Filtration fraction US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Filtration fraction. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 1: A 55-year-old woman presents to a physician’s clinic for a diabetes follow-up. She recently lost weight and believes the diabetes is ‘winding down’ because the urinary frequency has slowed down compared to when her diabetes was "at its worst". She had been poorly compliant with medications, but she is now asking if she can decrease her medications as she feels like her diabetes is improving. Due to the decrease in urinary frequency, the physician is interested in interrogating her renal function. Which substance can be used to most accurately assess the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in this patient?
- A. Para-aminohippurate (PAH)
- B. Glucose
- C. Inulin (Correct Answer)
- D. Urea
- E. Creatinine
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***Correct Answer: Inulin***
- **Inulin** is freely filtered by the glomeruli and is neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the renal tubules, making its clearance rate an **accurate measure of GFR**.
- It is considered the **gold standard** for GFR measurement, although it is not routinely used in clinical practice due to its exogenous nature and the need for continuous infusion.
*Incorrect: Para-aminohippurate (PAH)*
- **PAH** is both filtered and actively secreted by the renal tubules, meaning its clearance reflects **renal plasma flow**, not GFR.
- Due to its high extraction fraction, it is used to measure **effective renal plasma flow (ERPF)**.
*Incorrect: Glucose*
- **Glucose** is freely filtered by the glomeruli but is almost completely reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule in healthy individuals, especially at normal blood glucose levels.
- Therefore, glucose clearance is typically **zero** and does not measure GFR.
*Incorrect: Urea*
- **Urea** is filtered by the glomeruli, but a significant portion is **reabsorbed** by the renal tubules, particularly in states of lower urine flow.
- Its clearance **underestimates GFR** and varies with hydration status and protein intake, making it an unreliable sole measure of GFR.
*Incorrect: Creatinine*
- **Creatinine** is freely filtered by the glomeruli, but a small amount is also **secreted** by the renal tubules, leading to an overestimation of GFR, especially in advanced kidney disease.
- Although commonly used as an **estimate of GFR** in clinical practice due to its endogenous production, it is not as accurate as inulin.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 2: A healthy 30-year-old female has a measured creatinine clearance of 100 mL/min. She has a filtration fraction (FF) of 25%. Serum analysis reveals a creatinine level of 0.9 mg/dL and an elevated hematocrit of 0.6. Which of the following is the best estimate of this patient’s renal blood flow?
- A. 1.2 L/min
- B. 600 mL/min
- C. 800 mL/min
- D. 400 mL/min
- E. 1.0 L/min (Correct Answer)
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***1.0 L/min***
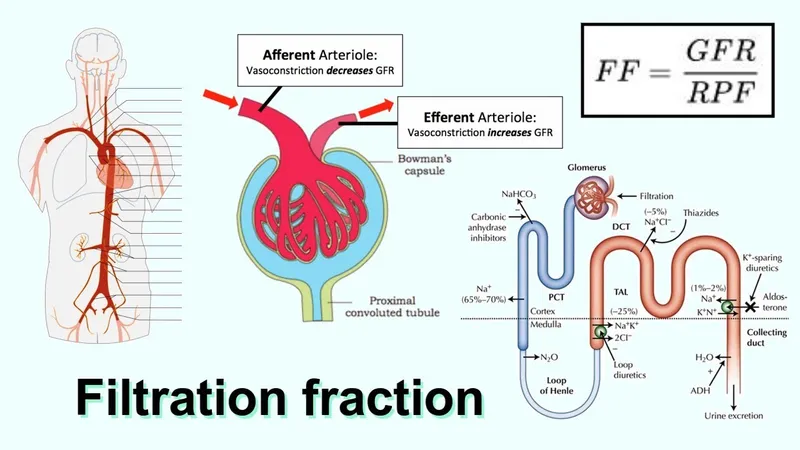
- The **renal plasma flow (RPF)** can be calculated by dividing the **creatinine clearance (which approximates GFR)** by the **filtration fraction (FF)**: RPF = GFR / FF = 100 mL/min / 0.25 = 400 mL/min.
- To find the **renal blood flow (RBF)**, we use the formula RBF = RPF / (1 - Hematocrit). Given RPF = 400 mL/min and Hematocrit = 0.6, RBF = 400 mL/min / (1 - 0.6) = 400 mL/min / 0.4 = 1000 mL/min, or **1.0 L/min**.
*1.2 L/min*
- This value would result if the hematocrit were lower (e.g., 0.5) or if the GFR or FF were different, leading to an incorrect RPF or RBF calculation.
- It does not align with the provided values when applying the standard physiological formulas relating GFR, FF, RPF, and hematocrit.
*600 mL/min*
- This value might be obtained if the hematocrit was significantly underestimated or if the RPF calculation was incorrect in determining the RBF.
- It arises from using an incorrect formula or misinterpreting the relationship between plasma flow and blood flow.
*800 mL/min*
- This result would occur if the calculation for RPF or the subsequent RBF was erroneous, possibly by using an incorrect denominator in the RBF formula.
- For example, if RPF was incorrectly assumed to be 320 mL/min and divided by 0.4 (1-Hematocrit).
*400 mL/min*
- This value represents the calculated **renal plasma flow (RPF)**, not the **renal blood flow (RBF)**.
- RBF is always higher than RPF because it includes both plasma and cellular components of blood.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 3: A 64-year-old African American female comes to the physician's office for a routine check-up. The patient's past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes, and osteoarthritis in her right knee. Her medications include metformin, glimepiride, lisinopril, metoprolol, hydrochlorothiazide, and ibuprofen as needed. Her only complaint is an unremitting cough that started about 3 weeks ago and she has noticed some swelling around her mouth. The drug most likely responsible for her recent symptoms causes its primary renal hemodynamic effect on which part of the kidney?
- A. Collecting duct
- B. Distal convoluted tubule
- C. Juxtaglomerular cells
- D. Efferent arteriole (Correct Answer)
- E. Afferent arteriole
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***Efferent arteriole***
- The patient's symptoms of an **unremitting cough** and **angioedema** (swelling around her mouth) are classic side effects of **ACE inhibitors**, such as **lisinopril**.
- ACE inhibitors primarily exert their renal hemodynamic effects by **dilating the efferent arteriole**, leading to a decrease in intraglomerular pressure and glomerular filtration rate.
*Collecting duct*
- The collecting duct is the primary site of action for **vasopressin (ADH)** and **aldosterone**, regulating water and sodium reabsorption, respectively.
- While other medications like **thiazides** (used by the patient) affect distal tubules and collecting ducts indirectly, their direct impact on the collecting duct is not the cause of angioedema or cough.
*Distal convoluted tubule*
- The distal convoluted tubule is the main site of action for **thiazide diuretics** (e.g., hydrochlorothiazide), which inhibit the Na-Cl cotransporter.
- This tubule segment is not directly involved in the mechanism leading to angioedema or cough caused by ACE inhibitors.
*Juxtaglomerular cells*
- Juxtaglomerular cells are responsible for producing **renin**, which is the initial step in the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)**.
- While ACE inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, they do not directly act on the juxtaglomerular cells themselves to cause their side effects.
*Afferent arteriole*
- The afferent arteriole is primarily regulated by **sympathetic tone** and local factors, and is the main site of action for medications like **NSAIDs** (e.g., ibuprofen, which the patient takes as needed).
- While NSAIDs cause **afferent arteriole constriction** and can impair renal function, they do not cause angioedema or a chronic cough.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 4: A 70-year-old female with chronic kidney failure secondary to diabetes asks her nephrologist to educate her about the techniques used to evaluate the degree of kidney failure progression. She learns about the concept of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and learns that it can be estimated by measuring the levels of some substances. The clearance of which of the following substances is the most accurate estimate for GFR?
- A. Paraaminohippurate (PAH)
- B. Sodium
- C. Inulin (Correct Answer)
- D. Creatinine
- E. Glucose
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***Inulin***
- **Inulin** is freely filtered by the glomeruli and is neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the renal tubules, making its clearance the **gold standard** for accurately measuring GFR.
- Due to its ideal physiological properties, inulin clearance perfectly reflects the rate at which plasma is filtered by the kidneys.
*Paraaminohippurate (PAH)*
- **PAH** is almost completely cleared from the blood by both glomerular filtration and **tubular secretion**, making its clearance an accurate measure of **renal plasma flow (RPF)**, not GFR.
- While important for assessing renal blood flow, it does not directly reflect the filtration capacity of the glomeruli.
*Sodium*
- **Sodium** is freely filtered at the glomerulus, but a significant portion (approximately **99%**) is **reabsorbed** by the renal tubules.
- Its clearance is highly variable and depends on various physiological factors, making it unsuitable for GFR estimation.
*Creatinine*
- **Creatinine** is freely filtered by the glomeruli and is also **modestly secreted** by the renal tubules, leading to an **overestimation of GFR** at lower kidney function levels.
- Despite being the most commonly used clinical marker due to its endogenous production, its tubular secretion makes it less accurate than inulin.
*Glucose*
- **Glucose** is freely filtered by the glomeruli but is almost **completely reabsorbed** by the renal tubules under normal physiological conditions.
- Its presence in urine (glycosuria) indicates a high plasma glucose level or tubular reabsorption defects, not a measure of GFR.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 5: A 75-year-old woman is brought to a physician’s office by her son with complaints of diarrhea and vomiting for 1 day. Her stool is loose, watery, and yellow-colored, while her vomitus contains partially digested food particles. She denies having blood or mucus in her stools and vomitus. Since the onset of her symptoms, she has not had anything to eat and her son adds that she is unable to tolerate fluids. The past medical history is unremarkable and she does not take any medications regularly. The pulse is 115/min, the respiratory rate is 16/min, the blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and the temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). The physical examination shows dry mucous membranes and slightly sunken eyes. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Which of the following physiologic changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal plasma flow (RPF), and filtration fraction (FF) are expected?
- A. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF
- B. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF
- C. Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF
- D. Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF
- E. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF (Correct Answer)
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF***
- Due to **dehydration** from diarrhea and vomiting, there is a decrease in blood volume leading to decreased renal blood flow and **renal plasma flow (RPF)**.
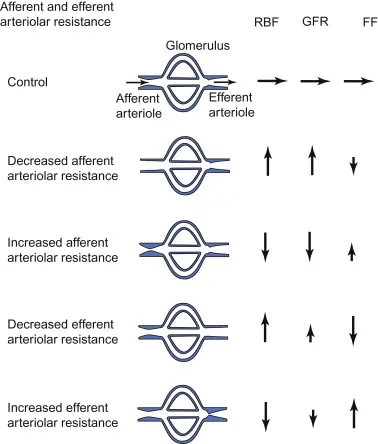
- The body responds to hypovolemia by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and sympathetic nervous system, which cause **preferential efferent arteriolar constriction** (more than afferent constriction). This helps maintain glomerular hydrostatic pressure despite reduced renal perfusion.
- As a result, **GFR decreases** but proportionally **less than RPF decreases**, causing the **filtration fraction (FF = GFR/RPF) to increase**.
- In this patient with significant dehydration (tachycardia, hypotension, dry mucous membranes), both GFR and RPF are reduced, but FF is elevated due to compensatory mechanisms.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF*
- While GFR and RPF will decrease due to dehydration, the **filtration fraction is expected to increase**, not decrease.
- A decreased FF would imply GFR fell proportionally more than RPF, which contradicts the physiologic response where efferent arteriolar constriction helps preserve GFR relative to RPF.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF*
- With significant fluid loss and compensatory mechanisms (efferent arteriolar constriction via angiotensin II), a change in **filtration fraction** is expected.
- The body actively alters arteriolar tone to prioritize GFR maintenance, which directly increases FF.
*Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF*
- This pattern suggests **hypervolemia** or increased renal perfusion, which directly contradicts the patient's severe dehydration.
- Both GFR and RPF are expected to decrease in volume depletion, not increase.
*Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF*
- An increase in GFR is physiologically impossible given the patient's severe volume depletion and reduced renal perfusion.
- While FF does increase in dehydration, this occurs in the context of **both GFR and RPF being decreased**, not with an increased GFR.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 6: A researcher is investigating the effects of a new antihypertensive medication on renal physiology. She gives a subject a dose of the new medication, and she then collects plasma and urine samples. She finds the following: Hematocrit: 40%; Serum creatinine: 0.0125 mg/mL; Urine creatinine: 1.25 mg/mL. Urinary output is 1 mL/min. Renal blood flow is 1 L/min. Based on the above information and approximating that the creatinine clearance is equal to the GFR, what answer best approximates filtration fraction in this case?
- A. 10%
- B. 17% (Correct Answer)
- C. 33%
- D. 50%
- E. 25%
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***17%***
- First, calculate **GFR** using the creatinine clearance formula: GFR = (Urine creatinine × Urinary output) / Serum creatinine = (1.25 mg/mL × 1 mL/min) / 0.0125 mg/mL = **100 mL/min**.
- Next, calculate **Renal Plasma Flow (RPF)** from Renal Blood Flow (RBF) and Hematocrit: RPF = RBF × (1 - Hematocrit) = 1000 mL/min × (1 - 0.40) = **600 mL/min**.
- Finally, calculate **Filtration Fraction (FF)** = GFR / RPF = 100 mL/min / 600 mL/min = 0.1667 = **16.7%, which approximates to 17%**.
- This is the correct answer based on the physiological calculations and represents a normal filtration fraction.
*10%*
- This would correspond to a filtration fraction of 0.10, which would require either a GFR of 60 mL/min (lower than calculated) or an RPF of 1000 mL/min (higher than calculated).
- This value is too low given the provided parameters and doesn't match the calculation from the given data.
*25%*
- This value would suggest FF = 0.25, requiring a GFR of 150 mL/min with the calculated RPF of 600 mL/min.
- This is higher than the calculated GFR of 100 mL/min and doesn't match the given creatinine values.
*33%*
- This would imply FF = 0.33, requiring a GFR of approximately 200 mL/min with RPF of 600 mL/min.
- This is significantly higher than the calculated GFR and would represent an abnormally elevated filtration fraction.
*50%*
- A filtration fraction of 50% is unphysiologically high and would indicate severe pathology.
- This would require a GFR of 300 mL/min with the calculated RPF, which is impossible given the provided creatinine clearance data.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 7: A 45-year-old man presents with a 3-day history of right-sided flank pain due to a lodged ureteral stone. What changes would be expected to be seen at the level of glomerular filtration?
- A. Increase in glomerular capillary oncotic pressure
- B. Increase in Bowman's space oncotic pressure
- C. Increase in filtration fraction
- D. Increase in Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure (Correct Answer)
- E. No change in filtration fraction
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***Increase in Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure***
- A lodged ureteral stone causes **obstruction** of urine flow, leading to a backup of fluid in the renal tubules and eventually into **Bowman's space**.
- This increased fluid volume in Bowman's space directly raises its **hydrostatic pressure**, which opposes glomerular filtration, thereby reducing the net filtration pressure.
*Increase in glomerular capillary oncotic pressure*
- **Glomerular capillary oncotic pressure** primarily reflects the protein concentration within the glomerular capillaries, which would not be directly increased by a ureteral stone.
- This parameter typically rises when fluid is filtered out, increasing protein concentration in the remaining blood, but not as the initial insult from obstruction.
*Increase in Bowman's space oncotic pressure*
- **Bowman's space oncotic pressure** is normally very low because the glomerular filtration barrier prevents significant protein filtration.
- An increase in this pressure would imply increased protein leakage into Bowman's space, which is not a direct consequence of a ureteral obstruction.
*Increase in filtration fraction*
- The **filtration fraction** is the ratio of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to renal plasma flow.
- Ureteral obstruction typically **decreases GFR** due to increased Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure, which would lead to a reduction, not an increase, in the filtration fraction, assuming renal plasma flow remains stable or slightly reduced.
*No change in filtration fraction*
- Ureteral obstruction significantly impacts the forces driving glomerular filtration, primarily by increasing **Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure**.
- This change inevitably leads to a **decrease in GFR**, thus altering the filtration fraction, meaning it would not remain unchanged.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 8: Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system yields a significant physiological effect on renal blood flow and filtration. Which of the following is most likely to occur in response to increased levels of Angiotensin-II?
- A. Decreased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction
- B. Decreased renal plasma flow, increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure
- C. Increased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction
- D. Increased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction
- E. Decreased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction (Correct Answer)
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***Decreased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction***
- **Angiotensin II** causes **efferent arteriolar constriction**, which reduces blood flow leaving the glomerulus, thereby **decreasing renal plasma flow**.
- This efferent constriction also increases **glomerular hydrostatic pressure** and reduces plasma flow distal to the glomerulus, leading to a **higher filtration fraction** (GFR/RPF).
*Decreased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction*
- While **renal plasma flow decreases**, a **decreased filtration fraction** would imply that either GFR decreases disproportionately more than RPF or GFR does not increase despite the RPF reduction, which is not the typical response to **angiotensin II** due to its predominant effect on the **efferent arteriole**.
*Decreased renal plasma flow, increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure*
- **Increased glomerular capillary oncotic pressure** is a consequence of increased filtration fraction, as more fluid is filtered out, leaving behind a more concentrated plasma. This option includes a correct element (decreased RPF) but pairs it with a less direct and defining outcome of acute Angiotensin II action as the primary physiological effect.
*Increased renal plasma flow, decreased filtration fraction*
- **Angiotensin II** causes **vasoconstriction**, predominantly of the efferent arteriole, which by definition would **decrease renal plasma flow**, not increase it.
- A **decreased filtration fraction** would be inconsistent with efferent arteriolar constriction which typically raises GFR relative to RPF.
*Increased renal plasma flow, increased filtration fraction*
- **Angiotensin II** causes **vasoconstriction**, leading to a **decrease in renal plasma flow**, not an increase.
- While **filtration fraction is increased**, the initial premise of increased renal plasma flow is incorrect.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 9: A scientist is studying the excretion of a novel toxin X by the kidney in order to understand the dynamics of this new substance. He discovers that this new toxin X has a clearance that is half that of inulin in a particular patient. This patient's filtration fraction is 20% and his para-aminohippuric acid (PAH) dynamics are as follows:
Urine volume: 100 mL/min
Urine PAH concentration: 30 mg/mL
Plasma PAH concentration: 5 mg/mL
Given these findings, what is the clearance of the novel toxin X?
- A. 1,500 mL/min
- B. 600 mL/min
- C. 300 mL/min
- D. 60 mL/min (Correct Answer)
- E. 120 mL/min
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***60 ml/min***
- First, calculate the **renal plasma flow (RPF)** using PAH clearance: RPF = (Urine PAH conc. × Urine vol.) / Plasma PAH conc. = (30 mg/mL × 100 mL/min) / 5 mg/mL = 600 mL/min.
- Next, calculate the **glomerular filtration rate (GFR)**, which is the clearance of inulin. GFR = RPF × Filtration Fraction = 600 mL/min × 0.20 = 120 mL/min. Toxin X clearance is half of inulin clearance, so 120 mL/min / 2 = **60 mL/min**.
*1,500 ml/min*
- This value is likely obtained if an incorrect formula or conversion was made, possibly by misinterpreting the units or the relationship between GFR, RPF, and filtration fraction.
- It significantly overestimates the clearance for a substance that is cleared at half the rate of inulin.
*600 ml/min*
- This value represents the **renal plasma flow (RPF)**, calculated using the PAH clearance data.
- It does not account for the filtration fraction or the fact that toxin X clearance is half of inulin clearance (GFR).
*300 ml/min*
- This value would be obtained if the renal plasma flow (RPF) was incorrectly halved, or if an intermediate calculation was misinterpreted as the final answer.
- It does not align with the given filtration fraction and the relationship between toxin X and inulin clearance.
*120 ml/min*
- This value represents the **glomerular filtration rate (GFR)**, which is equal to the clearance of inulin (RPF × Filtration Fraction = 600 mL/min × 0.20 = 120 mL/min).
- The question states that the clearance of toxin X is **half** that of inulin, so this is an intermediate step, not the final answer.
Filtration fraction US Medical PG Question 10: A 47-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He states that he has felt fatigued and dizzy on several occasions over the past week. He has back pain for which he takes ibuprofen. Digital rectal examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show a hemoglobin concentration of 15 g/dL, a serum urea nitrogen concentration of 22 mg/dL, a serum creatinine concentration of 1.4 mg/dL, and a serum calcium concentration of 8.4 mg/dL. His prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level is 0.3 ng/mL (N < 4.5). An intravenous infusion of para-aminohippurate (PAH) is administered and its clearance is calculated. The patient's effective renal plasma flow is estimated to be 660 mL/min (N = 500–1350). The filtration fraction is calculated to be 9% (N = 17–23). Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's laboratory abnormalities?
- A. Kidney stones
- B. Multiple myeloma
- C. Bacteremia
- D. Hypovolemia
- E. NSAID use (Correct Answer)
Filtration fraction Explanation: ***NSAID use***
- The patient's **low filtration fraction (9%)** and **slightly elevated creatinine (1.4 mg/dL)** despite a normal effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) are highly suggestive of **impaired autoregulation of GFR**.
- **NSAIDs** inhibit **prostaglandin synthesis**, which normally helps maintain GFR through **efferent arteriolar vasoconstriction**.
- Loss of prostaglandin-mediated efferent constriction leads to **efferent arteriolar vasodilation**, reducing glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure and causing a **disproportionate fall in GFR** compared to renal plasma flow, thus decreasing the filtration fraction.
- This mechanism is particularly important in states of decreased renal perfusion where prostaglandins play a critical compensatory role.
*Kidney stones*
- While kidney stones can cause back pain, they typically lead to **obstructive nephropathy**, which would present with a decrease in both GFR and ERPF, and often with **hematuria**, none of which are specifically indicated here.
- They do not directly cause the specific pattern of a low filtration fraction with preserved ERPF described.
*Multiple myeloma*
- Multiple myeloma commonly causes **renal impairment**, often due to **light chain cast nephropathy**, leading to elevated creatinine.
- However, it typically presents with **hypercalcemia**, **anemia**, and evidence of paraproteinemia, which are not seen in this patient (normal hemoglobin, normal calcium).
*Bacteremia*
- **Bacteremia** can lead to **sepsis** and **acute kidney injury (AKI)**, often characterized by **hypotension** and a significant drop in GFR and ERPF.
- This patient's symptoms are mild (fatigue, dizziness) and his ERPF is within the normal range, making severe sepsis less likely.
*Hypovolemia*
- **Hypovolemia** causes **prerenal acute kidney injury**, characterized by reduced ERPF, GFR, and an **increased BUN/creatinine ratio** due to increased tubular reabsorption of sodium and water.
- This patient has a normal ERPF and a normal BUN/creatinine ratio, making hypovolemia less likely to be the primary cause of his specific renal abnormalities.
More Filtration fraction US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.