Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Compliance measurement techniques. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 1: A 60-year-old woman with a history of emphysema has been referred by her pulmonologist for follow-up pulmonary function testing. During the test, the patient reaches a point where her airway pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure. Which of the following is most likely to be found during this respiratory state?
- A. Pulmonary vascular resistance is at a maximum
- B. Transmural pressure of the lung-chest wall system is at a maximum
- C. Transmural pressure of the chest wall is at a minimum
- D. Pulmonary vascular resistance is at a minimum (Correct Answer)
- E. Transmural pressure of the lung-chest wall system is at a minimum
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Pulmonary vascular resistance is at a minimum***
- When airway pressure equals atmospheric pressure during a pulmonary function test, the lungs are at **functional residual capacity (FRC)** or resting state.
- At FRC, **pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR)** is at its lowest point due to the optimal balance between alveolar and extra-alveolar vessel compression/distension.
- Extra-alveolar vessels are compressed at low lung volumes, while alveolar vessels are compressed at high lung volumes. At FRC, both are optimally distended, resulting in **minimal PVR**.
*Pulmonary vascular resistance is at a maximum*
- PVR increases at very low lung volumes (due to extra-alveolar vessel compression) and very high lung volumes (due to alveolar vessel compression).
- The resting state (airway pressure equals atmospheric pressure) corresponds to FRC, where PVR is **minimal, not maximal**.
*Transmural pressure of the lung-chest wall system is at a maximum*
- Transmural pressure of the lung-chest wall system represents the pressure difference across the entire respiratory system.
- This pressure is higher during inspiration or forced expiration when the system is stretched or compressed.
- At FRC (airway pressure equals atmospheric pressure), the system is at **resting equilibrium**, not at maximal transmural pressure.
*Transmural pressure of the chest wall is at a minimum*
- Transmural pressure across the chest wall is the difference between intrapleural pressure and atmospheric pressure.
- This pressure is not at a minimum when airway pressure equals atmospheric pressure.
- Chest wall transmural pressure is actually minimal near **residual volume (RV)**, where the chest wall recoils inward most strongly.
*Transmural pressure of the lung-chest wall system is at a minimum*
- Transmural pressure of the lung-chest wall system reflects the elastic recoil forces of the combined system.
- At FRC (airway pressure equals atmospheric pressure), elastic recoil forces are balanced at equilibrium, but transmural pressure is **not at a minimum**—it represents the neutral resting state.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 2: A 57-year-old man presents to the clinic for a chronic cough over the past 4 months. The patient reports a productive yellow/green cough that is worse at night. He denies any significant precipitating event prior to his symptoms. He denies fever, chest pain, palpitations, weight changes, or abdominal pain, but endorses some difficulty breathing that waxes and wanes. He denies alcohol usage but endorses a 35 pack-year smoking history. A physical examination demonstrates mild wheezes, bibasilar crackles, and mild clubbing of his fingertips. A pulmonary function test is subsequently ordered, and partial results are shown below:
Tidal volume: 500 mL
Residual volume: 1700 mL
Expiratory reserve volume: 1500 mL
Inspiratory reserve volume: 3000 mL
What is the functional residual capacity of this patient?
- A. 4500 mL
- B. 2000 mL
- C. 2200 mL
- D. 3200 mL (Correct Answer)
- E. 3500 mL
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***3200 mL***
- The **functional residual capacity (FRC)** is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration.
- It is calculated as the sum of the **expiratory reserve volume (ERV)** and the **residual volume (RV)**. In this case, 1500 mL (ERV) + 1700 mL (RV) = 3200 mL.
*4500 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **inspiratory reserve volume (3000 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which does not correspond to a standard lung volume or capacity.
- It does not logically relate to the definition of functional residual capacity.
*2000 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, which is incorrect for FRC.
- This would represent the inspiratory capacity minus the inspiratory reserve volume, which is not a standard measurement used in pulmonary function testing.
*2200 mL*
- This value could be obtained by incorrectly adding the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which is not the correct formula for FRC.
- This calculation represents a miscombination of lung volumes that does not correspond to any standard pulmonary capacity measurement.
*3500 mL*
- This value is the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)**, the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**.
- This would represent the FRC plus the tidal volume, which is not a standard measurement and does not represent the functional residual capacity.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 3: A 45-year-old man with a 15-pack-year smoking history is referred for pulmonary function testing. On physical exam, he appears barrel-chested and mildly overweight, but breathes normally. Which of the following tests will most accurately measure his total lung capacity?
- A. Exhaled nitric oxide
- B. Closed-circuit helium dilution
- C. Spirometry
- D. Body plethysmography (Correct Answer)
- E. Open-circuit nitrogen washout
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Body plethysmography***
- This method accurately measures **total lung capacity (TLC)** by applying **Boyle's Law**, assessing pressure and volume changes within an enclosed chamber.
- It is superior to gas dilution methods for patients with **air trapping** or **poor ventilation distribution**, as it measures all gas in the chest, including trapped air.
*Exhaled nitric oxide*
- This test measures **airway inflammation**, particularly in conditions like asthma, but does not assess lung volumes.
- It is useful for monitoring treatment response and disease severity but does not provide information about **Total Lung Capacity (TLC)**.
*Closed-circuit helium dilution*
- This method estimates **lung volumes** by diluting a known concentration of helium, but it underestimates **TLC** in patients with significant **air trapping** because helium cannot equilibrate with unventilated areas.
- Given the patient's **barrel chest** suggestive of air trapping, this method would be less accurate for measuring his true TLC.
*Spirometry*
- Spirometry measures **forced vital capacity (FVC)** and **forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1)**, which are dynamic lung volumes reflecting airflow limitation.
- It does not directly measure **Total Lung Capacity (TLC)** or **residual volume**, as it cannot measure the air remaining in the lungs after maximal exhalation.
*Open-circuit nitrogen washout*
- This method estimates **functional residual capacity (FRC)** by washing out nitrogen from the lungs with 100% oxygen, but like helium dilution, it can underestimate volumes in patients with **air trapping**.
- It provides an estimate of the gas that communicates with the airways, excluding any **trapped gas**.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 4: A 32-year-old woman comes to the physician for a screening health examination that is required for scuba diving certification. The physician asks her to perform a breathing technique: following deep inspiration, she is instructed to forcefully exhale against a closed airway and contract her abdominal muscles while different cardiovascular parameters are evaluated. Which of the following effects is most likely after 10 seconds in this position?
- A. Decreased intra-abdominal pressure
- B. Decreased left ventricular stroke volume (Correct Answer)
- C. Decreased pulse rate
- D. Decreased systemic vascular resistance
- E. Increased venous return to left atrium
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Decreased left ventricular stroke volume***
- After 10 seconds of performing the **Valsalva maneuver**, the increased intrathoracic pressure significantly reduces **venous return** to the heart.
- Reduced venous return leads to decreased **ventricular filling** (preload), which in turn diminishes **left ventricular stroke volume** and cardiac output.
*Decreased intra-abdominal pressure*
- The instruction to "contract her abdominal muscles" during forceful exhalation against a closed airway (Valsalva maneuver) directly leads to an **increase** in **intra-abdominal pressure**, not a decrease.
- This increase in intra-abdominal pressure further impedes venous return from the lower extremities to the heart.
*Decreased pulse rate*
- In the initial phase of the Valsalva maneuver (first 5-10 seconds), the decrease in cardiac output triggers a **reflex tachycardia** to maintain blood pressure, leading to an **increased pulse rate**.
- A decrease in pulse rate (bradycardia) is more characteristic of the release phase, not during the sustained strain.
*Decreased systemic vascular resistance*
- During the Valsalva maneuver, the body attempts to compensate for the drop in cardiac output and blood pressure by increasing **sympathetic tone**, which causes **vasoconstriction** and thus **increases systemic vascular resistance**.
- A decrease in systemic vascular resistance would further drop blood pressure and is not the physiological response during this phase.
*Increased venous return to left atrium*
- The Valsalva maneuver dramatically **reduces venous return** to both the right and left atria due to the high intrathoracic pressure compressing the great veins.
- This decreased venous return is the primary mechanism leading to the subsequent fall in cardiac output during the maneuver.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 5: A 72-year-old obese man presents as a new patient to his primary care physician because he has been feeling tired and short of breath after recently moving to Denver. He is a former 50 pack-year smoker and has previously had deep venous thrombosis. Furthermore, he previously had a lobe of the lung removed due to lung cancer. Finally, he has a family history of a progressive restrictive lung disease. Laboratory values are obtained as follows:
Oxygen tension in inspired air = 130 mmHg
Alveolar carbon dioxide tension = 48 mmHg
Arterial oxygen tension = 58 mmHg
Respiratory exchange ratio = 0.80
Respiratory rate = 20/min
Tidal volume = 500 mL
Which of the following mechanisms is consistent with these values?
- A. Shunt physiology
- B. High altitude
- C. V/Q mismatch
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Hypoventilation (Correct Answer)
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Hypoventilation***
- The arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) of 58 mmHg is consistent with hypoxemia, and the alveolar carbon dioxide tension (PACO2) of 48 mmHg (normal 35-45 mmHg) indicates **hypercapnia**, a hallmark of hypoventilation.
- The **alveolar-arterial (A-a) gradient** can be calculated using the alveolar gas equation: PAO2 = PiO2 - PACO2/R. Here, PAO2 = 130 mmHg - 48 mmHg/0.8 = 130 - 60 = 70 mmHg. The A-a gradient is PAO2 - PaO2 = 70 - 58 = 12 mmHg, which is within the normal range (5-15 mmHg), indicating that the hypoxemia is primarily due to **decreased alveolar ventilation**.
*Shunt physiology*
- A shunt would cause a significant reduction in PaO2 and a **widened A-a gradient** (typically >15 mmHg) due to deoxygenated blood bypassing ventilated areas.
- While shunts do not typically cause hypercapnia unless very severe, the normal A-a gradient here rules out a significant shunt as the primary mechanism for hypoxemia.
*High altitude*
- Moving to a high altitude (like Denver) causes a decrease in **inspired oxygen tension (PiO2)**, leading to hypoxemia.
- However, the provided inspired oxygen tension (130 mmHg) is above what would be expected for significant high-altitude hypoxemia at sea level equivalent, and the hypoxemia here is associated with hypercapnia, which is not a direct result of high altitude itself.
*V/Q mismatch*
- A V/Q mismatch leads to hypoxemia and a **widened A-a gradient**, as some areas of the lung are either underventilated or underperfused.
- While it can cause hypoxemia, a V/Q mismatch is typically associated with **normal or low PaCO2** due to compensatory hyperventilation, not hypercapnia, and the A-a gradient would be elevated.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- Pulmonary fibrosis is a restrictive lung disease that leads to impaired gas exchange, causing hypoxemia primarily due to **V/Q mismatch** and **diffusion limitation**.
- This would result in a **widened A-a gradient** and often a **low PaCO2** due to compensatory hyperventilation, rather than the elevated PaCO2 observed in this patient.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 6: A 21-year-old lacrosse player comes to the doctor for an annual health assessment. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She is 160 cm (5 ft 3 in) tall and weighs 57 kg (125 lb); BMI is 22 kg/m2. Pulmonary function tests show an FEV1 of 90% and an FVC of 3600 mL. Whole body plethysmography is performed to measure airway resistance. Which of the following structures of the respiratory tree is likely to have the highest contribution to total airway resistance?
- A. Conducting bronchioles
- B. Terminal bronchioles
- C. Segmental bronchi (Correct Answer)
- D. Respiratory bronchioles
- E. Mainstem bronchi
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Segmental bronchi***
- In healthy individuals, **medium-sized bronchi** (including segmental and subsegmental bronchi, approximately generations 4-8) contribute approximately **80% of total airway resistance**.
- While **Poiseuille's Law** states resistance is inversely proportional to radius to the fourth power (R ∝ 1/r⁴), the key factor is the **total cross-sectional area** and **degree of branching**.
- Medium-sized bronchi have moderate individual resistance and **limited parallel branching**, making them the dominant site of resistance.
- This is why diseases affecting medium-sized airways (e.g., asthma, bronchitis) cause significant increases in airway resistance.
*Terminal bronchioles*
- Although individual terminal bronchioles have small radii and high individual resistance, there are **millions of them arranged in parallel**.
- With parallel resistances, total resistance decreases: 1/R_total = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃...
- The **massive number** of small airways means their collective resistance is actually quite **low** (~10-20% of total).
- This is why small airways disease is called the "**silent zone**" - significant pathology can occur before detection.
*Conducting bronchioles*
- These airways also benefit from extensive **parallel branching**, reducing their contribution to total resistance.
- They contribute less than medium-sized bronchi due to their large cumulative cross-sectional area.
*Respiratory bronchioles*
- Part of the **respiratory zone** with the largest total cross-sectional area in the lungs.
- Minimal contribution to airway resistance due to enormous parallel arrangement.
- Primary function is **gas exchange**, not air conduction.
*Mainstem bronchi*
- These large airways have **low individual resistance** due to large diameter.
- Together with the trachea, they contribute approximately **20% of total airway resistance**.
- Not the primary site despite being early in the airway tree.
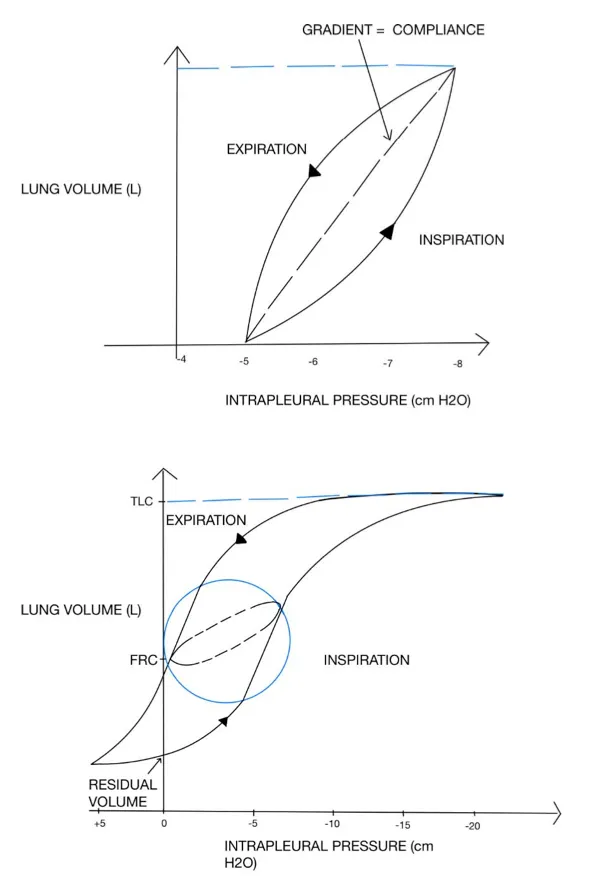
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 7: A 35-year-old woman volunteers for a study on respiratory physiology. Pressure probes A and B are placed as follows:
Probe A: between the parietal and visceral pleura
Probe B: within the cavity of an alveolus
The probes provide a pressure reading relative to atmospheric pressure. To obtain a baseline reading, she is asked to sit comfortably and breathe normally. Which of the following sets of values will most likely be seen at the end of inspiration?
- A. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- C. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg
- D. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- E. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg***
- At the **end of inspiration**, the **intrapleural pressure (Probe A)** is at its most negative, typically around -6 to -8 cm H2O (equivalent to -4 to -6 mmHg), reflecting the maximum expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- At the **end of inspiration**, just before exhalation begins, there is **no airflow**, so the **intrapulmonary pressure (Probe B)** equalizes with atmospheric pressure, resulting in a 0 mm Hg reading.
*Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of 0 mm Hg** would indicate a **pneumothorax** since it should always be negative to prevent lung collapse.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** would indicate that **inspiration is still ongoing**, as air would be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapulmonary pressure of 0 mm Hg** is correct at the end of inspiration, an **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is typical for the **end of expiration (Functional Residual Capacity)** during quiet breathing, not the end of inspiration.
- The **intrapleural pressure becomes more negative** during inspiration due to increased thoracic volume, so -4 mm Hg would be insufficient.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is the normal pressure at the **end of expiration**, not the end of inspiration, where it becomes more negative.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** indicates that **inspiration is still in progress**, not at its end, as air would still be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapleural pressure of -6 mm Hg** is consistent with the end of inspiration, an **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** means that **airflow is still occurring into the lungs**.
- At the **very end of inspiration**, just before the start of exhalation, airflow momentarily ceases, and intrapulmonary pressure becomes zero relative to the atmosphere.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 8: A 68-year-old man with both severe COPD (emphysema) and newly diagnosed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis presents with worsening dyspnea. His pressure-volume curve shows a complex pattern with features of both diseases. Static compliance measured at mid-lung volumes is 120 mL/cm H2O. His pulmonologist must decide on optimal management. Synthesizing the pathophysiology of both conditions, what represents the most significant clinical challenge in managing his combined disease?
- A. Pulmonary rehabilitation cannot address the opposing mechanical derangements
- B. The increased compliance from emphysema completely negates decreased compliance from fibrosis
- C. The opposing effects on compliance create a pseudonormal total respiratory compliance masking disease severity (Correct Answer)
- D. Emphysema treatment with bronchodilators will worsen fibrosis progression
- E. Oxygen therapy beneficial for COPD will accelerate fibrotic changes
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***The opposing effects on compliance create a pseudonormal total respiratory compliance masking disease severity***
- In **Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema (CPFE)**, the **increased lung compliance** from upper-lobe emphysema is offset by the **decreased compliance** from lower-lobe fibrosis.
- This results in a **pseudonormalization** of lung volumes (like FVC and TLC) and compliance measurements, which can lead to a significant **underestimation of disease severity** during clinical assessment.
*Pulmonary rehabilitation cannot address the opposing mechanical derangements*
- While mechanical derangements are complex, **pulmonary rehabilitation** remains a cornerstone of management to improve functional capacity and reduce dyspnea in both conditions.
- The challenge is not that rehabilitation is ineffective, but rather the **physiological monitoring** and objective assessment of progress are hampered by masked lung volumes.
*The increased compliance from emphysema completely negates decreased compliance from fibrosis*
- The two forces do not perfectly negate each other; rather, they coexist to produce a **paradoxical physiological profile** where static measurements appear mid-range while gas exchange is severely impaired.
- Patients often exhibit a **disproportionate reduction in DLCO** (diffusion capacity) despite relatively preserved lung volumes, indicating the negation is only superficial and numerical.
*Emphysema treatment with bronchodilators will worsen fibrosis progression*
- There is no clinical evidence suggesting that **bronchodilators** (beta-agonists or anticholinergics) used for COPD/emphysema accelerate the **pathological scarring** seen in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- Bronchodilators primarily target **airway smooth muscle** and do not interfere with the fibroblastic pathways driving interstitial lung disease.
*Oxygen therapy beneficial for COPD will accelerate fibrotic changes*
- **Long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT)** is used to treat chronic hypoxemia in both COPD and fibrosis and does not cause or accelerate **lung remodeling** or fibrosis.
- While high concentrations of inspired oxygen (FiO2) can cause **oxidative stress**, the flow rates used for clinical management do not contribute to the progression of pulmonary fibrosis.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 9: A 42-year-old woman with systemic sclerosis develops both pulmonary fibrosis and chest wall restriction from skin thickening. Her measured total respiratory system compliance is 30 mL/cm H2O. Testing with complete paralysis and positive pressure ventilation shows isolated lung compliance of 50 mL/cm H2O. She is being considered for immunosuppressive therapy versus supportive care. Evaluate which intervention would provide the greatest improvement in her respiratory mechanics.
- A. Supportive care only, as both components contribute equally and irreversibly
- B. Combined therapy targeting lung disease with chest wall mobilization (Correct Answer)
- C. Aggressive immunosuppression targeting both lung and skin disease
- D. Lung-directed therapy only, as it contributes more to total compliance reduction
- E. Chest wall-directed physical therapy, as it is the primary limiting factor
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Combined therapy targeting lung disease with chest wall mobilization*** - The total respiratory compliance (Ct) is calculated using the formula **1/Ct = 1/Clung + 1/Cchest wall**; here, 1/30 = 1/50 + 1/Ccw, which calculates the **chest wall compliance** as 75 mL/cm H2O. - Both the lungs (50 mL/cm H2O) and chest wall (75 mL/cm H2O) are significantly below the **normal value of ~200 mL/cm H2O**, meaning both require intervention for meaningful improvement. *Supportive care only, as both components contribute equally and irreversibly* - While both contribute, they are not strictly equal (50 vs 75), and **systemic sclerosis**-associated lung/skin disease may respond to modern therapeutic interventions. - Labeling these as **irreversible** ignores potential benefits from immunosuppression in the active inflammatory stages of **interstitial lung disease**. *Aggressive immunosuppression targeting both lung and skin disease* - While immunosuppression addresses the underlying **pathophysiology**, it may not provide immediate mechanical relief for fixed **chest wall restriction**. - Effective management often requires adding **physical therapy** and mobilization to address the extrinsic mechanical constraint caused by **scleroderma skin thickening**. *Lung-directed therapy only, as it contributes more to total compliance reduction* - Although lung compliance (50) is lower than chest wall compliance (75), ignoring the **chest wall component** neglects a significant portion of the patient's **work of breathing**. - Solely treating the lung disease will not bypass the **extrinsic restriction** imposed by the tight skin and musculoskeletal changes. *Chest wall-directed physical therapy, as it is the primary limiting factor* - The calculations show that **lung compliance** is actually more severely reduced (50) than chest wall compliance (75). - Focusing only on the **chest wall** would leave the primary cause of the **restrictive ventilatory defect** (pulmonary fibrosis) unaddressed.
Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old man with end-stage pulmonary fibrosis is being evaluated for lung transplantation. His current static compliance is 25 mL/cm H2O (normal: 200 mL/cm H2O). He also has mild obesity (BMI 32) and ankylosing spondylitis affecting chest wall mobility. Post-transplant, assuming successful bilateral lung transplant with normal donor lungs, what would be the expected change in his total respiratory system compliance?
- A. Improved lung compliance but worsened chest wall compliance from surgery
- B. Worse compliance initially due to transplant rejection and denervation
- C. Return to completely normal respiratory compliance matching healthy individuals
- D. Improved but still reduced compliance due to persistent chest wall restriction (Correct Answer)
- E. No significant change because the primary problem is muscular weakness
Compliance measurement techniques Explanation: ***Improved but still reduced compliance due to persistent chest wall restriction***
- Total respiratory system compliance follows the formula **1/C_total = 1/C_lungs + 1/C_chest_wall**, meaning the total compliance is limited by the stiffest component.
- While the lung transplant corrects the **pulmonary fibrosis**, the patient's **obesity** and **ankylosing spondylitis** cause extrinsic restriction that maintains a low **chest wall compliance**.
*Improved lung compliance but worsened chest wall compliance from surgery*
- Although surgical trauma can temporarily affect chest wall dynamics, the **ankylosing spondylitis** is the primary chronic factor limiting chest wall expansion here.
- The logic is flawed because the improvement in **lung compliance** from the donor lungs far outweighs any minor surgical stiffness in the long term.
*Worse compliance initially due to transplant rejection and denervation*
- **Denervation** typically leads to loss of the cough reflex but does not significantly alter the mechanical **elasticity** or compliance of the lung tissue itself.
- Acute rejection would decrease compliance, but the question asks for the "expected" outcome of a **successful bilateral transplant**.
*Return to completely normal respiratory compliance matching healthy individuals*
- Total compliance cannot return to normal because the **chest wall** remains stiff due to the patient's underlying skeletal and adipose conditions.
- Even with perfect donor lungs, the **extrapulmonary restriction** means the total system compliance will remain below the normal **200 mL/cm H2O**.
*No significant change because the primary problem is muscular weakness*
- The patient's primary problem in the lungs was **pulmonary fibrosis**, which is a mechanical parenchymal issue, not purely muscular weakness.
- Total compliance will definitely show a **significant increase** from the baseline of 25 mL/cm H2O because the severely stiff fibrotic lungs have been replaced.
More Compliance measurement techniques US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.