Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Aldosterone synthesis and release. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 1: A new drug has been shown to block epithelial sodium channels in the cortical collecting duct. Which of the following is most likely to be decreased upon drug administration?
- A. Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules
- B. Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules
- C. Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules (Correct Answer)
- D. Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules
- E. Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Potassium secretion in the collecting tubules***
- Blocking **epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)** in the cortical collecting duct reduces sodium reabsorption, which in turn diminishes the electrochemical gradient driving **potassium secretion** into the lumen.
- This is because sodium reabsorption creates a more negative luminal charge, attracting potassium ions to move from the cell into the tubule.
- This is the mechanism of **potassium-sparing diuretics** like amiloride and triamterene.
*Urea reabsorption in the collecting tubules*
- Urea **reabsorption** primarily occurs in the **medullary collecting duct** via urea transporters (UT-A1, UT-A3) and is influenced by the inner medullary osmolarity and ADH.
- Blocking ENaC would primarily affect sodium flux and potassium secretion, with minimal direct impact on urea reabsorption in the collecting duct.
*Hydrogen ion secretion in the collecting tubules*
- **Hydrogen ion (H+) secretion** occurs in the collecting tubules via intercalated cells (α-intercalated cells), which is important for acid-base balance.
- While blocking ENaC can indirectly reduce H+ secretion (by decreasing the lumen-negative potential), the primary and most significant effect is on **potassium secretion**, making this a less likely answer.
*Sodium secretion in the collecting tubules*
- The primary function of ENaC is to **reabsorb sodium** from the tubular lumen back into the blood, not to secrete it.
- Sodium is not normally secreted in the collecting tubules; blocking ENaC would decrease sodium **reabsorption**, not affect sodium secretion.
*Sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule*
- **Sodium chloride reabsorption** in the distal convoluted tubule is mainly mediated by the **thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl co-transporter (NCC)**.
- ENaC are predominantly located in the cortical collecting duct (downstream from the DCT), so blocking them would not directly impact NaCl reabsorption in the distal tubule.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 2: Which hormone's secretion is primarily stimulated by increased plasma osmolality?
- A. EPO
- B. PTH
- C. ADH (Correct Answer)
- D. Aldosterone
- E. ANP
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***ADH***
- **Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)**, also known as vasopressin, is primarily released in response to an increase in **plasma osmolality**.
- Its main function is to promote water reabsorption in the kidneys, thereby decreasing osmolality and concentrating urine.
*EPO*
- **Erythropoietin (EPO)** is a hormone primarily produced by the kidneys in response to **hypoxia** (low oxygen levels), not increased plasma osmolality.
- It stimulates the production of **red blood cells** in the bone marrow.
*PTH*
- **Parathyroid hormone (PTH)** regulates **calcium** and phosphate levels in the blood, primarily stimulated by low plasma calcium concentrations.
- It does not directly respond to changes in plasma osmolality.
*Aldosterone*
- **Aldosterone** is a mineralocorticoid hormone involved in regulating **blood pressure** and electrolyte balance, particularly sodium and potassium.
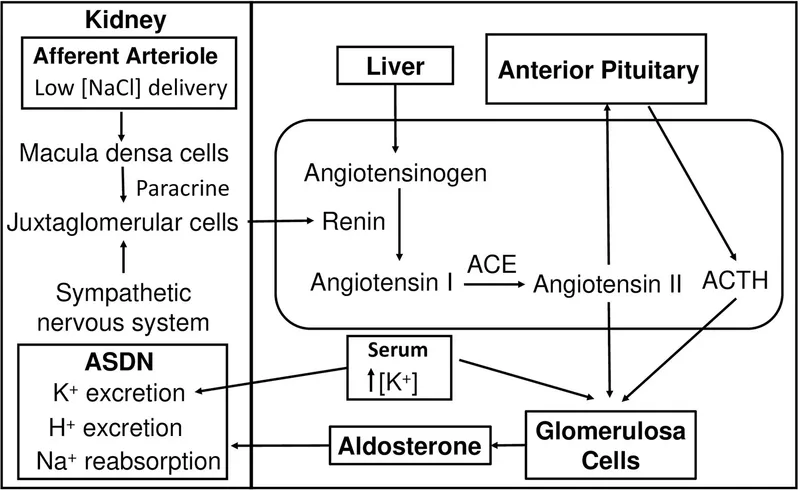
- Its secretion is primarily stimulated by the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system** in response to low blood volume or pressure, and high potassium levels, not plasma osmolality.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 3: A new drug X is being tested for its effect on renal function. During the experiments, the researchers found that in patients taking substance X, the urinary concentration of sodium decreases while urine potassium concentration increase. Which of the following affects the kidneys in the same way as does substance X?
- A. Aldosterone (Correct Answer)
- B. Furosemide
- C. Spironolactone
- D. Atrial natriuretic peptide
- E. Hydrochlorothiazide
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Aldosterone***
- **Aldosterone** acts on the **principal cells** of the **collecting duct** to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
- This action leads to a decrease in urinary sodium concentration and an increase in urinary potassium concentration, matching the effects of drug X.
*Furosemide*
- **Furosemide** is a **loop diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-K-2Cl cotransporter** in the **thick ascending limb** of the loop of Henle.
- This inhibition leads to increased excretion of sodium, potassium, and water, resulting in higher urinary sodium concentration.
*Spironolactone*
- **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that blocks aldosterone's effects on the collecting duct.
- This leads to increased sodium excretion and decreased potassium excretion (potassium-sparing effect), which is the opposite of drug X.
*Atrial natriuretic peptide*
- **Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** is released in response to atrial stretch and causes **natriuresis** (increased sodium excretion) and **diuresis**.
- It works by dilating afferent arterioles and constricting efferent arterioles, increasing GFR, and inhibiting sodium reabsorption, thus increasing urinary sodium concentration.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- **Hydrochlorothiazide** is a **thiazide diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-Cl cotransporter** in the **distal convoluted tubule**.
- This leads to increased sodium and chloride excretion but typically causes potassium wasting (hypokalemia), which differs from the increased urinary potassium concentration seen with drug X.
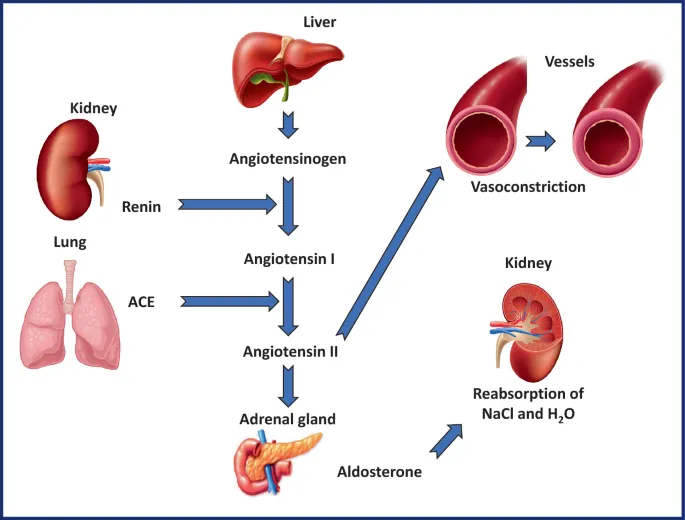
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 4: Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system yields a significant physiological effect on renal blood flow and filtration. Which of the following is most likely to occur in response to increased levels of Angiotensin-II?
- A. Decreased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction
- B. Decreased renal plasma flow, increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure
- C. Increased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction
- D. Increased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction
- E. Decreased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction (Correct Answer)
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Decreased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction***
- **Angiotensin II** causes **efferent arteriolar constriction**, which reduces blood flow leaving the glomerulus, thereby **decreasing renal plasma flow**.
- This efferent constriction also increases **glomerular hydrostatic pressure** and reduces plasma flow distal to the glomerulus, leading to a **higher filtration fraction** (GFR/RPF).
*Decreased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction*
- While **renal plasma flow decreases**, a **decreased filtration fraction** would imply that either GFR decreases disproportionately more than RPF or GFR does not increase despite the RPF reduction, which is not the typical response to **angiotensin II** due to its predominant effect on the **efferent arteriole**.
*Decreased renal plasma flow, increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure*
- **Increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure** is a consequence of increased filtration fraction, as more fluid is filtered out, leaving behind a more concentrated plasma. This option includes a correct element (decreased RPF) but pairs it with a less direct and defining outcome of acute Angiotensin II action as the primary physiological effect.
*Increased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction*
- **Angiotensin II** causes **vasoconstriction**, predominantly of the efferent arteriole, which by definition would **decrease renal plasma flow**, not increase it.
- A **decreased filtration fraction** would be inconsistent with efferent arteriolar constriction which typically raises GFR relative to RPF.
*Increased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction*
- **Angiotensin II** causes **vasoconstriction**, leading to a **decrease in renal plasma flow**, not an increase.
- While **filtration fraction is increased**, the initial premise of increased renal plasma flow is incorrect.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 5: A 35-year-old pregnant woman gives birth to a baby at term. The antepartum course was uneventful. She was compliant with all prenatal examinations and was given a prophylactic tetanus vaccine. While performing the neonatal examination, the pediatrician reports Apgar scores of 9 and 10 at 1 and 5 min, respectively. The pediatrician notices that the baby has ambiguous genitalia and blood pressure that is high for a neonate. The notable laboratory results are as follows:
Renin 0.4 nmoL/L/h
Aldosterone 70 pmoL/L
Cortisol 190 nmoL/L
Serum creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
Sex hormones are higher than the normal values at this age. Which of the following is responsible for the neonate's hypertension?
- A. Decreased amount of cortisol
- B. Decreased angiotensin response
- C. Increased amount of 11-deoxycorticosterone (Correct Answer)
- D. Decreased amount of aldosterone
- E. Increased concentration of sex hormones
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Increased amount of 11-deoxycorticosterone***
- The presented symptoms of **ambiguous genitalia**, **hypertension**, and **elevated sex hormones** alongside normal cortisol point to **11β-hydroxylase deficiency (CYP11B1)**.
- In this condition, **11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC)**, a potent mineralocorticoid, accumulates, leading to **volume expansion** and **hypertension**.
- The **low renin** (0.4 nmol/L/h) confirms volume expansion from DOC's mineralocorticoid activity.
*Decreased amount of cortisol*
- While adrenal enzyme deficiencies can lead to decreased cortisol, a normal cortisol level of **190 nmoL/L** makes this option unlikely.
- Decreased cortisol typically causes **adrenal crisis symptoms** (e.g., hypotension, hypoglycemia) rather than hypertension directly.
*Decreased angiotensin response*
- A decreased angiotensin response would likely contribute to **hypotension**, not hypertension, as angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor.
- The high blood pressure in this case indicates an overactive pressor system.
*Decreased amount of aldosterone*
- While aldosterone is **secondarily suppressed** in 11β-hydroxylase deficiency due to low renin (from DOC-mediated volume expansion), this is not the **primary mechanism** of hypertension.
- The hypertension is caused by **DOC accumulation**, not by aldosterone deficiency.
- Decreased aldosterone alone would typically lead to **salt wasting** and **hypotension**, but DOC's mineralocorticoid effects override this.
*Increased concentration of sex hormones*
- While **elevated sex hormones** contribute to the **ambiguous genitalia**, they are not the direct cause of the hypertension.
- The hypertension in this context is primarily mediated by the **mineralocorticoid effects** of accumulated adrenal precursors.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 6: A researcher is studying receptors that respond to epinephrine in the body and discovers a particular subset that is expressed in presynaptic adrenergic nerve terminals. She discovers that upon activation, these receptors will lead to decreased sympathetic nervous system activity. She then studies the intracellular second messenger changes that occur when this receptor is activated. She records these changes and begins searching for analogous receptor pathways. Which of the following receptors would cause the most similar set of intracellular second messenger changes?
- A. Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract
- B. Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system
- C. Vasopressin receptors in the kidney
- D. Dopamine receptors in the brain (Correct Answer)
- E. Aldosterone receptors in the kidney
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Dopamine receptors in the brain***
- The described presynaptic receptors for epinephrine that decrease sympathetic activity are **alpha-2 adrenergic receptors**, which are **G inhibitory protein (Gi)-coupled receptors**.
- Gi-coupled receptors **inhibit adenylyl cyclase**, leading to a **decrease in intracellular cAMP**, a signaling pathway shared by **D2 dopamine receptors**.
*Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract*
- Most muscarinic receptors (M1 and M3) in the GI tract are **Gq-coupled**, leading to an **increase in phospholipase C (PLC) activity**, ultimately increasing intracellular **IP3 and DAG** and promoting smooth muscle contraction.
- This mechanism is distinct from the **Gi-mediated inhibition of cAMP** described for the presynaptic adrenergic receptor.
*Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system*
- Growth hormone receptors are **tyrosine kinase-associated receptors** (specifically, they are linked to **JAK/STAT pathways**), not G protein-coupled receptors.
- Their intracellular signaling involves **protein phosphorylation cascades**, which are fundamentally different from second messenger changes involving cAMP.
*Vasopressin receptors in the kidney*
- Vasopressin (ADH) acts on **V2 receptors** in the kidney, which are **G stimulatory protein (Gs)-coupled receptors**.
- Activation of V2 receptors leads to an **increase in adenylyl cyclase activity** and thus an **increase in intracellular cAMP**, the opposite effect of the described Gi-coupled receptor.
*Aldosterone receptors in the kidney*
- Aldosterone receptors are **intracellular steroid hormone receptors** that directly bind to DNA and regulate gene transcription.
- They do not engage in rapid intracellular second messenger changes like G protein-coupled receptors, but rather alter **protein synthesis** over hours to days.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 7: A 33-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of headaches and muscle weakness. His physical exam is entirely within normal limits except for a blood pressure of 150/95. Subsequent routine blood lab work showed a sodium level of 146 and potassium level of 3.0. What is the best pharmacological therapy for this patient?
- A. Fludrocortisone
- B. Spironolactone (Correct Answer)
- C. Lisinopril
- D. Hydrochlorothiazide
- E. Propranolol
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Spironolactone***
- This patient's symptoms (hypertension, **hypokalemia**, and **hypernatremia**) are classic for **primary hyperaldosteronism**. **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that blocks the effects of aldosterone, effectively treating both the hypertension and electrolyte abnormalities.
- Aldosterone antagonists directly target the underlying pathology by countering the excessive mineralocorticoid activity, making it the most appropriate pharmacological therapy for primary hyperaldosteronism.
*Fludrocortisone*
- **Fludrocortisone** is a **mineralocorticoid** used to *replace* aldosterone in conditions like Addison's disease where aldosterone production is deficient.
- Administering fludrocortisone in a patient with excessive aldosterone (primary hyperaldosteronism) would worsen their condition by exacerbating hypertension, hypokalemia, and hypernatremia.
*Lisinopril*
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor** that works by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, leading to vasodilation and decreased aldosterone secretion.
- While ACE inhibitors can lower blood pressure, they are not the primary treatment for **primary hyperaldosteronism** because the condition involves autonomous aldosterone production **independent of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)**.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- **Hydrochlorothiazide** is a **thiazide diuretic** that works by increasing the excretion of sodium and water, thereby lowering blood pressure.
- However, thiazide diuretics also increase potassium excretion, which would further worsen the patient's existing **hypokalemia**, making it an inappropriate choice.
*Propranolol*
- **Propranolol** is a **non-selective beta-blocker** that lowers blood pressure by reducing heart rate and cardiac output.
- While useful for hypertension, beta-blockers do not address the underlying electrolyte disturbances characteristic of **primary hyperaldosteronism** and are not a first-line treatment for this specific condition.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 8: A 1-year-old male is found to have high blood pressure on multiple visits to your office. On examination, the patient has normal genitalia. Further laboratory workup reveals low serum aldosterone and high serum testosterone. Which of the following is most likely to be elevated in this patient?
- A. 17-hydroxyprogesterone
- B. progesterone
- C. corticosterone
- D. androstenedione
- E. 11-deoxycorticosterone (Correct Answer)
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***11-deoxycorticosterone***
- This clinical picture describes **11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency**, which blocks the conversion of 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol to cortisol.
- The accumulation of **11-deoxycorticosterone** acts as a mineralocorticoid, causing **hypertension** and **low renin/aldosterone levels**.
*17-hydroxyprogesterone*
- This is typically elevated in **21-hydroxylase deficiency**, which presents with **virilization** (due to increased testosterone) but usually causes **hypotension** (due to aldosterone deficiency), not hypertension.
- While testosterone is high, the low aldosterone and hypertension point away from 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
*Progesterone*
- Elevation of progesterone can occur in **3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency**, which would also lead to virilization but typically causes **salt wasting** and **hypotension**, not hypertension.
- It is not a primary marker for the specific type of hypertension seen here.
*Corticosterone*
- In 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency, the enzyme responsible for converting 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone is deficient, so **corticosterone levels would be low**, not elevated.
- Corticosterone is a precursor to aldosterone, and its reduced synthesis contributes to the hormonal imbalance.
*Androstenedione*
- While **androstenedione** would be elevated (as it is a precursor to testosterone, which is high), it is not the primary direct cause of the **hypertension** in this specific adrenal enzyme deficiency.
- The direct cause of hypertension is the accumulation of mineralocorticoid precursors like **11-deoxycorticosterone**.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 9: A 42-year-old gentleman presents to his primary care physician with complaints of persistent headaches and general weakness. He was recently diagnosed with severe hypertension that has been refractory to anti-hypertensive medications. Based on clinical suspicion, a basic metabolic panel is obtained which demonstrates a sodium level of 153 mg/dl and a potassium level of 2.9 mg/dl. The hormone that is the most likely cause of this patient's presentation is normally secreted by which region of the adrenal gland?
- A. Adrenal Medulla
- B. Adrenal Capsule
- C. Zona Reticularis
- D. Zona Glomerulosa (Correct Answer)
- E. Zona Fasciculata
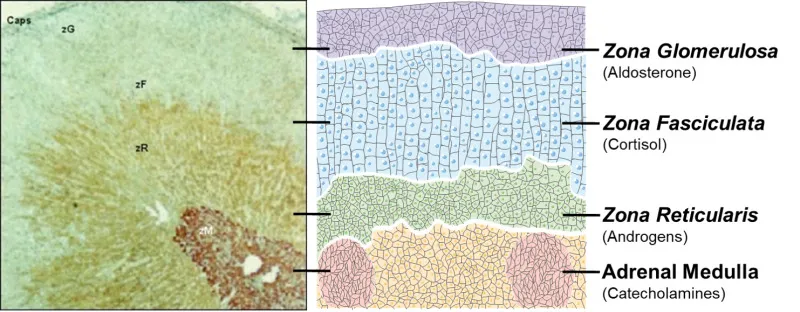
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Zona Glomerulosa***
- The patient's presentation of **severe hypertension refractory to treatment**, **hypernatremia** (sodium 153 mg/dl), and **hypokalemia** (potassium 2.9 mg/dl) is highly suggestive of **primary hyperaldosteronism**.
- **Aldosterone**, the hormone responsible for this clinical picture, is primarily secreted by the **zona glomerulosa** of the adrenal cortex.
*Adrenal Medulla*
- The adrenal medulla primarily secretes **catecholamines** (**epinephrine** and **norepinephrine**), which are involved in the "fight or flight" response.
- While excess catecholamines can cause hypertension, they do not typically lead to the characteristic electrolyte disturbances of hypernatremia and hypokalemia seen in this patient.
*Adrenal Capsule*
- The adrenal capsule is the **outer protective layer** of the adrenal gland and does not secrete hormones.
- Its primary function is structural support and protection for the underlying adrenal cortex and medulla.
*Zona Reticularis*
- The zona reticularis is the innermost layer of the adrenal cortex and primarily produces **androgens**, such as **dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)**.
- While androgen excess can have various effects, it does not explain the patient's severe hypertension, hypernatremia, and hypokalemia.
*Zona Fasciculata*
- The zona fasciculata is the middle and thickest layer of the adrenal cortex, responsible for secreting **glucocorticoids**, primarily **cortisol**.
- Excess cortisol (Cushing's syndrome) can cause hypertension and hypokalemia, but hypernatremia is less typical; indeed, **cortisol can have mineralocorticoid effects**, but primary hyperaldosteronism is a more specific fit for this electrolyte profile.
Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG Question 10: A 54-year-old man presents with 3 days of non-bloody and non-bilious emesis every time he eats or drinks. He has become progressively weaker and the emesis has not improved. He denies diarrhea, fever, or chills and thinks his symptoms may be related to a recent event that involved sampling many different foods. His temperature is 97.5°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 133/82 mmHg, pulse is 105/min, respirations are 15/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a weak appearing man with dry mucous membranes. His abdomen is nontender. Which of the following laboratory changes would most likely be seen in this patient?
- A. Metabolic alkalosis and hyperkalemia
- B. Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia
- C. Respiratory acidosis and hyperkalemia
- D. Metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Anion gap metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia
Aldosterone synthesis and release Explanation: ***Metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia***
- Persistent **vomiting** leads to the loss of **gastric acid** (HCl) and **potassium**, resulting in **metabolic alkalosis** and **hypokalemia**. The loss of HCl directly removes acid from the body, and the subsequent renal compensation to conserve volume often exacerbates potassium loss.
- The patient's presentation with **dry mucous membranes**, increased heart rate (pulse 105/min), and persistent non-bloody, non-bilious emesis suggests significant volume depletion and electrolyte imbalances consistent with prolonged vomiting.
*Metabolic alkalosis and hyperkalemia*
- While metabolic alkalosis is expected due to gastric acid loss from vomiting, **hyperkalemia** is unlikely. Vomiting typically causes **hypokalemia** due to direct potassium loss and renal compensation mechanisms.
- The body attempts to compensate for volume depletion, leading to increased activity of the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system**, which promotes potassium excretion in the urine.
*Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia*
- **Metabolic acidosis** is characterized by a decrease in blood pH and bicarbonate; however, profuse vomiting of gastric contents primarily leads to **alkalosis** due to the loss of hydrogen ions.
- **Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis** is usually seen in conditions involving bicarbonate loss from the kidneys or gut (e.g., diarrhea, renal tubular acidosis), not vomiting.
*Respiratory acidosis and hyperkalemia*
- **Respiratory acidosis** results from hypoventilation, leading to an increase in blood CO2, which is not suggested by the patient's normal respiratory rate and oxygen saturation.
- Profuse vomiting causes a loss of gastric acid and can lead to compensatory **hypoventilation** to retain CO2 (acid), but this is a secondary response to metabolic alkalosis, and primary respiratory acidosis is not the underlying issue.
*Anion gap metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia*
- **Anion gap metabolic acidosis** typically occurs with the accumulation of unmeasured acids (e.g., lactic acidosis, ketoacidosis, renal failure, poisoning), which is not indicated by the patient's symptoms.
- While **hypokalemia** is consistent with vomiting, the primary acid-base disturbance from prolonged emesis is metabolic alkalosis, not acidosis.
More Aldosterone synthesis and release US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.