Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old female with Crohn's disease diagnosed in her early 20s comes to your office for a follow-up appointment. She is complaining of headaches and fatigue. Which of the following arterial blood gas findings might you expect?
- A. High PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)
- B. Low PaO2, low O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2)
- C. Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)
- D. Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2) (Correct Answer)
- E. Low PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2)***
- Patients with **Crohn's disease** are prone to developing **iron deficiency anemia** due to chronic inflammation, malabsorption, and blood loss, leading to reduced hemoglobin levels.
- While PaO2 and SaO2 measure oxygen *tension* and *percentage saturation* of available hemoglobin, respectively, **O2 content (CaO2)** directly reflects the *total amount* of oxygen delivered to tissues, which is primarily dependent on hemoglobin concentration. Therefore, with anemia, CaO2 will be low despite normal PaO2 and SaO2 because there is less hemoglobin to carry oxygen.
*High PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)*
- High PaO2 would indicate **hyperoxygenation**, which is not an expected complication of Crohn's disease or its associated anemia.
- Normal O2 content is inconsistent with the presence of anemia, which significantly reduces the body's total oxygen-carrying capacity.
*Low PaO2, low O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2)*
- Low PaO2 and SaO2 suggest a primary **respiratory problem** or severe hypoxemia, which is not directly linked to Crohn's disease or the typical presentation of iron deficiency anemia.
- While low O2 content is correct for anemia, the accompanying low PaO2 and SaO2 indicate a different underlying pathology for oxygen transport issues.
*Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)*
- This finding would indicate **normal oxygenation** and oxygen-carrying capacity, which is contrary to the clinical scenario of a patient with Crohn's likely complicated by anemia.
- The patient's symptoms of headaches and fatigue are consistent with poor tissue oxygenation, which would not occur if all these parameters were normal.
*Low PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)*
- A low PaO2 with a normal SaO2 is physiologically unlikely unless there is a **left shift of the oxygen dissociation curve** with adequate hemoglobin, which doesn't fit the expected anemic state.
- Normal O2 content would rule out the presence of anemia as a cause for the symptoms, which is a common complication in Crohn's disease.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 2: Four days after undergoing an elective total hip replacement, a 65-year-old woman develops a DVT that embolizes to the lung. Along with tachypnea, tachycardia, and cough, the patient would most likely present with a PaO2 of what?
- A. 120 mmHg
- B. 100 mmHg
- C. 85 mmHg (Correct Answer)
- D. 110 mmHg
- E. 60 mmHg
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***85 mmHg***
- A pulmonary embolism (PE) causes a **ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch**, leading to **hypoxemia** and a reduced PaO2.
- While exact values vary, a PaO2 of 85 mmHg indicates **mild to moderate hypoxemia**, which is common in PE, especially with accompanying symptoms like tachypnea and tachycardia.
*120 mmHg*
- This value is significantly **higher than normal (75-100 mmHg)** and would indicate **hyperoxia**, which is inconsistent with acute pulmonary embolism causing respiratory distress.
- A patient with PE would typically have **reduced oxygenation**, not supernormal levels, unless receiving high-flow supplemental oxygen.
*100 mmHg*
- A PaO2 of 100 mmHg is at the **upper end of the normal range** (75-100 mmHg) and would imply **no significant hypoxemia**.
- Given the patient's symptoms of tachypnea, tachycardia, and cough following a DVT with embolization, a normal or high-normal PaO2 is unlikely without aggressive oxygen therapy (which is not stated).
*110 mmHg*
- This value is **above the normal range** and suggests **hyperoxia**, which is contrary to the pathophysiology of a pulmonary embolism.
- A PE impairs gas exchange, leading to a decrease in PaO2, not an increase.
*60 mmHg*
- A PaO2 of 60 mmHg indicates **significant hypoxemia**, which might occur in a severe, large pulmonary embolism or in a patient with underlying lung disease.
- While possible, 85 mmHg represents a more common, moderate hypoxemia seen in PE, especially given the prompt presentation of symptoms.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 3: A 63-year-old man presents to the clinic with fever accompanied by shortness of breath. The symptoms developed a week ago and have been progressively worsening over the last 2 days. He reports his cough is productive of thick, yellow sputum. He was diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 3 years ago and has been on treatment ever since. He quit smoking 10 years ago but occasionally experiences shortness of breath along with chest tightness that improves with the use of an inhaler. However, this time the symptoms seem to be more severe and unrelenting. His temperature is 38.6°C (101.4°F), the respirations are 21/min, the blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and the pulse is 105/min. Auscultation reveals bilateral crackles and expiratory wheezes. His oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. According to this patient’s history, which of the following should be the next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Chest X-ray (Correct Answer)
- B. Arterial blood gases
- C. Bronchoprovocation test
- D. Bronchoscopy
- E. CT scan
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Chest X-ray***
- A **chest X-ray** is a crucial initial step to evaluate for **pneumonia** or other acute pulmonary processes, given the fever, productive cough, and worsening respiratory symptoms in a patient with COPD [1].
- It can identify infiltrates, effusions, or other anatomical changes that explain the patient's acute decompensation [1].
*Arterial blood gases*
- While important for assessing **respiratory failure** and guiding ventilator management, **ABGs** are usually performed after initial imaging to quantify gas exchange abnormalities once an etiology is suspected [1].
- The patient's **oxygen saturation of 95% on room air** does not immediately suggest severe hypoxemia, although hypercapnia could still be present.
*Bronchoprovocation test*
- A **bronchoprovocation test** is used to diagnose **asthma** or assess **airway hyperresponsiveness** in stable patients.
- It is contraindicated in acute exacerbations due to the risk of worsening bronchoconstriction.
*Bronchoscopy*
- **Bronchoscopy** is an invasive procedure typically reserved for cases of suspicion of **tumor**, **foreign body aspiration**, or non-resolving infiltrates and would not be the immediate next step for fever and productive cough.
- It is not indicated for the initial diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia or COPD exacerbation.
*CT scan*
- A **CT scan** provides more detailed imaging but is usually reserved for cases where the chest X-ray is inconclusive or to look for specific pathologies like **pulmonary embolism** or **bronchiectasis**.
- It's not the initial imaging choice for suspected **pneumonia** due to cost, radiation exposure, and the adequacy of X-ray for this purpose [1].
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 4: A 50-year-old man presents to the urgent care clinic for 3 hours of worsening cough, shortness of breath, and dyspnea. He works as a long-haul truck driver, and he informs you that he recently returned to the west coast from a trip to Arkansas. His medical history is significant for gout, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus type 2, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and mild intellectual disability. He currently smokes 1 pack of cigarettes/day, drinks a 6-pack of beer/day, and he endorses a past history of injection drug use but currently denies any illicit drug use. The vital signs include: temperature 36.7°C (98.0°F), blood pressure 126/74 mm Hg, heart rate 87/min, and respiratory rate 23/min. His physical examination shows mild, bilateral, coarse rhonchi, but otherwise clear lungs on auscultation, grade 2/6 holosystolic murmur, and a benign abdominal physical examination. He states that he ran out of his albuterol inhaler 6 days ago and has been meaning to follow-up with his primary care physician (PCP) for a refill. Complete blood count (CBC) and complete metabolic panel are within normal limits. He also has a D-dimer result within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluation?
- A. Chest computed tomography (CT) with contrast
- B. Chest radiographs (Correct Answer)
- C. Pulmonary function tests
- D. Sputum gram stain and culture
- E. Arterial blood gas
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Chest radiographs***
- A **chest X-ray** is the most appropriate initial imaging study for evaluating acute respiratory symptoms in a patient with a history of COPD and recent exacerbating factors (running out of albuterol). It can help identify common causes like **pneumonia**, **pneumothorax**, or **acute exacerbation of COPD**.
- The patient's presentation with worsening cough, shortness of breath, and dyspnea, particularly in the context of running out of his albuterol inhaler, suggests a primary pulmonary issue that a chest X-ray can quickly assess.
*Chest computed tomography (CT) with contrast*
- A **chest CT with contrast** is more detailed but not the initial diagnostic study in this scenario, especially with a normal D-dimer ruling out pulmonary embolism as a high probability.
- It exposes the patient to **higher radiation** and risks associated with contrast, making it less suitable as a first-line investigation unless the chest X-ray is inconclusive or more specific findings are suspected.
*Pulmonary function tests*
- **Pulmonary function tests (PFTs)** are used to diagnose and monitor chronic lung conditions like COPD, but they are generally not performed in an acute urgent care setting for patients presenting with acute respiratory distress.
- PFTs require patient cooperation and are designed to assess baseline lung function, not to identify the **acute cause** of respiratory decompensation.
*Sputum gram stain and culture*
- A **sputum gram stain and culture** might be considered if there's strong suspicion of a bacterial infection (e.g., fever, purulent sputum), but the patient's current symptoms are more aligned with a COPD exacerbation or other acute pulmonary issue.
- Without clear signs of bacterial infection, this test is **not the most immediate or appropriate first step** in evaluating acute dyspnea, as it requires time for results and may delay more crucial diagnostic steps.
*Arterial blood gas*
- An **arterial blood gas (ABG)** can provide information on oxygenation, ventilation, and acid-base status, which is useful in assessing the severity of respiratory failure.
- However, it's typically ordered after an initial clinical and imaging assessment to quantify the physiological impact of the respiratory distress, rather than being the **very first diagnostic step** to identify the cause.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old man with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after his daughter found him unresponsive. Despite appropriate care, the patient dies. At autopsy, examination of the lungs shows enlargement of the airspaces in the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli. Enzymatic activity of which of the following cells is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Alveolar macrophages (Correct Answer)
- B. Ciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells
- C. Elastic fibers in alveolar septa
- D. Type I pneumocytes
- E. Alveolar septal cells
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Alveolar macrophages***
- In **alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency**, alveolar macrophages (and neutrophils) release **elastase**, which is normally inhibited by alpha-1-antitrypsin.
- Unchecked elastase activity from alveolar macrophages leads to the **destruction of elastic fibers** in the alveolar walls, causing emphysema with characteristic **panacinar** distribution (worse in lower lobes).
- This results in enlargement of airspaces distal to terminal bronchioles.
*Ciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells*
- These cells are primarily involved in **mucociliary clearance** and do not produce proteolytic enzymes that degrade elastic tissue.
- Their dysfunction would lead to impaired mucus clearance and increased susceptibility to infections, but not emphysema.
*Elastic fibers in alveolar septa*
- Elastic fibers are **extracellular matrix components**, not cells.
- While their destruction is the pathological mechanism of emphysema, they do not have enzymatic activity.
*Type I pneumocytes*
- **Type I pneumocytes** form the structural lining of the alveoli and are primarily involved in gas exchange.
- They do not produce elastase or other proteolytic enzymes responsible for tissue destruction in emphysema.
*Alveolar septal cells*
- This term broadly refers to structural cells including Type I and Type II pneumocytes.
- While these cells may be damaged secondarily in emphysema, they do not produce the elastase responsible for elastic fiber destruction.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 6: Two days after undergoing left hemicolectomy for a colonic mass, a 62-year-old man develops shortness of breath. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F), pulse is 80/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 88%. Cardiopulmonary examination shows decreased breath sounds and decreased fremitus at both lung bases. Arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows:
pH 7.35
PaO2 70 mm Hg
PCO2 40 mm Hg
An x-ray of the chest shows a collapse of the bases of both lungs. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's hypoxemia?
- A. Increased anatomic dead space
- B. Decreased hemoglobin oxygen-binding capacity
- C. Decreased chest wall compliance
- D. Increased tidal volume
- E. Decreased ratio of ventilated alveoli (Correct Answer)
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Decreased ratio of ventilated alveoli***
- The patient's presentation with **shortness of breath**, **decreased breath sounds and fremitus at both lung bases**, and **collapsed lung bases on chest x-ray** points to **atelectasis**.
- **Atelectasis** is a common cause of hypoxemia post-surgery. It occurs when alveoli collapse, leading to areas of the lung that are perfused but not ventilated, resulting in a **ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch** with a decreased ratio of ventilated alveoli.
*Increased anatomic dead space*
- **Anatomic dead space** refers to the conducting airways where gas exchange does not occur. This value is relatively constant and would not increase significantly to cause such profound hypoxemia in this context.
- Conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase dead space, but the patient's acute postoperative presentation and chest X-ray findings do not support this as the primary cause.
*Decreased hemoglobin oxygen-binding capacity*
- This would involve issues like **carbon monoxide poisoning** or specific hemoglobinopathies, which are not indicated by the clinical picture or ABG results (normal pH, PaO2 70 mmHg, PCO2 40 mmHg).
- The PaO2 and SaO2 values indicate a problem with oxygen uptake, not oxygen transport by hemoglobin once bound.
*Decreased chest wall compliance*
- While surgery can cause **pain leading to splinting** and reduced chest wall expansion, which impacts compliance, the primary mechanism of hypoxemia in atelectasis is the **collapse of alveoli**, not solely reduced chest wall movement.
- The **collapsed lung bases** on X-ray directly point to alveolar collapse rather than a general decrease in chest wall compliance as the primary problem.
*Increased tidal volume*
- **Increased tidal volume** would typically improve ventilation and oxygenation, not lead to hypoxemia.
- The patient's **hypoxemia (SaO2 88%, PaO2 70 mmHg)** clearly indicates a problem with oxygen uptake, not an enhancement of respiratory function.
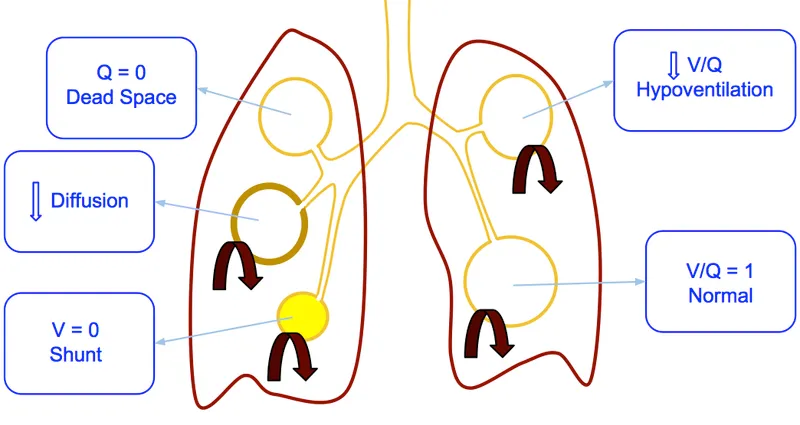
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 7: A 30-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with breathlessness for the last hour. She is unable to provide any history due to her dyspnea. Her vitals include: respiratory rate 20/min, pulse 100/min, and blood pressure 144/84 mm Hg. On physical examination, she is visibly obese, and her breathing is labored. There are decreased breath sounds and hyperresonance to percussion across all lung fields bilaterally. An arterial blood gas is drawn, and the patient is placed on inhaled oxygen. Laboratory findings reveal:
pH 7.34
pO2 63 mm Hg
pCO2 50 mm Hg
HCO3 22 mEq/L
Her alveolar partial pressure of oxygen is 70 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Right to left shunt
- B. Alveolar hypoventilation (Correct Answer)
- C. Ventricular septal defect
- D. Impaired gas diffusion
- E. Ventilation/perfusion mismatch
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Alveolar hypoventilation***
- The patient exhibits features of **obesity** and **labored breathing** with decreased breath sounds and hyperresonance, along with arterial blood gas results showing **respiratory acidosis** (pH 7.34, pCO2 50 mmHg) and **hypoxia** (pO2 63 mmHg).
- The calculated A-a gradient (Alveolar O2 - arterial O2) is low (70 mmHg - 63 mmHg = 7 mmHg), indicating that the problem is primarily with **overall ventilation** rather than a defect in gas exchange across the alveolar-capillary membrane.
*Right to left shunt*
- A right-to-left shunt would cause a **large A-a gradient**, as deoxygenated blood bypasses the lungs and mixes with oxygenated blood.
- While it causes **hypoxemia**, it would not typically be associated with hypercapnia unless very severe, and the A-a gradient calculation here does not support a significant shunt.
*Ventricular septal defect*
- A ventricular septal defect is a **structural heart abnormality** that can cause a left-to-right shunt initially, leading to pulmonary hypertension and eventually a right-to-left shunt (Eisenmenger syndrome).
- While it can cause hypoxemia due to shunting, it would not primarily manifest with increased pCO2 or the specific lung physical exam findings of decreased breath sounds and hyperresonance in the absence of other cardiac signs.
*Impaired gas diffusion*
- Impaired gas diffusion would lead to a **large A-a gradient** and **hypoxemia**, but typically not significant hypercapnia unless the impairment is extremely severe.
- Conditions like **pulmonary fibrosis** or **emphysema** cause impaired diffusion, but the patient's presentation and particularly the low A-a gradient do not support this.
*Ventilation/perfusion mismatch*
- A V/Q mismatch also causes a **large A-a gradient** and **hypoxemia**, as some areas of the lung are either poorly ventilated or poorly perfused.
- While it can cause hypercapnia in severe cases, the primary issue indicated by the low A-a gradient here is one of overall inadequate ventilation, not selective areas of ventilation-perfusion imbalance.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 8: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of coughing and difficulty breathing that started shortly after his mother found him in the living room playing with his older brother's toys. He appears anxious. Respirations are 33/min and pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 88%. Physical examination shows nasal flaring and intercostal retractions. Auscultation of the lungs shows a high-pitched inspiratory wheeze and absent breath sounds on the right side. There is no improvement in his oxygen saturation after applying a non-rebreather mask with 100% FiO2. Which of the following terms best describes the most likely underlying mechanism of the right lung's impaired ventilation?
- A. Alveolar hyperventilation
- B. Alveolar dead space
- C. Diffusion limitation
- D. Alveolar hypoventilation (Correct Answer)
- E. Right-to-left shunt
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Alveolar hypoventilation***
- The clinical presentation strongly suggests **foreign body aspiration** causing complete obstruction of the right main bronchus, leading to **alveolar hypoventilation** of the entire right lung.
- **Alveolar hypoventilation** means reduced or absent air movement into the alveoli. In this case, the mechanical obstruction prevents ventilation (V/Q = 0), while perfusion continues normally, creating severe V/Q mismatch.
- The **hypoxemia unresponsive to 100% FiO2** occurs because blood perfusing the unventilated right lung remains deoxygenated (shunt-like physiology), but the underlying mechanism is **ventilation failure** (hypoventilation), not an anatomical shunt.
- **Absent breath sounds** on the right confirm no air entry to that lung, which is the definition of regional hypoventilation.
*Right-to-left shunt*
- A **true anatomical right-to-left shunt** refers to blood bypassing the lungs entirely through intracardiac defects (VSD, ASD, PDA with Eisenmenger syndrome) or intrapulmonary arteriovenous malformations.
- While the obstructed lung creates **shunt-like physiology** (blood passes unventilated alveoli), the mechanism is **hypoventilation due to airway obstruction**, not an anatomical shunt.
- The distinction is important: shunt describes the physiological effect (V/Q = 0), but hypoventilation describes the mechanism (airway obstruction preventing ventilation).
*Alveolar hyperventilation*
- This refers to **increased alveolar ventilation** beyond metabolic needs, leading to increased CO2 elimination and respiratory alkalosis.
- The patient shows tachypnea (33/min), which represents compensatory effort, but the right lung has **decreased ventilation** (hypoventilation), not hyperventilation.
*Alveolar dead space*
- **Alveolar dead space** occurs when alveoli are **ventilated but not perfused** (V/Q approaching infinity), as seen in pulmonary embolism.
- This scenario shows the opposite: the right lung is **perfused but not ventilated** due to airway obstruction.
*Diffusion limitation*
- **Diffusion limitation** occurs when gas exchange across the alveolar-capillary membrane is impaired (pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial lung disease).
- This patient has **mechanical obstruction preventing air from reaching the alveoli**, not a problem with diffusion across intact membranes.
- Diffusion limitation typically responds partially to supplemental oxygen, unlike complete obstruction.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 9: A 67-year-old man presents to the surgical clinic with swelling of his right leg, fever, and chills for 2 days. The maximum recorded temperature was 38.3°C (101.0°F) at home. His right leg is red and swollen from the dorsum of the foot to the thigh with an ill-defined edge. Venous stasis ulcers are present in both of his limbs, but those on the right have a yellow discharge. His vitals include the following: blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg, heart rate is 94/min, temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F), and respiratory rate is 16/min. On physical examination, there is tenderness and warmth compared with his normal leg. Dorsalis pedis pulses are present on both of the ankles. What is the most likely cause of the right shift of the hemoglobin dissociation curve for his condition?
- A. Decrease in temperature
- B. Increase in CO2 production
- C. Increase in pH
- D. Increase in temperature (Correct Answer)
- E. Decrease in 2,3-DPG
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Increase in temperature***
- The patient presents with **fever (38.3°C)**, which is explicitly mentioned multiple times in the clinical scenario and represents a **systemic response** to infection.
- **Increased temperature** directly causes a **right shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve by **decreasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen**.
- This facilitates oxygen release to metabolically active tissues, particularly important in areas of infection and inflammation.
- While multiple factors can cause right shifts during infection, the **fever is the most prominently featured clinical finding** in this case and represents a measurable systemic change.
*Decrease in temperature*
- A **decrease in temperature** causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, **increasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen**.
- This would impair oxygen release to tissues, which is counterproductive during infection when tissues require increased oxygen delivery.
*Increase in CO2 production*
- While **increased CO2 production** does occur during infection due to increased tissue metabolism and does cause a **right shift** via the **Bohr effect** (CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3-, leading to decreased pH), this is not the primary factor being highlighted in this clinical presentation.
- The Bohr effect (acidosis from increased CO2 and metabolic acids) is an important physiological response, but the question emphasizes the **fever** as the key feature of this patient's condition.
- In the context of this question asking about "his condition," the **temperature elevation is the most direct and measurable systemic change** presented.
*Increase in pH*
- An **increase in pH** (alkalosis) causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, **increasing hemoglobin's oxygen affinity**.
- This would hinder oxygen delivery to tissues, which is not beneficial during infection when tissue oxygen demand is elevated.
*Decrease in 2,3-DPG*
- A **decrease in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG)** causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
- This increases hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, making oxygen release to tissues more difficult.
- During infection, 2,3-DPG levels typically remain stable or may increase slightly, not decrease.
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG Question 10: A male infant is born at 27 weeks following premature rupture of membranes and a precipitous labor to a G4P3 female. Given the speed of delivery steroids are not given. Shortly after delivery he develops respiratory distress and the decision is made to administer surfactant replacement therapy. While the components of the surfactant used in surfactant therapy may vary based on institution, what is the main component of pulmonary surfactant produced by type II pneumocytes?
- A. Cholesterol
- B. Protein S
- C. Surfactant-associated proteins
- D. Phospholipids (Correct Answer)
- E. Zinc finger protein
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient Explanation: ***Phospholipids***
- The main component of **pulmonary surfactant** produced by **type II pneumocytes** is **dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC)**, a type of **phospholipid**.
- These **phospholipids** reduce **alveolar surface tension**, preventing alveolar collapse at the end of expiration.
*Cholesterol*
- While **cholesterol** is present in biological membranes, it is a minor component of pulmonary surfactant and does not primarily determine its function.
- Its role is mainly in regulating the fluidity of the **surfactant film**, rather than reducing surface tension.
*Protein S*
- **Protein S** is a **vitamin K-dependent plasma protein** that functions as a **natural anticoagulant**; it is not a component of pulmonary surfactant.
- Its deficiency is associated with **thrombotic disorders**.
*Surfactant-associated proteins*
- **Surfactant-associated proteins (SPs)**, such as SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, and SP-D, are crucial for the **function and regulation** of pulmonary surfactant.
- However, they constitute a much smaller proportion by mass compared to **phospholipids**, which are the main structural and functional components.
*Zinc finger protein*
- **Zinc finger proteins** are a diverse class of proteins that bind to DNA, RNA, or other proteins and are involved in various cellular processes, including **gene regulation**.
- They are not a structural or functional component of **pulmonary surfactant**.
More Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.