PR interval significance US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for PR interval significance. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 1: A 21-year-old woman presents with palpitations and anxiety. She had a recent outpatient ECG that was suggestive of supraventricular tachycardia, but her previous physician failed to find any underlying disease. No other significant past medical history. Her vital signs include blood pressure 102/65 mm Hg, pulse 120/min, respiratory rate 17/min, and temperature 36.5℃ (97.7℉). Electrophysiological studies reveal an atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. The patient refuses an ablation procedure so it is decided to perform synchronized cardioversion with consequent ongoing management with verapamil. Which of the following ECG features should be monitored in this patient during treatment?
- A. Amplitude and direction of the T wave
- B. Length of QRS complex
- C. Length of QT interval
- D. Length of PR interval (Correct Answer)
- E. QRS complex amplitude
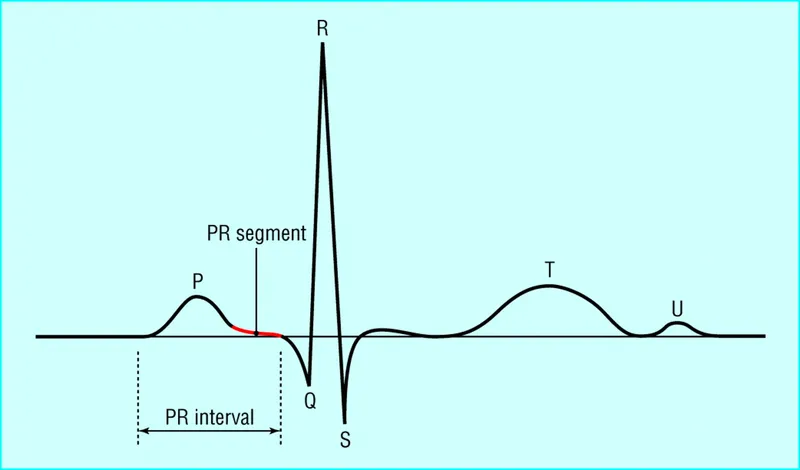
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Length of PR interval***
- Verapamil is a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** that primarily acts on the **AV node** to slow conduction.
- Monitoring the **PR interval** is crucial because excessive slowing of AV nodal conduction can lead to **AV block**, which is indicated by a prolonged PR interval.
*Amplitude and direction of the T wave*
- Changes in T-wave amplitude and direction are often associated with **myocardial ischemia** or **electrolyte imbalances**, which are not the primary concerns with verapamil.
- While verapamil can affect repolarization, the most direct and common adverse effect related to its mechanism of action on the AV node is not primarily reflected in T-wave changes.
*Length of QRS complex*
- The QRS complex duration primarily reflects **ventricular depolarization** and is typically affected by medications that alter conduction through the His-Purkinje system or within the ventricles, such as antiarrhythmics like **flecainide** or **amiodarone**.
- Verapamil's main action is on the AV node, so it generally does not significantly prolong the QRS complex unless there is pre-existing conduction system disease.
*Length of QT interval*
- The QT interval represents **ventricular repolarization**, and its prolongation can lead to **Torsades de Pointes**, a life-threatening arrhythmia.
- While many antiarrhythmics can prolong the QT interval, **verapamil is not known to significantly prolong the QT interval** and is generally considered safe in this regard.
*QRS complex amplitude*
- Changes in QRS amplitude can indicate conditions like **pericardial effusion**, **cardiomyopathy**, or changes in ventricular mass.
- These are generally not direct or common side effects of verapamil therapy, which primarily focuses on AV nodal conduction.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 2: An ECG from an 8-year-old male with neurosensory deafness and a family history of sudden cardiac arrest demonstrates QT-interval prolongation. Which of the following is this patient most at risk of developing?
- A. Hypertrophic cardiac myopathy
- B. Cardiac tamponade
- C. Essential hypertension
- D. Torsades de pointes (Correct Answer)
- E. First degree atrioventricular block
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Torsades de pointes***
- The combination of **neurosensory deafness**, **QT-interval prolongation**, and a family history of **sudden cardiac arrest** is highly suggestive of **Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome**, a form of **long QT syndrome**.
- Patients with long QT syndrome are at significant risk for developing **polymorphic ventricular tachycardia** known as **Torsades de pointes**, which can degenerate into **ventricular fibrillation** and cause sudden cardiac death.
*Hypertrophic cardiac myopathy*
- This condition involves thickening of the **ventricular walls** and is associated with outflow tract obstruction, not primarily with QT prolongation.
- While it can cause sudden cardiac arrest, it typically presents with symptoms like **dyspnea, chest pain**, or syncope during exertion, and its ECG findings usually include **left ventricular hypertrophy** and **deep Q waves**.
*Cardiac tamponade*
- **Cardiac tamponade** results from the accumulation of fluid in the **pericardial sac**, compressing the heart and impairing its filling.
- This condition is not related to **QT prolongation** or **sensorineural deafness** and would present with signs of **hemodynamic instability**, such as **pulsus paradoxus** and muffled heart sounds.
*Essential hypertension*
- **Essential hypertension** is chronic high blood pressure with no identifiable secondary cause, commonly affecting adults.
- It is not associated with **congenital neurosensory deafness** or significant **QT-interval prolongation** in childhood.
*First degree atrioventricular block*
- **First-degree AV block** is characterized by a prolonged **PR interval** on ECG, indicating delayed conduction through the AV node.
- While it's an electrical abnormality, it is distinct from **QT prolongation** and is not typically associated with **neurosensory deafness** or the same risk of sudden cardiac arrest as long QT syndrome.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 3: A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after his wife found him unconscious on the bathroom floor. On arrival, he is conscious and alert. He remembers having palpitations and feeling lightheaded and short of breath before losing consciousness. He takes captopril for hypertension and glyburide for type 2 diabetes mellitus. His vitals are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Random serum glucose concentration is 85 mg/dL. An ECG shows a short PR interval and a wide QRS complex with initial slurring. Transthoracic echocardiography reveals normal echocardiographic findings with normal left ventricular systolic function. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's findings?
- A. Ischemic myocardial necrosis
- B. Ectopic foci within the ventricles
- C. Accessory atrioventricular pathway (Correct Answer)
- D. A dysfunctional AV node
- E. Low serum glucose levels
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Accessory atrioventricular pathway***
- The ECG findings of a **short PR interval**, **wide QRS complex**, and **initial slurring (delta wave)** are characteristic of **Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome**, which is caused by an **accessory atrioventricular pathway**.
- Symptoms like **palpitations, lightheadedness, and syncope** in a patient with these ECG findings suggest an underlying **tachyarrhythmia originating from the accessory pathway**.
*Ischemic myocardial necrosis*
- While syncope can be a symptom of **myocardial ischemia**, the ECG findings (short PR, wide QRS with delta wave) are not typical for **ischemia or infarction**.
- The **normal echocardiogram** and absence of chest pain also make **ischemic myocardial necrosis** less likely.
*Ectopic foci within the ventricles*
- **Ventricular ectopic foci** can cause wide QRS complexes (e.g., in ventricular tachycardia), but they typically do not involve a **short PR interval or a delta wave**.
- The characteristic ECG pattern observed points away from primary **ventricular ectopy** as the underlying cause.
*A dysfunctional AV node*
- A **dysfunctional AV node** typically leads to **AV blocks** (prolonged PR interval, dropped beats) or sometimes reentrant tachycardias, but it does not cause a **short PR interval with a delta wave and wide QRS complex**.
- The described ECG pattern indicates a bypass of the **AV node's normal delay function**.
*Low serum glucose levels*
- Although the patient takes **glyburide** (which can cause hypoglycemia), his **random serum glucose** was 85 mg/dL, which is within the normal range and does not indicate **hypoglycemia**.
- While hypoglycemia can cause syncope, it does not explain the specific ECG abnormalities observed.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 4: A 23-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of palpitations, dizziness, and substernal chest pain for three hours. The day prior, he was at a friend’s wedding, where he consumed seven glasses of wine. The patient appears diaphoretic. His pulse is 220/min and blood pressure is 120/84 mm Hg. Based on the patient's findings on electrocardiography, the physician diagnoses atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and administers verapamil for rate control. Ten minutes later, the patient is unresponsive and loses consciousness. Despite resuscitative efforts, the patient dies. Histopathologic examination of the heart at autopsy shows an accessory atrioventricular conduction pathway. Electrocardiography prior to the onset of this patient's symptoms would most likely have shown which of the following findings?
- A. Epsilon wave following the QRS complex
- B. Prolongation of the QT interval
- C. Cyclic alteration of the QRS axis
- D. Slurred upstroke of the QRS complex (Correct Answer)
- E. Positive Sokolow-Lyon index
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Slurred upstroke of the QRS complex***
- The patient's presentation with **atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response** and subsequent collapse after verapamil administration—a calcium channel blocker—is classic for a pre-excitation syndrome like **Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome**.
- In WPW, an accessory pathway (bundle of Kent) bypasses the AV node, leading to a **short PR interval** and a **delta wave** (slurred upstroke of the QRS complex) on ECG during normal sinus rhythm.
*Epsilon wave following the QRS complex*
- An **epsilon wave** is characteristic of **arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)**, representing delayed depolarization of the right ventricle.
- While ARVC can cause arrhythmias, it is distinctly different from the pre-excitation syndrome described, which involves an accessory pathway.
*Prolongation of the QT interval*
- **Prolonged QT interval** is associated with an increased risk of **torsades de pointes**, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
- This finding is typical of **long QT syndrome** and does not directly relate to an accessory atrioventricular conduction pathway.
*Cyclic alteration of the QRS axis*
- **Cyclic alteration of the QRS axis** or electrical alternans is seen in conditions causing swings in cardiac position, most notably **pericardial effusion with tamponade**.
- This ECG finding is unrelated to accessory pathways or the mechanisms of pre-excitation syndromes.
*Positive Sokolow-Lyon index*
- A **positive Sokolow-Lyon index** signifies **left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)**, characterized by large QRS voltages (e.g., SV1 + RV5/V6 ≥ 35 mm).
- While LVH can be associated with various cardiac conditions, it is not a direct ECG manifestation of an accessory atrioventricular conduction pathway.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 5: A researcher is studying how electrical activity propagates across the heart. In order to do this, he decides to measure the rate at which an action potential moves within various groups of cardiac muscle tissue. In particular, he isolates fibers from areas of the heart with the following characteristics:
A) Dysfunction leads to fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
B) Dysfunction leads to increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
C) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex
D) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram
Which of the following is the proper order of these tissues from fastest action potential propagation to slowest action potential propagation.
- A. B > D > C > A
- B. D > C > A > B
- C. B > C > D > A
- D. A > D > C > B (Correct Answer)
- E. A > C > D > B
PR interval significance Explanation: ***A > D > C > B***
* **Purkinje fibers (A)** have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart to ensure rapid and synchronous ventricular depolarization. The description of "fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" in **Mobitz type II second-degree AV block** indicates an issue with conduction distal to the AV node, often in the His-Purkinje system, while still maintaining typical conduction through the atria and AV node for conducted beats.
* **Atrial muscle (D)** has a faster conduction velocity than the AV node but slower than Purkinje fibers. The "sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram" unequivocally points to **atrial flutter**, which is characterized by rapid, regular depolarization of the atria.
* **Ventricular muscle (C)** has a conduction velocity slower than Purkinje fibers but faster than the AV node. "Tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex" is characteristic of **ventricular tachycardia (VT)**, which arises from abnormal electrical activity within the ventricles.
* **AV node (B)** has the slowest conduction velocity in the heart, which allows for proper ventricular filling. "Increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" describes **Mobitz type I second-degree AV block (Wenckebach phenomenon)**, which is due to progressive prolongation of conduction delay within the AV node itself.
*B > D > C > A*
* This order incorrectly places the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest, which is contrary to the known conduction velocities in the heart.
* The AV node is critical for delaying the impulse, making it the slowest, while Purkinje fibers are designed for rapid spread, making them the fastest.
*D > C > A > B*
* This option incorrectly places **atrial muscle (D)** as faster than **Purkinje fibers (A)**. Purkinje fibers have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart, considerably faster than atrial muscle.
*B > C > D > A*
* This arrangement incorrectly lists the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest. The AV node is the slowest for its physiological role of delaying ventricular contraction, while Purkinje fibers are optimized for rapid conduction.
*A > C > D > B*
* While placing **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the fastest and the **AV node (B)** as the slowest is correct, this order incorrectly places **ventricular muscle (C)** as faster than **atrial muscle (D)**. Atrial muscle generally conducts faster than ventricular muscle in normal physiology.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 6: A 71-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of increasing confusion, weakness, and vomiting for 1 day. He has had 5 episodes of vomiting and blurry vision; he told his wife that "everything appears in different colors." He has been unable to recall his wife's name or their address. His wife reports that his drug regimen was adjusted because of worsening tibial edema 1 week ago. He has congestive heart failure, atrial fibrillation, hypothyroidism, and osteoarthritis. Current medications include rivaroxaban, metoprolol, digoxin, levothyroxine, spironolactone, and furosemide. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 56/min, and blood pressure is 98/68 mm Hg. He is confused and oriented only to person. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. The abdomen is soft, and there is tenderness to palpation of both lower quadrants without guarding or rebound. There is 1+ pitting edema of both ankles. This patient is most likely to have which of the following ECG findings?
- A. Low QRS voltage
- B. Increased PR interval (Correct Answer)
- C. Mobitz type 2 atrioventricular block
- D. Prolonged QT interval
- E. Peaked T waves
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Increased PR interval***
- The patient's symptoms (confusion, weakness, vomiting, blurry vision with "everything appears in different colors," bradycardia) are classic signs of **digoxin toxicity**. Digoxin primarily affects the **AV node**, leading to slowed conduction and thus an **increased PR interval** on ECG.
- The recent adjustment of his diuretic regimen (spironolactone and furosemide) for worsening edema suggests possible **hypokalemia** or **renal impairment**, which can precipitate digoxin toxicity even at therapeutic levels.
*Low QRS voltage*
- **Low QRS voltage** is typically associated with conditions like **pericardial effusion**, severe hypothyroidism, or diffuse myocardial disease, which are not directly suggested by the patient's acute presentation.
- While the patient has hypothyroidism, acute digoxin toxicity does not primarily cause low QRS voltage.
*Mobitz type 2 atrioventricular block*
- While digoxin toxicity can cause various arrhythmias, **Mobitz type 2 AV block** (characterized by constant PR interval before a dropped beat) usually indicates issues deeper in the His-Purkinje system.
- **First-degree AV block** (increased PR interval) and **Wenckebach (Mobitz type 1) AV block** are more common manifestations of digoxin's direct inhibitory effect on the AV node.
*Prolonged QT interval*
- A **prolonged QT interval** is associated with an increased risk of **Torsades de Pointes** and can be caused by certain antiarrhythmics (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) or electrolyte imbalances, but it is not a direct or typical ECG finding of digoxin toxicity.
- Digoxin toxicity is more commonly associated with a **shortened QT interval** or "scooping" of the ST segment.
*Peaked T waves*
- **Peaked T waves** are a hallmark of **hyperkalemia**, an electrolyte disturbance that can cause cardiac arrhythmias and muscle weakness.
- While electrolyte imbalances can contribute to digoxin toxicity, peaked T waves themselves are not a direct consequence of digoxin.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 7: A 17-year-old girl suddenly grabs her chest and collapses to the ground while playing volleyball at school. The teacher rushes to evaluate the situation and finds that the girl has no pulse and is not breathing. He starts chest compressions. An automated external defibrillator (AED) is brought to the scene within 3 minutes and a shock is delivered. The girl regains consciousness and regular sinus rhythm. She is rushed to the emergency department. The vital signs include: blood pressure 122/77 mm Hg and pulse 65/min. The pulse is regular. An electrocardiogram (ECG) shows a shortened PR interval, a wide QRS complex, a delta wave, and an inverted T wave. Which of the following is the most likely pathology in the conduction system of this patient’s heart?
- A. Impulse generation by tissue in atrioventricular node
- B. Accessory pathway from atria to ventricles (Correct Answer)
- C. Automatic discharge of irregular impulses in the atria
- D. Wandering atrial pacemaker
- E. Blockage in conduction pathway
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Accessory pathway from atria to ventricles***
- The ECG findings of a **shortened PR interval**, **delta wave**, and **wide QRS complex** are characteristic of **Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome**, which involves an **accessory pathway** (Bundle of Kent) bypassing the AV node.
- This accessory pathway allows for pre-excitation of the ventricles, predisposing patients to **tachyarrhythmias** like the one experienced by the patient (sudden cardiac arrest).
*Impulse generation by tissue in atrioventricular node*
- This describes a **junctional rhythm**, which would present with a **normal or long PR interval** and a **narrow QRS complex**, contrasting with the given ECG findings.
- A junctional rhythm typically results in a slower heart rate and is not generally associated with sudden cardiac arrest in healthy individuals.
*Automatic discharge of irregular impulses in the atria*
- This typically refers to **atrial fibrillation** or multifocal atrial tachycardia, which would show an **irregularly irregular rhythm** or multiple P-wave morphologies, not the specific PR and QRS abnormalities seen.
- While atrial fibrillation can occur with WPW, the primary pathology described by the ECG findings is the accessory pathway itself.
*Wandering atrial pacemaker*
- A **wandering atrial pacemaker** is characterized by varying P-wave morphology and PR intervals as the pacemaker shifts between different atrial sites, but it generally maintains a normal QRS duration.
- It is typically a benign arrhythmia and does not cause the pre-excitation or the risk of sudden cardiac death seen in this patient.
*Blockage in conduction pathway*
- A **blockage in the conduction pathway** (e.g., AV block) would result in a **prolonged PR interval** or dropped QRS complexes, which is the opposite of the shortened PR interval observed.
- While heart block can cause syncope, it wouldn't explain the pre-excitation pattern (delta wave, wide QRS) seen in the ECG.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 8: A 23-year-old man comes to the physician with a 1-week history of sharp, substernal chest pain that is worse with inspiration and relieved with leaning forward. He has also had nausea and myalgias. His father has coronary artery disease. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 130/84 mm Hg. Cardiac examination shows a high-pitched rubbing sound between S1 and S2 that is best heard at the left sternal border. An ECG shows depressed PR interval and diffuse ST elevations. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Dressler syndrome
- B. Acute pericarditis (Correct Answer)
- C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- D. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- E. Acute myocardial infarction
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Acute pericarditis***
- The patient's **sharp, substernal chest pain** that is **worse with inspiration** and **relieved by leaning forward** is a classic presentation of acute pericarditis.
- The **pericardial friction rub** on cardiac examination and **diffuse ST elevations** with a **depressed PR interval** on ECG are highly characteristic findings.
*Dressler syndrome*
- Dressler syndrome is a **late complication of myocardial infarction or cardiac surgery**, typically occurring weeks to months afterward.
- This patient's symptoms developed over a week and are not preceded by such events.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection*
- While *Mycobacterium tuberculosis* can cause pericarditis, it typically presents as **chronic constrictive pericarditis** with effusions and more systemic symptoms like significant fever and night sweats.
- The acute onset and classic ECG findings are less consistent with tuberculous pericarditis.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- SLE can cause pericarditis, but it's usually part of a **multi-system inflammatory picture** with other classic SLE symptoms (e.g., malar rash, arthralgias, renal involvement).
- There are no other features to suggest SLE in this case, and the isolated, acute presentation points more directly to infectious or idiopathic pericarditis.
*Acute myocardial infarction*
- While an MI causes chest pain and ST elevations, the pain is usually described as **crushing or heavy**, not typically pleuritic or relieved by leaning forward.
- **PR depression** is not seen in MI, and the ST elevations are usually localized to specific arterial territories, not diffuse.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 9: A 33-year-old man is evaluated by paramedics after being found unconscious outside of his home. He has no palpable pulses. Physical examination shows erythematous marks in a fern-leaf pattern on his lower extremities. An ECG shows ventricular fibrillation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
- A. Infective endocarditis
- B. Lightning strike (Correct Answer)
- C. Opioid overdose
- D. Hypothermia
- E. Cholesterol emboli
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Lightning strike***
- The **fern-leaf pattern** on the skin, known as **Lichtenberg figures**, is pathognomonic for a lightning strike.
- **Ventricular fibrillation** is a common and often fatal cardiac arrhythmia caused by the massive electrical discharge from lightning.
*Infective endocarditis*
- While it can cause cardiac arrhythmias or collapse due to **embolism**, it does not produce **Lichtenberg figures**.
- Typical signs include **fever**, **murmurs**, and **Osler's nodes** or **Janeway lesions**, which are not mentioned here.
*Opioid overdose*
- Leads to **respiratory depression**, **miosis (pinpoint pupils)**, and potentially **bradycardia**, but not ventricular fibrillation or fern-leaf skin patterns.
- The patient would typically present with a **depressed level of consciousness** but usually has palpable pulses initially.
*Hypothermia*
- Can cause cardiac arrhythmias, including **ventricular fibrillation** in severe cases, but would not produce **Lichtenberg figures**.
- The patient's skin would typically be **cold to the touch**, and there might be **J-waves** on the ECG.
*Cholesterol emboli*
- Typically results in widespread **ischemic symptoms** in various organs and can cause skin manifestations like **livedo reticularis** or **"trash foot"**.
- It does not cause **ventricular fibrillation** or the characteristic **fern-leaf pattern** seen in lightning strike victims.
PR interval significance US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of intermittent palpitations and shortness of breath. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no other abnormalities. An ECG shows an absence of P waves, an oscillating baseline, and irregular RR intervals at a rate of approximately 95 beats per minute. The difference between atrial and ventricular rates in this patient is most likely due to which of the following?
- A. Prolonged influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the bundle of His
- B. Transient activation of K+ current in Purkinje fibers
- C. Inhibition of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump in ventricular cells
- D. Limited speed of conduction through the left bundle branch
- E. Temporary inactivation of Na+ channels in the AV node (Correct Answer)
PR interval significance Explanation: ***Temporary inactivation of Na+ channels in the AV node***
- The ECG findings are classic for **atrial fibrillation**, characterized by a rapid, irregular atrial rhythm (oscillating baseline with no P waves) and an irregularly irregular ventricular response.
- The **AV node's refractory period** and the number of sodium channels available for conduction dictate the rate at which atrial impulses can pass to the ventricles, preventing a dangerously fast ventricular rate.
*Prolonged influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the bundle of His*
- The **bundle of His** primarily conducts impulses rather than primarily regulating the rate difference between atria and ventricles through calcium channel kinetics.
- Prolonged calcium influx would generally **slow conduction** or decrease excitability, but it's not the primary mechanism explaining the ventricular rate control in atrial fibrillation.
*Transient activation of K+ current in Purkinje fibers*
- **Purkinje fibers** are involved in rapid ventricular depolarization, but their primary role is not to mediate the rate difference between atria and ventricles in atrial fibrillation.
- Activation of K+ current typically leads to **repolarization**, affecting action potential duration, not the overall filtering of atrial impulses.
*Inhibition of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump in ventricular cells*
- Inhibition of the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump** would lead to intracellular sodium accumulation and depolarization, potentially causing arrhythmias, not regulating the ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation.
- This is the mechanism of action for **digoxin**, which can slow AV nodal conduction but through a different primary pathway affecting the pump.
*Limited speed of conduction through the left bundle branch*
- While conduction system abnormalities can occur, a **limited speed of conduction** specifically in the left bundle branch would cause a wide QRS complex or bundle branch block, not the inherent rate-limiting seen in atrial fibrillation.
- The AV node is the primary regulator of ventricular response rate in atrial fibrillation due to its inherent physiological properties.
More PR interval significance US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.