Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bile production and secretion. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 1 hour history of bruising and bleeding. He says that he fell and scraped his knee on the ground. Since then, he has been unable to stop the bleeding and has developed extensive bruising around the area. He has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation for which he is taking an oral medication. He says that he recently started taking omeprazole for reflux. Which of the following processes is most likely inhibited in this patient?
- A. Sulfation
- B. Oxidation (Correct Answer)
- C. Filtration
- D. Acetylation
- E. Glucuronidation
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Oxidation***
- The patient is taking **omeprazole**, a proton pump inhibitor, which is a known **CYP450 inhibitor**.
- Since the patient is also on an **oral anticoagulant** for atrial fibrillation, inhibition of CYP450 enzymes can reduce the metabolism of the anticoagulant, leading to **increased anticoagulant effect** and subsequent bleeding and bruising.
*Sulfation*
- **Sulfation** is a phase II metabolic reaction that converts compounds into more polar and excretable forms, but omeprazole primarily affects phase I metabolism involving CYP450 enzymes.
- While sulfation can be important for the metabolism of some drugs, it is not the primary process inhibited by omeprazole to cause increased bleeding with oral anticoagulants.
*Filtration*
- **Filtration** is a renal process and not a metabolic enzyme pathway affected by omeprazole.
- Omeprazole's interaction with anticoagulants mainly occurs through hepatic metabolism, not renal filtration.
*Acetylation*
- **Acetylation** is a phase II metabolic reaction, primarily carried out by **N-acetyltransferases**.
- Omeprazole is primarily known to interact with **CYP450 enzymes** (phase I metabolism) rather than N-acetyltransferases.
*Glucuronidation*
- **Glucuronidation** is a phase II metabolic reaction involving **UGT enzymes** that typically inactivates and increases the excretion of drugs.
- While important for drug metabolism, omeprazole's primary drug interactions leading to increased anticoagulant effects are via **CYP450 inhibition** (phase I metabolism), not directly through glucuronidation.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 2: A scientist is studying the mechanism by which the gastrointestinal system coordinates the process of food digestion. Specifically, she is interested in how distension of the lower esophagus by a bolus of food changes responses in the downstream segments of the digestive system. She observes that there is a resulting relaxation and opening of the lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter after the introduction of a food bolus. She also observes a simultaneous relaxation of the orad stomach during this time. Which of the following substances is most likely involved in the process being observed here?
- A. Neuropeptide-Y
- B. Secretin
- C. Ghrelin
- D. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (Correct Answer)
- E. Motilin
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide***
- **VIP (Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide)** is a neuropeptide that mediates **relaxation** of the **smooth muscle** in the gastrointestinal tract, including the **lower esophageal sphincter** and the **orad stomach**, facilitating the passage of food.
- This relaxation is part of the **receptive relaxation** process, allowing the stomach to accommodate food without a significant increase in intragastric pressure.
*Neuropeptide-Y*
- **Neuropeptide-Y (NPY)** is primarily involved in stimulating **food intake** and **reducing energy expenditure**, acting as an orexigenic peptide.
- It does not directly mediate the relaxation of the **lower esophageal sphincter** or **orad stomach** in response to food bolus distension.
*Secretin*
- **Secretin** is a hormone released in response to **acid in the duodenum** and primarily stimulates the pancreas to release **bicarbonate-rich fluid**.
- Its main role is to neutralize stomach acid, not to mediate sphincter relaxation or stomach accommodation.
*Ghrelin*
- **Ghrelin** is known as the "**hunger hormone**" and primarily stimulates **appetite** and **growth hormone release**.
- It does not play a direct role in the relaxation of the **lower esophageal sphincter** or **orad stomach** during swallowing.
*Motilin*
- **Motilin** promotes **gastric and intestinal motility** during the **interdigestive phase**, responsible for the migrating motor complex (MMC).
- Its actions are generally prokinetic, rather than causing relaxation of the upper GI tract in response to a food bolus.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 3: A 55-year-old woman presents with acute onset abdominal pain radiating to her back, nausea, and vomiting. CT scan suggests a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. The pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis relates to inappropriate activation of trypsinogen to trypsin. Which of the following activates trypsin in normal digestion?
- A. Secretin
- B. Lipase
- C. Cholecystokinin
- D. Enterokinase (Correct Answer)
- E. Amylase
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Enterokinase***
- **Enterokinase** (also known as enteropeptidase) is a brush border enzyme of the duodenum that specifically cleaves and activates pancreatic **trypsinogen** into its active form, **trypsin**.
- Once activated, **trypsin** then activates other pancreatic proteases (e.g., chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases, proelastase) within the intestinal lumen.
*Secretin*
- **Secretin** is a hormone released by S cells in the duodenum in response to acidic chyme and acts on the pancreas to stimulate the secretion of **bicarbonate-rich fluid**, which neutralizes gastric acid.
- It does not directly activate digestive enzymes like trypsinogen.
*Lipase*
- **Lipase** is a pancreatic enzyme secreted in its active form that breaks down **dietary fats** (triglycerides) into fatty acids and monoglycerides.
- It plays no role in the activation of trypsinogen.
*Cholecystokinin*
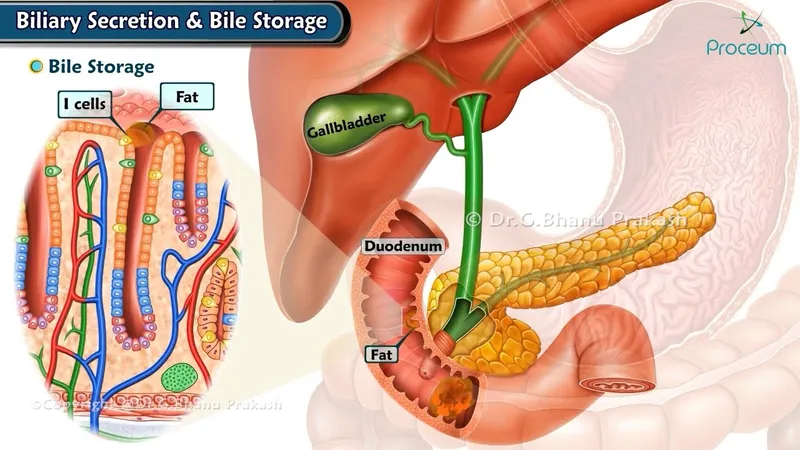
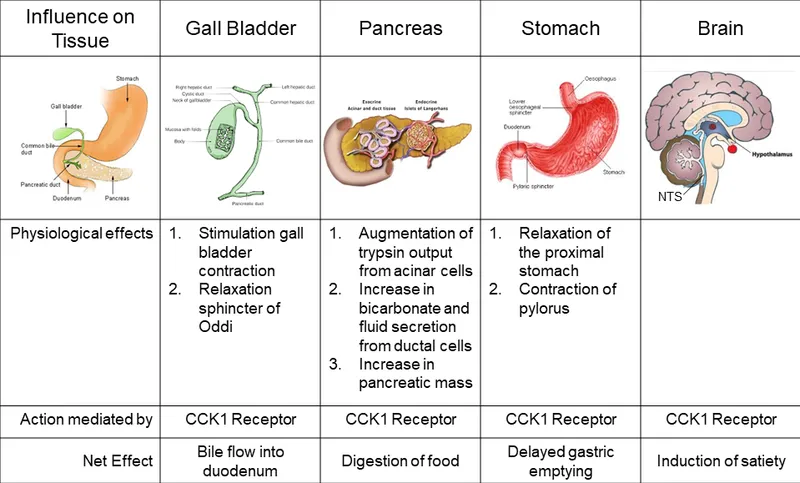
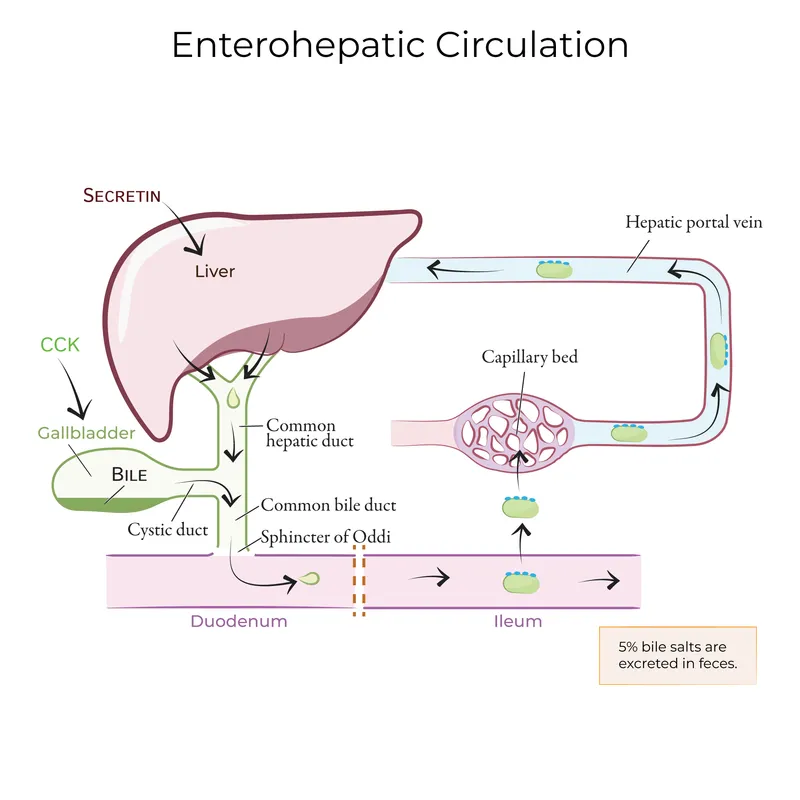
- **Cholecystokinin (CCK)** is a hormone released by I cells in the duodenum in response to fats and proteins, stimulating the contraction of the **gallbladder** and the secretion of **pancreatic enzymes**.
- While it promotes the release of pancreatic enzymes, it does not directly activate trypsinogen.
*Amylase*
- **Amylase** is a pancreatic enzyme secreted in its active form that breaks down **complex carbohydrates** (starches) into simpler sugars (disaccharides and oligosaccharides).
- It is not involved in the activation cascade of pancreatic proteases.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 4: Two hours after undergoing elective cholecystectomy with general anesthesia, a 41-year-old woman is evaluated for decreased mental status. BMI is 36.6 kg/m2. Respirations are 18/min and blood pressure is 126/73 mm Hg. Physical examination shows the endotracheal tube in normal position. She does not respond to sternal rub and gag reflex is absent. Arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows normal PO2 and PCO2 levels. Which of the following anesthetic properties is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Low blood solubility
- B. High lipid solubility (Correct Answer)
- C. Low brain-blood partition coefficient
- D. High minimal alveolar concentration
- E. Low cytochrome P450 activity
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***High lipid solubility***
- Anesthetics with **high lipid solubility** accumulate in **adipose tissue** and are slowly released, prolonging their effect, especially in obese patients.
- The patient's **obesity (BMI 36.6 kg/m2)** contributes to a larger reservoir for lipid-soluble drugs, leading to delayed recovery and decreased mental status.
*Low blood solubility*
- **Low blood solubility** implies a rapid equilibrium between the lungs and the blood, leading to a **faster onset and offset** of anesthetic action.
- This property would result in a quicker recovery from anesthesia, which contradicts the patient's prolonged unconsciousness.
*Low brain-blood partition coefficient*
- A **low brain-blood partition coefficient** means the anesthetic does not accumulate significantly in brain tissue relative to blood.
- Agents with this property equilibrate quickly and leave the brain rapidly upon discontinuation, resulting in **fast recovery**, which is inconsistent with the patient's persistent decreased mental status.
*High minimal alveolar concentration*
- **High minimal alveolar concentration (MAC)** means that a higher concentration of the anesthetic gas is required to produce immobility in 50% of patients.
- A high MAC describes the **potency** of an anesthetic and does not directly explain prolonged recovery or decreased mental status in an obese patient, but rather indicates that a larger dose or concentration was needed to achieve anesthesia.
*Low cytochrome P450 activity*
- **Low cytochrome P450 activity** would lead to slower metabolism of drugs that are primarily cleared by this system, potentially prolonging their effects.
- While relevant for some drugs, the primary issue for inhaled anesthetics is their **physical distribution and elimination**, not typically metabolic clearance via Cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 5: A 57-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of fever and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Examination shows jaundice. Ultrasonography of the abdomen shows cholelithiasis and marked dilation of the biliary duct. An ERCP is performed and reveals pus with multiple brown concrements draining from the common bile duct. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of the patient's findings?
- A. Biliary stricture
- B. Pancreatic cancer
- C. Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- D. Mirizzi syndrome
- E. Choledocholithiasis (Correct Answer)
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Choledocholithiasis***
- The patient presents with **fever**, **right upper quadrant pain**, and **jaundice** (Charcot's triad), highly suggestive of **acute cholangitis**.
- The presence of **cholelithiasis** on ultrasound, **dilated common bile duct**, and **pus with multiple brown concrements** draining from the CBD during ERCP confirm **choledocholithiasis** (stones in the common bile duct) as the underlying cause of biliary obstruction and subsequent cholangitis.
- **Brown pigment stones** form within the bile duct itself due to bacterial infection and bile stasis, and their presence is pathognomonic for choledocholithiasis with secondary infection.
*Biliary stricture*
- While a biliary stricture can cause biliary dilation and potentially cholangitis, it typically doesn't present with **multiple brown concrements** draining during ERCP.
- The primary pathology would be ductal narrowing, not intraductal stones.
*Pancreatic cancer*
- Pancreatic cancer can cause biliary obstruction and jaundice, but typically presents with **painless jaundice** rather than the acute febrile presentation seen here.
- Ultrasound would more likely show a pancreatic mass rather than primarily cholelithiasis with intraductal stones.
*Primary sclerosing cholangitis*
- This condition involves chronic **inflammation and fibrosis** of bile ducts leading to multifocal strictures, but is not typically associated with **acute presentation** or **brown pigment stones**.
- PSC often presents with chronic symptoms and is associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
*Mirizzi syndrome*
- Mirizzi syndrome involves an **impacted gallstone in the cystic duct or gallbladder neck** causing extrinsic compression of the common hepatic duct.
- While it can cause biliary obstruction, the key finding of **multiple brown concrements within the common bile duct** indicates primary intraductal stone disease rather than extrinsic compression from a single impacted stone.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 6: Steroid hormone synthesis, lipid synthesis, and chemical detoxification are activities of which of the following?
- A. Peroxisomes
- B. Nucleolus
- C. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- D. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Correct Answer)
- E. Golgi bodies
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum***
- The **smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)** is rich in enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of **lipids**, including steroid hormones, and is crucial for the detoxification of drugs and poisons, particularly in liver cells.
- Its tubular structure, devoid of ribosomes, differentiates its functions from the rough ER, focusing on metabolic processes like **calcium ion storage** and carbohydrate metabolism.
*Peroxisomes*
- Peroxisomes are primarily involved in the breakdown of **fatty acids** and amino acids, producing hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct.
- They also play a role in detoxification but are not the primary site for steroid hormone or general lipid synthesis.
*Nucleolus*
- The **nucleolus** is a dense structure within the nucleus responsible for synthesizing **ribosomal RNA (rRNA)** and assembling ribosomes.
- It has no direct role in steroid hormone synthesis, lipid metabolism, or chemical detoxification.
*Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum*
- The **rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)** is studded with **ribosomes** and is primarily involved in the synthesis and modification of **proteins** destined for secretion or insertion into membranes.
- While it's part of the endomembrane system, it does not directly perform lipid synthesis or chemical detoxification as its main functions.
*Golgi bodies*
- **Golgi bodies (or Golgi apparatus)** are responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging **proteins and lipids** synthesized in the ER into vesicles for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
- They do not perform the initial synthesis of steroid hormones or lipids, nor are they the primary site for chemical detoxification.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 8: A 56-year-old man comes to the physician for evaluation of gradually worsening fatigue, increased urinary frequency, and blurry vision for 5 months. He has not seen a doctor in several years. Physical examination shows decreased vibratory sense and proprioception in the lower extremities. His hemoglobin A1c is 10.4%. Treatment for his condition with an appropriate medication is begun. In response to this drug, pancreatic islet cells begin producing increasing amounts of secretory granules. The patient was most likely treated with which of the following drugs?
- A. Glimepiride (Correct Answer)
- B. Metformin
- C. Insulin
- D. Pioglitazone
- E. Acarbose
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Glimepiride***
- **Glimepiride** is a sulfonylurea that stimulates pancreatic beta cells to increase **insulin secretion**, leading to an increase in secretory granules.
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, polyuria, blurry vision, neurological deficits) and **high HbA1c (10.4%)** are consistent with poorly controlled **Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus**, for which sulfonylureas are an appropriate treatment.
*Metformin*
- **Metformin** primarily reduces **hepatic glucose production** and improves insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues, rather than directly increasing insulin secretion or secretory granules from beta cells.
- While it is a common first-line treatment for Type 2 Diabetes, its mechanism of action does not involve increasing pancreatic islet cell secretory granules.
*Insulin*
- While insulin would effectively lower blood glucose, it is an **exogenous hormone** and does not stimulate the patient's own pancreatic beta cells to produce more secretory granules.
- Insulin therapy is often used in cases of beta-cell exhaustion or severe hyperglycemia, but the question specifies a drug that increases **pancreatic islet cell production** of granules.
*Pioglitazone*
- **Pioglitazone** is a thiazolidinedione that improves **insulin sensitivity** in peripheral tissues by activating PPAR-gamma receptors.
- It does not directly stimulate the pancreas to increase insulin secretion or the number of secretory granules.
*Acarbose*
- **Acarbose** is an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor that works by delaying **carbohydrate absorption** in the gut, thereby reducing postprandial glucose spikes.
- Its mechanism does not involve any direct effect on pancreatic islet cell insulin production or secretory granules.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 9: A neurophysiology expert is teaching his students the physiology of the neuromuscular junction. While describing the sequence of events that takes place at the neuromuscular junction, he mentions that as the action potential travels down the motor neuron, it causes depolarization of the presynaptic membrane. This results in the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, which leads to an influx of calcium into the synapse of the motor neuron. Consequently, the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ ions increases. Which of the following occurs at the neuromuscular junction as a result of this increase in cytosolic Ca2+?
- A. Generation of an end plate potential
- B. Exocytosis of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased Na+ and K+ conductance of the motor end plate
- D. Binding of Ca2+ ions to NM receptors
- E. Release of Ca2+ ions into the synaptic cleft
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Exocytosis of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles***
- The increase in **cytosolic Ca2+** within the presynaptic terminal is the primary trigger for the fusion of **synaptic vesicles** filled with **acetylcholine (ACh)** with the presynaptic membrane.
- This fusion process, known as **exocytosis**, releases ACh into the **synaptic cleft**, initiating synaptic transmission.
*Generation of an end plate potential*
- The **end plate potential (EPP)** is generated *after* acetylcholine (ACh) is released into the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the motor end plate.
- This event occurs *following* the Ca2+-induced release of neurotransmitter, not as a direct result of the Ca2+ increase itself.
*Increased Na+ and K+ conductance of the motor end plate*
- Increased **Na+ and K+ conductance** across the motor end plate membrane is a direct consequence of acetylcholine binding to its receptors, which are **ligand-gated ion channels**.
- This change in conductance *generates the end plate potential*, occurring after ACh release.
*Binding of Ca2+ ions to NM receptors*
- **NM receptors** (nicotinic muscle receptors) are located on the **postsynaptic membrane** (motor end plate) and bind to **acetylcholine (ACh)**, not Ca2+ ions.
- Calcium's primary role in this context is presynaptic: triggering ACh release.
*Release of Ca2+ ions into the synaptic cleft*
- Calcium ions enter the **presynaptic terminal** from the synaptic cleft, and their increased cytosolic concentration within the presynaptic terminal drives neurotransmitter release.
- Calcium itself is not released *into* the synaptic cleft in this process; rather, it enters the presynaptic neuron from the cleft.
Bile production and secretion US Medical PG Question 10: A 50-year-old woman with long-standing diabetes presents with severe, watery diarrhea that wakes her at night. Stool studies show normal osmotic gap and negative stool cultures. Colonoscopy is normal. Trial of fasting does not improve diarrhea. Gastric emptying study shows delayed emptying. What neurotransmitter deficiency in the enteric nervous system best explains both her gastric and colonic dysmotility?
- A. Acetylcholine
- B. Serotonin
- C. Nitric oxide (Correct Answer)
- D. Substance P
- E. Vasoactive intestinal peptide
Bile production and secretion Explanation: ***Nitric oxide***
- **Nitric oxide (NO)** is the primary **inhibitory neurotransmitter** in the enteric nervous system responsible for mediating **receptive relaxation** of the stomach and smooth muscle inhibition during peristalsis.
- In **diabetic autonomic neuropathy**, loss of nitrergic neurons leads to **gastroparesis** (failed pyloric relaxation) and **diabetic diarrhea** due to uncoordinated colonic motility and loss of descending inhibition.
*Acetylcholine*
- **Acetylcholine** is the primary **excitatory neurotransmitter** responsible for muscle contraction; a deficiency would likely lead to paralytic ileus rather than secretory-pattern diarrhea.
- Though diabetic neuropathy affects cholinergic fibers, the hallmark of the inhibitory dysmotility seen in **gastroparesis** is specifically linked to the NO pathway.
*Serotonin*
- **Serotonin (5-HT)** is predominantly involved in the initiation of the **peristaltic reflex** and intestinal secretion via enterochromaffin cells.
- While 5-HT levels can be altered in IBS, it is not the classic neurotransmitter deficiency cited for the specific combination of **delayed gastric emptying** and autonomic diarrhea in diabetics.
*Substance P*
- **Substance P** acts as a **co-transmitter** with acetylcholine to promote smooth muscle contraction and pain transmission.
- Deficiency of Substance P would impair motor activity but does not explain the loss of **inhibitory control** and relaxation necessary for normal gastric emptying.
*Vasoactive intestinal peptide*
- **Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)** is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that promotes intestinal secretion and smooth muscle relaxation.
- While VIP is involved in relaxation, **Nitric oxide** is considered the more critical mediator for the **pyloric and fundal relaxation** that is specifically impaired in diabetic gastropathy.
More Bile production and secretion US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.