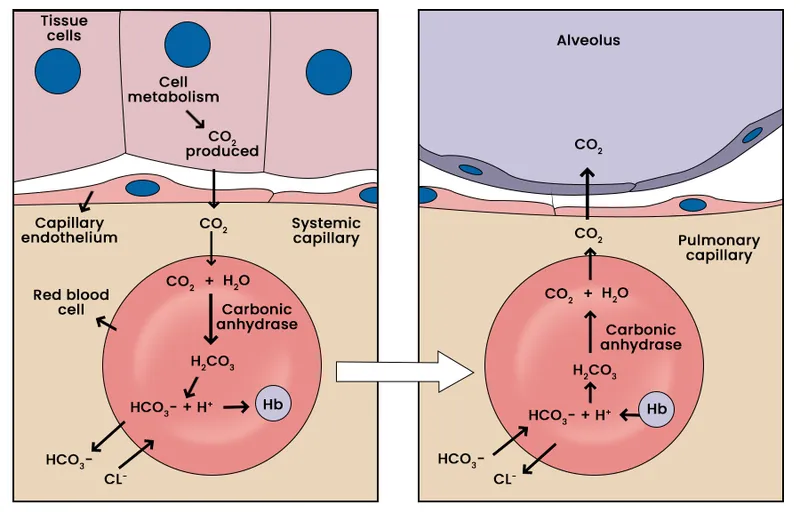
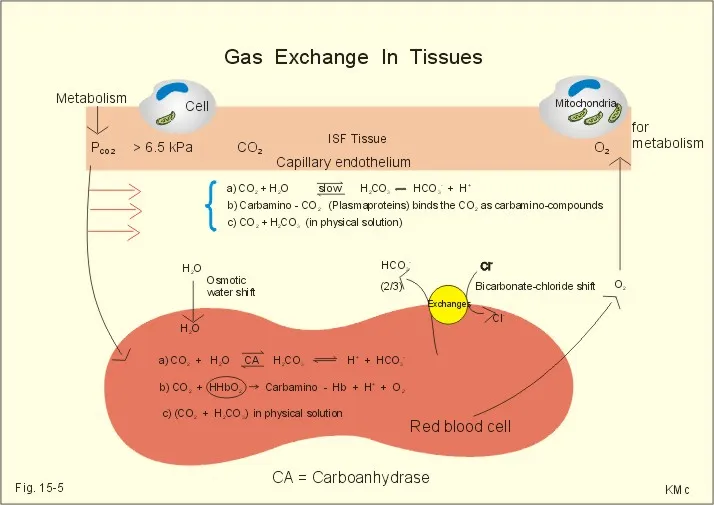
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Carbon dioxide transport. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 1: A 33-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after being rescued from a fire in her apartment. She reports nausea, headache, and dizziness. Physical examination shows black discoloration of her oral mucosa. Pulse oximetry shows an oxygen saturation of 99% on room air. The substance most likely causing symptoms in this patient primarily produces toxicity by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Inhibition of mitochondrial complex V
- B. Degradation of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
- C. Oxidation of Fe2+
- D. Rise in serum pH
- E. Competitive binding to heme (Correct Answer)
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***Competitive binding to heme***
- The patient's symptoms (nausea, headache, dizziness, black oral mucosa) and history of being rescued from a fire strongly suggest **carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning** [1].
- **Carbon monoxide** primarily exerts its toxicity by competitively binding to the **heme iron** in hemoglobin with an affinity 200-250 times greater than oxygen, forming **carboxyhemoglobin (COHb)** and displacing oxygen [2].
*Inhibition of mitochondrial complex V*
- **Cyanide poisoning** inhibits **mitochondrial complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase)**, not complex V, leading to impaired cellular respiration.
- While both cyanide and CO poisoning can occur in fires, CO is more common due to incomplete combustion, and the specific presentation points toward CO.
*Degradation of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate*
- **2,3-BPG** is an important regulator of oxygen affinity for hemoglobin, promoting oxygen release to tissues [2]. Its degradation would increase hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, thus reducing oxygen unloading, but this is not the primary mechanism of toxicity for CO or common fire-related toxins.
- No common toxin directly causes widespread degradation of 2,3-BPG as its primary mechanism of acute toxicity or symptoms.
*Oxidation of Fe2+*
- The oxidation of **ferrous iron (Fe2+)** to **ferric iron (Fe3+)** in hemoglobin leads to the formation of **methemoglobin**, which cannot bind oxygen. This occurs in **methemoglobinemia** induced by certain drugs or toxins (e.g., nitrites, dapsone).
- While **methemoglobinemia** impairs oxygen transport, it does not explain the black oral mucosa or the strong association with fire smoke toxicity in the context of CO.
*Rise in serum pH*
- A rise in serum pH (alkalosis) is not a direct or primary mechanism of toxicity for common fire-related toxins like carbon monoxide or cyanide.
- Most severe forms of toxicity, including CO and cyanide poisoning, tend to cause **lactic acidosis** due to cellular hypoxia and anaerobic metabolism, leading to a
**decrease** in serum pH.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 2: A 24-year-old professional athlete is advised to train in the mountains to enhance his performance. After 5 months of training at an altitude of 1.5 km (5,000 feet), he is able to increase his running pace while competing at sea-level venues. Which of the following changes would produce the same effect on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve as this athlete's training did?
- A. Decreased 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased carbon monoxide inhalation
- C. Decreased temperature
- D. Decreased pH
- E. Increased partial pressure of oxygen
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***Decreased 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate***
- This is **NOT** the correct physiological adaptation from altitude training, making this question conceptually flawed.
- Altitude training causes **increased erythropoietin → polycythemia → increased total hemoglobin**, which increases oxygen-carrying capacity.
- 2,3-BPG is **initially increased** at altitude (right shift) to facilitate O2 release, and remains elevated or returns to normal with acclimatization, **not decreased**.
- While decreased 2,3-BPG would cause a left shift (increased O2 affinity), this does NOT replicate altitude training adaptations.
*Increased carbon monoxide inhalation*
- Carbon monoxide binds hemoglobin with **200-250× higher affinity** than oxygen, forming carboxyhemoglobin.
- This **reduces oxygen-carrying capacity** and causes a left shift for remaining hemoglobin.
- This is harmful and does NOT replicate beneficial altitude adaptations.
*Decreased temperature*
- Decreases metabolic rate and causes a **left shift** (increased O2 affinity).
- Oxygen is held more tightly and released less readily to tissues.
- This does NOT replicate altitude training benefits.
*Decreased pH*
- Acidosis causes the **Bohr effect**: **right shift** (decreased O2 affinity).
- Facilitates O2 release to tissues during exercise.
- This is beneficial during exercise but does NOT replicate the chronic altitude adaptation of increased oxygen-carrying capacity.
*Increased partial pressure of oxygen*
- Higher PO2 increases hemoglobin saturation but does NOT shift the curve.
- This increases oxygen availability but does NOT replicate the physiological adaptation (polycythemia) from altitude training.
**Note:** This question is conceptually problematic as none of the options accurately replicate the primary altitude training adaptation (increased RBC mass/hemoglobin concentration).
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is studying the changes that occur in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve of different types of hemoglobin under various conditions. The blood obtained from a male infant shows decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid. Which of the following is the most likely composition of the hemoglobin molecule in this sample?
- A. α2βS2
- B. α2β2
- C. α2δ2
- D. α2γ2 (Correct Answer)
- E. β4
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***α2γ2***
- This formula represents **fetal hemoglobin (HbF)**, which is the predominant hemoglobin in infants.
- HbF has **decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (2,3-BPG)** compared to adult hemoglobin (HbA) because 2,3-BPG binds less avidly to the gamma chains.
- This decreased 2,3-BPG binding results in HbF having **higher oxygen affinity** than HbA (left-shifted oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve).
- The higher oxygen affinity allows fetal blood to efficiently extract oxygen from maternal blood across the placenta.
*α2βS2*
- This represents **hemoglobin S (HbS)**, found in **sickle cell disease**.
- HbS has similar 2,3-BPG binding to HbA, not decreased affinity.
- Its primary characteristic is polymerization and red blood cell sickling under deoxygenated conditions.
*α2β2*
- This represents **adult hemoglobin (HbA)**, the most common type of hemoglobin in adults.
- HbA has **higher affinity for 2,3-BPG** compared to HbF because 2,3-BPG binds strongly to the beta chains.
- The binding of 2,3-BPG to HbA decreases oxygen affinity, facilitating oxygen release to tissues.
*α2δ2*
- This represents **hemoglobin A2 (HbA2)**, a minor component of adult hemoglobin (typically <3.5%).
- HbA2 has normal 2,3-BPG binding similar to HbA, not decreased affinity.
- This doesn't fit the clinical description of an infant with decreased 2,3-BPG affinity.
*β4*
- This represents **hemoglobin H (HbH)**, which occurs in **alpha-thalassemia** where there is an excess of beta chains that form tetramers.
- HbH has **extremely high oxygen affinity** and does not release oxygen well to tissues.
- While HbH also has decreased 2,3-BPG binding, it is not found in healthy infants and represents a pathological condition.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 4: On cardiology service rounds, your team sees a patient admitted with an acute congestive heart failure exacerbation. In congestive heart failure, decreased cardiac function leads to decreased renal perfusion, which eventually leads to excess volume retention. To test your knowledge of physiology, your attending asks you which segment of the nephron is responsible for the majority of water absorption. Which of the following is a correct pairing of the segment of the nephron that reabsorbs the majority of all filtered water with the means by which that segment absorbs water?
- A. Distal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption
- B. Distal convoluted tubule via aquaporin channels
- C. Thick ascending loop of Henle via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption
- D. Proximal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption (Correct Answer)
- E. Collecting duct via aquaporin channels
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***Proximal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption***
- The **proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)** is responsible for reabsorbing approximately **65-70% of filtered water**, making it the primary site of water reabsorption in the nephron.
- This water reabsorption primarily occurs **passively**, following the active reabsorption of solutes (especially **sodium ions**), which creates an osmotic gradient.
*Distal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption*
- The **distal convoluted tubule (DCT)** reabsorbs a much smaller percentage of filtered water (around 5-10%) and its water reabsorption is largely **regulated by ADH**, not primarily simple passive diffusion following bulk ion reabsorption.
- While some passive water movement occurs, it is not the main mechanism or location for the majority of water reabsorption.
*Distal convoluted tubule via aquaporin channels*
- While aquaporin channels do play a role in water reabsorption in the DCT, particularly under the influence of **ADH**, the DCT is not the segment responsible for the **majority of all filtered water absorption**.
- The bulk of water reabsorption occurs earlier in the nephron, independently of ADH for the most part.
*Thick ascending loop of Henle via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption*
- The **thick ascending loop of Henle** is primarily involved in reabsorbing ions like Na+, K+, and Cl- but is largely **impermeable to water**.
- Its impermeability to water is crucial for creating the **osmotic gradient** in the renal medulla, which is necessary for later water reabsorption.
*Collecting duct via aquaporin channels*
- The **collecting duct** is critically important for **regulated water reabsorption** via **aquaporin-2 channels** under the influence of **ADH**, allowing for fine-tuning of urine concentration.
- However, it reabsorbs only a variable portion (typically 5-19%) of the remaining filtered water, not the **majority of all filtered water**.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 5: A group of researchers is studying various inhaled substances to determine their anesthetic properties. In particular, they are trying to identify an anesthetic with fast onset and quick recovery for use in emergencies. They determine the following data:
Inhalational anesthetic Blood-gas partition coefficient
A 0.15
B 0.92
C 5.42
Which of the following statements is accurate with regard to these inhaled anesthetic substances?
- A. Agent C has the fastest onset of action
- B. Agent A has the fastest onset of action (Correct Answer)
- C. Agent B is the most potent
- D. Agent B has the fastest onset of action
- E. Agent A is the most potent
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***Agent A has the fastest onset of action***
- **Agent A** has the lowest blood-gas partition coefficient (0.15), indicating very low solubility in blood.
- A **low blood-gas partition coefficient** means the anesthetic quickly equilibrates between the lungs and blood, leading to a rapid rise in partial pressure in the brain and thus **fast onset of action** and **quick recovery**.
*Agent C has the fastest onset of action*
- **Agent C** has the highest blood-gas partition coefficient (5.42), indicating high solubility in blood.
- High solubility means the anesthetic takes longer to saturate the blood and reach the brain, resulting in a **slow onset of action** and **slow recovery**.
*Agent B is the most potent*
- **Potency** of an inhaled anesthetic is inversely related to its **Minimum Alveolar Concentration (MAC)**, not directly to its blood-gas partition coefficient.
- While a higher blood-gas coefficient can sometimes correlate with other properties, it does not directly determine potency.
*Agent B has the fastest onset of action*
- **Agent B** has a blood-gas partition coefficient of 0.92, which is higher than Agent A (0.15).
- A higher blood-gas partition coefficient means the anesthetic is more soluble in blood, leading to a **slower onset of action** compared to Agent A.
*Agent A is the most potent*
- **Agent A** has the lowest blood-gas partition coefficient (0.15), which indicates **fast onset** and **rapid recovery**, but not necessarily high potency.
- **Potency** is determined by MAC (Minimum Alveolar Concentration), which is the concentration of anesthetic at 1 atmosphere that produces immobility in 50% of patients challenged with a surgical incision.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 6: A person is exercising strenuously on a treadmill for 1 hour. An arterial blood gas measurement is then taken. Which of the following are the most likely values?
- A. pH 7.56, PaO2 100, PCO2 44, HCO3 38
- B. pH 7.32, PaO2 42, PCO2 50, HCO3 27
- C. pH 7.57 PaO2 100, PCO2 23, HCO3 21 (Correct Answer)
- D. pH 7.38, PaO2 100, PCO2 69 HCO3 42
- E. pH 7.36, PaO2 100, PCO2 40, HCO3 23
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***pH 7.57, PaO2 100, PCO2 23, HCO3 21***
- After 1 hour of strenuous exercise, this represents **respiratory alkalosis with mild metabolic compensation**, which is the expected finding in a healthy individual during sustained vigorous exercise.
- The **low PCO2 (23 mmHg)** reflects appropriate **hyperventilation** in response to increased metabolic demands and lactic acid production. During intense exercise, minute ventilation increases dramatically, often exceeding the rate of CO2 production.
- The **slightly elevated pH (7.57)** and **mildly decreased HCO3 (21 mEq/L)** indicate that respiratory compensation has slightly overshot, creating mild alkalosis, while the bicarbonate is consumed both in buffering lactate and through renal compensation.
- **Normal PaO2 (100 mmHg)** confirms adequate oxygenation maintained by increased ventilation.
*pH 7.36, PaO2 100, PCO2 40, HCO3 23*
- These are **completely normal arterial blood gas values** with no evidence of any physiological stress or compensation.
- After 1 hour of strenuous exercise, we would expect **hyperventilation with decreased PCO2**, not a normal PCO2 of 40 mmHg. This profile would be consistent with rest, not vigorous exercise.
- The absence of any respiratory or metabolic changes makes this inconsistent with the clinical scenario.
*pH 7.56, PaO2 100, PCO2 44, HCO3 38*
- This profile suggests **metabolic alkalosis** (high pH, high HCO3) with inadequate respiratory compensation (normal to slightly elevated PCO2).
- This is **not consistent with strenuous exercise**, which produces metabolic acid (lactate), not metabolic base. The elevated HCO3 suggests vomiting, diuretic use, or other causes of metabolic alkalosis.
*pH 7.32, PaO2 42, PCO2 50, HCO3 27*
- This indicates **respiratory acidosis** (low pH, high PCO2) with **severe hypoxemia** (PaO2 42 mmHg).
- During strenuous exercise, healthy individuals **increase ventilation** to enhance O2 delivery and remove CO2, so both hypoxemia and hypercapnia are unexpected and would suggest severe cardiopulmonary disease or hypoventilation.
*pH 7.38, PaO2 100, PCO2 69, HCO3 42*
- This demonstrates **compensated respiratory acidosis** (normal pH, markedly elevated PCO2 and HCO3).
- The **very high PCO2 (69 mmHg)** indicates severe **hypoventilation**, which is the opposite of what occurs during exercise. This profile suggests chronic respiratory failure with metabolic compensation, such as in severe COPD.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 7: A 29-year-old man presents for the evaluation of infertility. He has a history of recurrent lower respiratory tract infections, productive cough, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Physical examination reveals clubbing and bilateral crackles on chest auscultation. Chest X-ray reveals increased pulmonary markings and peripheral bronchi with a ‘tram track’ appearance. Which of the following pathophysiologies is responsible for the patient’s condition?
- A. Fibrosis of the lung parenchyma
- B. Bronchial hypersensitivity
- C. Abnormal ciliary motion
- D. Gluten hypersensitivity
- E. Defective chloride transport (Correct Answer)
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***Defective chloride transport***
- The patient's presentation with **recurrent respiratory infections**, **bronchiectasis** (tram track appearance on CXR), **clubbing**, and **infertility** is highly suggestive of **cystic fibrosis**.
- **Cystic fibrosis** is caused by mutations in the **CFTR gene**, leading to **defective chloride transport** across epithelial cells, resulting in thick, viscous secretions.
*Fibrosis of the lung parenchyma*
- While chronic lung disease can lead to some **pulmonary fibrosis**, it is not the primary underlying pathophysiology described here.
- Pulmonary fibrosis typically presents with **restrictive lung disease** and interstitial patterns on imaging, rather than the prominent **bronchiectasis** seen in this patient.
*Bronchial hypersensitivity*
- This is characteristic of **asthma**, which involves airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction, but typically does not cause the extensive **recurrent infections**, **bronchiectasis**, or **infertility** seen in this case.
- Asthma is less likely to result in **clubbing** or the progressive lung damage implied by a "tram track" appearance.
*Abnormal ciliary motion*
- This describes **primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD)**, which can also cause recurrent respiratory infections and male infertility due to **immotile sperm**.
- However, PCD typically presents with **situs inversus** in a significant proportion of cases and does not involve the characteristic **exocrine gland dysfunction** (e.g., severe abdominal symptoms, pancreatic insufficiency leading to diarrhea) often seen in cystic fibrosis implied by the broad clinical picture.
*Gluten hypersensitivity*
- Also known as **celiac disease**, this is primarily a **gastrointestinal condition** characterized by malabsorption due to immune reactions to gluten.
- While celiac disease can cause **abdominal pain** and **diarrhea**, it does not explain the **recurrent respiratory infections**, **bronchiectasis**, **clubbing**, or **male infertility**.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator is conducting a study on hematological factors that affect the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. An illustration of two graphs (A and B) that represent the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen is shown. Which of the following best explains a shift from A to B?
- A. Decreased serum pCO2
- B. Increased serum pH
- C. Decreased serum 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate concentration
- D. Increased body temperature (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased hemoglobin γ-chain synthesis
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***Increased body temperature***
- A shift from A to B represents a **rightward shift** of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, indicating **decreased hemoglobin affinity for oxygen**.
- **Increased body temperature** (e.g., during exercise, fever) reduces hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, facilitating **oxygen release to tissues**.
*Decreased serum pCO2*
- A **decrease in serum pCO2** leads to an **increase in pH** (alkalosis) and a **leftward shift** of the curve, meaning an increased affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
- This is part of the **Bohr effect**, where lower CO2 levels signal decreased tissue metabolic activity, thus reducing oxygen unloading.
*Increased serum pH*
- An **increase in serum pH** (alkalosis) causes a **leftward shift** of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, signifying **increased hemoglobin affinity for oxygen**.
- This response is beneficial in the lungs, where higher pH promotes oxygen binding to hemoglobin.
*Decreased serum 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate concentration*
- A **decrease in 2,3-BPG** concentration leads to a **leftward shift** of the curve, representing **increased hemoglobin affinity for oxygen**.
- 2,3-BPG typically binds to deoxyhemoglobin, stabilizing its T-state and promoting oxygen release; thus, less 2,3-BPG means less release.
*Increased hemoglobin γ-chain synthesis*
- Increased **hemoglobin γ-chain synthesis** is characteristic of **fetal hemoglobin (HbF)**, which has a **higher affinity for oxygen** than adult hemoglobin (HbA).
- This would result in a **leftward shift** of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, enhancing oxygen uptake by the fetus.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying muscle contraction in tissue obtained from the thigh muscle of an experimental animal. After injection of radiolabeled ATP, the tissue is stimulated with electrical impulses. Radioassay of these muscle cells is most likely to show greatest activity in which of the following structures?
- A. H zone
- B. M line
- C. A band (Correct Answer)
- D. Z line
- E. I band
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***A band***
- The **A band** contains the entire length of the **thick myosin filaments** along with the **overlap zone** where myosin and actin interact. Myosin has **ATPase activity**, meaning it binds and hydrolyzes **ATP** to power muscle contraction through cross-bridge cycling.
- Therefore, the greatest accumulation of **radiolabeled ATP** and its breakdown products would be found where **myosin heads** are located throughout the A band.
- The A band represents the most complete answer as it encompasses all regions containing myosin ATPase activity.
*H zone*
- The **H zone** is the central part of the **A band** where only **thick myosin filaments** are present, with no overlap with thin actin filaments.
- While myosin heads with ATPase activity are present here and would show radiolabeled ATP, the **H zone** is only a **subset** of the A band. The **A band** is the more comprehensive answer as it includes both the H zone and the overlap regions where most cross-bridge cycling occurs.
*M line*
- The **M line** is the very center of the **H zone** and anchors the **thick filaments**.
- It consists of structural proteins like **myomesin** and **creatine kinase**. While creatine kinase can phosphorylate ADP to regenerate ATP, it does not directly hydrolyze ATP for muscle contraction the way myosin ATPase does.
*Z line*
- The **Z line** (or Z disc) marks the boundaries of a **sarcomere** and anchors the **thin actin filaments**.
- It contains proteins like **alpha-actinin** and **desmin** but does not directly consume ATP for muscle contraction.
*I band*
- The **I band** contains only **thin actin filaments** and extends from the edge of the A band to the Z line.
- While actin is crucial for contraction, it does not possess **ATPase activity**; ATP hydrolysis primarily occurs at the **myosin heads** located in the A band.
Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG Question 10: A 67-year-old man presents to the surgical clinic with swelling of his right leg, fever, and chills for 2 days. The maximum recorded temperature was 38.3°C (101.0°F) at home. His right leg is red and swollen from the dorsum of the foot to the thigh with an ill-defined edge. Venous stasis ulcers are present in both of his limbs, but those on the right have a yellow discharge. His vitals include the following: blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg, heart rate is 94/min, temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F), and respiratory rate is 16/min. On physical examination, there is tenderness and warmth compared with his normal leg. Dorsalis pedis pulses are present on both of the ankles. What is the most likely cause of the right shift of the hemoglobin dissociation curve for his condition?
- A. Decrease in temperature
- B. Increase in CO2 production
- C. Increase in pH
- D. Increase in temperature (Correct Answer)
- E. Decrease in 2,3-DPG
Carbon dioxide transport Explanation: ***Increase in temperature***
- The patient presents with **fever (38.3°C)**, which is explicitly mentioned multiple times in the clinical scenario and represents a **systemic response** to infection.
- **Increased temperature** directly causes a **right shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve by **decreasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen**.
- This facilitates oxygen release to metabolically active tissues, particularly important in areas of infection and inflammation.
- While multiple factors can cause right shifts during infection, the **fever is the most prominently featured clinical finding** in this case and represents a measurable systemic change.
*Decrease in temperature*
- A **decrease in temperature** causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, **increasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen**.
- This would impair oxygen release to tissues, which is counterproductive during infection when tissues require increased oxygen delivery.
*Increase in CO2 production*
- While **increased CO2 production** does occur during infection due to increased tissue metabolism and does cause a **right shift** via the **Bohr effect** (CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3-, leading to decreased pH), this is not the primary factor being highlighted in this clinical presentation.
- The Bohr effect (acidosis from increased CO2 and metabolic acids) is an important physiological response, but the question emphasizes the **fever** as the key feature of this patient's condition.
- In the context of this question asking about "his condition," the **temperature elevation is the most direct and measurable systemic change** presented.
*Increase in pH*
- An **increase in pH** (alkalosis) causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, **increasing hemoglobin's oxygen affinity**.
- This would hinder oxygen delivery to tissues, which is not beneficial during infection when tissue oxygen demand is elevated.
*Decrease in 2,3-DPG*
- A **decrease in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG)** causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
- This increases hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, making oxygen release to tissues more difficult.
- During infection, 2,3-DPG levels typically remain stable or may increase slightly, not decrease.
More Carbon dioxide transport US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.