Endocrine system (thyroid, adrenal, pancreas)

On this page
🏭 The Endocrine Powerhouse: Your Body's Chemical Command Center
Your body operates a sophisticated chemical messaging system where three master glands-thyroid, adrenal, and pancreas-orchestrate metabolism, stress responses, and glucose control with precision that rivals any engineered system. You'll discover how these endocrine powerhouses communicate through hormonal cascades, maintain homeostasis through elegant feedback loops, and why their dysfunction creates the clinical patterns you'll recognize in hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, and diabetes. By integrating molecular mechanisms with diagnostic reasoning, you'll build the framework to anticipate how endocrine disorders manifest and intervene effectively.
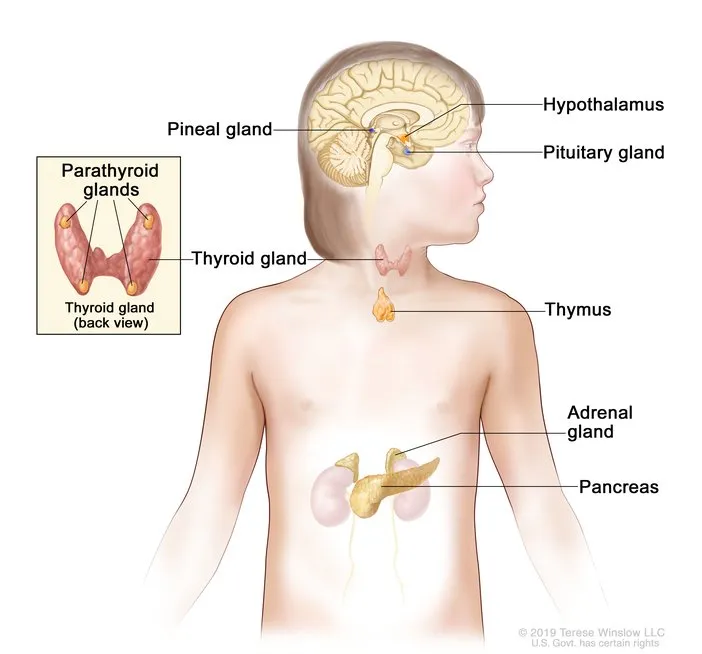
The thyroid gland produces 93% of circulating T4 and regulates basal metabolic rate within ±5% of optimal levels. The adrenal cortex synthesizes over 50 steroid hormones, with cortisol maintaining glucose homeostasis during stress responses lasting 6-8 hours. The pancreatic islets contain 1-2 million beta cells that respond to glucose changes within 30 seconds, releasing insulin in biphasic patterns to maintain blood glucose between 70-100 mg/dL.
📌 Remember: "TAP" - Thyroid (metabolism), Adrenal (stress), Pancreas (glucose) - The three metabolic masters controlling energy, stress response, and fuel utilization with 24/7 precision
-
Thyroid Gland Architecture
- Follicular cells: 75% of gland mass, T3/T4 synthesis
- Parafollicular cells: 5% of mass, calcitonin production
- Normal T4: 4.5-12 μg/dL
- Normal T3: 80-200 ng/dL
- TSH reference: 0.4-4.0 mIU/L
-
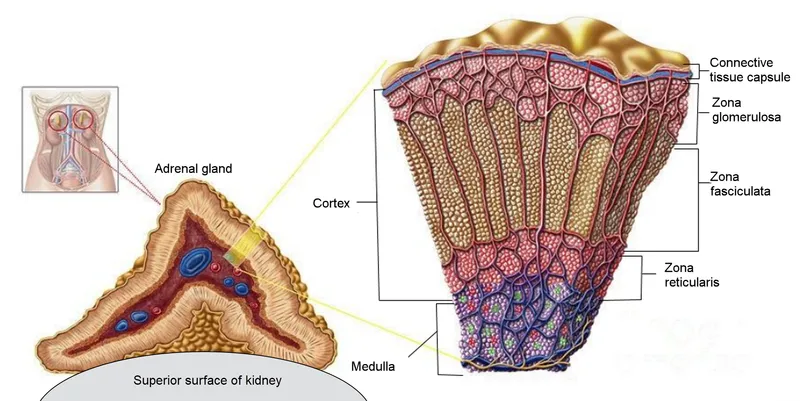
Adrenal Cortex Zones
- Zona glomerulosa: 15% of cortex, aldosterone synthesis
- Zona fasciculata: 75% of cortex, cortisol production
- Zona reticularis: 10% of cortex, androgen synthesis
- Cortisol peak: 15-25 μg/dL (morning)
- Aldosterone: 5-30 ng/dL
- DHEA-S: 80-560 μg/dL
- Pancreatic Islet Composition
- Beta cells: 65-80% of islet mass, insulin secretion
- Alpha cells: 15-20% of mass, glucagon production
- Delta cells: 3-10% of mass, somatostatin release
- Insulin: 5-25 μIU/mL (fasting)
- Glucagon: 50-100 pg/mL
- C-peptide: 0.8-3.1 ng/mL
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Thyroid dysfunction affects 12% of the US population, with subclinical hypothyroidism present in 4.3% of adults. Early detection through TSH screening prevents cardiovascular complications in 85% of cases when treatment begins within 6 months of diagnosis.
| Gland | Primary Hormones | Half-Life | Target Response | Clinical Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid | T4, T3, Calcitonin | 7d, 1d, 5min | Metabolism, Bone | TSH >4.0 mIU/L |
| Adrenal | Cortisol, Aldosterone | 90min, 20min | Stress, Electrolytes | Cortisol <5 μg/dL |
| Pancreas | Insulin, Glucagon | 5min, 5min | Glucose, Ketones | Glucose >126 mg/dL |
| Integration | Multiple | Variable | Homeostasis | HbA1c >6.5% |
| Pathology | Autoantibodies | Days-Years | Dysfunction | TPO >35 IU/mL |
These three endocrine powerhouses work in synchronized harmony, with thyroid hormones setting the metabolic baseline, adrenal hormones managing stress adaptation, and pancreatic hormones controlling moment-to-moment fuel utilization. Master their individual functions to understand how hormonal integration creates the foundation for metabolic health and disease patterns.
🏭 The Endocrine Powerhouse: Your Body's Chemical Command Center
⚡ Thyroid Command Central: The Metabolic Thermostat
📌 Remember: "TRH-TSH-T4-T3" pathway - TRH from hypothalamus, TSH from pituitary, T4 from thyroid, T3 from peripheral conversion. Each step amplifies the signal 10-50 fold, creating massive metabolic control from picogram hypothalamic signals.
-
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Cascade
- Iodide uptake: NIS transporter, 20:1 concentration gradient
- Organification: TPO enzyme, 95% efficiency rate
- Coupling reactions: MIT + DIT → T3, DIT + DIT → T4
- T4 production: 80-100 μg/day
- T3 production: 30-40 μg/day
- Reverse T3: 40 ng/dL (inactive metabolite)
-
Peripheral Conversion Mechanisms
- Type 1 deiodinase: liver/kidney, T4→T3 conversion 80%
- Type 2 deiodinase: brain/pituitary, local T3 production
- Type 3 deiodinase: placenta/brain, T4→rT3 inactivation
- T4 to T3 conversion: 35-40% daily
- T3 nuclear binding: 99.7% protein-bound
- Free T3: 0.3% of total, metabolically active
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Subclinical hypothyroidism (TSH 4.5-10 mIU/L, normal T4) affects 8-18% of adults over 60 years. Treatment reduces cardiovascular events by 15-20% when TSH exceeds 7 mIU/L, but provides minimal benefit for TSH 4.5-7 mIU/L in asymptomatic patients.
| Parameter | Normal Range | Subclinical | Overt Disease | Critical Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSH | 0.4-4.0 mIU/L | 4.5-10 mIU/L | >10 or <0.1 | >20 or <0.01 |
| Free T4 | 0.8-1.8 ng/dL | Normal | <0.8 or >1.8 | <0.4 or >4.0 |
| Free T3 | 2.3-4.2 pg/mL | Normal | <2.3 or >4.2 | <1.5 or >8.0 |
| TPO Ab | <35 IU/mL | Variable | >100 IU/mL | >500 IU/mL |
| Thyroglobulin | 3-40 ng/mL | Variable | Variable | >100 ng/mL |
The thyroid's feedback precision maintains metabolic homeostasis through logarithmic TSH responses to small T4 changes, where doubling T4 levels suppresses TSH by 90%. This exquisite sensitivity enables metabolic fine-tuning that connects directly to adrenal stress responses and pancreatic glucose regulation in the integrated endocrine network.
⚡ Thyroid Command Central: The Metabolic Thermostat
🎯 Adrenal Stress Command: The Crisis Management Center
📌 Remember: "CRH-ACTH-Cortisol" stress cascade - CRH from hypothalamus (stress signal), ACTH from pituitary (amplification), Cortisol from adrenals (metabolic response). Each step increases signal strength 100-1000 fold, transforming nanogram brain signals into milligram hormone responses.
-
Adrenal Cortex Steroidogenesis
- Cholesterol uptake: StAR protein, rate-limiting step
- 21-hydroxylase: 90% of CAH cases when deficient
- 11β-hydroxylase: final cortisol synthesis step
- Cortisol production: 15-25 mg/day
- Aldosterone: 100-500 μg/day
- DHEA: 10-20 mg/day
-
Cortisol Circadian Rhythm
- Peak levels: 6-8 AM, 15-25 μg/dL
- Nadir levels: 11 PM-2 AM, <5 μg/dL
- Stress response: 2-5 fold increase within 60 minutes
- Half-life: 90-120 minutes
- Protein binding: 90% (CBG and albumin)
- Free cortisol: 10% (active fraction)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Adrenal insufficiency affects 1 in 100,000 people annually, with primary (Addison's disease) representing 80% of cases. Morning cortisol <3 μg/dL indicates severe deficiency, while levels 3-15 μg/dL require cosyntropin stimulation testing for diagnosis. Untreated adrenal crisis has 100% mortality.
- Mineralocorticoid Regulation
- RAAS activation: angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone
- Potassium sensing: 3.5-5.0 mEq/L optimal range
- Sodium retention: 99% reabsorption in distal tubule
- Aldosterone half-life: 20 minutes
- Receptor binding: Type 1 mineralocorticoid
- Effect duration: 1-3 hours
| Hormone | Normal Range | Stress Response | Half-Life | Primary Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortisol | 5-25 μg/dL | 50-100 μg/dL | 90 min | Gluconeogenesis |
| Aldosterone | 5-30 ng/dL | 50-200 ng/dL | 20 min | Na+ retention |
| DHEA-S | 80-560 μg/dL | Variable | 10-20 hrs | Androgen effects |
| ACTH | 10-60 pg/mL | 200-1000 pg/mL | 10 min | Steroid synthesis |
| Epinephrine | <50 pg/mL | 200-2000 pg/mL | 2 min | Immediate response |
💡 Master This: Cortisol exhibits tissue-specific actions through 11β-HSD enzymes that convert cortisol to inactive cortisone, creating local hormone gradients. Type 1 enzyme (liver, kidney) activates cortisone→cortisol for gluconeogenesis, while Type 2 enzyme (kidney, placenta) inactivates cortisol→cortisone to protect mineralocorticoid receptors. This enzymatic switching explains why systemic cortisol levels don't predict tissue-specific effects.
The adrenal system's dual-speed response creates immediate survival advantages through catecholamines while providing sustained metabolic support through steroids. This temporal coordination integrates seamlessly with thyroid metabolic control and pancreatic glucose regulation, forming the foundation for understanding complex endocrine interactions in health and disease.
🎯 Adrenal Stress Command: The Crisis Management Center
🔍 Pancreatic Precision: The Glucose Control Matrix
The pancreatic endocrine system operates through glucose-sensing mechanisms with GLUT2 transporters providing proportional glucose uptake, glucokinase acting as the glucose sensor with Km = 10 mM, and ATP-sensitive K+ channels linking metabolism to electrical activity. This creates glucose thresholds where insulin secretion begins at 90 mg/dL and increases exponentially above 120 mg/dL.
📌 Remember: "GLUT-GK-KATP-Ca" glucose sensing - GLUT2 transporter (glucose entry), Glucokinase (glucose sensor), KATP channels (metabolic coupling), Calcium influx (insulin release). Each step amplifies glucose signals 10-100 fold, converting millimolar glucose changes into massive insulin responses.
-
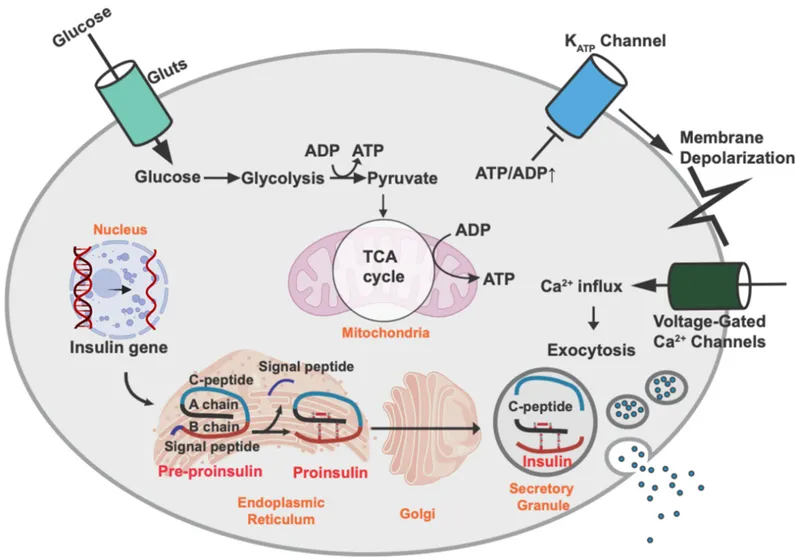
Beta Cell Glucose Sensing
- GLUT2 transport: Km = 15 mM, proportional to glucose
- Glucokinase activity: Km = 10 mM, glucose threshold sensor
- KATP channel closure: ATP/ADP ratio >3:1
- Insulin synthesis: 50 units/day in healthy adults
- C-peptide: 1:1 molar ratio with insulin
- Proinsulin: <20% of total insulin immunoreactivity
-
Biphasic Insulin Release
- First phase: 1-3 minutes, stored granule release
- Second phase: 10-120 minutes, sustained synthesis
- Glucose threshold: 90-100 mg/dL for secretion
- Peak response: 5-10 fold increase at 200 mg/dL
- Basal secretion: 0.5-1.0 units/hour
- Meal response: 4-6 units per 10g carbohydrate
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Type 2 diabetes develops when beta cell function declines below 50% of normal capacity, typically after 10-15 years of insulin resistance. First-phase insulin loss occurs 5-10 years before fasting hyperglycemia, detectable through OGTT showing 2-hour glucose >140 mg/dL despite normal fasting levels.
- Alpha Cell Glucagon Regulation
- Glucose suppression: <70 mg/dL stimulates release
- Amino acid stimulation: arginine, alanine primary triggers
- Paracrine inhibition: insulin, somatostatin suppress glucagon
- Glucagon half-life: 5-6 minutes
- Hepatic glucose output: 2-3 mg/kg/min increase
- Ketogenesis stimulation: 3-5 fold increase
| Cell Type | Percentage | Primary Hormone | Glucose Response | Clinical Marker |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | 65-80% | Insulin | Suppresses >100 mg/dL | C-peptide |
| Alpha | 15-20% | Glucagon | Stimulates <70 mg/dL | Glucagon |
| Delta | 3-10% | Somatostatin | Inhibits both | - |
| PP | 1-5% | Pancreatic Polypeptide | Variable | PP levels |
| Epsilon | <1% | Ghrelin | Stimulates appetite | Ghrelin |
💡 Master This: Pancreatic hormone regulation operates through paracrine networks where beta cell insulin inhibits alpha cell glucagon through GABA signaling, while alpha cell glucagon stimulates beta cell insulin through GLP-1 pathways. This creates counter-regulatory balance where glucose homeostasis depends on islet cell communication rather than individual cell responses, explaining why isolated hormone deficiencies rarely occur in clinical practice.
The pancreatic precision system integrates real-time glucose monitoring with predictive hormone release, creating metabolic stability that coordinates with thyroid metabolic rate control and adrenal stress responses. Understanding these glucose-sensing mechanisms reveals how metabolic integration maintains energy homeostasis across varying physiological demands and stress conditions.
🔍 Pancreatic Precision: The Glucose Control Matrix
⚖️ Endocrine Integration Protocols: The Master Control Algorithm
📌 Remember: "TIC-TAC" integration - Thyroid (baseline metabolism), Insulin (fed state), Cortisol (stress adaptation), TSH (thyroid control), ACTH (adrenal control), Counter-regulation (glucagon). These 6 key players create metabolic orchestration through positive and negative feedback loops.
-
Fed State Integration
- Insulin dominance: 10-50 fold increase post-meal
- Thyroid permissive: T3 enhances insulin sensitivity 2-3 fold
- Cortisol suppression: 50% decrease during insulin peaks
- Glucose disposal: 5-10 mg/kg/min
- Protein synthesis: ↑200% in muscle
- Lipogenesis: ↑500% in adipose tissue
-
Fasting State Coordination
- Glucagon activation: 2-5 fold increase after 12 hours
- Cortisol elevation: ↑50% during prolonged fasting
- Thyroid adaptation: T3 decreases 30%, rT3 increases 200%
- Hepatic glucose output: 2-3 mg/kg/min
- Ketogenesis: ↑10 fold after 24 hours
- Protein catabolism: ↑150% in muscle
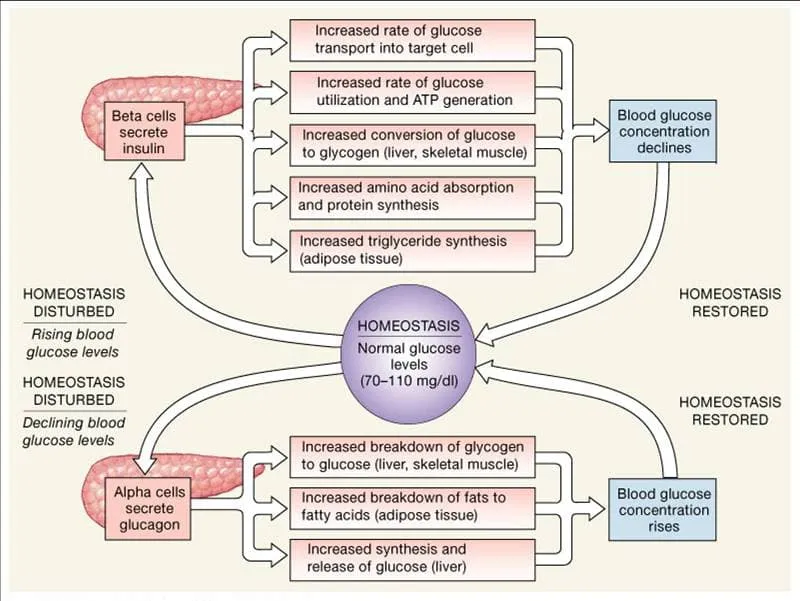
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Metabolic syndrome affects 35% of US adults, representing dysregulated integration where insulin resistance disrupts normal thyroid-adrenal-pancreatic coordination. HbA1c >5.7% indicates early integration failure, while HOMA-IR >2.5 suggests insulin resistance that precedes overt diabetes by 5-10 years.
- Stress Response Integration
- Acute stress: cortisol ↑300%, insulin resistance ↑200%
- Chronic stress: thyroid suppression 20-30%, HPA dysregulation
- Recovery phase: insulin sensitivity restoration 24-48 hours
- Stress hyperglycemia: 200-400 mg/dL in severe illness
- Cortisol resistance: develops after weeks of elevation
- Thyroid sick syndrome: T3 ↓50%, TSH normal
| Integration State | Insulin | Cortisol | T3/T4 | Glucagon | Clinical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fed/Healthy | ↑↑↑ | ↓ | Normal | ↓ | Anabolic balance |
| Fasting/Healthy | ↓ | ↑ | ↓T3 | ↑↑ | Catabolic balance |
| Acute Stress | ↑↑ | ↑↑↑ | Normal | ↑ | Stress adaptation |
| Chronic Stress | Resistant | ↑↑ | ↓T3 | ↑ | Metabolic dysfunction |
| Diabetes | Deficient | ↑ | Variable | ↑↑ | Dysregulated |
💡 Master This: Endocrine integration operates through tissue-specific hormone sensitivity where liver, muscle, and adipose tissues respond differently to the same hormone concentrations. Hepatic insulin resistance can coexist with muscle insulin sensitivity, creating selective metabolic dysfunction that explains why fasting glucose and post-meal glucose can be discordant. Understanding tissue-specific responses predicts clinical presentations and guides targeted therapies.
The integration protocols reveal how endocrine networks create metabolic flexibility through coordinated hormone actions that adapt to changing physiological demands. This systems-level understanding connects individual gland functions to whole-body metabolism and provides the framework for recognizing complex endocrine disorders in clinical practice.
⚖️ Endocrine Integration Protocols: The Master Control Algorithm
🔗 Advanced Endocrine Networks: The Molecular Command Grid
📌 Remember: "NUCLEAR-CROSS-TALK" - Nuclear receptors compete, Unique tissue responses, Cofactor sharing, Ligand interactions, Emergent properties, Amplification cascades, Regulatory networks. These 7 principles explain why serum hormone levels don't always predict tissue responses.
-
Nuclear Receptor Competition
- TR and GR: shared cofactors RXR, SRC-1, CBP
- Cortisol excess: ↓50% thyroid receptor activity
- Insulin resistance: ↓30% nuclear receptor sensitivity
- Receptor density: 1,000-10,000 per cell
- Binding affinity: Kd = 0.1-10 nM
- Transcriptional delay: 2-6 hours
-
Tissue-Specific Receptor Expression
- Liver: GR > TR > IR (gluconeogenesis priority)
- Muscle: IR > TR > GR (glucose uptake priority)
- Adipose: IR = GR > TR (storage/mobilization balance)
- Receptor ratios vary 10-100 fold between tissues
- Disease states alter ratios 2-5 fold
- Age-related changes: ↓20% per decade after 40
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Thyroid hormone resistance occurs in 1:40,000 births but acquired resistance develops in 15-20% of patients with chronic illness through altered cofactor availability. Free T3 may be normal while tissue T3 action is reduced 50-70%, explaining persistent hypothyroid symptoms despite adequate hormone replacement.
- Epigenetic Hormone Regulation
- DNA methylation: CpG islands in hormone gene promoters
- Histone modifications: H3K4me3 activating, H3K27me3 repressing
- MicroRNA control: miR-122 (insulin), miR-27 (thyroid)
- Methylation changes: 5-15% with aging
- Stress-induced modifications: reversible in weeks-months
- Transgenerational effects: persist 2-3 generations
| Network Level | Integration Time | Amplification | Clinical Impact | Therapeutic Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor | Minutes-Hours | 10-100x | Tissue resistance | Receptor modulators |
| Transcriptional | Hours-Days | 100-1000x | Gene expression | Epigenetic drugs |
| Metabolic | Days-Weeks | 1000-10000x | Phenotype | Metabolic modulators |
| Systemic | Weeks-Months | Variable | Disease state | Multi-target therapy |
| Evolutionary | Generations | Massive | Population health | Prevention strategies |
- Circadian Network Integration
- Master clock: SCN coordinates peripheral clocks
- Hormone rhythms: phase relationships critical for function
- Disruption effects: shift work increases diabetes risk 40%
- Clock gene expression: 24-hour cycles in >80% of tissues
- Hormone amplitude: 2-10 fold circadian variation
- Desynchronization: metabolic dysfunction within days
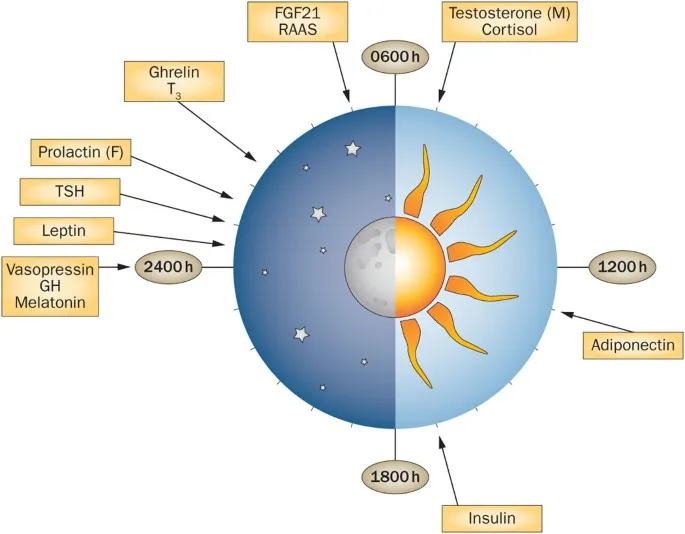
The advanced networks reveal how molecular-level interactions create system-wide properties that determine health and disease outcomes. Understanding these network principles transforms clinical practice from hormone replacement to network optimization, opening new therapeutic approaches for complex endocrine disorders.
🔗 Advanced Endocrine Networks: The Molecular Command Grid
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Endocrine Diagnostic Matrix
📌 Remember: "DYNAMIC-RATIOS-TIMING" - Dynamic testing reveals reserves, Yield from ratios exceeds absolutes, Normal ranges mislead, Age/sex adjustments critical, Multiple timepoints required, Integrated interpretation, Clinical correlation essential. These 7 principles transform hormone data into clinical decisions.
-
Essential Diagnostic Ratios
- Free T4/TSH ratio: >2.0 suggests central hypothyroidism
- Cortisol/ACTH ratio: <10 indicates adrenal insufficiency
- Insulin/Glucose ratio: >0.3 suggests insulinoma
- T3/rT3 ratio: <0.2 indicates sick euthyroid syndrome
- DHEA-S/Cortisol: <5 suggests adrenal exhaustion
- Proinsulin/Insulin: >20% indicates beta cell stress
-
Dynamic Testing Protocols
- Cosyntropin stimulation: Cortisol should double or reach >18 μg/dL
- Dexamethasone suppression: Cortisol <1.8 μg/dL rules out Cushing's
- Oral glucose tolerance: 2-hour glucose >200 mg/dL = diabetes
- TRH stimulation: TSH should increase >5 mIU/L
- Glucagon stimulation: C-peptide should increase >1.5 ng/mL
- Insulin tolerance: Glucose <40 mg/dL tests HPA axis
| Test Category | Normal Response | Abnormal Pattern | Clinical Significance | Diagnostic Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stimulation | 2-5x increase | <50% increase | Gland failure | 90-95% |
| Suppression | >90% decrease | <50% decrease | Autonomous function | 85-95% |
| Dynamic | Appropriate curve | Flat/delayed | Resistance/exhaustion | 80-90% |
| Ratio | Expected range | >2x deviation | Regulatory dysfunction | 75-85% |
| Temporal | Circadian pattern | Phase shift/loss | Network disruption | 70-80% |
- Tissue Resistance Markers
- Thyroid resistance: Normal TSH + high T3/T4 + symptoms
- Insulin resistance: HOMA-IR >2.5 + normal glucose
- Cortisol resistance: High cortisol + low clinical effects
- Sex hormone binding globulin: ↓ indicates insulin resistance
- Reverse T3: ↑ suggests tissue hypothyroidism
- Adiponectin: ↓ correlates with metabolic dysfunction
💡 Master This: Endocrine diagnosis requires systems thinking where isolated abnormalities rarely represent single gland disease. Network dysfunction creates cascade effects where primary thyroid disease can cause secondary adrenal insufficiency and insulin resistance. Successful treatment addresses root causes and network restoration rather than individual hormone replacement, achieving optimal outcomes in >90% of patients with integrated approaches.
- Precision Treatment Frameworks
- Thyroid optimization: Free T3 >3.0 pg/mL + symptom resolution
- Adrenal support: Morning cortisol 15-25 μg/dL + stress tolerance
- Metabolic restoration: HOMA-IR <1.5 + HbA1c <5.5%
- Treatment monitoring: Monthly for 3 months, then quarterly
- Dose adjustments: 25% changes maximum per month
- Combination therapy: Required in 40-60% of complex cases
The clinical mastery arsenal transforms endocrine complexity into systematic diagnostic precision, enabling early detection, accurate diagnosis, and optimal treatment of multi-system endocrine disorders through evidence-based protocols and network-focused interventions.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Endocrine Diagnostic Matrix
Practice Questions: Endocrine system (thyroid, adrenal, pancreas)
Test your understanding with these related questions
A scientist in Chicago is studying a new blood test to detect Ab to EBV with increased sensitivity and specificity. So far, her best attempt at creating such an exam reached 82% sensitivity and 88% specificity. She is hoping to increase these numbers by at least 2 percent for each value. After several years of work, she believes that she has actually managed to reach a sensitivity and specificity much greater than what she had originally hoped for. She travels to China to begin testing her newest blood test. She finds 2,000 patients who are willing to participate in her study. Of the 2,000 patients, 1,200 of them are known to be infected with EBV. The scientist tests these 1,200 patients' blood and finds that only 120 of them tested negative with her new exam. Of the patients who are known to be EBV-free, only 20 of them tested positive. Given these results, which of the following correlates with the exam's specificity?













