry, non-productive cough** in approximately 5-20% of patients.
- This cough is thought to be due to the accumulation of **bradykinin** and **substance P** in the airways.
*Aspirin*
- While aspirin can cause respiratory symptoms in some individuals, it is typically associated with **aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD)**, which involves **bronchospasm** and nasal polyps, not a persistent dry cough as a primary side effect.
- Aspirin's common side effects are usually gastrointestinal, such as **gastric irritation** or bleeding.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- Hydrochlorothiazide is a **thiazide diuretic** primarily used for hypertension.
- It works by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule and is not typically associated with **chronic dry cough** as a side effect.
*Metoprolol*
- Metoprolol is a **beta-blocker** used for hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias.
- While beta-blockers can cause **bronchospasm** in susceptible individuals (especially those with asthma), they are not commonly linked to a persistent **dry, non-productive cough** in the general population.
*Nifedipine*
- Nifedipine is a **calcium channel blocker** (dihydropyridine type) used for hypertension and angina.
- Common side effects include **peripheral edema**, headache, and flushing, but it is not known to cause a **dry cough**.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old male with a history of congestive heart failure and hypertension comes to you with the chief complaint of new-onset cough as well as increased serum potassium in the setting of a new medication. Which of the following medications is most likely responsible for these findings?
- A. Lisinopril (Correct Answer)
- B. Metoprolol
- C. Furosemide
- D. Amiodarone
- E. Digoxin
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Lisinopril***
- **Lisinopril** is an ACE inhibitor, which can cause a **persistent dry cough** due to the accumulation of bradykinin.
- ACE inhibitors can also cause **hyperkalemia** by inhibiting aldosterone secretion, which normally promotes potassium excretion.
*Metoprolol*
- **Metoprolol** is a beta-blocker that primarily decreases heart rate and blood pressure; it is not typically associated with cough or hyperkalemia.
- While it can be used in CHF, its common side effects include bradycardia and fatigue, not the described symptoms.
*Furosemide*
- **Furosemide** is a loop diuretic that promotes potassium excretion, leading to **hypokalemia**, not hyperkalemia.
- It does not typically cause cough; instead, it can help reduce fluid accumulation in the lungs associated with CHF.
*Amiodarone*
- **Amiodarone** is an antiarrhythmic drug known for several significant side effects, including **pulmonary fibrosis** (which can cause cough) and thyroid dysfunction.
- However, it does not typically cause hyperkalemia; instead, it can cause changes in electrolyte levels, but not the specific combination seen here.
*Digoxin*
- **Digoxin** is a cardiac glycoside used to increase cardiac contractility and slow heart rate in heart failure and arrhythmias.
- It does not typically cause cough or hyperkalemia; its toxicity is often associated with nausea, visual disturbances, and arrhythmias.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 3: A 34-year-old man is being evaluated in an emergency clinic for dizziness and headache after a stressful event at work. He also reports that his face often becomes swollen and he occasionally has difficulty breathing during these spells. Family history is significant for his father who died of a stroke and his mother who often suffers from similar facial swelling. The patient’s blood pressure is 170/80 mm Hg. On physical examination, the patient appears well. Which of the following medications is most likely contraindicated in this patient?
- A. The patient has no contraindications.
- B. Enalapril (Correct Answer)
- C. Sulfadiazine
- D. Penicillin
- E. Losartan
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: **Enalapril**
- The patient's presentation with recurrent facial swelling, occasional difficulty breathing, and a family history of similar symptoms in his mother and stroke in his father is highly suggestive of **hereditary angioedema (HAE)**.
- **ACE inhibitors**, such as enalapril, are absolutely contraindicated in patients with HAE because they increase bradykinin levels, which can precipitate or worsen angioedema attacks.
*The patient has no contraindications.*
- The patient's history of recurrent angioedema episodes and a significant family history strongly suggest an underlying condition, likely HAE, which has clear contraindications for certain medications.
- Dismissing contraindications without further investigation into the cause of his angioedema would be unsafe and medically negligent.
*Sulfadiazine*
- **Sulfonamide antibiotics** are not directly contraindicated in HAE.
- While some individuals may have allergies to sulfa drugs, there is no specific link between sulfadiazine and triggering HAE attacks.
*Penicillin*
- Penicillin is a **beta-lactam antibiotic** and is not known to exacerbate or be contraindicated in hereditary angioedema.
- Allergic reactions to penicillin are common, but this is a Type I hypersensitivity, distinct from bradykinin-mediated angioedema.
*Losartan*
- **Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)** like losartan generally do not significantly increase bradykinin levels and are typically considered a safer alternative to ACE inhibitors in patients who might develop ACE inhibitor–induced angioedema.
- While rare cases of ARB-induced angioedema have been reported, the risk is considerably lower than with ACE inhibitors, making it a less likely contraindication in this context.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 4: A new drug X is being tested for its effect on renal function. During the experiments, the researchers found that in patients taking substance X, the urinary concentration of sodium decreases while urine potassium concentration increase. Which of the following affects the kidneys in the same way as does substance X?
- A. Aldosterone (Correct Answer)
- B. Furosemide
- C. Spironolactone
- D. Atrial natriuretic peptide
- E. Hydrochlorothiazide
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Aldosterone***
- **Aldosterone** acts on the **principal cells** of the **collecting duct** to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
- This action leads to a decrease in urinary sodium concentration and an increase in urinary potassium concentration, matching the effects of drug X.
*Furosemide*
- **Furosemide** is a **loop diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-K-2Cl cotransporter** in the **thick ascending limb** of the loop of Henle.
- This inhibition leads to increased excretion of sodium, potassium, and water, resulting in higher urinary sodium concentration.
*Spironolactone*
- **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that blocks aldosterone's effects on the collecting duct.
- This leads to increased sodium excretion and decreased potassium excretion (potassium-sparing effect), which is the opposite of drug X.
*Atrial natriuretic peptide*
- **Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** is released in response to atrial stretch and causes **natriuresis** (increased sodium excretion) and **diuresis**.
- It works by dilating afferent arterioles and constricting efferent arterioles, increasing GFR, and inhibiting sodium reabsorption, thus increasing urinary sodium concentration.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- **Hydrochlorothiazide** is a **thiazide diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-Cl cotransporter** in the **distal convoluted tubule**.
- This leads to increased sodium and chloride excretion but typically causes potassium wasting (hypokalemia), which differs from the increased urinary potassium concentration seen with drug X.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 5: A physician is choosing whether to prescribe losartan or lisinopril to treat hypertension in a 56-year-old male. Relative to losartan, one would expect treatment with lisinopril to produce which of the following changes in the circulating levels of these peptides?
- A. Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease
- B. Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease
- C. Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase
- D. Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease (Correct Answer)
- E. Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease***
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor**, which directly blocks the conversion of **angiotensin I** to **angiotensin II**, leading to a decrease in circulating **angiotensin II** levels.
- ACE is also responsible for the breakdown of **bradykinin**, so inhibiting ACE with lisinopril will lead to an **increase in bradykinin** levels, contributing to vasodilation but also the characteristic cough.
*Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** (an ACE inhibitor) decreases **angiotensin II**, which in turn leads to a **decrease in aldosterone** synthesis and release, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase due to ACE inhibition, as ACE is involved in its degradation.
*Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** directly inhibits the enzyme responsible for producing **angiotensin II**, thus leading to its **decrease**, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase because its degradation pathway (via ACE) is blocked, not decrease.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase*
- **Lisinopril** reduces the negative feedback on **renin** release, leading to an **increase in renin** levels, not a decrease.
- While ACE is inhibited by lisinopril, this leads to an accumulation of its substrate, **angiotensin I**, resulting in an increase of angiotensin I.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase*
- As an ACE inhibitor, lisinopril would lead to an **increase in renin** due to reduced negative feedback from angiotensin II, not a decrease.
- **Angiotensin II** levels would **decrease** because its production from angiotensin I is directly inhibited by lisinopril.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 6: A 71-year-old African American man diagnosed with high blood pressure presents to the outpatient clinic. In the clinic, his blood pressure is 161/88 mm Hg with a pulse of 88/min. He has had similar blood pressure measurements in the past, and you initiate captopril. He presents back shortly after initiation with extremely swollen lips, tongue, and face. After captopril is discontinued, what is the most appropriate step for the management of his high blood pressure?
- A. Initiate a beta-blocker
- B. Switch to ramipril
- C. Initiate a thiazide diuretic (Correct Answer)
- D. Reinitiate captopril
- E. Initiate an ARB
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Initiate a thiazide diuretic***
- The patient experienced **angioedema** after taking **captopril**, which is an **ACE inhibitor**. This is a life-threatening adverse effect, and it indicates that all **ACE inhibitors** should be avoided in the future.
- Due to the risk of angioedema, a different class of antihypertensive should be used. Given his African American ethnicity, a **thiazide diuretic** or **calcium channel blocker** would be an appropriate initial choice for monotherapy if hypertension is stage 1, or combination therapy if stage 2 hypertension, otherwise, a second agent, such as a **calcium channel blocker**, can be added.
*Initiate a beta-blocker*
- While beta-blockers are a class of antihypertensive drugs, they are generally not preferred as **first-line monotherapy** for **hypertension**, especially in older African American patients, unless there are specific comorbidities like heart failure or coronary artery disease.
- The most appropriate first-line choice after **ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema** would be a thiazide diuretic or calcium channel blocker, as per ACC/AHA guidelines for primary hypertension.
*Switch to ramipril*
- **Ramipril** is also an **ACE inhibitor**, and the patient experienced **angioedema** with **captopril** (another ACE inhibitor).
- Cross-reactivity and recurrence of angioedema are high with other ACE inhibitors, making this choice extremely dangerous and contraindicated.
*Reinitiate captopril*
- The patient developed **angioedema**, a severe and potentially fatal hypersensitivity reaction, to **captopril**.
- Reinitiating the same drug could lead to recurrent, and potentially more severe, angioedema and is therefore absolutely contraindicated.
*Initiate an ARB*
- **Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)**, while a different class from ACE inhibitors, act on the renin-angiotensin system and carry a **small but significant risk of cross-reactivity** leading to angioedema, especially in patients who have experienced it with an ACE inhibitor.
- Given the life-threatening nature of angioedema, it is generally recommended to avoid ARBs if a patient has a history of ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 7: A 75-year-old woman is brought to a physician’s office by her son with complaints of diarrhea and vomiting for 1 day. Her stool is loose, watery, and yellow-colored, while her vomitus contains partially digested food particles. She denies having blood or mucus in her stools and vomitus. Since the onset of her symptoms, she has not had anything to eat and her son adds that she is unable to tolerate fluids. The past medical history is unremarkable and she does not take any medications regularly. The pulse is 115/min, the respiratory rate is 16/min, the blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and the temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). The physical examination shows dry mucous membranes and slightly sunken eyes. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Which of the following physiologic changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal plasma flow (RPF), and filtration fraction (FF) are expected?
- A. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF
- B. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF
- C. Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF
- D. Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF
- E. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF (Correct Answer)
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF***
- Due to **dehydration** from diarrhea and vomiting, there is a decrease in blood volume leading to decreased renal blood flow and **renal plasma flow (RPF)**.
- The body responds to hypovolemia by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and sympathetic nervous system, which cause **preferential efferent arteriolar constriction** (more than afferent constriction). This helps maintain glomerular hydrostatic pressure despite reduced renal perfusion.
- As a result, **GFR decreases** but proportionally **less than RPF decreases**, causing the **filtration fraction (FF = GFR/RPF) to increase**.
- In this patient with significant dehydration (tachycardia, hypotension, dry mucous membranes), both GFR and RPF are reduced, but FF is elevated due to compensatory mechanisms.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF*
- While GFR and RPF will decrease due to dehydration, the **filtration fraction is expected to increase**, not decrease.
- A decreased FF would imply GFR fell proportionally more than RPF, which contradicts the physiologic response where efferent arteriolar constriction helps preserve GFR relative to RPF.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF*
- With significant fluid loss and compensatory mechanisms (efferent arteriolar constriction via angiotensin II), a change in **filtration fraction** is expected.
- The body actively alters arteriolar tone to prioritize GFR maintenance, which directly increases FF.
*Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF*
- This pattern suggests **hypervolemia** or increased renal perfusion, which directly contradicts the patient's severe dehydration.
- Both GFR and RPF are expected to decrease in volume depletion, not increase.
*Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF*
- An increase in GFR is physiologically impossible given the patient's severe volume depletion and reduced renal perfusion.
- While FF does increase in dehydration, this occurs in the context of **both GFR and RPF being decreased**, not with an increased GFR.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 8: A 52-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after a motor vehicle accident. He was an unrestrained passenger who was ejected from the vehicle. On presentation, he is found to be actively bleeding from numerous wounds. His blood pressure is 76/42 mmHg and pulse is 152/min. Attempts at resuscitation fail, and he dies 25 minutes later. Autopsy shows blood in the peritoneal cavity, and histology of the kidney reveals swelling of the proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cells. Which of the following is most likely the mechanism underlying the renal cell findings?
- A. Decreased activity of caspase 7
- B. Increased activity of caspase 9
- C. Increased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase
- D. Increased activity of caspase 8
- E. Decreased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase (Correct Answer)
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Decreased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase***
- The patient experienced **hypovolemic shock** due to severe blood loss, leading to a significant drop in blood pressure and organ perfusion. This results in **ischemia** of the renal cells.
- **Ischemic injury** impairs ATP production, which is essential for the function of the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump**. Failure of this pump leads to intracellular accumulation of sodium and water, causing **cellular swelling**, particularly noticeable in the proximal convoluted tubules.
*Decreased activity of caspase 7*
- **Caspases**, including caspase 7, are involved in **apoptosis** (programmed cell death), which involves cell shrinkage and fragmentation, not the swelling observed here.
- Decreased caspase activity would generally *reduce* apoptosis, which is not the primary mechanism of acute cell injury in shock.
*Increased activity of caspase 9*
- Increased activity of **caspase 9** is indicative of the **intrinsic apoptotic pathway**, typically initiated by mitochondrial damage.
- While prolonged ischemia can eventually lead to apoptotic changes, the acute finding of **cellular swelling** points more directly to immediate membrane pump dysfunction due to ATP depletion.
*Increased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase*
- **Increased function** of the Na+/K+-ATPase would actively pump sodium out of the cell and potassium in, *preventing* intracellular swelling.
- This option contradicts the observed finding of proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cell swelling, which is characteristic of acute cellular injury due to pump failure.
*Increased activity of caspase 8*
- **Caspase 8** is a key initiator caspase in the **extrinsic apoptotic pathway**, often triggered by death receptor signaling.
- Similar to caspase 9, increased caspase 8 activity would lead to apoptosis, characterized by cell shrinkage, not the **cellular swelling** seen in acute ischemic injury.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 9: A 68-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for a regular check-up. She complains of swelling of her legs and face, which is worse in the morning and decreases during the day. She was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus a year ago and prescribed metformin, but she has not been compliant with it preferring 'natural remedies' over the medications. She does not have a history of cardiovascular disease or malignancy. Her vital signs are as follows: blood pressure measured on the right hand is 130/85 mm Hg, on the left hand, is 110/80 mm Hg, heart rate is 79/min, respiratory rate is 16/min, and the temperature is 36.6℃ (97.9°F). Physical examination reveals S1 accentuation best heard in the second intercostal space at the right sternal border. Facial and lower limbs edema are evident. The results of the laboratory tests are shown in the table below.
Fasting plasma glucose 164 mg/dL
HbA1c 10.4%
Total cholesterol 243.2 mg/dL
Triglycerides 194.7 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.8 mg/dL
Urea nitrogen 22.4 mg/dL
Ca2+ 9.6 mg/dL
PO42- 3.84 mg/dL
Which of the following statements best describes this patient's condition?
- A. There is an error in Ca2+ measurement because the level of serum calcium is always decreased in the patient’s condition.
- B. If measured in this patient, there would be an increased PTH level. (Correct Answer)
- C. Increase in 1α, 25(OH)2D3 production is likely to contribute to alteration of the patient’s laboratory values.
- D. The calcitriol level is unlikely to be affected in this patient.
- E. Hypoparathyroidism is most likely the cause of the patient’s altered laboratory results.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***If measured in this patient, there would be an increased PTH level.***
- This patient presents with signs of **chronic kidney disease (CKD)**, indicated by **elevated creatinine (1.8 mg/dL)** and **urea nitrogen (22.4 mg/dL)**, along with edema.
- In CKD, the kidneys are less able to excrete phosphate and synthesize calcitriol (active vitamin D), leading to **hyperphosphatemia (PO42- 3.84 mg/dL)** and **hypocalcemia**. These imbalances stimulate the parathyroid glands to produce more **parathyroid hormone (PTH)** as a compensatory mechanism, a condition known as **secondary hyperparathyroidism**.
*There is an error in Ca2+ measurement because the level of serum calcium is always decreased in the patient's condition.*
- While **hypocalcemia** is common in CKD, it's not universally present, especially in early or moderate stages.
- The measured **calcium level (9.6 mg/dL)** is within the normal range, suggesting that the compensatory increase in **PTH** might be maintaining **normocalcemia** or that severe hypocalcemia has not yet developed.
*Increase in 1α, 25(OH)2D3 production is likely to contribute to alteration of the patient's laboratory values.*
- In CKD, there is a **decreased production of 1α,25(OH)2D3 (calcitriol)** by the kidneys, not an increase.
- The enzyme **1-alpha-hydroxylase**, responsible for converting 25-hydroxyvitamin D to active calcitriol, becomes deficient as renal function declines.
*The calcitriol level is unlikely to be affected in this patient.*
- The **calcitriol level is significantly affected in CKD**, specifically it is reduced.
- Reduced calcitriol synthesis is a key factor in the development of **secondary hyperparathyroidism** and **renal osteodystrophy**.
*Hypoparathyroidism is most likely the cause of the patient's altered laboratory results.*
- **Hypoparathyroidism** would lead to **low PTH levels**, typically resulting in **hypocalcemia** and **hyperphosphatemia** due to impaired renal phosphate excretion.
- This patient's presentation, particularly the high phosphate and normal calcium (suggesting compensation), is consistent with **hyperparathyroidism secondary to chronic kidney disease**, not hypoparathyroidism.
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG Question 10: A 63-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and muscle cramps for 6 weeks. He also noticed several episodes of tingling around the mouth and in the fingers and toes. He has osteoarthritis of his knees and hypertension. Current medications include ibuprofen and ramipril. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 35 years. Tapping over the facial nerve area in front of the ear elicits twitching of the facial muscles on the same side of the face. His serum alkaline phosphatase activity is 66 U/L. An ECG shows sinus rhythm with a prolonged QT interval. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Medication side effect
- B. Ectopic hormone production
- C. Vitamin D deficiency
- D. Destruction of parathyroid glands (Correct Answer)
- E. Albright hereditary osteodystrophy
Pharmacological targeting of RAAS Explanation: ***Destruction of parathyroid glands***
- The patient presents with **fatigue**, **muscle cramps**, and **paresthesias** (tingling around the mouth, fingers, and toes), which are classic symptoms of **hypocalcemia**.
- The positive **Chvostek's sign** (tapping over the facial nerve leading to facial muscle twitching) further confirms hypocalcemia, and a **prolonged QT interval** on ECG is also a known manifestation of low calcium levels. Destruction of the parathyroid glands (e.g., due to surgery, autoimmune disease, or radiation) leads to primary hypoparathyroidism and subsequent hypocalcemia.
*Medication side effect*
- While some medications can affect calcium levels, neither **ibuprofen** nor **ramipril** are typically associated with profound hypocalcemia leading to such prominent symptoms.
- The constellation of symptoms and signs (Chvostek's sign, prolonged QT) strongly points to an underlying calcium metabolism disorder, not a common drug side effect.
*Ectopic hormone production*
- **Ectopic hormone production** (e.g., PTHrP from tumors) usually causes **hypercalcemia**, not hypocalcemia, by mimicking parathyroid hormone action.
- Tumors that could lead to hypocalcemia are rare and usually involve extensive osteoblastic metastases consuming calcium, which is not suggested by the patient's presentation.
*Vitamin D deficiency*
- **Vitamin D deficiency** primarily causes osteomalacia in adults and rickets in children and can lead to **secondary hyperparathyroidism** as the body tries to compensate for low calcium.
- While severe vitamin D deficiency can cause some hypocalcemia symptoms, it doesn't typically present with the acute, symptomatic hypocalcemia signs like Chvostek's sign and prolonged QT interval in this direct manner without other signs of bone disease.
*Albright hereditary osteodystrophy*
- **Albright hereditary osteodystrophy** is a genetic disorder causing **pseudohypoparathyroidism**, where the body is resistant to PTH, leading to hypocalcemia.
- This condition is often associated with characteristic physical features such as **short stature**, **brachydactyly**, and **obesity**, which are not mentioned in this patient.
More Pharmacological targeting of RAAS US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.