RAAS

On this page
🌊 The Pressure Control Command Center
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system orchestrates blood pressure and volume through an elegant enzymatic cascade that touches nearly every organ system. You'll trace how a single kidney enzyme triggers a multi-step amplification sequence, learn why this pathway becomes both lifesaver and disease driver, and master how modern medicine intercepts it at precise molecular checkpoints. By connecting the biochemical machinery to clinical patterns-from heart failure to hyperkalemia-you'll build the diagnostic intuition and therapeutic command needed to manipulate this system safely and effectively in real patients.

📌 Remember: RAAS-PACE - Renin triggers, Angiotensinogen converts, ACE transforms, Squeeze vessels, Potassium drops, Aldosterone acts, Conserve sodium, Expand volume
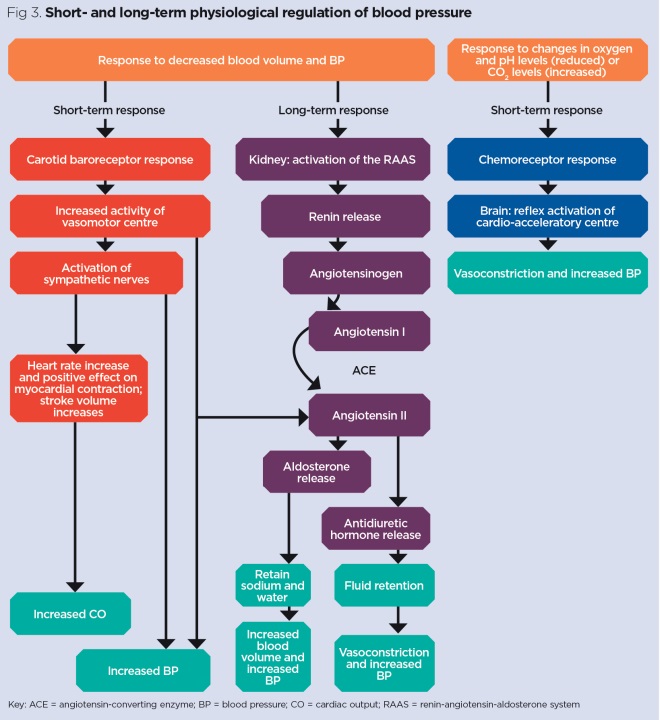
The system operates through three primary components: the renin-producing juxtaglomerular apparatus, circulating angiotensin peptides, and aldosterone-responsive distal nephron. Each component responds to specific stimuli with quantifiable thresholds that determine activation intensity.
- Renin Release Triggers
- Decreased renal perfusion pressure (<90 mmHg systolic)
- Sympathetic stimulation (β1-adrenergic activation)
- Decreased sodium delivery to macula densa (<20 mEq/L tubular concentration)
- Baroreceptor sensitivity: ±5 mmHg pressure changes
- Chemoreceptor threshold: ±2 mEq/L sodium variations
- Neural response time: <30 seconds from stimulus
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Renin levels increase 3-5 fold within 15 minutes of volume depletion, with peak response occurring at 60-90 minutes. This rapid activation explains why acute blood loss triggers immediate RAAS-mediated compensation.
| Component | Normal Range | Activation Threshold | Peak Response Time | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Renin Activity | 0.5-3.3 ng/mL/hr | >5.0 ng/mL/hr | 60-90 minutes | Hypertension screening |
| Angiotensin II | 10-25 pg/mL | >50 pg/mL | 15-30 minutes | Vasoconstriction onset |
| Aldosterone | 5-30 ng/dL | >50 ng/dL | 2-4 hours | Volume retention |
| Plasma Volume | 40-45 mL/kg | <35 mL/kg | 6-12 hours | Compensation complete |
| Sodium Retention | 1-2 mEq/day | >10 mEq/day | 24-48 hours | Edema formation |
The juxtaglomerular apparatus functions as the system's primary sensor, with specialized baroreceptor cells detecting pressure changes as small as ±3 mmHg. These cells contain renin-filled granules that release their contents through calcium-dependent exocytosis within seconds of appropriate stimulation.
Understanding this foundational architecture prepares you to master the enzymatic cascade that amplifies these initial signals into powerful cardiovascular responses.
🌊 The Pressure Control Command Center
⚡ The Enzymatic Amplification Engine
📌 Remember: ACE-LUNG - Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, Concentrated in Endothelium, Lung has highest density, Ubiquitous distribution, Ninety percent conversion efficiency, Generates Angiotensin II
The renin-angiotensinogen reaction represents the rate-limiting step, with Km = 2.5 μM and Vmax achieving 90% conversion within 15 minutes under physiological conditions. Renin demonstrates absolute specificity for the Leu10-Val11 bond in angiotensinogen, ensuring precise peptide generation without off-target effects.
- Renin Enzymatic Properties
- Molecular weight: 37,000 Da (active form)
- Optimal pH: 6.0-7.4 (physiological range)
- Half-life: 15-20 minutes in circulation
- Kidney clearance: 60-70% of total elimination
- Hepatic metabolism: 25-30% contribution
- Plasma protein binding: <5% (mostly free)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: ACE demonstrates tissue-specific expression patterns with lung endothelium containing 100-fold higher concentrations than plasma. This explains why pulmonary embolism can acutely elevate circulating angiotensin II through massive ACE release from damaged lung tissue.
| Enzyme | Tissue Distribution | Conversion Efficiency | Inhibitor Class | Clinical Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renin | JGA cells, plasma | 90% in 15 min | Direct renin inhibitors | Aliskiren |
| ACE | Lung, endothelium | 95% single pass | ACE inhibitors | Lisinopril, enalapril |
| Chymase | Heart, vessels | 60% alternative | Chymase inhibitors | Experimental |
| ACE2 | Heart, kidney | 80% Ang II → Ang(1-7) | None available | Protective pathway |
| Neprilysin | Kidney, brain | 70% peptide degradation | NEP inhibitors | Sacubitril |
💡 Master This: The enzymatic cascade provides signal amplification - one renin molecule generates >1000 angiotensin II molecules over its 15-minute half-life. This amplification explains why small changes in renin release produce dramatic cardiovascular effects and why enzyme inhibitors are so therapeutically effective.
- Alternative Pathways
- Chymase pathway: 40% of cardiac angiotensin II production
- Cathepsin G: 15% contribution in vascular tissue
- Tonin: <5% but important in salt-sensitive hypertension
- Tissue-specific expression varies 10-fold between individuals
- Genetic polymorphisms affect enzyme efficiency by ±30%
- Age-related changes: ACE activity increases 2% annually after age 40
Understanding these enzymatic mechanisms reveals how pattern recognition of enzyme activity guides therapeutic targeting and diagnostic interpretation in cardiovascular disease.
⚡ The Enzymatic Amplification Engine
🎯 The Cardiovascular Response Matrix
📌 Remember: AT1-VACS - Vasoconstriction, Aldosterone stimulation, Cardiac hypertrophy, Sympathetic activation. AT2-DIVE - Dilation, Inhibits growth, Vasodilation, Endothelial protection
The AT1 receptor pathway mediates >90% of pathological RAAS effects, operating through Gq/G11 protein coupling that activates phospholipase C and generates IP3/DAG second messengers. This cascade produces measurable responses within 15-30 seconds of receptor binding.
- AT1 Receptor-Mediated Effects
- Vascular smooth muscle contraction: EC50 = 0.1-1.0 nM
- Aldosterone synthesis stimulation: 3-5 fold increase within 30 minutes
- Cardiac contractility enhancement: +20-30% inotropy
- Coronary vasoconstriction: 15-25% diameter reduction
- Renal vasoconstriction: 30-40% blood flow decrease
- Sympathetic nervous system activation: 2-3 fold norepinephrine release
⭐ Clinical Pearl: AT1 receptor density increases 2-4 fold in heart failure, creating enhanced sensitivity to circulating angiotensin II. This upregulation explains why ARBs (Angiotensin Receptor Blockers) provide greater benefit in advanced heart failure compared to early-stage disease.
| Receptor | Tissue Distribution | Primary Actions | Response Time | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT1 | Heart, vessels, adrenals | Vasoconstriction, aldosterone | 15-30 seconds | Hypertension, HF |
| AT2 | Fetal tissues, adult brain | Vasodilation, anti-growth | 2-5 minutes | Cardioprotection |
| Mas | Heart, kidney, brain | Ang(1-7) effects, protection | 1-3 minutes | Counter-regulatory |
| AT4 | Brain, heart, kidney | Cognitive, renal protection | 5-15 minutes | Neuroprotection |
| IRAP | Multiple tissues | Insulin regulation | 10-30 minutes | Metabolic effects |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||||
| flowchart TD |
ANG2["<b>🩸 Angiotensin II</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Effector peptide</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• RAAS component</span>"]
REC["<b>🧬 Receptor Type</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• GPCR pathway</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Binding site</span>"]
GQ["<b>🔗 Gq/G11 Protein</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Signal coupling</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• AT1 mediated</span>"]
GI["<b>🔗 Gi/Go Protein</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Signal coupling</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• AT2 mediated</span>"]
PLC["<b>🧪 PLC Activation</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Phospholipase C</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Enzyme catalysis</span>"]
IP3["<b>🧪 IP3/DAG</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Second messenger</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Lipid signaling</span>"]
CGMP["<b>🧪 ⬆️ cGMP</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Cyclic GMP</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬆️ Nitric oxide</span>"]
CA2["<b>⚡ Ca2+ Release</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Intracellular</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Ion influx</span>"]
PKC["<b>🧪 PKC Activation</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Protein Kinase C</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Phosphorylation</span>"]
VCON["<b>⚠️ Vasoconstriction</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Muscle squeeze</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬆️ BP response</span>"]
GENE["<b>🧬 Gene Expression</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Transcription</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Growth factors</span>"]
VDIL["<b>✅ Vasodilation</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Vessel relax</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Counter-regulates</span>"]
ANG2 --> REC
REC -->|AT1| GQ
REC -->|AT2| GI
GQ --> PLC
GQ --> IP3
PLC --> CA2
CA2 --> VCON
IP3 --> PKC
PKC --> GENE
GI --> CGMP
CGMP --> VDIL
style ANG2 fill:#F7F5FD,stroke:#F0EDFA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#6B21A8
style REC fill:#FEF8EC,stroke:#FBECCA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#854D0E
style GQ fill:#F7F5FD,stroke:#F0EDFA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#6B21A8
style GI fill:#F7F5FD,stroke:#F0EDFA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#6B21A8
style PLC fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C
style IP3 fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C
style CGMP fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C
style CA2 fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C
style PKC fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C
style VCON fill:#FDF4F3,stroke:#FCE6E4,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#B91C1C
style GENE fill:#F6F5F5,stroke:#E7E6E6,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#525252
style VDIL fill:#F1FCF5,stroke:#BEF4D8,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#166534
The **dose-response relationship** follows **sigmoidal kinetics** with **physiological concentrations** (**10-25 pg/mL**) producing **minimal effects**, while **pathological levels** (**>50 pg/mL**) trigger **maximal responses**. This **threshold effect** explains why **RAAS activation** produces **dramatic clinical changes** rather than **gradual progression**.
> 💡 **Master This**: **Pattern Recognition Framework** - When you see **elevated angiotensin II** (**>50 pg/mL**), expect **systolic BP increase** of **15-25 mmHg** within **5 minutes**, **aldosterone rise** of **200-300%** within **30 minutes**, and **sodium retention** of **50-100 mEq** within **24 hours**.
* **Cardiovascular Integration Patterns**
- **Acute Response** (**<5 minutes**): Vasoconstriction dominates
- **Intermediate Response** (**30 minutes-2 hours**): Aldosterone effects begin
- **Chronic Response** (**>24 hours**): Volume expansion and remodeling
+ **Cardiac output**: Initially decreases **10-15%**, then normalizes
+ **Peripheral resistance**: Increases **25-40%** and remains elevated
+ **Blood volume**: Expands **5-10%** over **48-72 hours**
The **AT2 receptor** provides **counter-regulatory effects**, increasing **cGMP levels** by **200-400%** and promoting **nitric oxide synthesis**. This pathway becomes **therapeutically important** when **AT1 receptors** are blocked, allowing **unopposed AT2 activation** to provide **cardioprotective benefits**.
Understanding these response patterns enables **precise prediction** of **therapeutic outcomes** and **optimal timing** of **cardiovascular interventions**.
---
🎯 The Cardiovascular Response Matrix
🔬 The Diagnostic Discrimination Arsenal
📌 Remember: ARR-SALT - Aldosterone-to-Renin Ratio, Salt loading test, Aldosterone suppression, Lateral sampling, Tumor localization
The Aldosterone-to-Renin Ratio (ARR) serves as the primary screening tool, with normal values <20 and suspicious values >30. However, medication effects and dietary sodium can alter these ratios by ±50%, requiring standardized testing conditions for accurate interpretation.
- ARR Interpretation Framework
- ARR <20: Primary aldosteronism unlikely (<5% probability)
- ARR 20-30: Borderline range, requires confirmatory testing
- ARR >30: High suspicion (>80% probability of primary aldosteronism)
- Medication washout: 2-4 weeks for ACE inhibitors/ARBs
- Dietary preparation: >150 mEq sodium daily for 3 days
- Timing considerations: Morning collection after 2 hours upright
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Spironolactone therapy can suppress aldosterone for 4-6 weeks after discontinuation, creating false-negative ARR results. Always verify medication history and allow adequate washout periods before definitive testing.
| Condition | Renin Activity | Aldosterone | ARR | Confirmatory Test | Diagnostic Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Aldosteronism | <1.0 ng/mL/hr | >15 ng/dL | >30 | Salt suppression | 95% |
| Renovascular HTN | >5.0 ng/mL/hr | >20 ng/dL | <10 | Captopril test | 90% |
| Essential HTN | 1-3 ng/mL/hr | 5-15 ng/dL | 10-20 | None needed | 85% |
| Secondary HTN | Variable | Variable | Variable | Specific tests | 80-95% |
| Low-renin HTN | <0.5 ng/mL/hr | Normal | >20 | Volume studies | 75% |
💡 Master This: Diagnostic Pattern Recognition - ARR >50 with aldosterone >20 ng/dL and renin <0.5 ng/mL/hr indicates >95% probability of aldosterone-producing adenoma. This pattern predicts excellent surgical outcomes with >90% cure rates.
- Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- Adrenal venous sampling: Gold standard for lateralization
- Selectivity index: >2.0 confirms adequate catheter placement
- Lateralization index: >4.0 indicates unilateral disease
- Success rate: 85-90% in experienced centers
- Complication rate: <2% for major adverse events
- Cost-effectiveness: Superior to empirical medical therapy
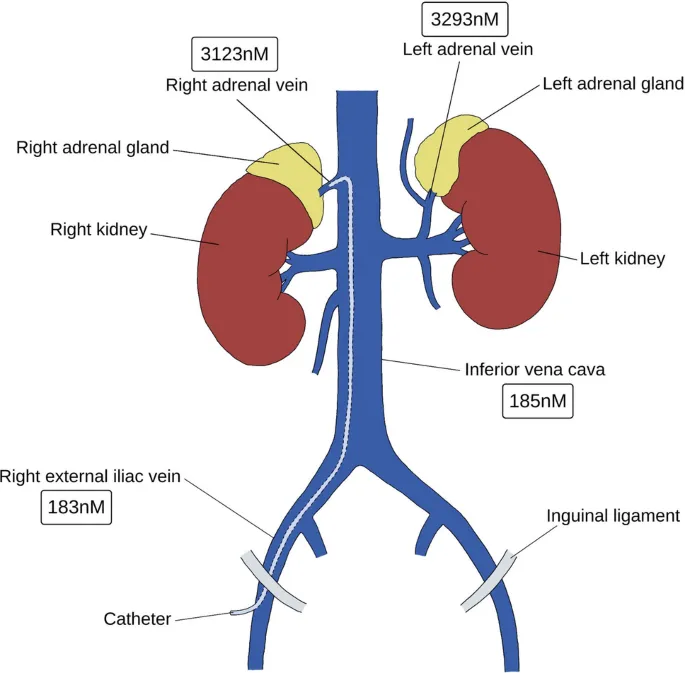
The captopril stimulation test differentiates renovascular hypertension from essential hypertension, with renin increase >150% and blood pressure drop >10% indicating >90% probability of renal artery stenosis.
- Renovascular Hypertension Markers
- Baseline renin: >3.0 ng/mL/hr (sensitivity 85%)
- Post-captopril renin: >12 ng/mL/hr (specificity 95%)
- Blood pressure response: >10 mmHg drop (positive predictive value 80%)
- Renal vein renin ratio: >1.5 confirms functional significance
- Imaging correlation: >70% stenosis required for hemodynamic effect
- Treatment response: ACE inhibitors may cause acute renal failure
Understanding these discriminatory frameworks enables precise diagnosis and optimal therapeutic targeting in complex RAAS disorders.
🔬 The Diagnostic Discrimination Arsenal
⚕️ The Therapeutic Targeting Command Center
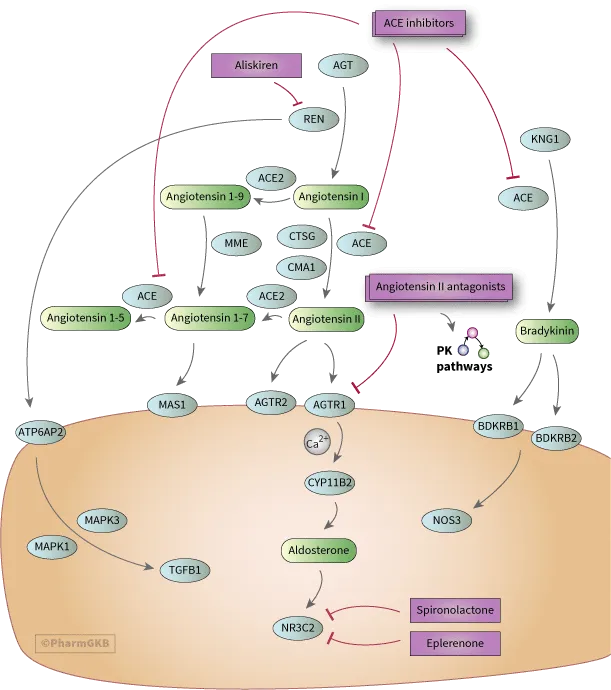
📌 Remember: RAAS-BLOCK - Renin inhibitors, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, Spironolactone, Beta-blockers, Loop diuretics, Other agents, Combination therapy, Kidney protection
The ACE inhibitor class provides dual benefits through angiotensin II reduction and bradykinin preservation, achieving systolic BP reductions of 15-25 mmHg with cardiovascular mortality reduction of 20-25% in high-risk populations.
- ACE Inhibitor Mechanisms
- Angiotensin II reduction: 70-85% decrease in circulating levels
- Bradykinin preservation: 2-3 fold increase in tissue concentrations
- Aldosterone suppression: 40-60% reduction in plasma levels
- Onset of action: 1-2 hours for acute effects
- Peak effect: 4-6 hours for maximum BP reduction
- Duration: 12-24 hours depending on half-life
⭐ Clinical Pearl: ACE inhibitor cough occurs in 10-15% of patients due to bradykinin accumulation. This effect is dose-independent and reversible within 1-4 weeks of discontinuation. ARBs provide equivalent efficacy without bradykinin effects.
| Drug Class | BP Reduction | Mortality Benefit | Major Side Effects | Contraindications | Cost Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitors | 15-25 mmHg | 20-25% reduction | Cough (10-15%) | Pregnancy, angioedema | 1.0x |
| ARBs | 12-20 mmHg | 15-20% reduction | Minimal (<5%) | Pregnancy | 2-3x |
| Aldosterone Antagonists | 8-15 mmHg | 30% in HF | Hyperkalemia (8-12%) | CKD, hyperkalemia | 1.5x |
| Renin Inhibitors | 10-18 mmHg | Unknown | GI effects (5-8%) | Pregnancy | 10-15x |
| Combination Therapy | 25-35 mmHg | 35-40% reduction | Additive effects | Multiple | 2-4x |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | |||||
| flowchart TD |
RAAS["🔄 RAAS Activation
• Systemic response• BP regulation"]
Target{"🎯 Drug Target
• Protein site• Enzyme/Receptor"}
Alis["💊 Aliskiren
• Direct inhibitor• Renin block"]
ACEI["💊 ACE Inhibitors
• Lisinopril/Enalap• ACE blockade"]
ARB["💊 ARBs
• Losartan/Valsartan• AT1 blockade"]
MRA["💊 Spirono/Eplere
• Spironolactone• Aldosterone antag"]
RenInh["🧪 Renin Inhibition
• Block enzyme• Rate limiting step"]
ACEBlk["🧪 ACE Blockade
• No Ang I to II• Bradykinin ⬆️"]
AT1Blk["🧪 AT1 Blockade
• Specific receptor• AT2 activation"]
AldoAnt["🧪 Aldo Antagonism
• Mineralocorticoid• Distal tubule act"]
Res1["✅ Reduced Ang I
• ⬇️ Angiotensin I• BP ⬇️"]
Res2["✅ ACE Results
• ⬇️ Ang II levels• ⬆️ Bradykinin"]
Res3["✅ ARB Results
• AT1 Blocked• AT2 Activated"]
Res4["✅ Na+ Results
• ⬇️ Na+ Retention• ⬇️ Blood Volume"]
RAAS --> Target Target -->|Renin| Alis Target -->|ACE| ACEI Target -->|AT1 Rec| ARB Target -->|Aldosterone| MRA
Alis --> RenInh --> Res1 ACEI --> ACEBlk --> Res2 ARB --> AT1Blk --> Res3 MRA --> AldoAnt --> Res4
style RAAS fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Target fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Alis fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style ACEI fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style ARB fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style MRA fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style RenInh fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style ACEBlk fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style AT1Blk fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style AldoAnt fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style Res1 fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style Res2 fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style Res3 fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style Res4 fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252
The **ARB class** offers **selective AT1 receptor blockade** without **bradykinin effects**, providing **equivalent cardiovascular protection** with **superior tolerability**. **ARBs allow unopposed AT2 receptor activation**, potentially providing **additional cardioprotective benefits**.
> 💡 **Master This**: **Combination therapy** with **ACE inhibitor + ARB** provides **additive BP reduction** (**5-10 mmHg additional**) but **increases hyperkalemia risk** by **200-300%**. Reserve this combination for **resistant hypertension** with **careful electrolyte monitoring**.
* **Aldosterone Antagonist Benefits**
- **Spironolactone**: **25-50 mg daily** reduces **cardiovascular mortality** by **30%** in **heart failure**
- **Eplerenone**: **Selective mineralocorticoid receptor** antagonist with **fewer hormonal side effects**
- **Potassium effects**: **Serum K+ increases** by **0.3-0.5 mEq/L** on average
+ **Monitoring requirements**: **Weekly K+ checks** for **first month**
+ **Dose adjustment**: **Reduce by 50%** if **K+ >5.0 mEq/L**
+ **Discontinuation**: **Required** if **K+ >5.5 mEq/L** despite **dose reduction**
The **renin inhibitor aliskiren** provides **upstream RAAS blockade** but offers **limited clinical advantages** over **established therapies** while costing **10-15 times more**. **Clinical trials** have not demonstrated **superior outcomes** compared to **ACE inhibitors** or **ARBs**.
* **Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithms**
- **First-line therapy**: **ACE inhibitor** or **ARB** plus **thiazide diuretic**
- **Second-line addition**: **Calcium channel blocker** or **aldosterone antagonist**
- **Resistant hypertension**: **Triple therapy** plus **spironolactone**
+ **Target BP**: **<130/80 mmHg** for **most patients**
+ **High-risk patients**: **<120/80 mmHg** if **tolerated**
+ **Elderly patients**: **<140/90 mmHg** to **avoid hypotension**
Understanding these **therapeutic principles** enables **optimal drug selection** and **combination strategies** that maximize **cardiovascular protection** while **minimizing adverse effects**.
---
⚕️ The Therapeutic Targeting Command Center
🌐 The Multi-System Integration Network
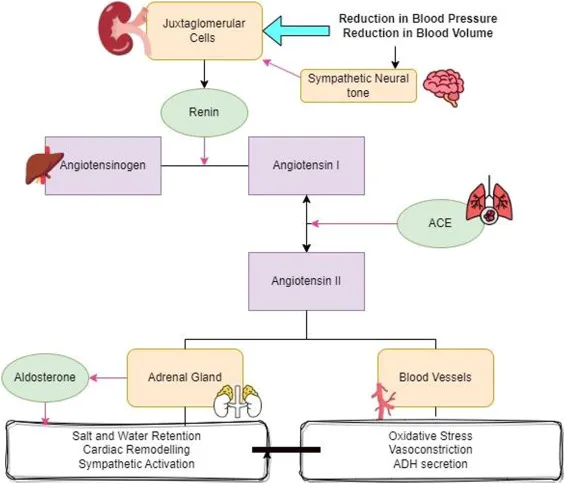
📌 Remember: RAAS-SYNC - Sympathetic activation, Younger patients more responsive, Neurohormonal cascade, Cardiac remodeling
The sympathetic nervous system provides bidirectional RAAS interaction, with angiotensin II stimulating central sympathetic outflow by 200-300% while sympathetic activation increases renin release through β1-adrenergic stimulation. This positive feedback loop amplifies cardiovascular responses and explains resistant hypertension patterns.
- Neurohormonal Integration Patterns
- Central angiotensin II effects: Sympathetic activation within 5-10 minutes
- Peripheral sympathetic stimulation: Renin release increases 3-5 fold
- Baroreceptor sensitivity: Reduced by 40-60% with chronic RAAS activation
- Heart rate variability: Decreased by 25-35% in RAAS-mediated hypertension
- Circadian patterns: Blunted nocturnal dipping in >70% of patients
- Exercise response: Exaggerated BP rise during physical stress
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Non-classical RAAS pathways become therapeutically important in advanced disease states. ACE2/Angiotensin(1-7)/Mas receptor axis provides counter-regulatory effects that are enhanced when classical RAAS is pharmacologically blocked.
| System | RAAS Effect | Integration Mechanism | Clinical Manifestation | Therapeutic Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Vasoconstriction, hypertrophy | AT1 receptor activation | Hypertension, LVH | ACE-I, ARB |
| Renal | Sodium retention, GFR reduction | Aldosterone, Ang II | Edema, CKD progression | Aldosterone antagonists |
| Endocrine | Aldosterone, vasopressin | Adrenal stimulation | Hypokalemia, volume expansion | Spironolactone |
| Nervous | Sympathetic activation | Central Ang II effects | Increased HR, vasoconstriction | Beta-blockers |
| Metabolic | Insulin resistance | Aldosterone effects | Diabetes risk | Lifestyle, metformin |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||||
| flowchart TD |
RAAS["🧬 RAAS Activation
• Renin-Angiotensin• Systemic response"]
CV["🫀 CV Effects
• Vascular impact• Heart stress"]
HTN["🩺 Hypertension
• ⬆️ BP pressure• Vessel strain"]
REM["🏗️ Remodeling
• Cardiac hypertrophy• Tissue fibrosis"]
REN["💧 Renal Effects
• Kidney function• Fluid balance"]
VOL["🌊 Vol. Retention
• Salt/Water intake• ⬆️ Blood volume"]
EDE["🦶 Edema
• Fluid in tissues• Visible swelling"]
END["💊 Endocrine
• Hormonal shift• Glandular output"]
ALD["🧪 Aldosterone ⬆️
• Mineralocorticoid• Adrenal secretion"]
ELY["⚖️ Electrolytes
• ⬇️ Potassium K+• Ion imbalance"]
NEU["🧠 Neurological
• CNS involvement• Nerve signaling"]
SYM["⚡ Sympathetic
• Fight or flight• Adrenergic tonus"]
INR["⬆️ Renin
• Feedback loop• ⬆️ RAAS trigger"]
RAAS --> CV CV --> HTN HTN --> REM
RAAS --> REN REN --> VOL VOL --> EDE
RAAS --> END END --> ALD ALD --> ELY
RAAS --> NEU NEU --> SYM SYM --> INR INR -.-> RAAS
style RAAS fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style CV fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style HTN fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style REM fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style REN fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style VOL fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1 style EDE fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style END fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style ALD fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style ELY fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style NEU fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style SYM fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style INR fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
The **cardiac remodeling process** involves **complex molecular pathways** beyond **simple pressure overload**. **Angiotensin II** directly stimulates **collagen synthesis** by **300-400%** and **cardiomyocyte hypertrophy** through **AT1 receptor-mediated gene transcription**. These effects occur **independently** of **blood pressure changes**.
> 💡 **Master This**: **RAAS-mediated cardiac remodeling** follows **predictable patterns** - **concentric hypertrophy** develops within **6-12 months** of **sustained activation**, followed by **diastolic dysfunction** and eventually **systolic heart failure** if **untreated**. **Early intervention** with **RAAS blockade** can **reverse** these changes.
* **Advanced Integration Concepts**
- **Tissue RAAS systems**: **Local hormone production** independent of **circulating levels**
- **Genetic polymorphisms**: **ACE I/D polymorphism** affects **cardiovascular risk** by **±25%**
- **Age-related changes**: **RAAS sensitivity** decreases **2-3% annually** after **age 65**
+ **Gender differences**: **Premenopausal women** show **reduced RAAS activation**
+ **Ethnic variations**: **African Americans** demonstrate **low-renin hypertension** patterns
+ **Comorbidity interactions**: **Diabetes** amplifies **RAAS-mediated kidney damage**
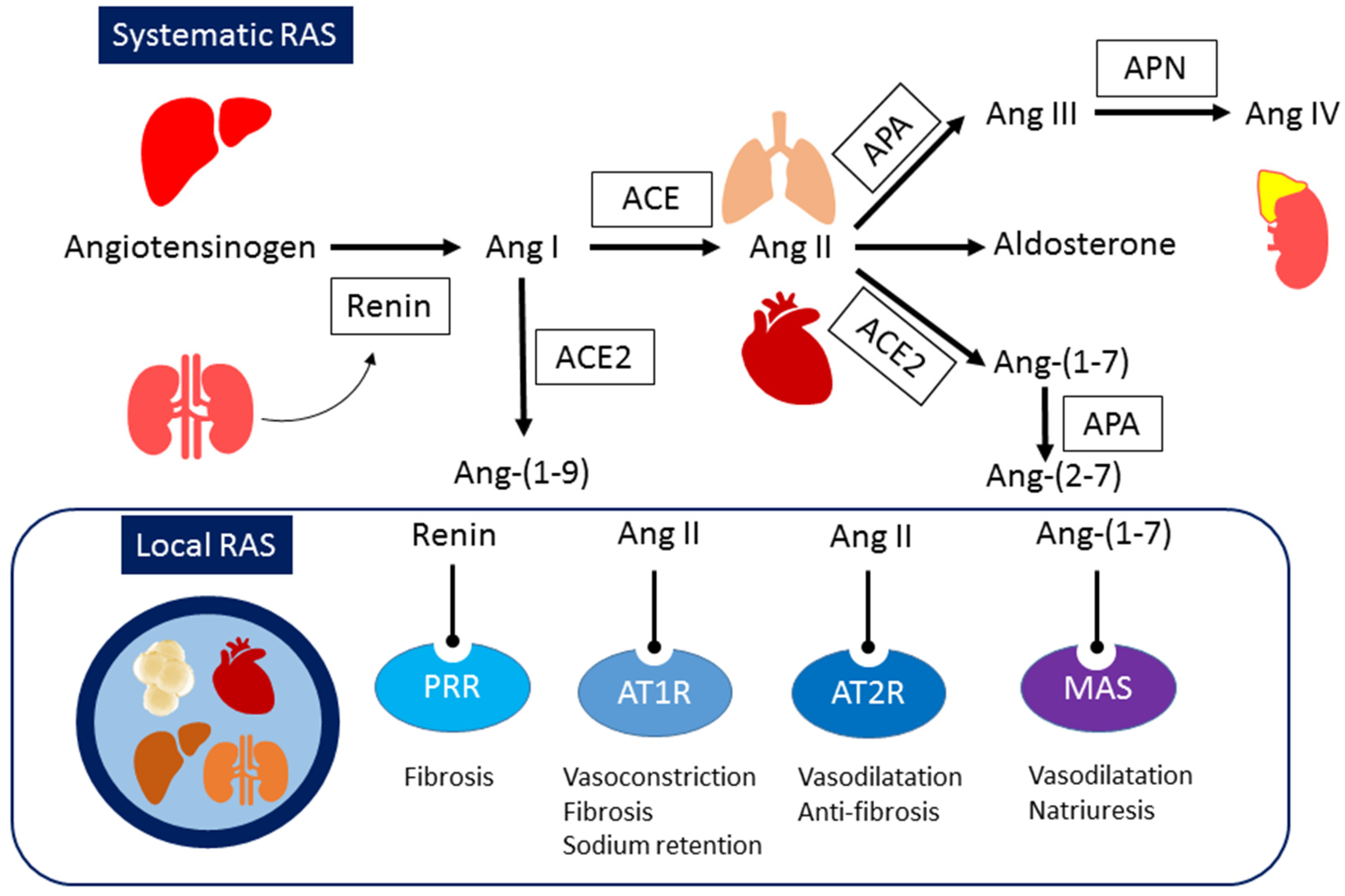
The **metabolic syndrome connection** reveals **bidirectional relationships** between **RAAS activation** and **insulin resistance**. **Aldosterone** directly impairs **glucose metabolism** while **hyperinsulinemia** stimulates **aldosterone synthesis**, creating **pathological feedback loops**.
* **Cutting-Edge Research Insights**
- **ACE2/SARS-CoV-2 interactions**: **Viral binding** reduces **protective ACE2 activity**
- **Microbiome influences**: **Gut bacteria** affect **RAAS component expression**
- **Epigenetic modifications**: **Environmental factors** alter **RAAS gene expression**
+ **Exercise effects**: **Regular activity** reduces **tissue RAAS activation** by **20-30%**
+ **Dietary influences**: **High sodium** upregulates **aldosterone sensitivity**
+ **Stress responses**: **Chronic stress** amplifies **RAAS-sympathetic interactions**
Understanding these **multi-system relationships** enables **comprehensive treatment approaches** that address **underlying pathophysiology** rather than **isolated symptoms**.
---
🌐 The Multi-System Integration Network
🎯 The Clinical Mastery Toolkit
📌 Remember: RAAS-MASTER - Monitor electrolytes, Assess kidney function, Screen for aldosteronism, Target BP goals, Evaluate drug interactions, Recognize contraindications
Essential Clinical Thresholds for immediate reference:
- Diagnostic Values
- Normal ARR: <20 (screening threshold)
- Suspicious ARR: >30 (requires confirmation)
- Primary aldosteronism: ARR >50 + aldosterone >15 ng/dL
- Renin suppression: <1.0 ng/mL/hr confirms autonomous aldosterone
- Salt suppression failure: Aldosterone >10 ng/dL after saline load
- Lateralization index: >4.0 indicates surgical candidate
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Hyperkalemia risk increases exponentially when combining RAAS inhibitors - ACE inhibitor + ARB + spironolactone increases severe hyperkalemia risk by 500-800%. Monitor K+ weekly for first month of combination therapy.
| Clinical Scenario | Key Values | Immediate Action | Monitoring Requirements | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertensive Crisis | BP >180/120 | IV nicardipine, avoid ACE-I | BP q15min, neuro checks | 10-20% reduction/hr |
| Hyperkalemia >6.0 | K+ >6.0 mEq/L | Stop RAAS drugs, calcium | ECG, K+ q2-4hr | Normalize in 4-6hr |
| Acute Renal Failure | Cr increase >50% | Hold ACE-I/ARB | Daily Cr, urine output | Stabilize in 48-72hr |
| Aldosterone Excess | ARR >50 | Confirm with suppression | K+, BP, imaging | Surgery vs medical Rx |
| Heart Failure | EF <40% | ACE-I + spironolactone | BNP, K+, Cr | Mortality reduction 30% |
Rapid Assessment Framework:
- Primary Aldosteronism Screening (30-second evaluation)
- Hypertension + Hypokalemia = Screen immediately
- Resistant hypertension = ARR mandatory
- Adrenal incidentaloma = Functional assessment required
- Prevalence: 5-10% of all hypertensive patients
- Cure rate: >90% with unilateral adenoma
- Missed diagnosis cost: $50,000+ in cardiovascular complications
Drug Interaction Alert System:
- High-Risk Combinations
- ACE inhibitor + ARB + Spironolactone: Hyperkalemia risk 500-800%
- NSAIDS + ACE inhibitors: Acute kidney injury risk 200-300%
- Trimethoprim + Spironolactone: Severe hyperkalemia within 48-72 hours
- Monitoring intensity: Weekly labs for high-risk combinations
- Dose adjustments: Reduce by 50% if K+ >5.0 mEq/L
- Emergency protocols: Immediate discontinuation if K+ >6.0 mEq/L
Treatment Optimization Checklist:
- Maximize Cardiovascular Protection
- Target BP: <130/80 mmHg for most patients
- Combination therapy: ACE inhibitor/ARB + thiazide + CCB
- Heart failure: Add spironolactone for EF <40%
- Diabetes protection: ACE inhibitors reduce nephropathy by 50%
- Stroke prevention: ARBs provide equivalent protection to ACE inhibitors
- Cost considerations: Generic ACE inhibitors offer best value
This clinical mastery framework provides immediate access to critical decision points and evidence-based protocols that optimize patient outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
🎯 The Clinical Mastery Toolkit
Practice Questions: RAAS
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 75 year-old gentleman presents to his general practitioner. He is currently being treated for hypertension and is on a multi-drug regimen. His current blood pressure is 180/100. The physician would like to begin treatment with minoxidil or hydralazine. Which of the following side effects is associated with administration of these drugs?













