Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Thyroid hormone synthesis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 1: A patient with Graves' disease is treated with thiocyanate (a historical antithyroid agent). Thiocyanate helps reduce thyroid hormone production by:
- A. Inhibiting thyroid peroxidase
- B. Inhibiting 5'-deiodinase
- C. Inhibiting iodide follicular uptake (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibiting beta-adrenergic receptors
- E. Inhibiting thyroid deiodinase
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Inhibiting iodide follicular uptake***
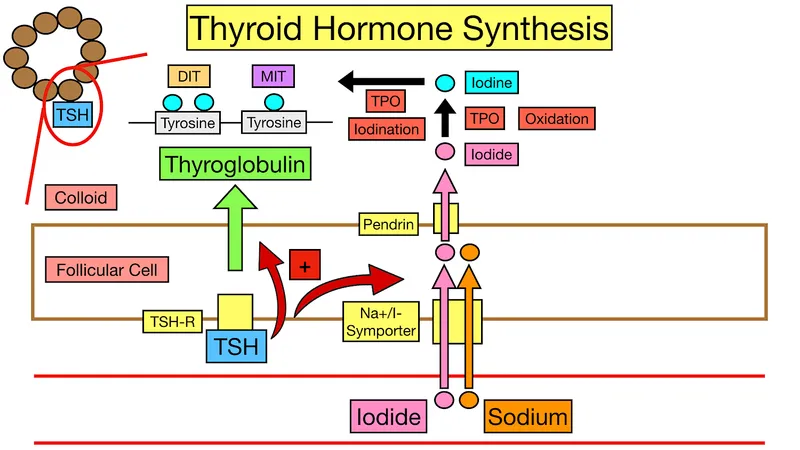
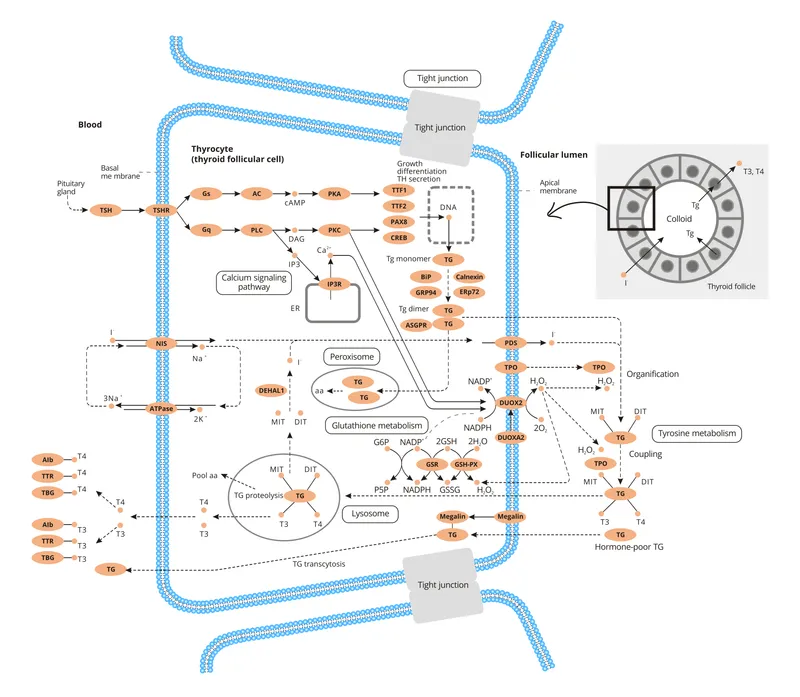
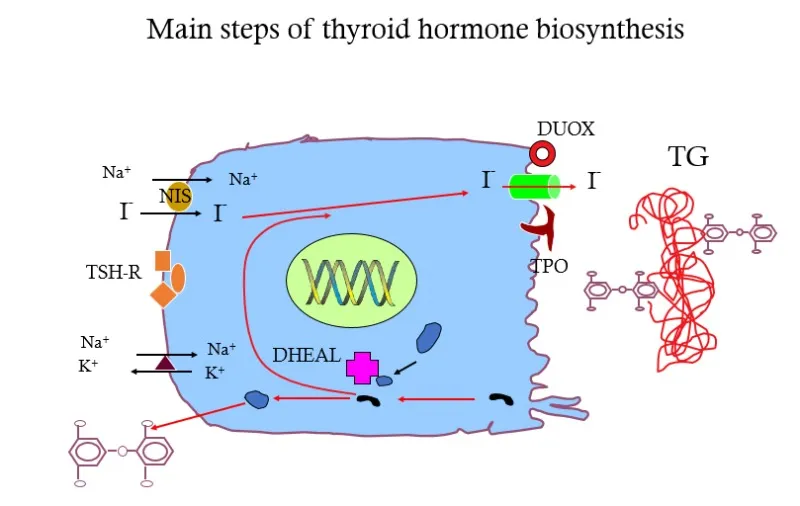
- Thiocyanate is a competitive inhibitor of the **sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)** on thyroid follicular cells, blocking the uptake of iodide into the thyroid gland.
- By preventing iodide entry, thiocyanate reduces the raw material needed for thyroid hormone synthesis, thereby mitigating the **hyperthyroidism** seen in Graves' disease.
*Inhibiting thyroid peroxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **thionamide drugs** (e.g., methimazole, propylthiouracil), which block the oxidation of iodide and its organification.
- While effective in Graves' disease, thiocyanate does not directly inhibit thyroid peroxidase activity.
*Inhibiting 5'-deiodinase*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)**, but not thiocyanate, inhibits the peripheral conversion of T4 to the more active T3 by blocking 5'-deiodinase enzymes.
- This action helps to reduce the overall effect of thyroid hormones in the body.
*Inhibiting beta-adrenergic receptors*
- **Beta-blockers** (e.g., propranolol) are used to manage the symptomatic effects of hyperthyroidism, such as palpitations, tremor, and anxiety.
- They do not affect thyroid hormone synthesis or release, but rather block the peripheral actions of thyroid hormones on adrenergic receptors.
*Inhibiting thyroid deiodinase*
- This option refers to the enzymes responsible for removing iodine from thyroid hormones, which is part of the normal catabolism of these hormones or for converting T4 to T3.
- Thiocyanate does not primarily act by inhibiting these deiodinase enzymes within the thyroid gland or peripherally; its main action is on iodide uptake.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 2: A 49-year-old woman presents to the office because of tremors for 2 months. She says that her hands have been shaking a lot, especially when she feels stressed. In addition, she has been sweating more than usual and has lost 8 kg (17.6 lb) in the last 2 months. She has a past medical history of vitiligo. Her vital signs are a heart rate of 98/min, a respiratory rate of 14/min, a temperature of 37.6°C (99.7°F), and a blood pressure of 115/75 mm Hg. Physical examination shows a fine, bilateral hand tremor and a diffuse goiter. Which of the following hormonal imbalances is most likely present?
- A. Low TSH, high free T4, and high free T3 (Correct Answer)
- B. High TSH, high free T4, and high free T3
- C. High TSH, normal free T4, and normal free T3
- D. Low TSH, normal free T4, and normal free T3
- E. High TSH, low free T4, and low free T3
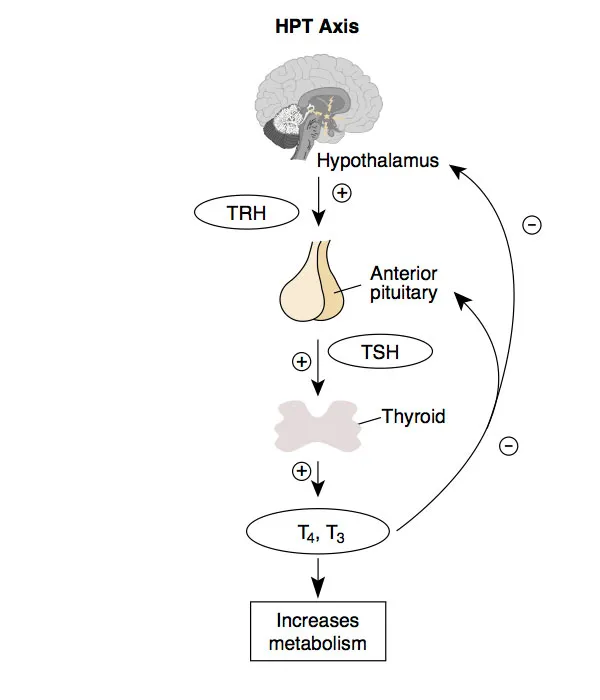
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Low TSH, high free T4, and high free T3***
- The patient's symptoms (tremors, sweating, weight loss, tachycardia, goiter) are classic for **hyperthyroidism**, which is typically characterized by **low TSH** due to negative feedback and **elevated free T4 and T3** levels.
- Her history of **vitiligo**, an autoimmune condition, further supports an autoimmune thyroid disorder like **Graves' disease**, a common cause of hyperthyroidism.
*High TSH, high free T4, and high free T3*
- This pattern would indicate **secondary hyperthyroidism**, caused by a TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma.
- While TSH would be high, it is a much rarer cause of hyperthyroidism compared to primary causes.
*High TSH, normal free T4, and normal free T3*
- This hormonal profile is characteristic of **subclinical hypothyroidism** or a **compensated primary hypothyroidism** early in its course.
- The patient's symptoms are inconsistent with hypothyroidism.
*Low TSH, normal free T4, and normal free T3*
- This suggests **subclinical hyperthyroidism**, where TSH is suppressed but thyroid hormone levels are still within the normal range.
- The patient's prominent and severe symptoms (tremors, significant weight loss, goiter) indicate overt hyperthyroidism, not subclinical disease.
*High TSH, low free T4, and low free T3*
- This is the classic hormonal profile for **primary hypothyroidism**, where the thyroid gland is failing to produce sufficient hormones, leading to elevated TSH.
- The patient's symptoms of nervousness, weight loss, and tremors are directly opposite to those seen in hypothyroidism.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 3: A 31-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with a 2-week history of diarrhea. She says that she has also noticed that she is losing weight, which makes her feel anxious since she has relatives who have suffered from anorexia. Finally, she says that she is worried she has a fever because she feels warm and has been sweating profusely. On physical examination she is found to have proptosis, fine tremor of her hands, and symmetrical, non-tender thyroid enlargement. Which of the following types of enzymes is targeted by a treatment for this disease?
- A. Peroxidase (Correct Answer)
- B. Kinase
- C. Catalase
- D. Cyclooxygenase
- E. Phosphatase
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Peroxidase***
- The patient's symptoms (diarrhea, weight loss, anxiety, sweating, proptosis, fine tremor, and symmetrical thyroid enlargement) are classic for **Graves' disease**, a form of **hyperthyroidism**.
- **Thionamides** (e.g., propylthiouracil, methimazole) are a primary treatment for Graves' disease, and they work by inhibiting **thyroid peroxidase (TPO)**, an enzyme crucial for thyroid hormone synthesis.
*Kinase*
- **Kinases** are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups, often involved in signaling pathways. While kinases are important drug targets, they are not directly involved in the primary treatment mechanism for Graves' disease.
- Examples of kinase inhibitors include those used in cancer therapy, but not for hyperthyroidism's specific pathophysiology.
*Catalase*
- **Catalase** is an enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- It has no direct role in the synthesis of thyroid hormones or as a target for hyperthyroidism treatment.
*Cyclooxygenase*
- **Cyclooxygenase (COX)** enzymes are involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes, key mediators of inflammation and pain.
- COX inhibitors (like NSAIDs) are used for pain and inflammation, not for managing the hyperactive thyroid gland in Graves' disease.
*Phosphatase*
- **Phosphatases** are enzymes that remove phosphate groups from molecules. They play a role in various cellular processes but are not the primary target for drugs treating Graves' disease.
- While important in metabolic regulation, they are not directly inhibited by thionamide drugs used in hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 4: A 41-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of anxiety, difficulty falling asleep, heat intolerance, and a 6-kg (13.2-lb) weight loss. The patient's nephew, who is studying medicine, mentioned that her symptoms might be caused by a condition that is due to somatic activating mutations of the genes for the TSH receptor. Examination shows warm, moist skin and a 2-cm, nontender, subcutaneous mass on the anterior neck. Which of the following additional findings should most raise concern for a different underlying etiology of her symptoms?
- A. Atrial fibrillation
- B. Hyperreflexia
- C. Nonpitting edema (Correct Answer)
- D. Fine tremor
- E. Lid lag
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Nonpitting edema***
- Nonpitting edema, often referred to as **myxedema**, is a classic sign of **hypothyroidism**, not hyperthyroidism.
- The patient's symptoms (anxiety, insomnia, heat intolerance, weight loss) are indicative of **hyperthyroidism**, making myxedema an inconsistent finding that suggests a different underlying etiology.
*Atrial fibrillation*
- **Atrial fibrillation** is a common cardiovascular manifestation of **hyperthyroidism** due to the direct effects of thyroid hormones on the heart.
- Its presence would support, rather than contradict, the suspected diagnosis of hyperthyroidism.
*Hyperreflexia*
- **Hyperreflexia** is a neurological finding often associated with the hypermetabolic state of **hyperthyroidism**.
- Increased thyroid hormone levels can enhance neural excitability, making hyperreflexia an expected finding.
*Fine tremor*
- A **fine tremor** is a common and characteristic symptom of **hyperthyroidism**, resulting from increased adrenergic activity.
- This finding would be consistent with the patient's other symptoms of thyroid overactivity.
*Lid lag*
- **Lid lag** is an ocular sign of **hyperthyroidism**, caused by sympathetic overstimulation of the Müller's muscle in the eyelid.
- While not indicative of Graves' ophthalmopathy, it is a common finding in thyrotoxicosis and would be consistent with the patient's clinical picture.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old woman presents to her doctor complaining of pain in her neck that radiates to her left ear. The pain has been more or less constant for the last 3 weeks and increases when she chews and swallows. She was in her normal state of health before the pain started. She also mentions that she has been experiencing palpitations, muscle weakness, and increased sweating for the last 2 weeks. Past medical history is significant for a flu-like illness 2 months ago. She currently takes no medication and neither consumes alcohol nor smokes cigarettes. Her pulse is 104/min and irregular with a blood pressure of 140/80 mm Hg. On examination, the physician notices that the patient is restless. There is a presence of fine tremors in both hands. The anterior neck is swollen, warm to the touch, and markedly tender on palpation. Thyroid function tests and a biopsy are ordered. Which of the following deviations from the normal is expected to be seen in her thyroid function tests?
- A. Normal Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, Normal Free T4, Normal I131 Uptake
- B. ↓ Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, ↑ Free T4, ↑ I131 Uptake
- C. Normal Serum TSH, ↓ Total T4, Normal Free T4, Normal I131 Uptake
- D. ↑ Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, ↑ Free T4, ↑ I 131 Uptake
- E. ↓ Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, ↑ Free T4, ↓ I131 Uptake (Correct Answer)
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***↓ Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, ↑ Free T4, ↓ I131 Uptake***
- This pattern is characteristic of **thyrotoxicosis** (increased thyroid hormone levels) combined with decreased thyroid gland activity, which is typical for conditions like **subacute thyroiditis** (as suggested by the flu-like illness and painful, tender thyroid).
- The elevated **T3/T4** (Total and Free) results from the release of preformed hormones from the inflamed thyroid, while the **low TSH** is due to negative feedback. The **decreased I-131 uptake** indicates that the thyroid gland is not actively synthesizing new hormones.
*Normal Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, Normal Free T4, Normal I131 Uptake*
- This combination is inconsistent with the patient's symptoms of hyperthyroidism (palpitations, sweating, tremors) and a **tender, swollen thyroid**.
- **Normal Free T4** and **Normal TSH** would suggest euthyroid status, which is not what the clinical presentation indicates.
*↓ Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, ↑ Free T4, ↑ I131 Uptake*
- This pattern suggests a hyperthyroid state where the thyroid gland is actively overproducing hormones, as seen in **Graves' disease** or toxic nodular goiter.
- However, subacute thyroiditis is characterized by **low I-131 uptake** because the thyroid gland is damaged and releases preformed hormones rather than actively synthesizing new ones.
*Normal Serum TSH, ↓ Total T4, Normal Free T4, Normal I131 Uptake*
- This combination is not indicative of the patient's hyperthyroid symptoms (- **palpitations, muscle weakness, increased sweating**).
- **Normal Free T4** and **Normal TSH** would suggest euthyroid status, which is inconsistent with the clinical picture.
*↑ Serum TSH, ↑ Total T4, ↑ Free T4, ↑ I 131 Uptake*
- An **elevated TSH** would indicate **primary hypothyroidism**, where the thyroid gland is underactive, and the pituitary tries to stimulate it.
- This contradicts the patient's clinical signs of **hyperthyroidism** (palpitations, sweating, tremors) and the elevated Total and Free T4.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 6: A 52-year-old male presents to clinic with complaints of anxiety and fatigue for 4 months. He has also been experiencing palpitations, muscle weakness, increased sweating, and an increase in the frequency of defecation. Past medical history is insignificant. He neither consumes alcohol nor smokes cigarettes. His pulse is 104/min and irregular, blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg. On examination, you notice that he has bilateral exophthalmos. There are fine tremors in both hands. Which of the following results would you expect to see on a thyroid panel?
- A. High TSH; Low T4; Low T3
- B. High TSH; High T4; High T3
- C. Normal TSH; Low total T4; Normal Free T4 and T3
- D. Low TSH; High T4; High T3 (Correct Answer)
- E. Normal TSH; Low T4; Low T3
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Low TSH; High T4; High T3***
- The patient's symptoms (anxiety, fatigue, palpitations, muscle weakness, increased sweating, increased defecation frequency, tachycardia, hypertension, exophthalmos, fine tremors) are classic for **hyperthyroidism**, particularly **Graves' disease**.
- In primary hyperthyroidism, the thyroid gland overproduces T3 and T4, leading to **high levels of T4 and T3**. This then causes a negative feedback loop to the pituitary, resulting in **suppressed (low) TSH** levels.
*High TSH; Low T4; Low T3*
- This pattern is indicative of **primary hypothyroidism**, where the thyroid gland is underactive and cannot produce sufficient T4 and T3, leading to low levels of these hormones and a compensatory rise in TSH.
- The presented symptoms are directly opposite to those seen in hypothyroidism.
*High TSH; High T4; High T3*
- This combination is characteristic of **secondary hyperthyroidism**, which is much rarer and caused by a TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma.
- While it presents with hyperthyroid symptoms, the TSH level would be elevated or inappropriately normal, not suppressed.
*Normal TSH; Low total T4; Normal Free T4 and T3*
- This pattern is often seen in **euthyroid sick syndrome** or conditions causing a decrease in thyroid-binding globulin (TBG).
- The patient's clinical presentation is clearly that of hyperthyroidism, not a euthyroid state.
*Normal TSH; Low T4; Low T3*
- This result is atypical for any specific thyroid disorder and does not align with the patient's symptoms of hyperthyroidism, which demand high circulating thyroid hormone levels.
- A "normal TSH, low T4, low T3" might suggest central hypothyroidism if TSH was inappropriately normal for the low thyroid hormones, but this patient's symptoms definitively point to thyroid hormone excess.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 7: A previously healthy 27-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of anxiety, diarrhea, and a 4.1-kg (9-lb) weight loss. On questioning, he also reports that he noticed a painless mass on his left testicle 2 weeks ago. His pulse is 110/min and irregular and blood pressure is 150/70 mm Hg. Examination shows diaphoresis and a fine tremor of the outstretched fingers. Testicular examination shows a 3-cm, firm, nontender mass on the left scrotum that does not transilluminate. This patient's underlying condition is most likely to be associated with which of the following findings?
- A. Elevated serum AFP
- B. Elevated serum hCG (Correct Answer)
- C. Elevated serum TSH
- D. Proptosis on exophthalmometry
- E. Positive urine metanephrines
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Elevated serum hCG***
- The patient presents with symptoms of **hyperthyroidism** (anxiety, weight loss, tachycardia, tremor, diaphoresis) and a **testicular mass**.
- Some **testicular germ cell tumors**, particularly **choriocarcinoma** and some **mixed germ cell tumors**, can produce **hCG**, which has structural similarity to TSH and can stimulate the thyroid gland, leading to **paraneoplastic hyperthyroidism**.
- **Serum hCG** is an important tumor marker for germ cell tumors and would be elevated in this clinical scenario.
*Elevated serum AFP*
- **Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)** is a tumor marker often elevated in **non-seminomatous germ cell tumors** like **yolk sac tumors** and **embryonal carcinomas**.
- While AFP may be elevated in some testicular tumors, it does not explain the hyperthyroid symptoms, as hCG (not AFP) has TSH-like activity.
*Elevated serum TSH*
- In **hyperthyroidism**, the **thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)** level is typically **suppressed** due to negative feedback from high thyroid hormone levels.
- An elevated TSH would indicate **primary hypothyroidism**, which contradicts the patient's clinical presentation.
*Proptosis on exophthalmometry*
- **Proptosis** (exophthalmos) is a common finding in **Graves' disease**, an autoimmune cause of hyperthyroidism.
- However, the presence of a **testicular mass** strongly suggests a paraneoplastic etiology for the hyperthyroidism, making Graves' disease less likely as the primary underlying condition.
*Positive urine metanephrines*
- **Urine metanephrines** are markers elevated in **pheochromocytoma**, a tumor of the adrenal medulla that secretes catecholamines.
- While pheochromocytoma can cause hypertension, tachycardia, and anxiety, it does not typically present with a testicular mass or directly cause weight loss through a thyroid-like mechanism.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 8: An 18-year-old girl comes to the clinic because she is concerned about her weight. She states that she is on her school’s cheerleading team and is upset because she feels she is the “fattest” girl on the team despite her healthy diet. She says that in the last 2 weeks since practice began, she has lost 2 lbs. The patient has bipolar disorder I. Her medications include lithium and a combined oral contraceptive that was recently started by her gynecologist, because “everyone is on it." Her mother has hypothyroidism and is treated with levothyroxine. The patient’s BMI is 23.2 kg/m2. Thyroid function labs are drawn and shown below:
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): 4.0 mIU/L
Serum thyroxine (T4): 18 ug/dL
Free thyroxine (Free T4): 1.4 ng/dl (normal range: 0.7-1.9 ng/dL)
Serum triiodothyronine (T3): 210 ng/dL
Free triiodothyronine (T3): 6.0 pg/mL (normal range: 3.0-7.0 pg/mL)
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s abnormal lab values?
- A. Familial hyperthyroidism
- B. Hypocholesterolemia
- C. Lithium
- D. Oral contraception-induced (Correct Answer)
- E. Surreptitious use of levothyroxine
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Oral contraception-induced***
- The patient's **total T4 and T3 are elevated**, while **free T4 and T3** are within normal limits, indicating an increase in thyroid-binding globulin (TBG).
- Oral contraceptives, specifically **estrogen**, increase the synthesis of TBG in the liver, leading to higher total thyroid hormone levels as more hormone is bound.
*Familial hyperthyroidism*
- Familial hyperthyroidism would present with genuinely **elevated free T4 and T3** levels, alongside suppressed TSH, indicating true hyperthyroidism.
- The patient's **normal free T4 and T3** and slightly elevated TSH rule out true hyperthyroidism.
*Hypocholesterolemia*
- While thyroid hormones can affect lipid metabolism, **hypocholesterolemia is not a direct cause** of altered thyroid lab values.
- It is also not a common side effect of oral contraceptives, nor is it related to the specific pattern of elevated total T4/T3 with normal free hormones.
*Lithium*
- Lithium is known to **cause hypothyroidism** (elevated TSH, low T4/T3) or, less commonly, hyperthyroidism, but not isolated elevated total T4/T3 with normal free hormones due to increased TBG.
- The patient's normal free thyroid hormones and only slightly elevated TSH are not consistent with significant lithium-induced thyroid dysfunction.
*Surreptitious use of levothyroxine*
- Surreptitious use of exogenous **levothyroxine** would typically result in suppressed TSH and elevated free T4, as the gland would be overstimulated or shut down.
- The patient's normal free T4 and elevated total T4/T3 are not indicative of levothyroxine abuse.
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 9: A researcher is studying physiologic and hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. Specifically, they examine the behavior of progesterone over the course of the menstrual cycle and find that it normally decreases over time; however, during pregnancy this decrease does not occur in the usual time frame. The researcher identifies a circulating factor that appears to be responsible for this difference in progesterone behavior. In order to further examine this factor, the researcher denatures the circulating factor and examines the sizes of its components on a western blot as compared to several other hormones. One of the bands the researcher identifies in this circulating factor is identical to that of another known hormone with which of the following sites of action?
- A. Thyroid gland (Correct Answer)
- B. Adrenal gland
- C. Adipocytes
- D. Bones
- E. Kidney tubules
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Correct: Thyroid gland***
- The circulating factor described is **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**, which maintains the corpus luteum and progesterone production during early pregnancy
- hCG is a **glycoprotein hormone** composed of an **α subunit** and a **β subunit**
- The **α subunit of hCG is identical** to the α subunits of **TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)**, **LH (luteinizing hormone)**, and **FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone)**
- When denatured and examined on Western blot, one of the bands (the α subunit) would be identical to that of **TSH**
- **TSH acts on the thyroid gland** to stimulate thyroid hormone synthesis and release
- This structural similarity explains why very high levels of hCG (as in molar pregnancy or hyperemesis gravidarum) can sometimes cause **thyrotoxicosis** due to cross-reactivity with TSH receptors
*Incorrect: Adrenal gland*
- **ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)** acts on the adrenal cortex to stimulate cortisol production
- ACTH is a **peptide hormone** derived from POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) and does **NOT share any structural components** with hCG
- There is no identical band between hCG and ACTH on Western blot
*Incorrect: Adipocytes*
- Adipocytes are regulated by hormones like **insulin** and **leptin**
- Neither of these hormones share structural components with hCG
*Incorrect: Bones*
- Bones are primarily regulated by **PTH (parathyroid hormone)**, **calcitonin**, and **vitamin D**
- None of these hormones share structural components with hCG
*Incorrect: Kidney tubules*
- Kidney tubules are regulated by **ADH (antidiuretic hormone/vasopressin)** and **aldosterone**
- Neither shares structural components with hCG
Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG Question 10: A 43-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of tremor, diarrhea, and a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss. Her pulse is 110/min. Examination shows protrusion of the eyeball when looking forward. A bruit is heard over the anterior neck on auscultation. Serum studies show autoantibodies to the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor. The patient decides to undergo definitive treatment for her condition with a radioactive tracer. The success of this treatment directly depends on the activity of which of the following?
- A. Anion-oxidizing enzyme
- B. Transmembrane carrier (Correct Answer)
- C. Lysosomal protease
- D. Binding globulin
- E. Hormone-activating enzyme
Thyroid hormone synthesis Explanation: ***Transmembrane carrier***
- Radioactive iodine treatment relies on the uptake of iodine by thyroid follicular cells via the **sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)**, a **transmembrane carrier protein**.
- NIS actively transports iodide into thyroid cells, allowing the radioactive iodine to concentrate in the thyroid and destroy overactive tissue.
*Anion-oxidizing enzyme*
- This refers to **thyroid peroxidase (TPO)**, an enzyme that oxidizes iodide to iodine, incorporates iodine into thyroglobulin, and couples iodinated tyrosines.
- While essential for thyroid hormone synthesis, TPO's activity does not directly determine the success of **radioactive iodine uptake** for treatment.
*Lysosomal protease*
- **Lysosomal proteases** are involved in the breakdown of thyroglobulin to release thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) into circulation.
- They are important for the *release* of hormones but not for the *uptake* of iodine for radioactive treatment.
*Binding globulin*
- **Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)** is a plasma protein that transports thyroid hormones in the blood, maintaining a reservoir of T3 and T4.
- TBG's activity affects the availability of free thyroid hormones but has no direct role in the cellular uptake of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland.
*Hormone-activating enzyme*
- This typically refers to deiodinases, enzymes that convert T4 (prohormone) into the more active T3 in peripheral tissues.
- These enzymes act *outside* the thyroid gland to activate hormones, and their activity does not directly influence the uptake of radioactive iodine.
More Thyroid hormone synthesis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.