Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Arterial pressure waveform. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old woman comes to the office for a regular follow-up. She was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus 4 years ago. Her last blood test showed a fasting blood glucose level of 6.6 mmol/L (118.9 mg/dL) and HbA1c of 5.1%. No other significant past medical history. Current medications are metformin and a daily multivitamin. No significant family history. The physician wants to take her blood pressure measurements, but the patient states that she measures it every day in the morning and in the evening and even shows him a blood pressure diary with all the measurements being within normal limits. Which of the following statements is correct?
- A. The physician has to measure the patient’s blood pressure because it is a standard of care for any person with diabetes mellitus who presents for a check-up. (Correct Answer)
- B. Assessment of blood pressure only needs to be done at the initial visit; it is not necessary to measure blood pressure in this patient at any follow-up appointments.
- C. The physician should not measure the blood pressure in this patient and should simply make a note in a record showing the results from the patient’s diary.
- D. The physician should not measure the blood pressure in this patient because she does not have hypertension or risk factors for hypertension.
- E. The physician should not measure the blood pressure in this patient because the local standards of care in the physician's office differ from the national standards of care so measurements of this patient's blood pressure cannot be compared to diabetes care guidelines.
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: **The physician has to measure the patient’s blood pressure because it is a standard of care for any person with diabetes mellitus who presents for a check-up.**
- For individuals with **diabetes mellitus**, regular **blood pressure monitoring** by a healthcare professional is a fundamental component of their routine care, regardless of home measurements.
- This practice ensures accuracy, identifies **white coat hypertension**, and allows for early detection and management of **cardiovascular risks** inherent to diabetes.
*Assessment of blood pressure only needs to be done at the initial visit; it is not necessary to measure blood pressure in this patient at any follow-up appointments.*
- This statement is incorrect as **regular blood pressure monitoring** is essential for all follow-up visits in diabetic patients due to their elevated risk of developing **hypertension** and associated complications.
- Even if initial measurements are normal, blood pressure can change over time, necessitating continuous assessment to maintain optimal **cardiovascular health**.
*The physician should not measure the blood pressure in this patient and should simply make a note in a record showing the results from the patient’s diary.*
- Relying solely on **patient-recorded blood pressure** measurements, while valuable, does not replace the need for an **in-office measurement** by a healthcare provider.
- This is crucial for verifying the accuracy of home devices, assessing for **masked hypertension**, and ensuring compliance with **clinical guidelines**.
*The physician should not measure the blood pressure in this patient because she does not have hypertension or risk factors for hypertension.*
- This is incorrect; the patient's diagnosis of **Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus** itself is a significant **risk factor for hypertension** and cardiovascular disease.
- All individuals with diabetes require ongoing **blood pressure monitoring**, irrespective of their current blood pressure status or other obvious risk factors.
*The physician should not measure the blood pressure in this patient because the local standards of care in the physician's office differ from the national standards of care so measurements of this patient's blood pressure cannot be compared to diabetes care guidelines.*
- This statement is generally incorrect and illogical; **national guidelines** for diabetes care, including blood pressure monitoring, are established to ensure consistent and high-quality care across different settings.
- Healthcare providers are expected to adhere to these **national standards of care** or explain any deviations, making the measurement of blood pressure a critical part of a diabetic patient's visit.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 2: A 27-year-old male arrives in the emergency department with a stab wound over the precordial chest wall. The patient is in distress and is cold, sweaty, and pale. Initial physical examination is significant for muffled heart sounds, distended neck veins, and a 3 cm stab wound near the left sternal border. Breath sounds are present bilaterally without evidence of tracheal deviation. Which of the following additional findings would be expected on further evaluation?
- A. Decrease in central venous pressure by 5 mmHg with inspiration
- B. 15 mmHg decrease in systolic blood pressure with inspiration (Correct Answer)
- C. Decrease in the patient's heart rate by 15 beats per minute with inspiration
- D. Steadily decreasing heart rate to 60 beats per minute
- E. Elevated blood pressure to 170/110
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***15 mmHg decrease in systolic blood pressure with inspiration***
- The constellation of muffled heart sounds, distended neck veins, and hypotension (implied by cold, sweaty, and pale appearance) following a precordial stab wound points to **cardiac tamponade**, an acutely life-threatening condition.
- A significant drop in systolic blood pressure (>10 mmHg) during inspiration, known as **pulsus paradoxus**, is a classic sign of cardiac tamponade as the increased venous return to the right heart during inspiration bows the interventricular septum, impinging on left ventricular filling.
*Decrease in central venous pressure by 5 mmHg with inspiration*
- In cardiac tamponade, the **central venous pressure (CVP) is typically elevated** and would not decrease significantly with inspiration due to impaired right ventricular filling.
- The elevated CVP contributes to the observed **distended neck veins**.
*Decrease in the patient's heart rate by 15 beats per minute with inspiration*
- In cardiac tamponade, the body attempts to compensate for reduced cardiac output with **reflex tachycardia**, so a decrease in heart rate is unexpected.
- Heart rate usually remains elevated or variable as the heart struggles to maintain perfusion.
*Steadily decreasing heart rate to 60 beats per minute*
- A steadily decreasing heart rate to 60 bpm (bradycardia) is contrary to the expected physiological response of **tachycardia** in cardiac tamponade as the body compensates for hypoperfusion.
- Bradycardia in this context would indicate severe decompensation and imminent cardiac arrest rather than a compensatory mechanism.
*Elevated blood pressure to 170/110*
- This patient is in **obstructive shock** due to cardiac tamponade; therefore, their blood pressure would be **hypotensive**, not hypertensive.
- **Hypotension** is a key component of Beck's triad (muffled heart sounds, distended neck veins, hypotension) which strongly suggests cardiac tamponade.
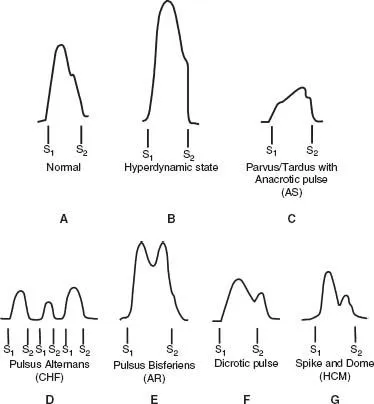
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 3: A 17-year-old previously healthy, athletic male suddenly falls unconscious while playing soccer. His athletic trainer comes to his aid and notes that he is pulseless. He begins performing CPR on the patient until the ambulance arrives but the teenager is pronounced dead when the paramedics arrived. Upon investigation of his primary care physician's office notes, it was found that the child had a recognized murmur that was ruled to be "benign." Which of the following conditions would have increased the intensity of the murmur?
- A. Inspiration
- B. Placing the patient in a squatting position
- C. Valsalva (Correct Answer)
- D. Passive leg raise
- E. Handgrip
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***Valsalva***
- The patient's sudden death after collapsing during soccer, coupled with a previously noted "benign" murmur, strongly suggests **hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)**, which is a common cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes. The **Valsalva maneuver** decreases preload and left ventricular volume, thereby **increasing the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction** and hence the intensity of the HOCM murmur.
- This maneuver reduces venous return to the heart, leading to reduced ventricular filling and decreased stroke volume. This exacerbates the obstruction in HOCM, making the murmur louder.
*Inspiration*
- **Inspiration** typically **increases venous return to the right side of the heart**, which would generally intensify right-sided murmurs (e.g., tricuspid regurgitation).
- It would have **minimal effect or slightly decrease** the intensity of a left-sided obstructive murmur like that in HOCM, as it does not directly increase the LVOT obstruction.
*Placing the patient in a squatting position*
- Squatting increases both **preload** and **afterload** by increasing systemic vascular resistance and venous return.
- This increase in ventricular volume would **reduce the outflow tract obstruction** in HOCM, thereby **decreasing the intensity of the murmur**.
*Passive leg raise*
- A **passive leg raise** increases **venous return** and thus **preload**, leading to increased ventricular filling.
- Similar to squatting, this increased left ventricular volume would **reduce the left ventricular outflow tract obstruction** associated with HOCM, thereby **decreasing the murmur's intensity**.
*Handgrip*
- The **handgrip maneuver** primarily **increases afterload** and, to some extent, preload by increasing systemic vascular resistance.
- While it can increase the intensity of murmurs like mitral regurgitation and ventricular septal defect, it would generally **decrease or have no significant effect** on the murmur of HOCM due to the increased ventricular volume reducing the outflow obstruction.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 4: An experiment to determine the effects of gravity on blood pressure is conducted on 3 individuals of equal height and blood pressure oriented in different positions in space. Participant A is strapped in a supine position on a bed turned upside down in a vertical orientation with his head towards the floor and his feet towards the ceiling. Participant B is strapped in a supine position on a bed turned downwards in a vertical orientation with his head towards the ceiling and his feet just about touching the floor. Participant C is strapped in a supine position on a bed in a horizontal orientation. Blood pressure readings are then taken at the level of the head, heart, and feet from all 3 participants. Which of these positions will have the lowest recorded blood pressure reading?
- A. Participant B: at the level of the feet
- B. Participant A: at the level of the head
- C. Participant C: at the level of the heart
- D. Participant A: at the level of the feet (Correct Answer)
- E. Participant C: at the level of the feet
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***Participant A: at the level of the feet***
- In Participant A, the feet are positioned **highest vertically** relative to the heart and are also above the head due to the upside-down vertical orientation. Due to gravity, blood pressure decreases with increasing height above the heart.
- This position would result in the lowest hydrostatic pressure at the feet, leading to the **lowest recorded blood pressure reading**.
*Participant B: at the level of the feet*
- In Participant B, the feet are positioned **below the heart** (towards the floor) in a vertical orientation.
- This position would experience some of the **highest hydrostatic pressure** due to gravity, leading to a high blood pressure reading, not the lowest.
*Participant A: at the level of the head*
- In Participant A, the head is positioned **below the heart** (towards the floor) in an upside-down vertical orientation.
- This position would experience increased hydrostatic pressure, hence a **higher blood pressure** compared to the feet.
*Participant C: at the level of the heart*
- Participant C is in a horizontal position, meaning all body parts are at roughly the same hydrostatic level relative to the heart.
- Blood pressure readings would be **similar across all points** (head, heart, feet) and would reflect the systemic arterial pressure without significant hydrostatic effects, thus not the lowest compared to other extreme positions.
*Participant C: at the level of the feet*
- In Participant C (horizontal), the feet are at approximately the **same hydrostatic level** as the heart.
- The reading at the feet in this position would be close to the **baseline arterial pressure**, not the lowest, as there's minimal hydrostatic gradient.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 5: An 83-year-old male presents with dyspnea, orthopnea, and a chest radiograph demonstrating pulmonary edema. A diagnosis of congestive heart failure is considered. The following clinical measurements are obtained: 100 bpm heart rate, 0.2 mL O2/mL systemic blood arterial oxygen content, 0.1 mL O2/mL pulmonary arterial oxygen content, and 400 mL O2/min oxygen consumption. Using the above information, which of the following values represents this patient's cardiac stroke volume?
- A. 30 mL/beat
- B. 70 mL/beat
- C. 40 mL/beat (Correct Answer)
- D. 60 mL/beat
- E. 50 mL/beat
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***40 mL/beat***
- First, calculate cardiac output (CO) using the **Fick principle**: CO = Oxygen Consumption / (Arterial O2 content - Venous O2 content). Here, CO = 400 mL O2/min / (0.2 mL O2/mL - 0.1 mL O2/mL) = 400 mL O2/min / 0.1 mL O2/mL = **4000 mL/min**.
- Next, calculate stroke volume (SV) using the formula: SV = CO / Heart Rate. Given a heart rate of 100 bpm, SV = 4000 mL/min / 100 beats/min = **40 mL/beat**.
*30 mL/beat*
- This answer would result if there was an error in calculating either the **cardiac output** or if the **arteriovenous oxygen difference** was overestimated.
- A stroke volume of 30 mL/beat with a heart rate of 100 bpm would yield a cardiac output of 3 L/min, which is sub-physiologic for an oxygen consumption of 400 mL/min given the provided oxygen content values.
*70 mL/beat*
- This stroke volume is higher than calculated and would imply either a significantly **lower heart rate** or a much **higher cardiac output** than derived from the Fick principle with the given values.
- A stroke volume of 70 mL/beat at a heart rate of 100 bpm would mean a cardiac output of 7 L/min, which is inconsistent with the provided oxygen consumption and arteriovenous oxygen difference.
*60 mL/beat*
- This value is higher than the correct calculation, suggesting an error in the initial calculation of **cardiac output** or the **avO2 difference**.
- To get 60 mL/beat, the cardiac output would need to be 6000 mL/min, which would mean an avO2 difference of 0.067 mL O2/mL, not 0.1 mL O2/mL.
*50 mL/beat*
- This stroke volume would result from an incorrect calculation of the **cardiac output**, potentially from a slight miscalculation of the **arteriovenous oxygen difference**.
- A stroke volume of 50 mL/beat at 100 bpm would mean a cardiac output of 5 L/min, requiring an avO2 difference of 0.08 mL O2/mL, which is not consistent with the given values.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 6: A 60-year-old male engineer who complains of shortness of breath when walking a few blocks undergoes a cardiac stress test because of concern for coronary artery disease. During the test he asks his cardiologist about what variables are usually used to quantify the functioning of the heart. He learns that one of these variables is stroke volume. Which of the following scenarios would be most likely to lead to a decrease in stroke volume?
- A. Anxiety
- B. Heart failure (Correct Answer)
- C. Exercise
- D. Pregnancy
- E. Digitalis
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***Heart failure***
- In **heart failure**, the heart's pumping ability is impaired, leading to a reduced **ejection fraction** and thus a decreased **stroke volume**.
- The weakened myocardium cannot effectively contract to expel the normal volume of blood, resulting in lower blood output per beat.
*Anxiety*
- **Anxiety** typically causes an increase in **sympathetic nervous system** activity, leading to increased heart rate and myocardial contractility.
- This often results in a temporary **increase in stroke volume** due to enhanced cardiac performance, not a decrease.
*Exercise*
- During **exercise**, there is a significant **increase in venous return** and sympathetic stimulation, leading to increased **end-diastolic volume** and contractility.
- This physiological response causes a substantial **increase in stroke volume** to meet the body's higher oxygen demands.
*Pregnancy*
- **Pregnancy** leads to significant **physiological adaptations** to accommodate the growing fetus, including a substantial increase in **blood volume**.
- This increased blood volume and cardiac output result in an **increase in stroke volume** to maintain adequate perfusion for both mother and fetus.
*Digitalis*
- **Digitalis** is a cardiac glycoside that **increases intracellular calcium** in myocardial cells, enhancing the **force of contraction**.
- This positive inotropic effect leads to an **increased stroke volume** by improving the heart's pumping efficiency.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old man is running on the treadmill at his gym. His blood pressure prior to beginning his workout was 110/72. Which of the following changes in his cardiovascular system may be seen in this man now that he is exercising?
- A. Decreased blood pressure
- B. Decreased systemic vascular resistance (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased systemic vascular resistance
- D. Decreased stroke volume
- E. Decreased heart rate
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***Decreased systemic vascular resistance***
- During dynamic exercise, metabolic vasodilation in exercising muscles leads to a substantial **decrease in systemic vascular resistance (SVR)** to accommodate increased blood flow.
- This vasodilation overrides the systemic vasoconstriction driven by the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in a net decrease in overall SVR.
*Decreased blood pressure*
- While SVR decreases, **systolic blood pressure typically increases** during exercise due to increased cardiac output.
- **Diastolic blood pressure** usually remains stable or may slightly decrease, but overall blood pressure, specifically the mean arterial pressure, is generally maintained or elevated.
*Increased systemic vascular resistance*
- This is incorrect as **vasodilation in active muscles** causes a significant decrease in overall systemic vascular resistance.
- An increase in SVR would typically hinder blood flow to working muscles and is not a characteristic cardiovascular response to dynamic exercise.
*Decreased stroke volume*
- Stroke volume generally **increases significantly** during exercise due to enhanced venous return, increased contractility, and reduced afterload (from decreased SVR).
- A decreased stroke volume would limit cardiac output and exercise performance.
*Decreased heart rate*
- Heart rate **increases proportionally with exercise intensity** to boost cardiac output and oxygen delivery to active muscles.
- A decreased heart rate would counteract the body's physiological demand for increased blood flow during physical activity.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 8: A 34-year-old male is brought to the emergency department. He has prior hospitalizations for opiate overdoses, but today presents with fever, chills, rigors and malaise. On physical exam vitals are temperature: 100.5 deg F (38.1 deg C), pulse is 105/min, blood pressure is 135/60 mmHg, and respirations are 22/min. You note the following findings on the patient's hands (Figures A and B). You note that as the patient is seated, his head bobs with each successive heart beat. Which of the following findings is most likely present in this patient?
- A. A holosystolic murmur at the 4th intercostal midclavicular line
- B. A water-hammer pulse when palpating the radial artery (Correct Answer)
- C. Decreased blood pressure as measured in the lower extremities compared to the upper extremities
- D. A harsh crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur in the right second intercostal space
- E. A consistent gallop with an S4 component
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***A water-hammer pulse when palpating the radial artery***
- The patient's history of **opiate overdose**, fever, chills, and the presence of **Janeway lesions** (Figures A and B) on the hands strongly suggest **infective endocarditis**. The head bobbing (Musset's sign) indicates **severe aortic regurgitation**.
- **Water-hammer pulse** (Corrigan's pulse) is a classic sign of **severe aortic regurgitation**, characterized by a rapid, forceful arterial pulse that quickly collapses due to a large stroke volume and rapid diastolic runoff.
*A holosystolic murmur at the 4th intercostal midclavicular line*
- A holosystolic murmur at the 4th intercostal midclavicular line is typically associated with **mitral regurgitation**, which is less likely given the prominent signs of aortic regurgitation.
- While endocarditis can affect the mitral valve, the specific clinical signs point towards **aortic valve involvement**.
*Decreased blood pressure as measured in the lower extremities compared to the upper extremities*
- This finding is characteristic of **coarctation of the aorta**, a congenital heart defect, which is not suggested by the patient's presentation or risk factors.
- The patient's symptoms are more consistent with an acute infectious process affecting the heart valves.
*A harsh crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur in the right second intercostal space*
- A harsh crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur in the right second intercostal space is typical of **aortic stenosis**.
- While aortic insufficiency is present, the murmur for uncomplicated aortic insufficiency is usually a **diastolic decrescendo murmur**, not a harsh systolic murmur.
*A consistent gallop with an S4 component*
- An S4 gallop is typically heard in conditions involving **decreased ventricular compliance** (e.g., severe hypertension, aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy).
- While endocarditis can cause heart failure, an S4 gallop is not a direct or primary sign of **aortic regurgitation**. An S3 gallop is more commonly associated with **volume overload** and heart failure, which might develop in severe aortic regurgitation.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of recurrent nosebleeds and fatigue for the past 2 months. He also frequently complains his head hurts. The patient has met all motoric milestones for his age but does not like to run because his legs start to hurt if he does. He is at the 40th percentile for both height and weight. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse is 125/min, respirations are 32/min, and blood pressure in the right arm is 130/85 mm Hg. A grade 2/6 systolic murmur is heard in the left paravertebral region. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Inferior rib notching
- B. Delayed pulse in lower extremities (Correct Answer)
- C. Interarm difference in tissue oxygenation
- D. Pulmonary valve stenosis
- E. Left-axis deviation on ECG
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: ***Delayed pulse in lower extremities***
- The patient's symptoms, including **recurrent nosebleeds**, **headaches**, **leg pain with activity**, **hypertension** (especially in the right arm), and a **systolic murmur in the left paravertebral region**, are highly suggestive of **coarctation of the aorta**.
- A key physical finding in coarctation of the aorta is a **delayed and diminished femoral pulse** compared to the radial pulse due to obstruction of blood flow to the lower body.
*Inferior rib notching*
- This finding is characteristic of **collateral circulation** developing around a coarctation in older children and adults, as the **intercostal arteries** become enlarged to supply blood to the lower body.
- While associated with coarctation, it is typically seen on **chest X-rays** in older patients and is less likely to be present or pronounced in a 3-year-old.
*Interarm difference in tissue oxygenation*
- While coarctation can cause an **interarm blood pressure difference**, it typically does not directly cause a significant interarm difference in **tissue oxygenation** unless severe unilateral subclavian artery involvement is present, which is not the primary mechanism.
- The primary oxygenation concern in coarctation is usually related to overall cardiac output or systemic effects rather than a localized interarm difference.
*Pulmonary valve stenosis*
- **Pulmonary valve stenosis** would typically present with a **systolic ejection murmur** heard best at the left upper sternal border, often radiating to the back.
- It does not explain the specific constellation of symptoms such as **hypertension in the upper extremities**, **leg pain with activity**, or differential pulses characteristic of coarctation of the aorta.
*Left-axis deviation on ECG*
- **Left-axis deviation** on an ECG is often associated with conditions causing **left ventricular hypertrophy** or conduction defects.
- While severe coarctation can lead to left ventricular hypertrophy, left-axis deviation is not a specific or direct diagnostic finding for coarctation and is less characteristic than the described physical exam findings.
Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG Question 10: A 19-year-old man presents to the clinic with a complaint of increasing shortness of breath for the past 2 years. His shortness of breath is associated with mild chest pain and occasional syncopal attacks during strenuous activity. There is no history of significant illness in the past, however, one of his uncles had similar symptoms when he was his age and died while playing basketball a few years later. He denies alcohol use, tobacco consumption, and the use of recreational drugs. On examination, pulse rate is 76/min and is regular and bounding; blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg. A triple apical impulse is observed on the precordium and a systolic ejection crescendo-decrescendo murmur is audible between the apex and the left sternal border along with a prominent fourth heart sound. The physician then asks the patient to take a deep breath, close his mouth, and pinch his nose and try to breathe out without allowing his cheeks to bulge out. In doing so, the intensity of the murmur increases. Which of the following hemodynamic changes would be observed first during this maneuver?
- A. ↓ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↑ Heart rate, ↑ Baroreceptor activity, ↓ Parasympathetic Outflow
- B. ↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↓ Heart rate, ↑ Baroreceptor activity, ↑ Parasympathetic Outflow (Correct Answer)
- C. ↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↓ Heart rate, ↓ Baroreceptor activity, ↑ Parasympathetic Outflow
- D. ↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↑ Heart rate, ↓ Baroreceptor activity, ↓ Parasympathetic Outflow
- E. ↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↑ Heart rate, ↑ Baroreceptor activity, ↑ Parasympathetic Outflow
Arterial pressure waveform Explanation: **↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↓ Heart rate, ↑ Baroreceptor activity, ↑ Parasympathetic Outflow**
- This maneuver is the **Valsalva Maneuver**, which involves forced expiration against a closed glottis. It causes a transient increase in **intrathoracic pressure**, compressing the great vessels and temporarily increasing **mean arterial pressure**.
- The initial rise in blood pressure is detected by **baroreceptors**, leading to a reflex decrease in **heart rate** via increased **parasympathetic outflow**.
*↓ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↑ Heart rate, ↑ Baroreceptor activity, ↓ Parasympathetic Outflow*
- This option describes changes more typical of the **later phases** of a Valsalva maneuver (Phase 2), where venous return and cardiac output decrease, leading to a fall in MAP and a compensatory increase in heart rate.
- It does not represent the **immediate hemodynamic changes** (Phase 1) that occur during the initial strain of the maneuver.
*↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↓ Heart rate, ↓ Baroreceptor activity, ↑ Parasympathetic Outflow*
- A decrease in **baroreceptor activity** would typically lead to an *increase* in heart rate and a *decrease* in parasympathetic outflow, contrary to the initial response to increased blood pressure.
- The initial increase in MAP correctly leads to *increased* baroreceptor activity.
*↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↑ Heart rate, ↓ Baroreceptor activity, ↓ Parasympathetic Outflow*
- An increase in **mean arterial pressure** (MAP) would reflexively cause a *decrease* in heart rate and an *increase* in parasympathetic outflow, mediated by *increased* baroreceptor activity, not decreased activity.
- Therefore, the proposed changes in heart rate, baroreceptor activity, and parasympathetic outflow are inconsistent with an initial increase in MAP.
*↑ Mean Arterial Pressure, ↑ Heart rate, ↑ Baroreceptor activity, ↑ Parasympathetic Outflow*
- While an increase in **mean arterial pressure** does lead to an increase in **baroreceptor activity** and **parasympathetic outflow**, the reflexive response to this increased pressure is a *decrease* in **heart rate**, not an increase.
- An increased heart rate combined with increased parasympathetic outflow is contradictory, as sympathetic and parasympathetic systems typically exert opposing effects on heart rate.
More Arterial pressure waveform US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.