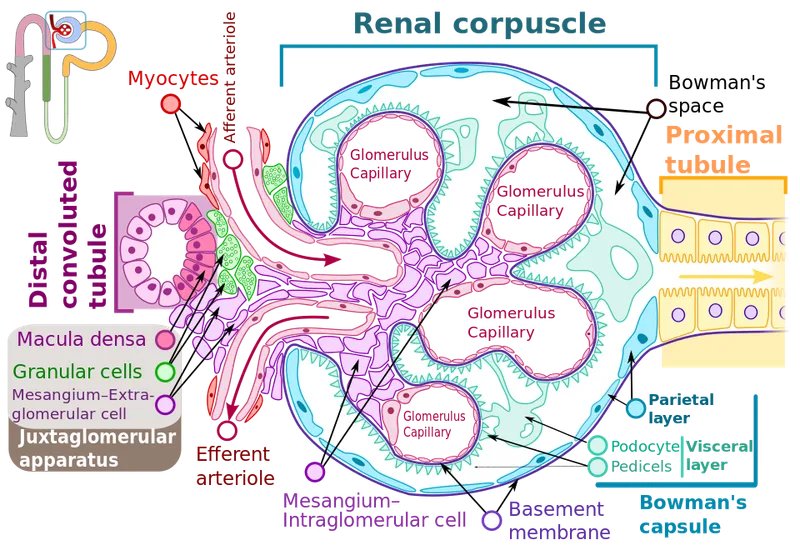
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Tubuloglomerular feedback. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 1: A 64-year-old African American female comes to the physician's office for a routine check-up. The patient's past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes, and osteoarthritis in her right knee. Her medications include metformin, glimepiride, lisinopril, metoprolol, hydrochlorothiazide, and ibuprofen as needed. Her only complaint is an unremitting cough that started about 3 weeks ago and she has noticed some swelling around her mouth. The drug most likely responsible for her recent symptoms causes its primary renal hemodynamic effect on which part of the kidney?
- A. Collecting duct
- B. Distal convoluted tubule
- C. Juxtaglomerular cells
- D. Efferent arteriole (Correct Answer)
- E. Afferent arteriole
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Efferent arteriole***
- The patient's symptoms of an **unremitting cough** and **angioedema** (swelling around her mouth) are classic side effects of **ACE inhibitors**, such as **lisinopril**.
- ACE inhibitors primarily exert their renal hemodynamic effects by **dilating the efferent arteriole**, leading to a decrease in intraglomerular pressure and glomerular filtration rate.
*Collecting duct*
- The collecting duct is the primary site of action for **vasopressin (ADH)** and **aldosterone**, regulating water and sodium reabsorption, respectively.
- While other medications like **thiazides** (used by the patient) affect distal tubules and collecting ducts indirectly, their direct impact on the collecting duct is not the cause of angioedema or cough.
*Distal convoluted tubule*
- The distal convoluted tubule is the main site of action for **thiazide diuretics** (e.g., hydrochlorothiazide), which inhibit the Na-Cl cotransporter.
- This tubule segment is not directly involved in the mechanism leading to angioedema or cough caused by ACE inhibitors.
*Juxtaglomerular cells*
- Juxtaglomerular cells are responsible for producing **renin**, which is the initial step in the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)**.
- While ACE inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, they do not directly act on the juxtaglomerular cells themselves to cause their side effects.
*Afferent arteriole*
- The afferent arteriole is primarily regulated by **sympathetic tone** and local factors, and is the main site of action for medications like **NSAIDs** (e.g., ibuprofen, which the patient takes as needed).
- While NSAIDs cause **afferent arteriole constriction** and can impair renal function, they do not cause angioedema or a chronic cough.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 2: Which transport mechanism is primarily responsible for calcium reabsorption in the proximal tubule?
- A. Paracellular transport (Correct Answer)
- B. Facilitated diffusion
- C. Active transport
- D. Antiport with sodium
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Paracellular transport***
- In the **proximal tubule**, approximately 60-70% of filtered calcium is reabsorbed primarily through the **paracellular pathway**, driven by the electrochemical gradient and solvent drag.
- This transport occurs between cells, moving through the **tight junctions**, and is passive, following the reabsorption of water.
*Facilitated diffusion*
- While a type of passive transport, **facilitated diffusion** typically involves membrane proteins and occurs across the cell membrane, not primarily between cells in the proximal tubule for calcium.
- This mechanism is prominent for calcium reabsorption in other nephron segments like the **distal convoluted tubule** via **TRPV5/6 channels**, but not the main route in the proximal tubule.
*Active transport*
- **Active transport** of calcium, mainly via **calcium ATPase** and the **Na+/Ca2+ exchanger**, occurs across the luminal and basolateral membranes, respectively, in specific nephron segments.
- However, in the **proximal tubule**, the bulk of calcium reabsorption is passive and paracellular, not ATP-dependent active transport across cell membranes.
*Antiport with sodium*
- The **Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX)** is an antiport mechanism that plays a crucial role in extruding calcium from the cell into the interstitium, particularly in the basolateral membrane of the distal tubule.
- However, it is not the primary mechanism for overall tubular reabsorption of calcium in the **proximal tubule**, where paracellular movement dominates.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 3: A new drug X is being tested for its effect on renal function. During the experiments, the researchers found that in patients taking substance X, the urinary concentration of sodium decreases while urine potassium concentration increase. Which of the following affects the kidneys in the same way as does substance X?
- A. Aldosterone (Correct Answer)
- B. Furosemide
- C. Spironolactone
- D. Atrial natriuretic peptide
- E. Hydrochlorothiazide
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Aldosterone***
- **Aldosterone** acts on the **principal cells** of the **collecting duct** to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
- This action leads to a decrease in urinary sodium concentration and an increase in urinary potassium concentration, matching the effects of drug X.
*Furosemide*
- **Furosemide** is a **loop diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-K-2Cl cotransporter** in the **thick ascending limb** of the loop of Henle.
- This inhibition leads to increased excretion of sodium, potassium, and water, resulting in higher urinary sodium concentration.
*Spironolactone*
- **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that blocks aldosterone's effects on the collecting duct.
- This leads to increased sodium excretion and decreased potassium excretion (potassium-sparing effect), which is the opposite of drug X.
*Atrial natriuretic peptide*
- **Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** is released in response to atrial stretch and causes **natriuresis** (increased sodium excretion) and **diuresis**.
- It works by dilating afferent arterioles and constricting efferent arterioles, increasing GFR, and inhibiting sodium reabsorption, thus increasing urinary sodium concentration.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- **Hydrochlorothiazide** is a **thiazide diuretic** that inhibits the **Na-Cl cotransporter** in the **distal convoluted tubule**.
- This leads to increased sodium and chloride excretion but typically causes potassium wasting (hypokalemia), which differs from the increased urinary potassium concentration seen with drug X.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 4: A 70-year-old female with chronic kidney failure secondary to diabetes asks her nephrologist to educate her about the techniques used to evaluate the degree of kidney failure progression. She learns about the concept of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and learns that it can be estimated by measuring the levels of some substances. The clearance of which of the following substances is the most accurate estimate for GFR?
- A. Paraaminohippurate (PAH)
- B. Sodium
- C. Inulin (Correct Answer)
- D. Creatinine
- E. Glucose
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Inulin***
- **Inulin** is freely filtered by the glomeruli and is neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the renal tubules, making its clearance the **gold standard** for accurately measuring GFR.
- Due to its ideal physiological properties, inulin clearance perfectly reflects the rate at which plasma is filtered by the kidneys.
*Paraaminohippurate (PAH)*
- **PAH** is almost completely cleared from the blood by both glomerular filtration and **tubular secretion**, making its clearance an accurate measure of **renal plasma flow (RPF)**, not GFR.
- While important for assessing renal blood flow, it does not directly reflect the filtration capacity of the glomeruli.
*Sodium*
- **Sodium** is freely filtered at the glomerulus, but a significant portion (approximately **99%**) is **reabsorbed** by the renal tubules.
- Its clearance is highly variable and depends on various physiological factors, making it unsuitable for GFR estimation.
*Creatinine*
- **Creatinine** is freely filtered by the glomeruli and is also **modestly secreted** by the renal tubules, leading to an **overestimation of GFR** at lower kidney function levels.
- Despite being the most commonly used clinical marker due to its endogenous production, its tubular secretion makes it less accurate than inulin.
*Glucose*
- **Glucose** is freely filtered by the glomeruli but is almost **completely reabsorbed** by the renal tubules under normal physiological conditions.
- Its presence in urine (glycosuria) indicates a high plasma glucose level or tubular reabsorption defects, not a measure of GFR.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 5: Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system yields a significant physiological effect on renal blood flow and filtration. Which of the following is most likely to occur in response to increased levels of Angiotensin-II?
- A. Decreased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction
- B. Decreased renal plasma flow, increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure
- C. Increased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction
- D. Increased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction
- E. Decreased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction (Correct Answer)
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Decreased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction***
- **Angiotensin II** causes **efferent arteriolar constriction**, which reduces blood flow leaving the glomerulus, thereby **decreasing renal plasma flow**.
- This efferent constriction also increases **glomerular hydrostatic pressure** and reduces plasma flow distal to the glomerulus, leading to a **higher filtration fraction** (GFR/RPF).
*Decreased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction*
- While **renal plasma flow decreases**, a **decreased filtration fraction** would imply that either GFR decreases disproportionately more than RPF or GFR does not increase despite the RPF reduction, which is not the typical response to **angiotensin II** due to its predominant effect on the **efferent arteriole**.
*Decreased renal plasma flow, increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure*
- **Increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure** is a consequence of increased filtration fraction, as more fluid is filtered out, leaving behind a more concentrated plasma. This option includes a correct element (decreased RPF) but pairs it with a less direct and defining outcome of acute Angiotensin II action as the primary physiological effect.
*Increased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction*
- **Angiotensin II** causes **vasoconstriction**, predominantly of the efferent arteriole, which by definition would **decrease renal plasma flow**, not increase it.
- A **decreased filtration fraction** would be inconsistent with efferent arteriolar constriction which typically raises GFR relative to RPF.
*Increased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction*
- **Angiotensin II** causes **vasoconstriction**, leading to a **decrease in renal plasma flow**, not an increase.
- While **filtration fraction is increased**, the initial premise of increased renal plasma flow is incorrect.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 6: A 48-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. At her visit 1 month ago, her glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was 100 mL/min/1.73 m2 and her renal plasma flow (RPF) was 588 mL/min. Today, her RPF is 540 mL/min and her filtration fraction (FF) is 0.2. After her previous appointment, this patient was most likely started on a drug that has which of the following effects?
- A. Inhibition of the renal Na-K-Cl cotransporter
- B. Constriction of the afferent arteriole
- C. Relaxation of urinary smooth muscle
- D. Constriction of the efferent arteriole (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibition of vasopressin
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Constriction of the efferent arteriole***
- The previous GFR was 100 mL/min and RPF was 588 mL/min. For the follow-up, RPF is 540 mL/min and FF is 0.2. The new GFR can be calculated as FF × RPF = 0.2 × 540 = **108 mL/min**.
- The patient shows **increased GFR** (100→108 mL/min) with **decreased RPF** (588→540 mL/min), resulting in an **increased filtration fraction**.
- Medications that **constrict the efferent arteriole**, such as **NSAIDs**, produce this pattern by blocking prostaglandin synthesis. Prostaglandins normally cause vasodilation (predominantly of the afferent arteriole). When blocked, there is relatively more **efferent arteriolar constriction**, which increases glomerular hydrostatic pressure, thereby **increasing GFR while reducing overall RPF**.
*Inhibition of the renal Na-K-Cl cotransporter*
- This effect describes **loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide), which increase sodium excretion and water diuresis.
- Loop diuretics typically cause a **decrease in GFR** due to reduced fluid volume and lower filtration pressure, which contradicts the slight increase in GFR observed.
*Constriction of the afferent arteriole*
- **Afferent arteriole constriction** (e.g., by NSAIDs in high doses or norepinephrine) would decrease blood flow into the glomerulus, leading to a **decrease in both RPF and GFR**.
- While RPF decreased in this case, GFR actually increased, making this option incorrect.
*Relaxation of urinary smooth muscle*
- Relaxation of urinary smooth muscle is characteristic of drugs like **alpha-blockers** (e.g., tamsulosin) or antimuscarinics used for conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia or overactive bladder.
- This effect primarily impacts urine flow out of the bladder and does **not directly affect GFR or RPF** in the way described.
*Inhibition of vasopressin*
- Vasopressin (ADH) inhibition leads to **increased water excretion** and is seen with drugs like **vasopressin receptor antagonists** (vaptans) or ethanol.
- While it affects fluid balance, it typically causes a **decrease in GFR** due to hypovolemia and has no direct mechanism to increase GFR with decreased RPF as observed.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 7: A 75-year-old woman is brought to a physician’s office by her son with complaints of diarrhea and vomiting for 1 day. Her stool is loose, watery, and yellow-colored, while her vomitus contains partially digested food particles. She denies having blood or mucus in her stools and vomitus. Since the onset of her symptoms, she has not had anything to eat and her son adds that she is unable to tolerate fluids. The past medical history is unremarkable and she does not take any medications regularly. The pulse is 115/min, the respiratory rate is 16/min, the blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and the temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). The physical examination shows dry mucous membranes and slightly sunken eyes. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Which of the following physiologic changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal plasma flow (RPF), and filtration fraction (FF) are expected?
- A. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF
- B. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF
- C. Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF
- D. Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF
- E. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF (Correct Answer)
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF***
- Due to **dehydration** from diarrhea and vomiting, there is a decrease in blood volume leading to decreased renal blood flow and **renal plasma flow (RPF)**.
- The body responds to hypovolemia by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and sympathetic nervous system, which cause **preferential efferent arteriolar constriction** (more than afferent constriction). This helps maintain glomerular hydrostatic pressure despite reduced renal perfusion.
- As a result, **GFR decreases** but proportionally **less than RPF decreases**, causing the **filtration fraction (FF = GFR/RPF) to increase**.
- In this patient with significant dehydration (tachycardia, hypotension, dry mucous membranes), both GFR and RPF are reduced, but FF is elevated due to compensatory mechanisms.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF*
- While GFR and RPF will decrease due to dehydration, the **filtration fraction is expected to increase**, not decrease.
- A decreased FF would imply GFR fell proportionally more than RPF, which contradicts the physiologic response where efferent arteriolar constriction helps preserve GFR relative to RPF.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF*
- With significant fluid loss and compensatory mechanisms (efferent arteriolar constriction via angiotensin II), a change in **filtration fraction** is expected.
- The body actively alters arteriolar tone to prioritize GFR maintenance, which directly increases FF.
*Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF*
- This pattern suggests **hypervolemia** or increased renal perfusion, which directly contradicts the patient's severe dehydration.
- Both GFR and RPF are expected to decrease in volume depletion, not increase.
*Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF*
- An increase in GFR is physiologically impossible given the patient's severe volume depletion and reduced renal perfusion.
- While FF does increase in dehydration, this occurs in the context of **both GFR and RPF being decreased**, not with an increased GFR.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 8: A 9-year-old boy is brought to the physician's office by his mother because of facial swelling for the past 2 days. The mother says that her son has always been healthy and active but is becoming increasingly lethargic and now has a puffy face. Upon inquiry, the boy describes a foamy appearance of his urine, but denies having blood in the urine, urinary frequency at night, or pain during urination. He has no history of renal or urinary diseases. Physical examination is unremarkable, except for generalized swelling of the face and pitting edema on the lower limbs. Dipstick analysis reveals 4+ proteinuria. An abdominal ultrasound shows normal kidney size and morphology. A renal biopsy yields no findings under light and fluorescence microscopy; however, glomerular podocyte foot effacement is noted on electron microscopy. Which of the following changes in Starling forces occurs in this patient's condition?
- A. Decreased oncotic pressure in the Bowman's capsule
- B. Increased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule
- C. Decreased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule
- D. Decreased glomerular oncotic pressure (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased glomerular hydrostatic pressure
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Decreased glomerular oncotic pressure***
- The patient presents with **nephrotic syndrome**, characterized by severe proteinuria (4+ on dipstick), edema, and **minimal change disease** (podocyte foot effacement on electron microscopy without changes on light or fluorescence microscopy).
- In nephrotic syndrome, large amounts of plasma proteins, particularly **albumin**, are lost in the urine, leading to **hypoalbuminemia** and a significant decrease in the **oncotic pressure of the plasma** (and thus the glomerular capillaries).
*Decreased oncotic pressure in the Bowman's capsule*
- The Bowman's capsule normally has a **very low oncotic pressure** due to the almost complete absence of proteins in the filtrate.
- While theoretically a massive increase in protein filtration could increase it, the primary Starling force affected by protein loss in nephrotic syndrome is the **plasma oncotic pressure**.
*Increased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule*
- This condition is not typically associated with nephrotic syndrome and would rather **impair filtration**.
- Increased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule is usually seen in conditions causing **urinary tract obstruction**, which is not present here.
*Decreased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule*
- This would tend to **increase glomerular filtration rate** by favoring filtration, which is not the primary physiological change driving edema in nephrotic syndrome.
- There is no clinical indication for such a change in this patient's presentation.
*Increased glomerular hydrostatic pressure*
- While sometimes seen in specific glomerular diseases, this is not the primary or defining Starling force change in nephrotic syndrome leading to systemic edema.
- Increased glomerular hydrostatic pressure would tend to **increase filtration**, potentially worsening proteinuria, but the fundamental issue in nephrotic syndrome is the **loss of oncotic pressure due to protein leakage**.
Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG Question 9: A 73-year-old male is brought in by ambulance after he was found to be lethargic and confused. He has not been routinely seeing a physician and is unable to recall how he came to be in the hospital. His temperature is 99°F (37°C), blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 18/min. His past medical history is significant for poorly controlled diabetes and longstanding hypertension, and he says that he has not been taking his medications recently. Labs are obtained and shown below:
Serum:
Na+: 142 mEq/L
Cl-: 105 mEq/L
K+: 5 mEq/L
HCO3-: 16 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 51 mg/dL
Glucose: 224 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.6 mg/dL
Which of the following changes would most likely improve the abnormal parameter that is responsible for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Increased Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure
- B. Decreased filtration coefficient
- C. Increased Bowman's space oncotic pressure
- D. Decreased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
- E. Increased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure (Correct Answer)
Tubuloglomerular feedback Explanation: ***Increased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure***
- This patient presents with **acute kidney injury (AKI)** evidenced by **elevated creatinine (2.6 mg/dL)** and **BUN (51 mg/dL)**, causing uremic symptoms of **lethargy and confusion**
- The "abnormal parameter" is the **reduced GFR** causing azotemia and uremia
- To improve AKI and restore adequate filtration, **GFR must be increased**
- **Increasing glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure** increases the net filtration pressure: **NFP = (PGC - PBS) - (πGC - πBS)**, where PGC is the primary driving force for filtration
- In prerenal AKI (likely in this patient with poor medication compliance for hypertension), restoring adequate renal perfusion pressure is the therapeutic goal
- While chronic hyperfiltration can contribute to long-term diabetic/hypertensive nephropathy, the **acute management priority** is restoring adequate GFR to clear uremic toxins
*Decreased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure*
- This would **decrease the net filtration pressure**, thereby **reducing GFR**
- Lower GFR would worsen azotemia and uremic symptoms
- This is the opposite of what's needed to improve acute kidney injury
*Increased Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure*
- This **opposes filtration** by increasing back-pressure against the glomerular capillaries
- Would **decrease GFR** and worsen the AKI
- Occurs pathologically in urinary tract obstruction
*Decreased filtration coefficient*
- The filtration coefficient (Kf) represents the permeability and surface area of the glomerular capillaries
- **Decreasing Kf reduces GFR**, worsening kidney function
- This represents glomerular damage, not a therapeutic intervention
*Increased Bowman's space oncotic pressure*
- This would theoretically **increase net filtration pressure** and GFR
- However, this is **physiologically implausible** as Bowman's space normally contains minimal protein (filtrate is protein-free)
- Significant protein in Bowman's space indicates severe glomerular damage with proteinuria, not a mechanism to improve function
More Tubuloglomerular feedback US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.