Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Oxygen consumption and VO2 max. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 1: A scientist in Chicago is studying a new blood test to detect Ab to EBV with increased sensitivity and specificity. So far, her best attempt at creating such an exam reached 82% sensitivity and 88% specificity. She is hoping to increase these numbers by at least 2 percent for each value. After several years of work, she believes that she has actually managed to reach a sensitivity and specificity much greater than what she had originally hoped for. She travels to China to begin testing her newest blood test. She finds 2,000 patients who are willing to participate in her study. Of the 2,000 patients, 1,200 of them are known to be infected with EBV. The scientist tests these 1,200 patients' blood and finds that only 120 of them tested negative with her new exam. Of the patients who are known to be EBV-free, only 20 of them tested positive. Given these results, which of the following correlates with the exam's specificity?
- A. 82%
- B. 90%
- C. 84%
- D. 86%
- E. 98% (Correct Answer)
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***98%***
- **Specificity** measures the proportion of **true negatives** among all actual negatives.
- In this case, 800 patients are known to be EBV-free (actual negatives), and 20 of them tested positive (false positives). This means 800 - 20 = 780 tested negative (true negatives). Specificity = (780 / 800) * 100% = **98%**.
*82%*
- This value represents the *original sensitivity* before the scientist’s new attempts to improve the test.
- It does not reflect the *newly calculated specificity* based on the provided data.
*90%*
- This value represents the *newly calculated sensitivity* of the test, not the specificity.
- Out of 1200 EBV-infected patients, 120 tested negative (false negatives), meaning 1080 tested positive (true positives). Sensitivity = (1080 / 1200) * 100% = 90%.
*84%*
- This percentage is not directly derived from the information given for either sensitivity or specificity after the new test results.
- It does not correspond to any of the calculated values for the new test's performance.
*86%*
- This percentage is not directly derived from the information given for either sensitivity or specificity after the new test results.
- It does not correspond to any of the calculated values for the new test's performance.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 2: A 40-year-old female volunteers for an invasive study to measure her cardiac function. She has no previous cardiovascular history and takes no medications. With the test subject at rest, the following data is collected using blood tests, intravascular probes, and a closed rebreathing circuit:
Blood hemoglobin concentration 14 g/dL
Arterial oxygen content 0.22 mL O2/mL
Arterial oxygen saturation 98%
Venous oxygen content 0.17 mL O2/mL
Venous oxygen saturation 78%
Oxygen consumption 250 mL/min
The patient's pulse is 75/min, respiratory rate is 14/ min, and blood pressure is 125/70 mm Hg. What is the cardiac output of this volunteer?
- A. Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.
- B. Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.
- C. 250 mL/min
- D. 5.0 L/min (Correct Answer)
- E. 50 L/min
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***5.0 L/min***
- Cardiac output can be calculated using the **Fick principle**: Cardiac Output $(\text{CO}) = \frac{{\text{Oxygen Consumption}}}{{\text{Arterial } \text{O}_2 \text{ Content} - \text{Venous O}_2 \text{ Content}}}$.
- Given Oxygen Consumption = 250 mL/min, Arterial O$_2$ Content = 0.22 mL/mL, and Venous O$_2$ Content = 0.17 mL/mL. Thus, CO = $\frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{(0.22 - 0.17) \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = \frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{0.05 \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = 5000 \text{ mL/min } = 5.0 \text{ L/min}$.
*Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- **Body surface area (BSA)** is used to calculate **cardiac index**, which is cardiac output normalized to body size, but not cardiac output directly.
- While a normal cardiac output might be compared to a patient's BSA for context, it is not a necessary component for calculating the absolute cardiac output.
*Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- Cardiac output can be calculated as **Stroke Volume (SV) x Heart Rate (HR)**. However, stroke volume is not provided directly in this question.
- The Fick principle allows for the calculation of cardiac output **without explicit knowledge of stroke volume** or heart rate, using oxygen consumption and arteriovenous oxygen difference.
*250 mL/min*
- 250 mL/min represents the **oxygen consumption**, not the cardiac output.
- Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute, which is influenced by both oxygen consumption and the difference in oxygen content between arterial and venous blood.
*50 L/min*
- A cardiac output of 50 L/min is an **extremely high and physiologically impossible** value for a resting individual.
- This value is 10 times higher than the calculated cardiac output and typically represents a calculation error.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 3: Which of the following physiologic changes decreases pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR)?
- A. Inhaling the inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
- B. Exhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)
- C. Exhaling the expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
- D. Breath holding maneuver at functional residual capacity (FRC)
- E. Inhaling the entire vital capacity (VC) (Correct Answer)
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***Inhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)***
- As lung volume increases from FRC to TLC (which includes inhaling the entire VC), alveolar vessels are **stretched open**, and extra-alveolar vessels are **pulled open** by the increased radial traction, leading to a decrease in PVR.
- This **maximizes the cross-sectional area** of the pulmonary vascular bed, lowering resistance.
*Inhaling the inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)*
- While inhaling IRV increases lung volume, it's not the maximal inspiration of the entire VC where **PVR is typically at its lowest**.
- PVR continues to decrease as lung volume approaches total lung capacity (TLC).
*Exhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)*
- Exhaling the entire vital capacity leads to very low lung volumes, where PVR significantly **increases**.
- At low lung volumes, **alveolar vessels become compressed** and extra-alveolar vessels **narrow**, increasing resistance.
*Exhaling the expiratory reserve volume (ERV)*
- Exhaling the ERV results in a lung volume below FRC, which causes a **marked increase in PVR**.
- This is due to the **compression of alveolar vessels** and decreased radial traction on extra-alveolar vessels.
*Breath holding maneuver at functional residual capacity (FRC)*
- At FRC, the PVR is at an **intermediate level**, not its lowest.
- This is the point where the opposing forces affecting alveolar and extra-alveolar vessels are somewhat balanced, but not optimized for minimal resistance.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 4: During a clinical study evaluating the effects of exercise on muscle perfusion, 15 healthy individuals perform a 20-minute treadmill run at submaximal effort. Before and after the treadmill session, perfusion of the quadriceps muscle is evaluated with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. The study shows a significant increase in muscle blood flow per unit of tissue mass. Which of the following local changes is most likely involved in the observed change in perfusion?
- A. Increase in adenosine (Correct Answer)
- B. Decrease in potassium
- C. Increase in thromboxane A2
- D. Increase in endothelin
- E. Decrease in prostacyclin
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***Increase in adenosine***
- **Adenosine** is a potent **vasodilator** released by metabolically active tissues, particularly in response to increased oxygen demand and ATP hydrolysis during exercise.
- Its accumulation leads to relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, increasing blood flow to meet the muscles' elevated metabolic needs.
*Decrease in potassium*
- An increase in **extracellular potassium** (not a decrease) generally causes vasodilation in skeletal muscle by hyperpolarizing smooth muscle cells.
- A decrease in potassium outside the cell would not be expected to cause vasodilation and increased perfusion during exercise.
*Increase in thromboxane A2*
- **Thromboxane A2** is primarily a **vasoconstrictor** and platelet aggregator, mainly involved in hemostasis and inflammation.
- Increased levels would lead to reduced blood flow, not the observed increase in perfusion during exercise.
*Increase in endothelin*
- **Endothelin** is one of the most potent **vasoconstrictors** known, primarily released from endothelial cells.
- An increase in endothelin would severely constrict blood vessels and decrease muscle perfusion, counteracting the effects of exercise.
*Decrease in prostacyclin*
- **Prostacyclin (PGI2)** is a potent **vasodilator** and inhibitor of platelet aggregation.
- A decrease in prostacyclin would lead to vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow, which is contrary to the increased perfusion seen during exercise.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 5: Which factor most strongly influences coronary blood flow during exercise?
- A. Endothelin release
- B. Metabolic demand (Correct Answer)
- C. Myogenic response
- D. Neural regulation
- E. Baroreceptor reflex
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: **Metabolic demand**
- During exercise, increased **myocardial activity** leads to a higher demand for oxygen and nutrients, prompting a significant increase in coronary blood flow.
- Local release of **metabolites** such as adenosine, nitric oxide, and hydrogen ions causes powerful vasodilation of coronary arteries, closely matching blood supply to demand.
*Endothelin release*
- **Endothelin** is a potent vasoconstrictor and plays a role in regulating vascular tone, but its primary influence is not the immediate or strongest factor dictating increased coronary flow during exercise.
- While it can modulate flow, metabolic changes are the dominant driver for the rapid and substantial increases needed during exertion.
*Myogenic response*
- The **myogenic response** is an intrinsic property of vascular smooth muscle cells to contract when stretched (due to increased pressure) and relax when pressure decreases, helping to maintain relatively constant blood flow.
- This mechanism primarily contributes to **autoregulation** and flow stability, but it does not account for the massive increase in flow required by the heart during exercise.
*Neural regulation*
- **Neural regulation**, primarily sympathetic stimulation, increases heart rate and contractility, which indirectly increases metabolic demand.
- However, direct neural effects on coronary arteries can be complex (both vasodilation and vasoconstriction depending on receptor type), and the overriding control during exercise is typically metabolic.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 6: A 35-year-old woman volunteers for a study on respiratory physiology. Pressure probes A and B are placed as follows:
Probe A: between the parietal and visceral pleura
Probe B: within the cavity of an alveolus
The probes provide a pressure reading relative to atmospheric pressure. To obtain a baseline reading, she is asked to sit comfortably and breathe normally. Which of the following sets of values will most likely be seen at the end of inspiration?
- A. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- C. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg
- D. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- E. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg***
- At the **end of inspiration**, the **intrapleural pressure (Probe A)** is at its most negative, typically around -6 to -8 cm H2O (equivalent to -4 to -6 mmHg), reflecting the maximum expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- At the **end of inspiration**, just before exhalation begins, there is **no airflow**, so the **intrapulmonary pressure (Probe B)** equalizes with atmospheric pressure, resulting in a 0 mm Hg reading.
*Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of 0 mm Hg** would indicate a **pneumothorax** since it should always be negative to prevent lung collapse.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** would indicate that **inspiration is still ongoing**, as air would be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapulmonary pressure of 0 mm Hg** is correct at the end of inspiration, an **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is typical for the **end of expiration (Functional Residual Capacity)** during quiet breathing, not the end of inspiration.
- The **intrapleural pressure becomes more negative** during inspiration due to increased thoracic volume, so -4 mm Hg would be insufficient.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is the normal pressure at the **end of expiration**, not the end of inspiration, where it becomes more negative.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** indicates that **inspiration is still in progress**, not at its end, as air would still be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapleural pressure of -6 mm Hg** is consistent with the end of inspiration, an **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** means that **airflow is still occurring into the lungs**.
- At the **very end of inspiration**, just before the start of exhalation, airflow momentarily ceases, and intrapulmonary pressure becomes zero relative to the atmosphere.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old man is running on the treadmill at his gym. His blood pressure prior to beginning his workout was 110/72. Which of the following changes in his cardiovascular system may be seen in this man now that he is exercising?
- A. Decreased blood pressure
- B. Decreased systemic vascular resistance (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased systemic vascular resistance
- D. Decreased stroke volume
- E. Decreased heart rate
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***Decreased systemic vascular resistance***
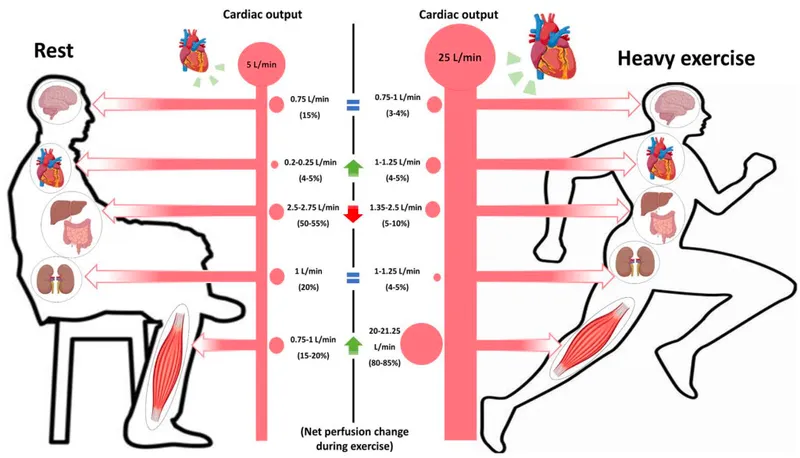
- During dynamic exercise, metabolic vasodilation in exercising muscles leads to a substantial **decrease in systemic vascular resistance (SVR)** to accommodate increased blood flow.
- This vasodilation overrides the systemic vasoconstriction driven by the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in a net decrease in overall SVR.
*Decreased blood pressure*
- While SVR decreases, **systolic blood pressure typically increases** during exercise due to increased cardiac output.
- **Diastolic blood pressure** usually remains stable or may slightly decrease, but overall blood pressure, specifically the mean arterial pressure, is generally maintained or elevated.
*Increased systemic vascular resistance*
- This is incorrect as **vasodilation in active muscles** causes a significant decrease in overall systemic vascular resistance.
- An increase in SVR would typically hinder blood flow to working muscles and is not a characteristic cardiovascular response to dynamic exercise.
*Decreased stroke volume*
- Stroke volume generally **increases significantly** during exercise due to enhanced venous return, increased contractility, and reduced afterload (from decreased SVR).
- A decreased stroke volume would limit cardiac output and exercise performance.
*Decreased heart rate*
- Heart rate **increases proportionally with exercise intensity** to boost cardiac output and oxygen delivery to active muscles.
- A decreased heart rate would counteract the body's physiological demand for increased blood flow during physical activity.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 8: A person is exercising strenuously on a treadmill for 1 hour. An arterial blood gas measurement is then taken. Which of the following are the most likely values?
- A. pH 7.56, PaO2 100, PCO2 44, HCO3 38
- B. pH 7.32, PaO2 42, PCO2 50, HCO3 27
- C. pH 7.57 PaO2 100, PCO2 23, HCO3 21 (Correct Answer)
- D. pH 7.38, PaO2 100, PCO2 69 HCO3 42
- E. pH 7.36, PaO2 100, PCO2 40, HCO3 23
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***pH 7.57, PaO2 100, PCO2 23, HCO3 21***
- After 1 hour of strenuous exercise, this represents **respiratory alkalosis with mild metabolic compensation**, which is the expected finding in a healthy individual during sustained vigorous exercise.
- The **low PCO2 (23 mmHg)** reflects appropriate **hyperventilation** in response to increased metabolic demands and lactic acid production. During intense exercise, minute ventilation increases dramatically, often exceeding the rate of CO2 production.
- The **slightly elevated pH (7.57)** and **mildly decreased HCO3 (21 mEq/L)** indicate that respiratory compensation has slightly overshot, creating mild alkalosis, while the bicarbonate is consumed both in buffering lactate and through renal compensation.
- **Normal PaO2 (100 mmHg)** confirms adequate oxygenation maintained by increased ventilation.
*pH 7.36, PaO2 100, PCO2 40, HCO3 23*
- These are **completely normal arterial blood gas values** with no evidence of any physiological stress or compensation.
- After 1 hour of strenuous exercise, we would expect **hyperventilation with decreased PCO2**, not a normal PCO2 of 40 mmHg. This profile would be consistent with rest, not vigorous exercise.
- The absence of any respiratory or metabolic changes makes this inconsistent with the clinical scenario.
*pH 7.56, PaO2 100, PCO2 44, HCO3 38*
- This profile suggests **metabolic alkalosis** (high pH, high HCO3) with inadequate respiratory compensation (normal to slightly elevated PCO2).
- This is **not consistent with strenuous exercise**, which produces metabolic acid (lactate), not metabolic base. The elevated HCO3 suggests vomiting, diuretic use, or other causes of metabolic alkalosis.
*pH 7.32, PaO2 42, PCO2 50, HCO3 27*
- This indicates **respiratory acidosis** (low pH, high PCO2) with **severe hypoxemia** (PaO2 42 mmHg).
- During strenuous exercise, healthy individuals **increase ventilation** to enhance O2 delivery and remove CO2, so both hypoxemia and hypercapnia are unexpected and would suggest severe cardiopulmonary disease or hypoventilation.
*pH 7.38, PaO2 100, PCO2 69, HCO3 42*
- This demonstrates **compensated respiratory acidosis** (normal pH, markedly elevated PCO2 and HCO3).
- The **very high PCO2 (69 mmHg)** indicates severe **hypoventilation**, which is the opposite of what occurs during exercise. This profile suggests chronic respiratory failure with metabolic compensation, such as in severe COPD.
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 9: A 32-year-old female with Crohn's disease diagnosed in her early 20s comes to your office for a follow-up appointment. She is complaining of headaches and fatigue. Which of the following arterial blood gas findings might you expect?
- A. High PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)
- B. Low PaO2, low O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2)
- C. Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)
- D. Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2) (Correct Answer)
- E. Low PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2)***
- Patients with **Crohn's disease** are prone to developing **iron deficiency anemia** due to chronic inflammation, malabsorption, and blood loss, leading to reduced hemoglobin levels.
- While PaO2 and SaO2 measure oxygen *tension* and *percentage saturation* of available hemoglobin, respectively, **O2 content (CaO2)** directly reflects the *total amount* of oxygen delivered to tissues, which is primarily dependent on hemoglobin concentration. Therefore, with anemia, CaO2 will be low despite normal PaO2 and SaO2 because there is less hemoglobin to carry oxygen.
*High PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)*
- High PaO2 would indicate **hyperoxygenation**, which is not an expected complication of Crohn's disease or its associated anemia.
- Normal O2 content is inconsistent with the presence of anemia, which significantly reduces the body's total oxygen-carrying capacity.
*Low PaO2, low O2 saturation (SaO2), low O2 content (CaO2)*
- Low PaO2 and SaO2 suggest a primary **respiratory problem** or severe hypoxemia, which is not directly linked to Crohn's disease or the typical presentation of iron deficiency anemia.
- While low O2 content is correct for anemia, the accompanying low PaO2 and SaO2 indicate a different underlying pathology for oxygen transport issues.
*Normal PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)*
- This finding would indicate **normal oxygenation** and oxygen-carrying capacity, which is contrary to the clinical scenario of a patient with Crohn's likely complicated by anemia.
- The patient's symptoms of headaches and fatigue are consistent with poor tissue oxygenation, which would not occur if all these parameters were normal.
*Low PaO2, normal O2 saturation (SaO2), normal O2 content (CaO2)*
- A low PaO2 with a normal SaO2 is physiologically unlikely unless there is a **left shift of the oxygen dissociation curve** with adequate hemoglobin, which doesn't fit the expected anemic state.
- Normal O2 content would rule out the presence of anemia as a cause for the symptoms, which is a common complication in Crohn's disease.
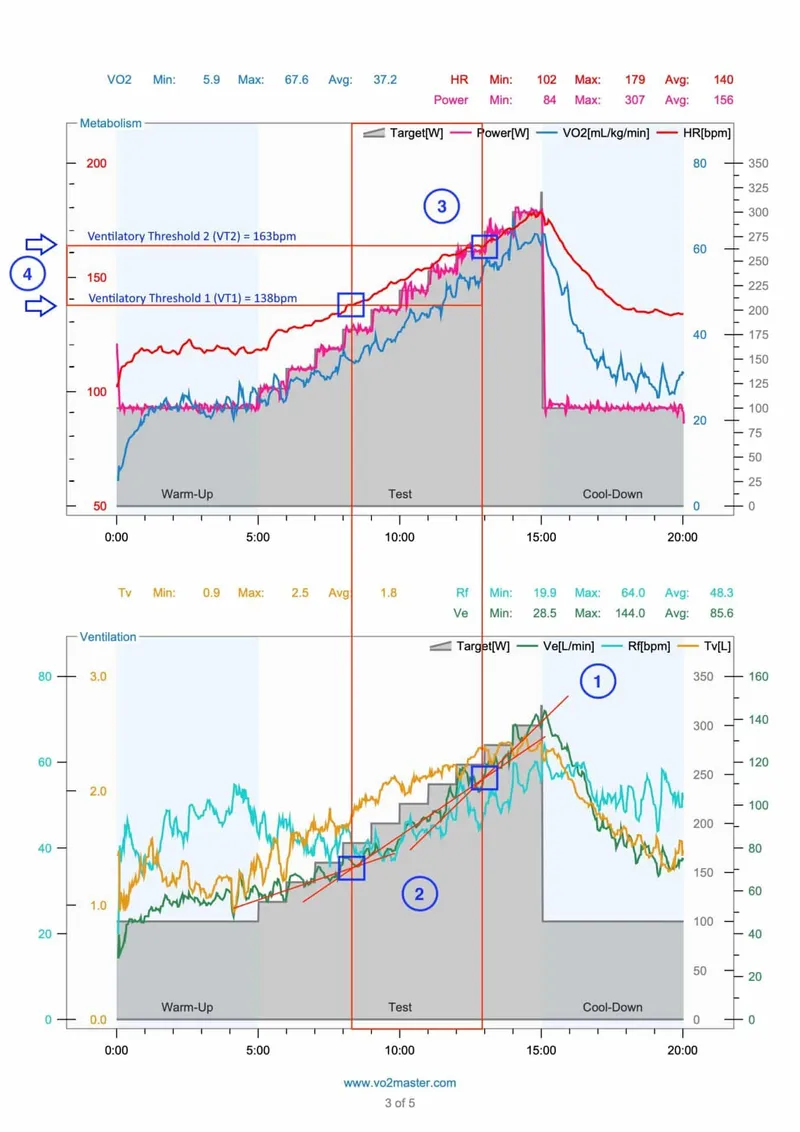
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG Question 10: A 42-year-old firefighter candidate undergoes VO2 max testing showing 32 mL/kg/min (below required 42 mL/kg/min). His body composition shows 28% body fat. He has normal cardiac function (ejection fraction 60%), hemoglobin 15.2 g/dL, and no respiratory disease. Lactate threshold occurs at 65% of VO2 max. Evaluate the most effective evidence-based training strategy to meet occupational requirements within 12 weeks.
- A. Resistance training focusing on muscular strength to improve work efficiency
- B. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) at 90-95% VO2 max with active recovery
- C. Threshold training at lactate threshold intensity for extended durations
- D. Continuous moderate-intensity training at 60-70% VO2 max for 60 minutes daily
- E. Combined approach: HIIT twice weekly plus threshold training three times weekly (Correct Answer)
Oxygen consumption and VO2 max Explanation: ***Combined approach: HIIT twice weekly plus threshold training three times weekly***
- A combined protocol is superior for maximizing **VO2 max** and improving the **lactate threshold** simultaneously within a short 12-week window.
- **High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)** effectively increases **stroke volume** and maximal cardiac output, while **threshold training** enhances peripheral adaptations like **mitochondrial density**.
*Resistance training focusing on muscular strength to improve work efficiency*
- While strength is important for firefighting, it does not significantly elevate **VO2 max** or the **aerobic capacity** needed to meet the 42 mL/kg/min requirement.
- This strategy primarily improves **neuromuscular recruitment** and absolute power rather than the **oxygen transport system**.
*High-intensity interval training (HIIT) at 90-95% VO2 max with active recovery*
- Although HIIT is a potent stimulus for cardiovascular gains, relying solely on HIIT may lead to **overtraining** or injury if performed at the frequency needed to meet the target.
- It lacks the high-volume metabolic stress provided by **threshold training** that is necessary to shift the **anaerobic threshold** optimally.
*Threshold training at lactate threshold intensity for extended durations*
- Threshold training alone improves **metabolic efficiency** but is less effective than HIIT at increasing the **central cardiovascular limits** like maximal stroke volume.
- This approach might improve endurance at current levels but often results in a plateau in **maximal aerobic power (VO2 max)**.
*Continuous moderate-intensity training at 60-70% VO2 max for 60 minutes daily*
- Moderate-intensity training is insufficient to stimulate the significant **10 mL/kg/min increase** required for this candidate within 12 weeks.
- This intensity primarily improves **lipid oxidation** and base endurance rather than the maximal **oxygen consumption** required for occupational clearance.
More Oxygen consumption and VO2 max US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.