2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for 2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 1: A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 26 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding and epistaxis for the past 2 days. She missed her last prenatal visit 2 weeks ago. Physical examination shows blood in the posterior pharynx and a uterus consistent in size with 23 weeks' gestation. Her hemoglobin concentration is 7.2 g/dL. Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine pregnancy with a small retroplacental hematoma and absent fetal cardiac activity. Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Decreased fibrinogen concentration (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased antithrombin concentration
- C. Increased factor V concentration
- D. Increased platelet count
- E. Decreased prothrombin time
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Decreased fibrinogen concentration***
- The patient's presentation with **vaginal bleeding**, **epistaxis**, a **small retroplacental hematoma**, and **absent fetal cardiac activity** strongly suggests **abruptio placentae** complicated by **disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)**.
- In DIC, widespread activation of the **coagulation cascade** leads to consumption of clotting factors, including **fibrinogen**, resulting in **decreased plasma levels**.
*Increased antithrombin concentration*
- **Antithrombin** is a natural anticoagulant that inhibits activated clotting factors; its concentration is typically **decreased** in DIC due to its consumption in an attempt to control widespread coagulation.
- An increase in antithrombin would generally **reduce** clot formation, which is contrary to the hypercoagulable state seen initially in DIC.
*Increased factor V concentration*
- **Factor V** is a procoagulant factor that is **consumed** during DIC, leading to **decreased** rather than increased concentrations.
- Increased factor V would promote clotting, which is overridden by the massive consumption of factors and platelets in DIC.
*Increased platelet count*
- **Platelets** are actively consumed in the widespread microthrombi formation characteristic of DIC, leading to **thrombocytopenia** (decreased platelet count), not an increase.
- An increased platelet count would be protective against bleeding, which is not the case here.
*Decreased prothrombin time*
- **Prothrombin time (PT)** measures the extrinsic and common coagulation pathways; in DIC, the consumption of coagulation factors, including **prothrombin**, leads to a **prolonged (increased)** PT, not a decreased one.
- A decreased PT would indicate a hypercoagulable state with enhanced clotting factor activity, which is eventually exhausted in DIC.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 2: A 2-day-old boy is examined on day of discharge from the newborn nursery. He was born at 39 weeks by vaginal delivery to a primigravid mother. The pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated, and the baby has been stooling, urinating, and feeding normally. Both the patient’s mother and father have no known past medical history and are found to have normal hemoglobin electrophoresis results. Compared to adult hemoglobin, the infant’s predominant hemoglobin is most likely to exhibit which of the following properties?
- A. Decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (Correct Answer)
- B. More likely to form hexagonal crystals
- C. More likely to cause red blood cell sickling
- D. Lower affinity for binding oxygen
- E. Increased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate***
- The baby's predominant hemoglobin is **hemoglobin F (HbF)**, which has a **gamma globin subunit** instead of the beta globin subunit found in adult hemoglobin (HbA).
- The gamma subunit of HbF results in a **reduced binding affinity to 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG)**, which in turn leads to a **higher affinity for oxygen** and more efficient oxygen transfer from the mother to the fetus.
*More likely to form hexagonal crystals*
- The formation of **hexagonal crystals** is characteristic of **hemoglobin C (HbC)** disease, a variant of adult hemoglobin, which is not predominant in a newborn.
- The parents have normal hemoglobin electrophoresis, ruling out the inheritance of significant hemoglobinopathies like HbC in a homozygous or compound heterozygous state.
*More likely to cause red blood cell sickling*
- **Red blood cell sickling** is a hallmark of **sickle cell anemia**, caused by hemoglobin S (HbS) which is an abnormal adult hemoglobin, not fetal hemoglobin.
- The parents have normal hemoglobin electrophoresis, meaning they are unlikely to carry the sickle cell trait, and the newborn's predominant HbF actually protects against sickling.
*Lower affinity for binding oxygen*
- HbF in newborns has a **higher affinity for oxygen** than adult hemoglobin (HbA) to facilitate efficient oxygen extraction from maternal blood across the placenta.
- A lower affinity for oxygen would be detrimental for a newborn as it would impair proper tissue oxygenation.
*Increased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate*
- HbF has a **decreased affinity for 2,3-BPG**. An increased affinity for 2,3-BPG would lead to a reduction in oxygen binding affinity, which is the opposite of the physiological need in a newborn.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 3: A 19-year-old male college student is brought to the emergency department by his girlfriend complaining of intense pain. They had been playing outside in the snow when the patient started to have severe hand and feet pain. He says the pain is 9 out of 10 and causing him to have trouble moving his fingers and toes. He also reports some difficulty “catching his breath.” He notes that he has been tiring easily for the past month but thought it was because he was studying and going out late. On physical examination, the patient appears uncomfortable. Bilateral conjunctivae are pale. His hands are swollen and tender to palpation. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. Hemoglobin is 9.0 g/dL. An electrocardiogram shows mild sinus tachycardia. Hemoglobin electrophoresis is performed, which confirms sickle cell disease. The patient’s pain is managed, and he is discharged on hydroxyurea. Which of the following is the most likely to occur as a result of the new medication?
- A. Increase in hemoglobin with higher oxygen affinity
- B. Decrease in hemoglobin with higher oxygen affinity
- C. Increase in hemoglobin A
- D. Decrease in hemoglobin A
- E. Increase in fetal hemoglobin (Correct Answer)
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Increase in fetal hemoglobin***
- **Hydroxyurea** stimulates the production of **fetal hemoglobin (HbF)**, which reduces the polymerization of **hemoglobin S (HbS)** and sickling of red blood cells.
- Increased HbF improves red blood cell survival and reduces the frequency of **vaso-occlusive crises** and other complications in **sickle cell disease**.
*Increase in hemoglobin with higher oxygen affinity*
- This option is too vague and does not describe the specific mechanism of hydroxyurea.
- While **HbF** does have higher oxygen affinity than **HbA**, the therapeutic benefit comes specifically from **increasing HbF**, not from a general increase in hemoglobin with higher oxygen affinity.
- The key mechanism is **HbF preventing sickling**, not simply having higher oxygen affinity.
*Decrease in hemoglobin with higher oxygen affinity*
- Hydroxyurea aims to *increase* functional hemoglobin and reduce anemia, not decrease it.
- A *decrease* in total hemoglobin would be detrimental and is not a therapeutic effect of hydroxyurea.
*Increase in hemoglobin A*
- Patients with **sickle cell disease** produce little to no **hemoglobin A (HbA)**, as their beta-globin genes produce **hemoglobin S (HbS)**.
- Hydroxyurea does not induce the production of **HbA**; its mechanism of action is through the upregulation of **HbF**.
*Decrease in hemoglobin A*
- Since patients with **sickle cell disease** already have an absence or very low levels of **hemoglobin A (HbA)**, a further decrease is not a relevant therapeutic effect.
- Hydroxyurea's action is to increase **fetal hemoglobin (HbF)**, which acts as a protective factor against sickling.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 4: A healthy 20-year-old male college student attempts to climb Mount Everest and travels to the Tibetan plateau by plane. Upon landing, he feels increasingly dizzy and fatigued. He notices that he is breathing faster than usual. What is the initial stimulus for the most likely acid-base disorder?
- A. Decreased partial pressure of alveolar oxygen (Correct Answer)
- B. Undiagnosed atrial septal defect
- C. Increasing arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide
- D. Worsened diffusion limitation of oxygen
- E. Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Decreased partial pressure of alveolar oxygen***
- Upon rapid ascent to high altitude (like the Tibetan plateau), the ambient atmospheric pressure decreases, leading to a significant drop in the **partial pressure of inspired oxygen (PiO2)**.
- This reduction in PiO2 directly causes a decrease in the **partial pressure of alveolar oxygen (PAO2)**, which is the primary stimulus for activation of peripheral chemoreceptors, leading to hyperventilation and a respiratory alkalosis.
*Undiagnosed atrial septal defect*
- An atrial septal defect (ASD) would cause a **left-to-right shunt** in a healthy young adult, not typically presenting with acute dizziness and fatigue immediately upon high-altitude exposure.
- While an ASD can lead to cyanosis and dyspnea with exertion, it would not be the initial stimulus for the observed hyperventilation response to high altitude.
*Increasing arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide*
- An increasing **arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2)** would stimulate central chemoreceptors and increase ventilation, but it is not the initial trigger in this scenario.
- In response to **hypoxia** at high altitude, the body *hyperventilates*, which would lead to a *decrease* in PaCO2, not an increase.
*Worsened diffusion limitation of oxygen*
- **Diffusion limitation** of oxygen refers to impaired gas exchange across the alveolar-capillary membrane, usually due to conditions like fibrosis or edema.
- While gas exchange can be affected at extreme altitudes, it is not the primary initial physiological trigger for the body's acute response (hyperventilation) in a healthy individual.
*Hypoxic pulmonary vasodilation*
- **Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction** (not vasodilation) is a physiological response in the lungs where pulmonary arterioles constrict in areas of low oxygen, redirecting blood flow to better-ventilated areas.
- This mechanism aims to optimize V/Q matching and is a *response* to hypoxia, not the initial stimulus for the systemic acid-base derangement leading to symptoms like dizziness and increased breathing rate.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 5: An investigator is studying the relationship between fetal blood oxygen saturation and intrauterine growth restriction using MRI studies. The magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time (T2) is inversely related to the concentration of deoxyhemoglobin so that high concentrations of deoxyhemoglobin produce a low signal intensity on T2-weighted MRI. In a normal fetus, the T2 signal is most likely to be the highest in which of the following vessels?
- A. Descending aorta
- B. Superior vena cava
- C. Ductus venosus (Correct Answer)
- D. Pulmonary veins
- E. Right atrium
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Ductus venosus***
- The **ductus venosus** shunts highly oxygenated blood directly from the **umbilical vein** to the inferior vena cava, bypassing the liver.
- This vessel carries the most oxygen-rich blood in the fetal circulation (lowest deoxyhemoglobin concentration), resulting in the **highest T2 signal intensity**.
*Descending aorta*
- The descending aorta receives a mixture of oxygenated blood from the left ventricle and deoxygenated blood from the **pulmonary artery** via the **ductus arteriosus**.
- This mixing reduces its overall oxygen saturation compared to the umbilical vein and ductus venosus.
*Superior vena cava*
- The superior vena cava carries **deoxygenated blood** from the upper body and head back to the right atrium.
- This vessel has a low oxygen saturation and high deoxyhemoglobin concentration, leading to a **low T2 signal**.
*Pulmonary veins*
- In a normal fetal circulation, the **lungs are not fully functional**, and pulmonary blood flow is relatively low.
- The pulmonary veins carry only a small amount of moderately oxygenated blood returning from the developing lungs, which is significantly less oxygenated than blood in the ductus venosus.
*Right atrium*
- The right atrium receives **mixed blood** from both the superior and inferior vena cava.
- While it receives some oxygenated blood from the inferior vena cava via the ductus venosus, this is diluted by deoxygenated blood, resulting in lower oxygen saturation than the blood within the ductus venosus itself.
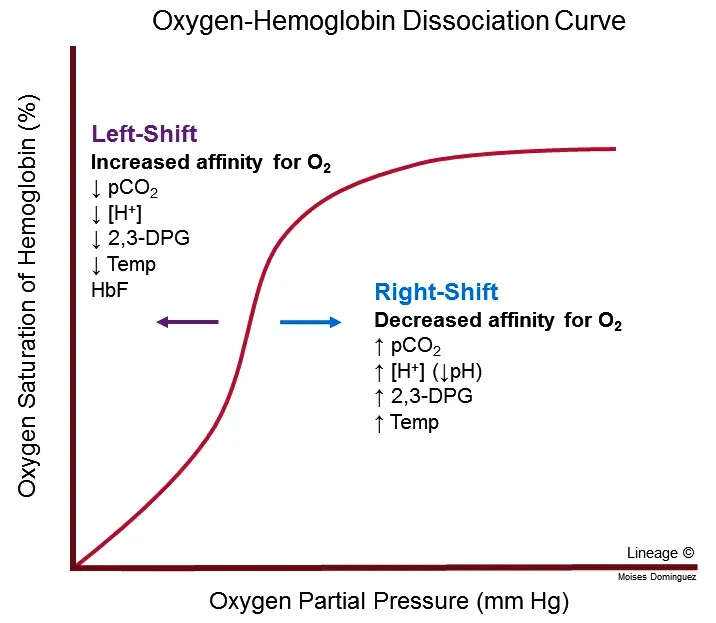
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is conducting a study on hematological factors that affect the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. An illustration of two graphs (A and B) that represent the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen is shown. Which of the following best explains a shift from A to B?
- A. Decreased serum pCO2
- B. Increased serum pH
- C. Decreased serum 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate concentration
- D. Increased body temperature (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased hemoglobin γ-chain synthesis
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Increased body temperature***
- A shift from A to B represents a **rightward shift** of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, indicating **decreased hemoglobin affinity for oxygen**.
- **Increased body temperature** (e.g., during exercise, fever) reduces hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, facilitating **oxygen release to tissues**.
*Decreased serum pCO2*
- A **decrease in serum pCO2** leads to an **increase in pH** (alkalosis) and a **leftward shift** of the curve, meaning an increased affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
- This is part of the **Bohr effect**, where lower CO2 levels signal decreased tissue metabolic activity, thus reducing oxygen unloading.
*Increased serum pH*
- An **increase in serum pH** (alkalosis) causes a **leftward shift** of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, signifying **increased hemoglobin affinity for oxygen**.
- This response is beneficial in the lungs, where higher pH promotes oxygen binding to hemoglobin.
*Decreased serum 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate concentration*
- A **decrease in 2,3-BPG** concentration leads to a **leftward shift** of the curve, representing **increased hemoglobin affinity for oxygen**.
- 2,3-BPG typically binds to deoxyhemoglobin, stabilizing its T-state and promoting oxygen release; thus, less 2,3-BPG means less release.
*Increased hemoglobin γ-chain synthesis*
- Increased **hemoglobin γ-chain synthesis** is characteristic of **fetal hemoglobin (HbF)**, which has a **higher affinity for oxygen** than adult hemoglobin (HbA).
- This would result in a **leftward shift** of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, enhancing oxygen uptake by the fetus.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 7: A 34-year-old woman comes to a physician for a routine health maintenance examination. She moved to Denver 1 week ago after having lived in New York City all her life. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Which of the following sets of changes is most likely on analysis of a blood sample obtained now compared to prior to her move?
Erythropoietin level | O2 saturation | Plasma volume
- A. ↑ unchanged unchanged
- B. ↑ ↓ ↓ (Correct Answer)
- C. Unchanged ↓ unchanged
- D. ↓ unchanged ↑
- E. Unchanged unchanged ↓
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***↑ ↓ ↓***
- Moving to a high altitude like Denver (from sea level NYC) leads to **hypoxia**, which triggers increased **erythropoietin (EPO)** production to stimulate red blood cell formation.
- The immediate physiological response to high altitude is a **decrease in arterial PO2** and thus **oxygen saturation**, along with a **reduction in plasma volume** due to increased diuresis and fluid shifts.
*↑ unchanged unchanged*
- While **erythropoietin** would increase due to hypoxia at higher altitudes, **oxygen saturation** would decrease, not remain unchanged.
- **Plasma volume** also tends to decrease acutely at high altitudes, rather than staying unchanged.
*Unchanged ↓ unchanged*
- **Erythropoietin** would be expected to increase, not remain unchanged, as a compensatory mechanism to hypoxia.
- While **oxygen saturation** would decrease, **plasma volume** typically decreases acutely, not remaining unchanged.
*↓ unchanged ↑*
- **Erythropoietin** would increase, not decrease, in response to the lower atmospheric oxygen.
- Both **oxygen saturation** and **plasma volume** would decrease, not remain unchanged or increase, respectively.
*Unchanged unchanged ↓*
- **Erythropoietin** would increase, not remain unchanged, to stimulate red blood cell production in response to hypoxia.
- **Oxygen saturation** would decrease, not remain unchanged, at higher altitudes.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old man presents to the surgical clinic with swelling of his right leg, fever, and chills for 2 days. The maximum recorded temperature was 38.3°C (101.0°F) at home. His right leg is red and swollen from the dorsum of the foot to the thigh with an ill-defined edge. Venous stasis ulcers are present in both of his limbs, but those on the right have a yellow discharge. His vitals include the following: blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg, heart rate is 94/min, temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F), and respiratory rate is 16/min. On physical examination, there is tenderness and warmth compared with his normal leg. Dorsalis pedis pulses are present on both of the ankles. What is the most likely cause of the right shift of the hemoglobin dissociation curve for his condition?
- A. Decrease in temperature
- B. Increase in CO2 production
- C. Increase in pH
- D. Increase in temperature (Correct Answer)
- E. Decrease in 2,3-DPG
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Increase in temperature***
- The patient presents with **fever (38.3°C)**, which is explicitly mentioned multiple times in the clinical scenario and represents a **systemic response** to infection.
- **Increased temperature** directly causes a **right shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve by **decreasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen**.
- This facilitates oxygen release to metabolically active tissues, particularly important in areas of infection and inflammation.
- While multiple factors can cause right shifts during infection, the **fever is the most prominently featured clinical finding** in this case and represents a measurable systemic change.
*Decrease in temperature*
- A **decrease in temperature** causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, **increasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen**.
- This would impair oxygen release to tissues, which is counterproductive during infection when tissues require increased oxygen delivery.
*Increase in CO2 production*
- While **increased CO2 production** does occur during infection due to increased tissue metabolism and does cause a **right shift** via the **Bohr effect** (CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3-, leading to decreased pH), this is not the primary factor being highlighted in this clinical presentation.
- The Bohr effect (acidosis from increased CO2 and metabolic acids) is an important physiological response, but the question emphasizes the **fever** as the key feature of this patient's condition.
- In the context of this question asking about "his condition," the **temperature elevation is the most direct and measurable systemic change** presented.
*Increase in pH*
- An **increase in pH** (alkalosis) causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, **increasing hemoglobin's oxygen affinity**.
- This would hinder oxygen delivery to tissues, which is not beneficial during infection when tissue oxygen demand is elevated.
*Decrease in 2,3-DPG*
- A **decrease in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG)** causes a **left shift** in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
- This increases hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, making oxygen release to tissues more difficult.
- During infection, 2,3-DPG levels typically remain stable or may increase slightly, not decrease.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 9: A male infant is born at 27 weeks following premature rupture of membranes and a precipitous labor to a G4P3 female. Given the speed of delivery steroids are not given. Shortly after delivery he develops respiratory distress and the decision is made to administer surfactant replacement therapy. While the components of the surfactant used in surfactant therapy may vary based on institution, what is the main component of pulmonary surfactant produced by type II pneumocytes?
- A. Cholesterol
- B. Protein S
- C. Surfactant-associated proteins
- D. Phospholipids (Correct Answer)
- E. Zinc finger protein
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Phospholipids***
- The main component of **pulmonary surfactant** produced by **type II pneumocytes** is **dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC)**, a type of **phospholipid**.
- These **phospholipids** reduce **alveolar surface tension**, preventing alveolar collapse at the end of expiration.
*Cholesterol*
- While **cholesterol** is present in biological membranes, it is a minor component of pulmonary surfactant and does not primarily determine its function.
- Its role is mainly in regulating the fluidity of the **surfactant film**, rather than reducing surface tension.
*Protein S*
- **Protein S** is a **vitamin K-dependent plasma protein** that functions as a **natural anticoagulant**; it is not a component of pulmonary surfactant.
- Its deficiency is associated with **thrombotic disorders**.
*Surfactant-associated proteins*
- **Surfactant-associated proteins (SPs)**, such as SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, and SP-D, are crucial for the **function and regulation** of pulmonary surfactant.
- However, they constitute a much smaller proportion by mass compared to **phospholipids**, which are the main structural and functional components.
*Zinc finger protein*
- **Zinc finger proteins** are a diverse class of proteins that bind to DNA, RNA, or other proteins and are involved in various cellular processes, including **gene regulation**.
- They are not a structural or functional component of **pulmonary surfactant**.
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG Question 10: A 30-year-old woman presents to clinic for a routine checkup. She reports that she is in good health but that she felt short of breath on her hiking and skiing trip to Colorado the week prior. She explains that this was the first time she has gone that high into the mountains and was slightly concerned for the first few days because she felt chronically short of breath. She reports a history of childhood asthma, but this experience did not feel the same. She was on the verge of seeking medical attention, but it resolved three days later, and she has felt fine ever since. What other listed physiological change results in a physiologic alteration similar to that which occurred in this patient?
- A. Increase in partial pressure of water in air
- B. Increase in blood pH
- C. Increase in concentration of dissolved carbon dioxide in blood
- D. Increase in concentration of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate in blood (Correct Answer)
- E. Decreased body temperature
2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity Explanation: ***Increase in concentration of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate in blood***
- At high altitude, the body **increases 2,3-BPG production** as a key acclimatization mechanism over several days, which is why the patient's symptoms resolved after 3 days.
- Increased 2,3-BPG shifts the **oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to the right**, decreasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen and facilitating **oxygen unloading at tissues**.
- This is one of the primary chronic adaptations to high altitude hypoxia, along with increased erythropoietin production.
*Increase in partial pressure of water in air*
- An increase in the partial pressure of water vapor in the air would decrease the partial pressure of inspired oxygen (PiO2 = FiO2 × (Patm - PH2O)).
- This would worsen hypoxia rather than represent an adaptive response to altitude.
*Decreased body temperature*
- Decreased body temperature shifts the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to the **left**, increasing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen.
- This would **impair oxygen unloading** at tissues, which is the opposite effect of increased 2,3-BPG.
- This is not a physiological response to high altitude.
*Increase in blood pH*
- An increase in blood pH (respiratory alkalosis) does occur acutely at high altitude due to hyperventilation in response to hypoxia.
- However, this shifts the curve to the **left** (Bohr effect), increasing oxygen affinity, which is the **opposite effect** of increased 2,3-BPG.
- While this occurs as an immediate response, the body compensates through renal bicarbonate excretion and increased 2,3-BPG production to maintain tissue oxygen delivery.
*Increase in concentration of dissolved carbon dioxide in blood*
- At high altitude, hyperventilation leads to **decreased CO2** (hypocapnia), not increased CO2.
- Increased CO2 would cause acidosis and shift the curve to the right (decreasing oxygen affinity), but this does not occur at high altitude.
- The opposite physiological change (decreased CO2) actually occurs.
More 2,3-DPG effects on oxygen affinity US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.