Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bundle branch blocks. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 1: A 39-year-old female with poorly controlled systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) presents to the emergency room with a cough and pleuritic chest pain. She states that she developed these symptoms 2 days prior. The pain appears to improve when the patient leans forward. She currently takes hydroxychloroquine for her systemic lupus erythematosus but has missed several doses recently. Her temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 135/80 mmHg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination reveals a rise in jugular venous pressure during inspiration. In addition to tachycardia, which of the following EKG patterns is most likely to be seen in this patient?
- A. Peaked T waves with flattened P waves
- B. Irregularly irregular QRS complexes with no P waves
- C. PR depressions and diffuse ST elevations (Correct Answer)
- D. ST segment depressions in leads II, III, and aVF
- E. Prolonged PR interval with normal QRS complexes
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***PR depressions and diffuse ST elevations***
- The patient's symptoms of **pleuritic chest pain** that improves with **leaning forward**, along with a history of **poorly controlled SLE**, are classic for **acute pericarditis**.
- **Elevated JVP during inspiration (Kussmaul's sign)** suggests pericardial involvement with possible early effusion, though this sign is more classically associated with constrictive pericarditis or tamponade. However, the **characteristic ECG findings in acute pericarditis** are diffuse **ST segment elevations** (concave upward) and **PR segment depressions**, typically seen in leads II, III, aVF, and V2-V6.
- These ECG changes reflect the inflammatory process affecting the pericardium and are the hallmark of acute pericarditis, regardless of whether early effusion is present.
*Peaked T waves with flattened P waves*
- This pattern is characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, which presents with muscle weakness, fatigue, and cardiac arrhythmias, none of which are present in this case.
- The patient's presentation with pleuritic chest pain relieved by leaning forward is not consistent with hyperkalemia.
*Irregularly irregular QRS complexes with no P waves*
- This EKG pattern is indicative of **atrial fibrillation**, which presents with palpitations and may cause shortness of breath.
- While tachycardia is present, the irregular rhythm and absence of P waves characteristic of atrial fibrillation are not typical findings in acute pericarditis.
*ST segment depressions in leads II, III, and aVF*
- **ST segment depressions** in these leads typically suggest **inferior myocardial ischemia** or infarction, which would cause chest pain that is usually substernal, pressure-like, and not improved by positional changes.
- The pleuritic nature of the pain and its relief with leaning forward point away from ischemia.
*Prolonged PR interval with normal QRS complexes*
- A prolonged PR interval indicates **first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block**, which is usually asymptomatic and not associated with pleuritic chest pain.
- While SLE can be associated with conduction abnormalities, first-degree AV block would not explain the acute presentation or the characteristic pericarditis symptoms.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 2: A researcher measures action potential propagation velocity in various regions of the heart in a 42-year-old Caucasian female. Which of the following set of measurements corresponds to the velocities found in the atrial muscle, AV Node, Purkinje system, and ventricular muscle, respectively?
- A. 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3.3 m/s
- B. 2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s
- C. 0.3 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s
- D. 0.5 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3 m/s
- E. 1.1 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s (Correct Answer)
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***1.1 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s***
- This option correctly lists the approximate conduction velocities for the **atrial muscle (1.1 m/s)**, **AV node (0.05 m/s)**, **Purkinje system (2.2 m/s)**, and **ventricular muscle (0.3 m/s)**, respectively.
- The **AV node has the slowest conduction velocity (~0.05 m/s)**, which is crucial for delaying ventricular contraction and allowing complete ventricular filling.
- The **Purkinje system has the fastest conduction velocity (~2-4 m/s)**, ensuring rapid and coordinated ventricular depolarization.
- **Atrial muscle (~1 m/s)** and **ventricular muscle (~0.3-0.5 m/s)** have intermediate velocities.
*0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3.3 m/s*
- This sequence is incorrect because it places the **AV node's velocity (0.05 m/s)** first (as atrial muscle) and significantly overestimates ventricular muscle velocity (3.3 m/s).
- Atrial muscle conducts faster than 0.05 m/s, and ventricular muscle velocity should be approximately 0.3-0.5 m/s, not 3.3 m/s.
*2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s*
- This option incorrectly assigns the **highest velocity (2.2 m/s)** to atrial muscle, which is characteristic of the Purkinje system, and misplaces the **slowest velocity (0.05 m/s)** in the Purkinje system instead of the AV node.
- The values do not align with known physiological conduction speeds across cardiac tissues.
*0.3 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s*
- This sequence incorrectly places the **slowest velocity (0.05 m/s)** in the Purkinje system, which is known for the most rapid conduction, and assigns an unrealistically high velocity (2.2 m/s) to the AV node.
- The arrangement directly contradicts the physiological function and relative speeds within the cardiac conduction system.
*0.5 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3 m/s*
- This option underestimates the **atrial muscle velocity** (0.5 m/s instead of ~1 m/s) and significantly overestimates the **ventricular muscle velocity** (3 m/s instead of ~0.3-0.5 m/s).
- The provided values do not accurately represent the typical ranges of conduction velocities for each specified cardiac region.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 3: A 77-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with lightheadedness and a feeling that he is going to "pass out". He has a history of hypertension that is treated with captopril. In the office, his temperature is 38.3°C (100.9°F), the pulse is 65/min, and the respiratory rate is 19/min. His sitting blood pressure is 133/91 mm Hg. Additionally, his supine blood pressure is 134/92 mm Hg and standing blood pressure is 127/88 mm Hg. These are similar to his baseline blood pressure measured during previous visits. An ECG rhythm strip is obtained in the office. Of the following, what is the likely cause of his presyncope?
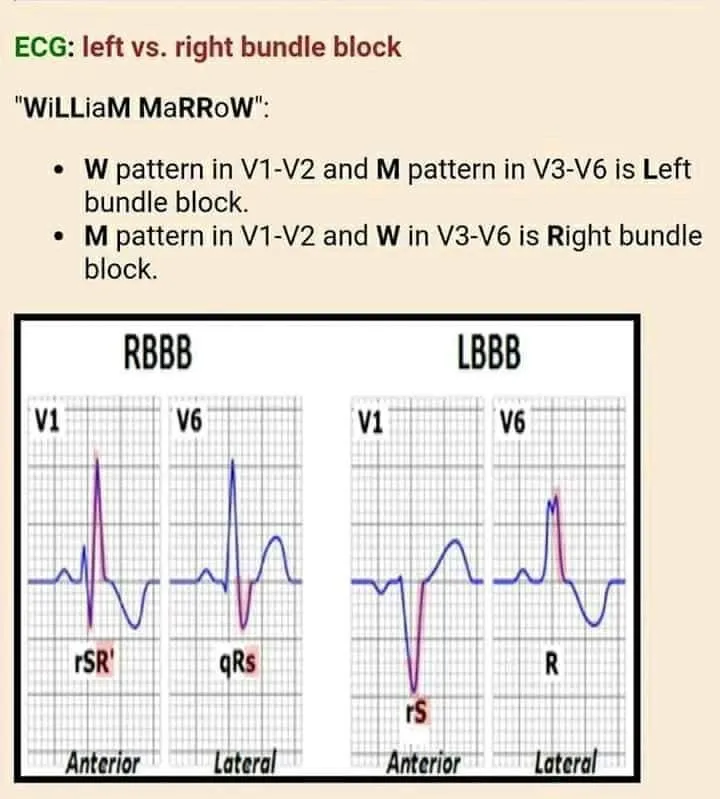
- A. Left bundle branch block
- B. Hypertension
- C. Captopril (Correct Answer)
- D. Right bundle branch block
- E. Orthostatic hypotension
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***Captopril***
- While **ACE inhibitors** like captopril can cause **vasodilation** and **hypotension** leading to presyncope, this patient's blood pressure readings are **stable and normal** (133/91, 134/92, 127/88 mmHg).
- There is **no evidence of hypotension** that would explain the presyncope, making captopril an unlikely direct cause in this presentation.
- **Note**: The clinical scenario of fever (38.3°C) with relative bradycardia (pulse 65/min) and presyncope actually suggests a **cardiac arrhythmia** (such as high-degree AV block), especially given that an ECG was obtained. However, this is not among the answer choices.
*Left bundle branch block*
- LBBB is an electrical conduction abnormality that typically does not directly cause presyncope unless it progresses to **high-degree AV block** or causes significant hemodynamic compromise.
- In the context of fever and relative bradycardia, if LBBB were associated with a bradyarrhythmia causing hemodynamic instability, it could contribute to presyncope.
- However, without the ECG findings mentioned in the stem, this cannot be confirmed.
*Hypertension*
- The patient's blood pressure is well-controlled and stable (ranging from 127-134/88-92 mmHg).
- Hypertension itself does not cause presyncope; in fact, **hypotension** (not hypertension) causes presyncope due to reduced cerebral perfusion.
- This is not the cause of his symptoms.
*Right bundle branch block*
- RBBB is generally **asymptomatic** and does not cause hemodynamic instability or presyncope.
- It is an incidental finding in most cases and would not explain the patient's symptoms of lightheadedness and near-syncope.
*Orthostatic hypotension*
- Orthostatic hypotension requires a drop in systolic BP ≥20 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥10 mmHg within 3 minutes of standing.
- This patient's BP changes from supine to standing (134/92 → 127/88 mmHg) show only a **7/4 mmHg drop**, which does **not meet diagnostic criteria**.
- Orthostatic hypotension is ruled out by the blood pressure measurements provided.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 4: The medical student on the pediatric cardiology team is examining a 9-year-old girl who was referred by her primary care physician for unexplained hypertension. She is accompanied by her mother who reveals that the child is generally well but has been significantly less active than her peers for the past year. On exam, the medical student notes a thin girl in no apparent distress appearing slightly younger than stated age. Vital signs reveal a BP is 160/80, HR 80, RR 16. Physical exam is notable only for a clicking sound is noted around the time of systole but otherwise the cardiac exam is normal. Pedal pulses could not be palpated. Which of the following physical exam findings was most likely missed by both the medical student and primary care physician?
- A. Long philtrum
- B. Prominent occiput
- C. Webbed neck (Correct Answer)
- D. Cleft palate
- E. Single palmar crease
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***Webbed neck***
- The combination of **hypertension** with **unpalpable pedal pulses** and a **systolic click** in a pediatric patient strongly suggests **coarctation of the aorta**.
- **Webbed neck** (or **pterygium colli**) is a classic phenotypic feature associated with **Turner syndrome**, which frequently co-occurs with coarctation of the aorta.
*Long philtrum*
- A **long philtrum** is a craniofacial feature sometimes associated with certain genetic syndromes like **fetal alcohol syndrome** or **Marfan syndrome**, but it is not specifically linked to coarctation of the aorta or Turner syndrome.
- While these syndromes can have cardiovascular manifestations, a long philtrum does not directly point to the specific findings presented.
*Prominent occiput*
- A **prominent occiput** is a non-specific finding that can be seen in various conditions, including some **chromosomal abnormalities** or **skeletal dysplasias**.
- It is not a characteristic feature of **Turner syndrome** or **coarctation of the aorta**.
*Cleft palate*
- **Cleft palate** is a birth defect affecting the roof of the mouth, often associated with a wide range of genetic or environmental factors.
- While patients with cleft palate can have associated congenital heart defects, it is not a direct or common association with **Turner syndrome** or **coarctation of the aorta**.
*Single palmar crease*
- A **single palmar crease** (simian crease) is a dermatoglyphic feature often associated with **Down syndrome** (Trisomy 21).
- While Down syndrome is associated with various congenital heart defects (e.g., AV septal defect), it is not typically associated with **coarctation of the aorta** or **Turner syndrome**.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 5: A cardiologist is studying how a new virus that infects the heart affects the electrical conduction system of the cardiac myocytes. He decides to obtain electrocardiograms on patients with this disease in order to see how the wave patterns and durations change over time. While studying these records, he asks a medical student who is working with him to interpret the traces. Specifically, he asks her to identify the part that represents initial ventricular depolarization. Which of the following characteristics is most consistent with this feature of the electrocardiogram?
- A. Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart
- B. Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia
- C. Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia
- D. Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds (Correct Answer)
- E. Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds***
- The question asks for the representation of **initial ventricular depolarization**, which corresponds to the **QRS complex** on an ECG.
- The normal duration of the **QRS complex** is typically less than **0.12 seconds (120 milliseconds)**, reflecting efficient ventricular depolarization.
*Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart*
- This description refers to the **ST segment elevation** seen in **ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)**, which represents myocardial injury, not initial ventricular depolarization.
- While related to cardiac electrical activity, **ST segment elevation** is a consequence of injury and refers to repolarization abnormalities, not the QRS complex itself.
*Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia*
- **Peaked T waves** are characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, indicating altered ventricular repolarization, not ventricular depolarization.
- The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, and its morphology changes significantly with potassium imbalances.
*Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia*
- A **prominent U wave** is sometimes observed in **hypokalemia**, which follows the T wave and is thought to represent repolarization of Purkinje fibers.
- The U wave is distinct from the QRS complex and does not represent initial ventricular depolarization.
*Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds*
- A duration of less than 200 milliseconds (0.20 seconds) typically refers to the normal duration of the **PR interval**, which represents atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node.
- The **QRS complex** (initial ventricular depolarization) has a shorter normal duration, typically less than 120 milliseconds.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 6: A researcher is studying how electrical activity propagates across the heart. In order to do this, he decides to measure the rate at which an action potential moves within various groups of cardiac muscle tissue. In particular, he isolates fibers from areas of the heart with the following characteristics:
A) Dysfunction leads to fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
B) Dysfunction leads to increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
C) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex
D) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram
Which of the following is the proper order of these tissues from fastest action potential propagation to slowest action potential propagation.
- A. B > D > C > A
- B. D > C > A > B
- C. B > C > D > A
- D. A > D > C > B (Correct Answer)
- E. A > C > D > B
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***A > D > C > B***
* **Purkinje fibers (A)** have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart to ensure rapid and synchronous ventricular depolarization. The description of "fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" in **Mobitz type II second-degree AV block** indicates an issue with conduction distal to the AV node, often in the His-Purkinje system, while still maintaining typical conduction through the atria and AV node for conducted beats.
* **Atrial muscle (D)** has a faster conduction velocity than the AV node but slower than Purkinje fibers. The "sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram" unequivocally points to **atrial flutter**, which is characterized by rapid, regular depolarization of the atria.
* **Ventricular muscle (C)** has a conduction velocity slower than Purkinje fibers but faster than the AV node. "Tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex" is characteristic of **ventricular tachycardia (VT)**, which arises from abnormal electrical activity within the ventricles.
* **AV node (B)** has the slowest conduction velocity in the heart, which allows for proper ventricular filling. "Increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" describes **Mobitz type I second-degree AV block (Wenckebach phenomenon)**, which is due to progressive prolongation of conduction delay within the AV node itself.
*B > D > C > A*
* This order incorrectly places the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest, which is contrary to the known conduction velocities in the heart.
* The AV node is critical for delaying the impulse, making it the slowest, while Purkinje fibers are designed for rapid spread, making them the fastest.
*D > C > A > B*
* This option incorrectly places **atrial muscle (D)** as faster than **Purkinje fibers (A)**. Purkinje fibers have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart, considerably faster than atrial muscle.
*B > C > D > A*
* This arrangement incorrectly lists the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest. The AV node is the slowest for its physiological role of delaying ventricular contraction, while Purkinje fibers are optimized for rapid conduction.
*A > C > D > B*
* While placing **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the fastest and the **AV node (B)** as the slowest is correct, this order incorrectly places **ventricular muscle (C)** as faster than **atrial muscle (D)**. Atrial muscle generally conducts faster than ventricular muscle in normal physiology.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 7: A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of intermittent palpitations and shortness of breath. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no other abnormalities. An ECG shows an absence of P waves, an oscillating baseline, and irregular RR intervals at a rate of approximately 95 beats per minute. The difference between atrial and ventricular rates in this patient is most likely due to which of the following?
- A. Prolonged influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the bundle of His
- B. Transient activation of K+ current in Purkinje fibers
- C. Inhibition of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump in ventricular cells
- D. Limited speed of conduction through the left bundle branch
- E. Temporary inactivation of Na+ channels in the AV node (Correct Answer)
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***Temporary inactivation of Na+ channels in the AV node***
- The ECG findings are classic for **atrial fibrillation**, characterized by a rapid, irregular atrial rhythm (oscillating baseline with no P waves) and an irregularly irregular ventricular response.
- The **AV node's refractory period** and the number of sodium channels available for conduction dictate the rate at which atrial impulses can pass to the ventricles, preventing a dangerously fast ventricular rate.
*Prolonged influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the bundle of His*
- The **bundle of His** primarily conducts impulses rather than primarily regulating the rate difference between atria and ventricles through calcium channel kinetics.
- Prolonged calcium influx would generally **slow conduction** or decrease excitability, but it's not the primary mechanism explaining the ventricular rate control in atrial fibrillation.
*Transient activation of K+ current in Purkinje fibers*
- **Purkinje fibers** are involved in rapid ventricular depolarization, but their primary role is not to mediate the rate difference between atria and ventricles in atrial fibrillation.
- Activation of K+ current typically leads to **repolarization**, affecting action potential duration, not the overall filtering of atrial impulses.
*Inhibition of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump in ventricular cells*
- Inhibition of the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump** would lead to intracellular sodium accumulation and depolarization, potentially causing arrhythmias, not regulating the ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation.
- This is the mechanism of action for **digoxin**, which can slow AV nodal conduction but through a different primary pathway affecting the pump.
*Limited speed of conduction through the left bundle branch*
- While conduction system abnormalities can occur, a **limited speed of conduction** specifically in the left bundle branch would cause a wide QRS complex or bundle branch block, not the inherent rate-limiting seen in atrial fibrillation.
- The AV node is the primary regulator of ventricular response rate in atrial fibrillation due to its inherent physiological properties.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator develops a new drug that decreases the number of voltage-gated potassium channels in cardiac muscle cell membranes. Which of the following is the most likely effect of this drug on the myocardial action potential?
- A. Delayed repolarization (Correct Answer)
- B. Delayed depolarization
- C. Accelerated repolarization
- D. Decreased resting membrane potential
- E. Accelerated depolarization
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***Delayed repolarization***
- **Voltage-gated potassium channels** are primarily responsible for the efflux of potassium ions during the **repolarization phase** (phase 3) of the cardiac action potential.
- A decrease in the number of these channels would reduce potassium efflux, thus slowing down the repolarization process and prolonging the **action potential duration**.
*Delayed depolarization*
- **Depolarization** (phase 0) of the cardiac action potential is primarily mediated by the rapid influx of **sodium ions** through voltage-gated sodium channels.
- Changes in potassium channels do not directly affect the speed of depolarization.
*Accelerated repolarization*
- Accelerated repolarization would occur if there were an *increase* in the number or activity of **potassium channels**, leading to a faster efflux of potassium ions.
- A *decrease* in these channels would have the opposite effect.
*Decreased resting membrane potential*
- The **resting membrane potential** is primarily maintained by the **leak potassium channels** and the **Na+/K+ ATPase pump**, not directly by voltage-gated potassium channels involved in repolarization.
- A decrease in voltage-gated potassium channels would not significantly alter the resting membrane potential.
*Accelerated depolarization*
- Accelerated depolarization would result from an *increase* in the speed or magnitude of **sodium influx** during phase 0.
- A reduction in potassium channels has no direct impact on the rate of sodium channel activation or current.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 9: A 17-year-old girl suddenly grabs her chest and collapses to the ground while playing volleyball at school. The teacher rushes to evaluate the situation and finds that the girl has no pulse and is not breathing. He starts chest compressions. An automated external defibrillator (AED) is brought to the scene within 3 minutes and a shock is delivered. The girl regains consciousness and regular sinus rhythm. She is rushed to the emergency department. The vital signs include: blood pressure 122/77 mm Hg and pulse 65/min. The pulse is regular. An electrocardiogram (ECG) shows a shortened PR interval, a wide QRS complex, a delta wave, and an inverted T wave. Which of the following is the most likely pathology in the conduction system of this patient’s heart?
- A. Impulse generation by tissue in atrioventricular node
- B. Accessory pathway from atria to ventricles (Correct Answer)
- C. Automatic discharge of irregular impulses in the atria
- D. Wandering atrial pacemaker
- E. Blockage in conduction pathway
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***Accessory pathway from atria to ventricles***
- The ECG findings of a **shortened PR interval**, **delta wave**, and **wide QRS complex** are characteristic of **Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome**, which involves an **accessory pathway** (Bundle of Kent) bypassing the AV node.
- This accessory pathway allows for pre-excitation of the ventricles, predisposing patients to **tachyarrhythmias** like the one experienced by the patient (sudden cardiac arrest).
*Impulse generation by tissue in atrioventricular node*
- This describes a **junctional rhythm**, which would present with a **normal or long PR interval** and a **narrow QRS complex**, contrasting with the given ECG findings.
- A junctional rhythm typically results in a slower heart rate and is not generally associated with sudden cardiac arrest in healthy individuals.
*Automatic discharge of irregular impulses in the atria*
- This typically refers to **atrial fibrillation** or multifocal atrial tachycardia, which would show an **irregularly irregular rhythm** or multiple P-wave morphologies, not the specific PR and QRS abnormalities seen.
- While atrial fibrillation can occur with WPW, the primary pathology described by the ECG findings is the accessory pathway itself.
*Wandering atrial pacemaker*
- A **wandering atrial pacemaker** is characterized by varying P-wave morphology and PR intervals as the pacemaker shifts between different atrial sites, but it generally maintains a normal QRS duration.
- It is typically a benign arrhythmia and does not cause the pre-excitation or the risk of sudden cardiac death seen in this patient.
*Blockage in conduction pathway*
- A **blockage in the conduction pathway** (e.g., AV block) would result in a **prolonged PR interval** or dropped QRS complexes, which is the opposite of the shortened PR interval observed.
- While heart block can cause syncope, it wouldn't explain the pre-excitation pattern (delta wave, wide QRS) seen in the ECG.
Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG Question 10: A 55-year-old man presents to his physician with weakness and fatigue for 1 week. There is no significant past medical history. He mentions that he is very health conscious and has heard about the health benefits of juices. He is following a juice-only diet for the last 2 weeks. His physical examination is completely normal, except for depressed deep tendon reflexes. The only abnormality in a complete laboratory evaluation is a serum potassium level of 6.0 mEq/L (6.0 mmol/L). There are significantly peaked T-waves on ECG. Which of the following pathophysiologic mechanisms best explains the patient’s symptoms?
- A. Decreased resting membrane potential of skeletal muscle cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Prolonged release of Ca2+ ions after stimulation of Ryanodine receptors
- C. Hyperpolarization of skeletal muscle cells
- D. Dysfunction of Na+ channels
- E. Dysfunction of dystrophin-glycoprotein complex
Bundle branch blocks Explanation: ***Decreased resting membrane potential of skeletal muscle cells***
- The patient's **hyperkalemia** (serum potassium 6.0 mEq/L), evidenced by peaked T-waves, reduces the electrochemical gradient for potassium, making the **resting membrane potential less negative (more depolarized)**.
- While seemingly contradictory, a persistent partial depolarization due to high extracellular potassium can lead to inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing the generation of new action potentials and causing **muscle weakness and depressed reflexes**.
*Prolonged release of Ca2+ ions after stimulation of Ryanodine receptors*
- This mechanism is associated with conditions like **malignant hyperthermia** or certain myopathies, characterized by muscle rigidity, cramps, or excessive heat production, which are not seen here.
- Hyperkalemia primarily affects **membrane excitability** rather than intracellular calcium release pathways directly.
*Hyperpolarization of skeletal muscle cells*
- **Hyperpolarization** would make the resting membrane potential more negative, making it harder to reach the threshold for an action potential, leading to weakness.
- This typically occurs in conditions causing **hypokalemia**, as a lower extracellular potassium concentration increases the electrochemical gradient and causes a net efflux of potassium ions.
*Dysfunction of Na+ channels*
- Dysfunction of **sodium channels** can cause various neuromuscular disorders, including periodic paralysis or myotonic conditions.
- While hyperkalemia indirectly affects sodium channel function by altering the resting membrane potential, the primary pathophysiologic insult here is the altered potassium gradient, not an intrinsic channel defect.
*Dysfunction of dystrophin-glycoprotein complex*
- This complex is crucial for maintaining muscle fiber integrity and is defective in **muscular dystrophies** (e.g., Duchenne muscular dystrophy).
- Such conditions cause progressive muscle degeneration and weakness, which develop over a much longer period than the acute symptoms described here and are not related to electrolyte imbalances.
More Bundle branch blocks US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.