Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Age-related changes in GFR. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 1: Which factor most strongly influences protein filtration at the glomerulus?
- A. Electrical charge
- B. Molecular size (Correct Answer)
- C. Shape
- D. Temperature
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Molecular size***
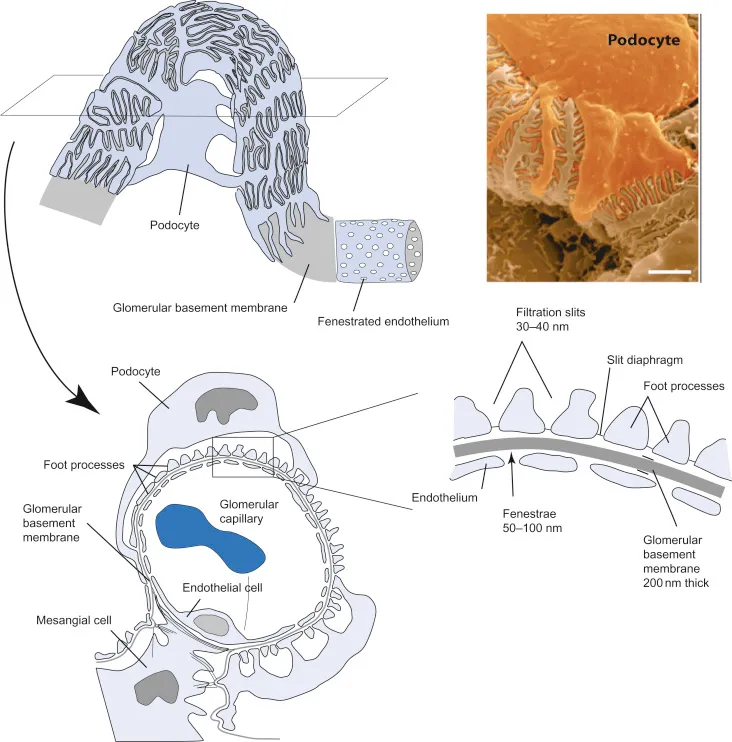
- The glomerular filtration barrier, particularly the **slit diaphragms** between podocytes, acts as a size-selective filter, restricting the passage of larger molecules.
- Proteins like **albumin** (molecular radius ~36 Å, molecular weight ~69 kDa) are significantly large, making them difficult to pass through the filtration barrier.
- Size selectivity is the **primary and most important** factor in protein filtration.
*Electrical charge*
- The glomerular basement membrane contains **negatively charged proteoglycans** (heparan sulfate), which repel negatively charged proteins like albumin, contributing to their retention.
- While important, the role of electrical charge is **secondary** to molecular size in preventing the bulk passage of most proteins.
*Shape*
- While abnormal protein shapes (e.g., **amyloid fibrils**) can impact filtration in specific disease states, the typical physiological filtration of most proteins is primarily governed by size and charge.
- The inherent shape of normal globular proteins plays a less direct role compared to their overall size.
*Temperature*
- **Physiological temperature** is relatively constant in the body and does not directly influence the molecular interactions and physical properties of the glomerular filtration barrier in a way that significantly alters protein filtration.
- Temperature changes would lead to denaturation or aggregation, which are not the primary determinants of normal protein filtration.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 2: A 62-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. One month ago, therapy with lisinopril was initiated for treatment of hypertension. His blood pressure is 136/86 mm Hg. Urinalysis shows a creatinine clearance of 92 mL/min. The patient's serum creatinine concentration is most likely closest to which of the following values?
- A. 1.7 mg/dL
- B. 1.1 mg/dL (Correct Answer)
- C. 2.0 mg/dL
- D. 1.4 mg/dL
- E. 2.3 mg/dL
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***1.1 mg/dL***
- For a 62-year-old man with a **creatinine clearance of 92 mL/min**, the serum creatinine can be estimated using the **Cockcroft-Gault relationship**.
- With CrCl of 92 mL/min (near-normal for age), the baseline serum creatinine would be approximately **0.9-1.0 mg/dL** for a typical male patient.
- **Lisinopril (ACE inhibitor)** commonly causes a **mild increase in serum creatinine (10-20%)** due to reduced efferent arteriolar tone, which is acceptable if <30% increase and creatinine clearance remains adequate.
- Therefore, **1.1 mg/dL** represents the expected value: baseline creatinine consistent with CrCl of 92 mL/min plus the typical mild ACE inhibitor-induced elevation.
*1.4 mg/dL*
- A serum creatinine of **1.4 mg/dL** would be inconsistent with a creatinine clearance of **92 mL/min** in this patient.
- Using the Cockcroft-Gault formula for a 62-year-old male, a creatinine of 1.4 mg/dL would correspond to a **CrCl of approximately 65-70 mL/min**, not 92 mL/min.
- This would represent a more significant decrease in GFR than is present in this patient.
*1.7 mg/dL*
- A serum creatinine of **1.7 mg/dL** is far too high for a creatinine clearance of **92 mL/min**.
- This level would correspond to a **CrCl of approximately 50-55 mL/min** in a 62-year-old male, indicating **moderate renal impairment**.
- Such an elevation with ACE inhibitors would warrant investigation for **bilateral renal artery stenosis** or other significant renal pathology.
*2.0 mg/dL*
- A serum creatinine of **2.0 mg/dL** would indicate **significant renal dysfunction** with an estimated CrCl of approximately **40-45 mL/min**, not the 92 mL/min observed.
- This degree of elevation is incompatible with the measured creatinine clearance.
- Would suggest **acute kidney injury** or **severe bilateral renal artery stenosis** and require immediate ACE inhibitor discontinuation.
*2.3 mg/dL*
- A serum creatinine of **2.3 mg/dL** indicates **severe renal impairment** with an estimated CrCl well below 40 mL/min.
- This is completely incompatible with the measured **creatinine clearance of 92 mL/min**.
- Would represent **acute kidney injury** requiring urgent evaluation and medication adjustment.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 3: A 62-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and decreased urine output for 2 weeks. He has not been to the physician for many years and takes no medications. Serum studies show a urea nitrogen concentration of 42 mg/dL and a creatinine concentration of 2.3 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows heavy proteinuria. A photomicrograph of a section of a kidney biopsy specimen is shown. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Amyloidosis
- B. Diabetes mellitus (Correct Answer)
- C. Dyslipidemia
- D. Fibromuscular dysplasia
- E. Severe hypertension
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Diabetes mellitus***
- The kidney biopsy shows **diffuse glomerulosclerosis** with **Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules** (nodular mesangial sclerosis), which are pathognomonic for **diabetic nephropathy**.
- **Heavy proteinuria**, elevated BUN (42 mg/dL) and creatinine (2.3 mg/dL), along with the patient's age, are consistent with long-standing diabetes mellitus, even if previously undiagnosed.
- Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States.
*Amyloidosis*
- While amyloidosis can cause nephrotic syndrome and renal failure, the characteristic histology shows **extracellular amorphous deposits** that stain with **Congo red** and demonstrate apple-green birefringence under polarized light.
- The mesangial nodular pattern seen in diabetic nephropathy is distinct from the amyloid deposits seen in amyloidosis.
- Systemic amyloidosis typically presents with other organ involvement such as **cardiomyopathy**, **hepatosplenomegaly**, or **macroglossia**.
*Dyslipidemia*
- **Dyslipidemia** is a common comorbidity of nephrotic syndrome and diabetic nephropathy, but it is not a direct cause of the structural glomerular damage.
- It represents a metabolic consequence rather than the underlying etiology of the renal pathology.
*Fibromuscular dysplasia*
- **Fibromuscular dysplasia** affects the **renal arteries**, causing **renovascular hypertension** and renal ischemia.
- It typically presents with hypertension in young to middle-aged women and an abdominal bruit, not with heavy proteinuria and glomerular nodular sclerosis.
- The histology would show arterial wall changes, not glomerular pathology.
*Severe hypertension*
- **Severe hypertension** causes hypertensive nephrosclerosis with arteriolosclerosis and global glomerulosclerosis, but not the characteristic **nodular mesangial expansion** (Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules) seen in diabetic nephropathy.
- While hypertension commonly accompanies diabetic nephropathy, the specific histological findings of nodular glomerulosclerosis are pathognomonic for diabetes mellitus.
- Hypertensive nephrosclerosis shows arteriolar hyalinosis and ischemic changes, which differ from diabetic glomerular changes.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 4: A laboratory technician processes basic metabolic panels for two patients. Patient A is 18 years old and patient B is 83 years old. Neither patient takes any medications regularly. Serum laboratory studies show:
Patient A Patient B
Na+ (mEq/L) 145 141
K+ (mEq/L) 3.9 4.4
Cl- (mEq/L) 103 109
HCO3- (mEq/L) 22 21
BUN (mg/dL) 18 12
Cr (mg/dL) 0.8 1.2
Glucose (mg/dL) 105 98
Which of the following most likely accounts for the difference in creatinine seen between these two patients?
- A. Volume depletion
- B. Low body mass index
- C. Insulin resistance
- D. Normal aging (Correct Answer)
- E. High serum aldosterone levels
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Normal aging***
- **Creatinine** is a byproduct of **muscle metabolism**, and serum levels reflect both production (muscle mass) and clearance (GFR).
- In **elderly individuals**, **GFR progressively declines** with age (approximately 1 mL/min/year after age 30).
- However, **muscle mass also decreases** with aging (sarcopenia), leading to **reduced creatinine production**.
- Patient B's creatinine of 1.2 mg/dL appears only mildly elevated, but this likely **underestimates the true decline in renal function** because decreased muscle mass reduces baseline creatinine production.
- This is why **estimated GFR calculations** (using Cockcroft-Gault or MDRD equations) incorporate age and weight to account for this phenomenon.
*Volume depletion*
- **Volume depletion** typically leads to an increase in both **BUN** and **creatinine**, often with a disproportionately higher **BUN:Cr ratio** (>20:1).
- Patient B's BUN is **lower** (12 mg/dL) than Patient A's (18 mg/dL), with a BUN:Cr ratio of 10:1, which argues **against volume depletion**.
*Low body mass index*
- **Low BMI** generally correlates with lower muscle mass, which would result in a **lower serum creatinine** level, not higher.
- Patient B has a **higher creatinine** compared to Patient A, making low BMI an unlikely explanation for the observed difference.
*Insulin resistance*
- **Insulin resistance** is associated with altered glucose metabolism and can contribute to conditions like diabetes and chronic kidney disease over time.
- However, it does not directly explain the **age-related creatinine differences** between these two patients with normal glucose levels and no evidence of diabetic nephropathy.
*High serum aldosterone levels*
- **High aldosterone levels** primarily affect **sodium and potassium balance** and fluid retention (causing hypokalemia and mild hypernatremia).
- Both patients have **normal electrolytes**, and aldosterone does not directly account for **age-related creatinine differences**.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 5: A researcher is investigating the effects of a new antihypertensive medication on renal physiology. She gives a subject a dose of the new medication, and she then collects plasma and urine samples. She finds the following: Hematocrit: 40%; Serum creatinine: 0.0125 mg/mL; Urine creatinine: 1.25 mg/mL. Urinary output is 1 mL/min. Renal blood flow is 1 L/min. Based on the above information and approximating that the creatinine clearance is equal to the GFR, what answer best approximates filtration fraction in this case?
- A. 10%
- B. 17% (Correct Answer)
- C. 33%
- D. 50%
- E. 25%
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***17%***
- First, calculate **GFR** using the creatinine clearance formula: GFR = (Urine creatinine × Urinary output) / Serum creatinine = (1.25 mg/mL × 1 mL/min) / 0.0125 mg/mL = **100 mL/min**.
- Next, calculate **Renal Plasma Flow (RPF)** from Renal Blood Flow (RBF) and Hematocrit: RPF = RBF × (1 - Hematocrit) = 1000 mL/min × (1 - 0.40) = **600 mL/min**.
- Finally, calculate **Filtration Fraction (FF)** = GFR / RPF = 100 mL/min / 600 mL/min = 0.1667 = **16.7%, which approximates to 17%**.
- This is the correct answer based on the physiological calculations and represents a normal filtration fraction.
*10%*
- This would correspond to a filtration fraction of 0.10, which would require either a GFR of 60 mL/min (lower than calculated) or an RPF of 1000 mL/min (higher than calculated).
- This value is too low given the provided parameters and doesn't match the calculation from the given data.
*25%*
- This value would suggest FF = 0.25, requiring a GFR of 150 mL/min with the calculated RPF of 600 mL/min.
- This is higher than the calculated GFR of 100 mL/min and doesn't match the given creatinine values.
*33%*
- This would imply FF = 0.33, requiring a GFR of approximately 200 mL/min with RPF of 600 mL/min.
- This is significantly higher than the calculated GFR and would represent an abnormally elevated filtration fraction.
*50%*
- A filtration fraction of 50% is unphysiologically high and would indicate severe pathology.
- This would require a GFR of 300 mL/min with the calculated RPF, which is impossible given the provided creatinine clearance data.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 6: A 75-year-old woman is brought to a physician’s office by her son with complaints of diarrhea and vomiting for 1 day. Her stool is loose, watery, and yellow-colored, while her vomitus contains partially digested food particles. She denies having blood or mucus in her stools and vomitus. Since the onset of her symptoms, she has not had anything to eat and her son adds that she is unable to tolerate fluids. The past medical history is unremarkable and she does not take any medications regularly. The pulse is 115/min, the respiratory rate is 16/min, the blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and the temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). The physical examination shows dry mucous membranes and slightly sunken eyes. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Which of the following physiologic changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal plasma flow (RPF), and filtration fraction (FF) are expected?
- A. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF
- B. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF
- C. Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF
- D. Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF
- E. Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF (Correct Answer)
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF***
- Due to **dehydration** from diarrhea and vomiting, there is a decrease in blood volume leading to decreased renal blood flow and **renal plasma flow (RPF)**.
- The body responds to hypovolemia by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and sympathetic nervous system, which cause **preferential efferent arteriolar constriction** (more than afferent constriction). This helps maintain glomerular hydrostatic pressure despite reduced renal perfusion.
- As a result, **GFR decreases** but proportionally **less than RPF decreases**, causing the **filtration fraction (FF = GFR/RPF) to increase**.
- In this patient with significant dehydration (tachycardia, hypotension, dry mucous membranes), both GFR and RPF are reduced, but FF is elevated due to compensatory mechanisms.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, decreased FF*
- While GFR and RPF will decrease due to dehydration, the **filtration fraction is expected to increase**, not decrease.
- A decreased FF would imply GFR fell proportionally more than RPF, which contradicts the physiologic response where efferent arteriolar constriction helps preserve GFR relative to RPF.
*Decreased GFR, decreased RPF, no change in FF*
- With significant fluid loss and compensatory mechanisms (efferent arteriolar constriction via angiotensin II), a change in **filtration fraction** is expected.
- The body actively alters arteriolar tone to prioritize GFR maintenance, which directly increases FF.
*Increased GFR, increased RPF, increased FF*
- This pattern suggests **hypervolemia** or increased renal perfusion, which directly contradicts the patient's severe dehydration.
- Both GFR and RPF are expected to decrease in volume depletion, not increase.
*Increased GFR, decreased RPF, increased FF*
- An increase in GFR is physiologically impossible given the patient's severe volume depletion and reduced renal perfusion.
- While FF does increase in dehydration, this occurs in the context of **both GFR and RPF being decreased**, not with an increased GFR.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 7: A 9-year-old boy is brought to the physician's office by his mother because of facial swelling for the past 2 days. The mother says that her son has always been healthy and active but is becoming increasingly lethargic and now has a puffy face. Upon inquiry, the boy describes a foamy appearance of his urine, but denies having blood in the urine, urinary frequency at night, or pain during urination. He has no history of renal or urinary diseases. Physical examination is unremarkable, except for generalized swelling of the face and pitting edema on the lower limbs. Dipstick analysis reveals 4+ proteinuria. An abdominal ultrasound shows normal kidney size and morphology. A renal biopsy yields no findings under light and fluorescence microscopy; however, glomerular podocyte foot effacement is noted on electron microscopy. Which of the following changes in Starling forces occurs in this patient's condition?
- A. Decreased oncotic pressure in the Bowman's capsule
- B. Increased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule
- C. Decreased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule
- D. Decreased glomerular oncotic pressure (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased glomerular hydrostatic pressure
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Decreased glomerular oncotic pressure***
- The patient presents with **nephrotic syndrome**, characterized by severe proteinuria (4+ on dipstick), edema, and **minimal change disease** (podocyte foot effacement on electron microscopy without changes on light or fluorescence microscopy).
- In nephrotic syndrome, large amounts of plasma proteins, particularly **albumin**, are lost in the urine, leading to **hypoalbuminemia** and a significant decrease in the **oncotic pressure of the plasma** (and thus the glomerular capillaries).
*Decreased oncotic pressure in the Bowman's capsule*
- The Bowman's capsule normally has a **very low oncotic pressure** due to the almost complete absence of proteins in the filtrate.
- While theoretically a massive increase in protein filtration could increase it, the primary Starling force affected by protein loss in nephrotic syndrome is the **plasma oncotic pressure**.
*Increased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule*
- This condition is not typically associated with nephrotic syndrome and would rather **impair filtration**.
- Increased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule is usually seen in conditions causing **urinary tract obstruction**, which is not present here.
*Decreased hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman's capsule*
- This would tend to **increase glomerular filtration rate** by favoring filtration, which is not the primary physiological change driving edema in nephrotic syndrome.
- There is no clinical indication for such a change in this patient's presentation.
*Increased glomerular hydrostatic pressure*
- While sometimes seen in specific glomerular diseases, this is not the primary or defining Starling force change in nephrotic syndrome leading to systemic edema.
- Increased glomerular hydrostatic pressure would tend to **increase filtration**, potentially worsening proteinuria, but the fundamental issue in nephrotic syndrome is the **loss of oncotic pressure due to protein leakage**.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 8: A 70-year-old female with chronic kidney failure secondary to diabetes asks her nephrologist to educate her about the techniques used to evaluate the degree of kidney failure progression. She learns about the concept of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and learns that it can be estimated by measuring the levels of some substances. The clearance of which of the following substances is the most accurate estimate for GFR?
- A. Paraaminohippurate (PAH)
- B. Sodium
- C. Inulin (Correct Answer)
- D. Creatinine
- E. Glucose
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Inulin***
- **Inulin** is freely filtered by the glomeruli and is neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the renal tubules, making its clearance the **gold standard** for accurately measuring GFR.
- Due to its ideal physiological properties, inulin clearance perfectly reflects the rate at which plasma is filtered by the kidneys.
*Paraaminohippurate (PAH)*
- **PAH** is almost completely cleared from the blood by both glomerular filtration and **tubular secretion**, making its clearance an accurate measure of **renal plasma flow (RPF)**, not GFR.
- While important for assessing renal blood flow, it does not directly reflect the filtration capacity of the glomeruli.
*Sodium*
- **Sodium** is freely filtered at the glomerulus, but a significant portion (approximately **99%**) is **reabsorbed** by the renal tubules.
- Its clearance is highly variable and depends on various physiological factors, making it unsuitable for GFR estimation.
*Creatinine*
- **Creatinine** is freely filtered by the glomeruli and is also **modestly secreted** by the renal tubules, leading to an **overestimation of GFR** at lower kidney function levels.
- Despite being the most commonly used clinical marker due to its endogenous production, its tubular secretion makes it less accurate than inulin.
*Glucose*
- **Glucose** is freely filtered by the glomeruli but is almost **completely reabsorbed** by the renal tubules under normal physiological conditions.
- Its presence in urine (glycosuria) indicates a high plasma glucose level or tubular reabsorption defects, not a measure of GFR.
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 9: A 73-year-old male is brought in by ambulance after he was found to be lethargic and confused. He has not been routinely seeing a physician and is unable to recall how he came to be in the hospital. His temperature is 99°F (37°C), blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 18/min. His past medical history is significant for poorly controlled diabetes and longstanding hypertension, and he says that he has not been taking his medications recently. Labs are obtained and shown below:
Serum:
Na+: 142 mEq/L
Cl-: 105 mEq/L
K+: 5 mEq/L
HCO3-: 16 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 51 mg/dL
Glucose: 224 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.6 mg/dL
Which of the following changes would most likely improve the abnormal parameter that is responsible for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Increased Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure
- B. Decreased filtration coefficient
- C. Increased Bowman's space oncotic pressure
- D. Decreased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
- E. Increased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure (Correct Answer)
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Increased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure***
- This patient presents with **acute kidney injury (AKI)** evidenced by **elevated creatinine (2.6 mg/dL)** and **BUN (51 mg/dL)**, causing uremic symptoms of **lethargy and confusion**
- The "abnormal parameter" is the **reduced GFR** causing azotemia and uremia
- To improve AKI and restore adequate filtration, **GFR must be increased**
- **Increasing glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure** increases the net filtration pressure: **NFP = (PGC - PBS) - (πGC - πBS)**, where PGC is the primary driving force for filtration
- In prerenal AKI (likely in this patient with poor medication compliance for hypertension), restoring adequate renal perfusion pressure is the therapeutic goal
- While chronic hyperfiltration can contribute to long-term diabetic/hypertensive nephropathy, the **acute management priority** is restoring adequate GFR to clear uremic toxins
*Decreased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure*
- This would **decrease the net filtration pressure**, thereby **reducing GFR**
- Lower GFR would worsen azotemia and uremic symptoms
- This is the opposite of what's needed to improve acute kidney injury
*Increased Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure*
- This **opposes filtration** by increasing back-pressure against the glomerular capillaries
- Would **decrease GFR** and worsen the AKI
- Occurs pathologically in urinary tract obstruction
*Decreased filtration coefficient*
- The filtration coefficient (Kf) represents the permeability and surface area of the glomerular capillaries
- **Decreasing Kf reduces GFR**, worsening kidney function
- This represents glomerular damage, not a therapeutic intervention
*Increased Bowman's space oncotic pressure*
- This would theoretically **increase net filtration pressure** and GFR
- However, this is **physiologically implausible** as Bowman's space normally contains minimal protein (filtrate is protein-free)
- Significant protein in Bowman's space indicates severe glomerular damage with proteinuria, not a mechanism to improve function
Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG Question 10: A large pharmaceutical company is seeking healthy volunteers to participate in a drug trial. The drug is excreted in the urine, and the volunteers must agree to laboratory testing before enrolling in the trial.
The laboratory results of one volunteer are shown below:
Serum glucose (random) 148 mg/dL
Sodium 140 mEq/L
Potassium 4 mEq/L
Chloride 100 mEq/L
Serum creatinine 1 mg/dL
Urinalysis test results:
Glucose absent
Sodium 35 mEq/L
Potassium 10 mEq/L
Chloride 45 mEq/L
Creatinine 100 mg/dL
Assuming a urine flow rate of 1 mL/min, which set of values below is the clearance of glucose, sodium, and creatinine in this patient?
- A. Glucose: 0 mL/min, Sodium: 45 mL/min, Creatinine: 100 mL/min
- B. Glucose: 0 mL/min, Sodium: 4 mL/min, Creatinine: 0.01 mL/min
- C. Glucose: 0 mL/min, Sodium: 48 mL/min, Creatinine: 100 mL/min
- D. Glucose: 0 mL/min, Sodium: 0.25 mL/min, Creatinine: 100 mL/min (Correct Answer)
- E. Glucose: 148 mL/min, Sodium: 105 mL/min, Creatinine: 99 mL/min
Age-related changes in GFR Explanation: ***Glucose: 0 mg/dL, Sodium: 0.25 mL/min, Creatinine: 100 mL/min***
- **Glucose clearance**: Since urine glucose is absent despite a random serum glucose of 148 mg/dL, it indicates **complete reabsorption** of filtered glucose, resulting in a clearance of 0.
- **Sodium clearance**: Calculated as (Urine Na * Urine Flow Rate) / Serum Na = (35 mEq/L * 1 mL/min) / 140 mEq/L = **0.25 mL/min**.
- **Creatinine clearance**: Calculated as (Urine Creatinine * Urine Flow Rate) / Serum Creatinine = (100 mg/dL * 1 mL/min) / 1 mg/dL = **100 mL/min**.
*Glucose: 0 mL/min, Sodium: 45 mL/min, Creatinine: 100 mL/min*
- This option correctly identifies **glucose clearance as 0** and **creatinine clearance as 100 mL/min**.
- However, the **sodium clearance calculation is incorrect**; 45 mEq/L is simply the urine sodium concentration, not the clearance value.
*Glucose: 0 mL/min, Sodium: 4 mL/min, Creatinine: 0.01 mL/min*
- While **glucose clearance is correctly identified as 0**, both **sodium and creatinine clearances are incorrect**.
- Sodium clearance is 0.25 mL/min, and creatinine clearance is 100 mL/min, making these values significantly underestimated.
*Glucose: 0 mL/min, Sodium: 48 mL/min, Creatinine: 100 mL/min*
- This option correctly identifies **glucose clearance as 0** and **creatinine clearance as 100 mL/min**.
- The **sodium clearance calculation is incorrect**; the value 48 mL/min does not correspond to the given data.
*Glucose: 148 mL/min, Sodium: 105 mL/min, Creatinine: 99 mL/min*
- This option is incorrect because **glucose clearance is 0**, not 148 mL/min, as glucose is completely reabsorbed.
- The calculated values for **sodium and creatinine clearance are also incorrect** based on the provided data and formulas.
More Age-related changes in GFR US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.