Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Chest wall compliance. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 1: An 85-year-old man with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of shortness of breath. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years. His temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), pulse is 100/min, respirations are 30/min, and blood pressure is 138/75 mm Hg. Pulmonary function testing shows decreased tidal volume and normal lung compliance. Which of the following is the most likely underlying etiology of this patient's tachypnea?
- A. Diabetic ketoacidosis
- B. Rib fracture
- C. Pulmonary edema (Correct Answer)
- D. Emphysema exacerbation
- E. Tension pneumothorax
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***Pulmonary edema***
- This patient's **hypertension** and **diabetes** are major risk factors for heart failure, and the acute onset of **shortness of breath** with **tachypnea** suggests cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
- **Decreased tidal volume** occurs because fluid accumulation in the interstitium and alveoli reduces functional lung capacity, prompting rapid, shallow breathing to maintain minute ventilation.
- While pulmonary edema typically causes **decreased lung compliance** due to fluid-stiffened lungs, early or mild cases may show relatively preserved compliance, or the normal compliance here may reflect measurement timing or technique. The clinical picture and decreased tidal volume strongly support pulmonary edema.
- The combination of cardiac risk factors, acute dyspnea, tachypnea, and altered breathing pattern make this the most likely diagnosis.
*Diabetic ketoacidosis*
- DKA causes **Kussmaul respirations** (deep, labored breathing) to compensate for metabolic acidosis, not the shallow breathing pattern (decreased tidal volume) seen here.
- DKA typically presents with polyuria, polydipsia, abdominal pain, nausea, and fruity breath odor, which are not mentioned.
- While this patient has diabetes, the respiratory pattern and absence of typical DKA symptoms make this less likely.
*Rib fracture*
- Rib fractures cause **pleuritic chest pain** that worsens with breathing, leading to voluntary splinting and reduced tidal volume.
- However, there is **no history of trauma** or chest pain reported.
- Pain from rib fractures would be localized, and the acute 2-day onset of dyspnea without trauma makes this unlikely.
*Emphysema exacerbation*
- Emphysema is characterized by **increased lung compliance** (hyperinflation) due to alveolar wall destruction, which contradicts the normal compliance finding.
- While the patient has a significant smoking history, the **normal lung compliance** argues against emphysema.
- COPD exacerbations typically present with wheezing, productive cough, and hyperinflation, not decreased tidal volume with normal compliance.
*Tension pneumothorax*
- Tension pneumothorax presents with **severe respiratory distress**, unilateral absent breath sounds, **hypotension**, tracheal deviation, and jugular venous distension.
- This patient's **blood pressure is normal** (138/75 mm Hg) and there's no mention of absent breath sounds or hemodynamic compromise.
- The clinical presentation does not support this life-threatening emergency.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 2: A 57-year-old man presents to the clinic for a chronic cough over the past 4 months. The patient reports a productive yellow/green cough that is worse at night. He denies any significant precipitating event prior to his symptoms. He denies fever, chest pain, palpitations, weight changes, or abdominal pain, but endorses some difficulty breathing that waxes and wanes. He denies alcohol usage but endorses a 35 pack-year smoking history. A physical examination demonstrates mild wheezes, bibasilar crackles, and mild clubbing of his fingertips. A pulmonary function test is subsequently ordered, and partial results are shown below:
Tidal volume: 500 mL
Residual volume: 1700 mL
Expiratory reserve volume: 1500 mL
Inspiratory reserve volume: 3000 mL
What is the functional residual capacity of this patient?
- A. 4500 mL
- B. 2000 mL
- C. 2200 mL
- D. 3200 mL (Correct Answer)
- E. 3500 mL
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***3200 mL***
- The **functional residual capacity (FRC)** is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration.
- It is calculated as the sum of the **expiratory reserve volume (ERV)** and the **residual volume (RV)**. In this case, 1500 mL (ERV) + 1700 mL (RV) = 3200 mL.
*4500 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **inspiratory reserve volume (3000 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which does not correspond to a standard lung volume or capacity.
- It does not logically relate to the definition of functional residual capacity.
*2000 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, which is incorrect for FRC.
- This would represent the inspiratory capacity minus the inspiratory reserve volume, which is not a standard measurement used in pulmonary function testing.
*2200 mL*
- This value could be obtained by incorrectly adding the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which is not the correct formula for FRC.
- This calculation represents a miscombination of lung volumes that does not correspond to any standard pulmonary capacity measurement.
*3500 mL*
- This value is the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)**, the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**.
- This would represent the FRC plus the tidal volume, which is not a standard measurement and does not represent the functional residual capacity.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 3: A 35-year-old woman volunteers for a study on respiratory physiology. Pressure probes A and B are placed as follows:
Probe A: between the parietal and visceral pleura
Probe B: within the cavity of an alveolus
The probes provide a pressure reading relative to atmospheric pressure. To obtain a baseline reading, she is asked to sit comfortably and breathe normally. Which of the following sets of values will most likely be seen at the end of inspiration?
- A. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- C. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg
- D. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- E. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg***
- At the **end of inspiration**, the **intrapleural pressure (Probe A)** is at its most negative, typically around -6 to -8 cm H2O (equivalent to -4 to -6 mmHg), reflecting the maximum expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- At the **end of inspiration**, just before exhalation begins, there is **no airflow**, so the **intrapulmonary pressure (Probe B)** equalizes with atmospheric pressure, resulting in a 0 mm Hg reading.
*Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of 0 mm Hg** would indicate a **pneumothorax** since it should always be negative to prevent lung collapse.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** would indicate that **inspiration is still ongoing**, as air would be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapulmonary pressure of 0 mm Hg** is correct at the end of inspiration, an **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is typical for the **end of expiration (Functional Residual Capacity)** during quiet breathing, not the end of inspiration.
- The **intrapleural pressure becomes more negative** during inspiration due to increased thoracic volume, so -4 mm Hg would be insufficient.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is the normal pressure at the **end of expiration**, not the end of inspiration, where it becomes more negative.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** indicates that **inspiration is still in progress**, not at its end, as air would still be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapleural pressure of -6 mm Hg** is consistent with the end of inspiration, an **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** means that **airflow is still occurring into the lungs**.
- At the **very end of inspiration**, just before the start of exhalation, airflow momentarily ceases, and intrapulmonary pressure becomes zero relative to the atmosphere.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 4: In which of the following pathological states would the oxygen content of the trachea resemble the oxygen content in the affected alveoli?
- A. Emphysema
- B. Exercise
- C. Pulmonary embolism (Correct Answer)
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***Pulmonary embolism***
- A pulmonary embolism blocks **blood flow** to a portion of the lung, creating **dead space ventilation** (high V/Q ratio).
- In the affected alveoli, **no blood perfusion** means no oxygen extraction occurs, so the alveolar oxygen content remains **high and similar to tracheal/inspired air**.
- This is the classic physiological state where ventilation continues but perfusion is absent, preventing gas exchange.
*Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea*
- A complete obstruction **prevents fresh air** from reaching the affected alveoli.
- The trapped gas undergoes **resorption atelectasis**: oxygen is absorbed into capillary blood, CO2 diffuses in, and alveolar gas equilibrates with **venous blood** composition.
- Alveolar oxygen content becomes **very low**, not similar to tracheal air.
*Emphysema*
- Emphysema involves destruction of **alveolar walls** and enlargement of airspaces with impaired gas exchange.
- While V/Q mismatch occurs, oxygen is still extracted by perfusing blood.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air** due to ongoing (though inefficient) gas exchange.
*Exercise*
- During exercise, **oxygen consumption increases** dramatically with enhanced cardiac output and oxygen extraction.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **significantly lower** than tracheal air due to increased oxygen uptake by blood.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- Pulmonary fibrosis causes **thickening of the alveolar-capillary membrane**, impairing oxygen diffusion.
- Despite diffusion limitation, blood still perfuses the alveoli and extracts oxygen.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air**, though the A-a gradient is increased.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old man undergoes workup for nocturnal dyspnea and what he describes as a "choking" sensation while sleeping. He also endorses fatigue and dyspnea on exertion. Physical exam reveals a normal S1, loud P2, and a neck circumference of 17 inches (43 cm) (normal < 14 inches (< 35 cm)). His temperature is 98.8°F (37°C), blood pressure is 128/82 mmHg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 19/min. He undergoes spirometry, which is unrevealing, and polysomnography, which shows 16 hypopneic and apneic events per hour. Mean pulmonary arterial pressure is 30 mmHg. Which of the following complications is this patient most at risk for?
- A. Left ventricular failure
- B. Right ventricular failure (Correct Answer)
- C. Pulmonary embolism
- D. Aspiration pneumonia
- E. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***Right ventricular failure***
- The patient's symptoms (nocturnal dyspnea, choking sensation, fatigue, exertional dyspnea), risk factors (large neck circumference), and polysomnography results (16 hypopneic/apneic events/hour) are consistent with **obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)**.
- OSA leads to **chronic intermittent hypoxia** and hypercapnia, causing **pulmonary vasoconstriction** and increased pulmonary arterial pressure (mean PAP 30 mmHg), which can result in **pulmonary hypertension** and eventually **right ventricular failure**.
*Left ventricular failure*
- While OSA can exacerbate cardiovascular conditions, the primary cardiac complication directly resulting from ongoing pulmonary hypertension due to OSA is typically right-sided, not primarily left-sided, failure.
- There are no specific findings in the description (e.g., S3 gallop, crackles) that strongly point to left ventricular dysfunction as the most immediate and direct complication.
*Pulmonary embolism*
- Although obesity (suggested by large neck circumference) is a risk factor for pulmonary embolism, there are no acute symptoms (e.g., sudden onset dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, hemoptysis) or signs (e.g., tachycardia, hypoxemia) to suggest a pulmonary embolism.
- The patient's symptoms are chronic and related to sleep-disordered breathing and pulmonary hypertension.
*Aspiration pneumonia*
- While a "choking" sensation could potentially lead to aspiration, there's no evidence of infection (e.g., fever, productive cough, crackles) or recurrent aspiration events.
- The primary respiratory pathology is clearly defined by the polysomnography and elevated pulmonary pressures.
*Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease*
- Spirometry was reported as "unrevealing," which rules out significant airflow limitation characteristic of COPD.
- The patient's symptoms are more indicative of sleep-disordered breathing and its cardiovascular consequences rather than an intrinsic obstructive lung disease like COPD.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 6: A 30-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with breathlessness for the last hour. She is unable to provide any history due to her dyspnea. Her vitals include: respiratory rate 20/min, pulse 100/min, and blood pressure 144/84 mm Hg. On physical examination, she is visibly obese, and her breathing is labored. There are decreased breath sounds and hyperresonance to percussion across all lung fields bilaterally. An arterial blood gas is drawn, and the patient is placed on inhaled oxygen. Laboratory findings reveal:
pH 7.34
pO2 63 mm Hg
pCO2 50 mm Hg
HCO3 22 mEq/L
Her alveolar partial pressure of oxygen is 70 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Right to left shunt
- B. Alveolar hypoventilation (Correct Answer)
- C. Ventricular septal defect
- D. Impaired gas diffusion
- E. Ventilation/perfusion mismatch
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***Alveolar hypoventilation***
- The patient exhibits features of **obesity** and **labored breathing** with decreased breath sounds and hyperresonance, along with arterial blood gas results showing **respiratory acidosis** (pH 7.34, pCO2 50 mmHg) and **hypoxia** (pO2 63 mmHg).
- The calculated A-a gradient (Alveolar O2 - arterial O2) is low (70 mmHg - 63 mmHg = 7 mmHg), indicating that the problem is primarily with **overall ventilation** rather than a defect in gas exchange across the alveolar-capillary membrane.
*Right to left shunt*
- A right-to-left shunt would cause a **large A-a gradient**, as deoxygenated blood bypasses the lungs and mixes with oxygenated blood.
- While it causes **hypoxemia**, it would not typically be associated with hypercapnia unless very severe, and the A-a gradient calculation here does not support a significant shunt.
*Ventricular septal defect*
- A ventricular septal defect is a **structural heart abnormality** that can cause a left-to-right shunt initially, leading to pulmonary hypertension and eventually a right-to-left shunt (Eisenmenger syndrome).
- While it can cause hypoxemia due to shunting, it would not primarily manifest with increased pCO2 or the specific lung physical exam findings of decreased breath sounds and hyperresonance in the absence of other cardiac signs.
*Impaired gas diffusion*
- Impaired gas diffusion would lead to a **large A-a gradient** and **hypoxemia**, but typically not significant hypercapnia unless the impairment is extremely severe.
- Conditions like **pulmonary fibrosis** or **emphysema** cause impaired diffusion, but the patient's presentation and particularly the low A-a gradient do not support this.
*Ventilation/perfusion mismatch*
- A V/Q mismatch also causes a **large A-a gradient** and **hypoxemia**, as some areas of the lung are either poorly ventilated or poorly perfused.
- While it can cause hypercapnia in severe cases, the primary issue indicated by the low A-a gradient here is one of overall inadequate ventilation, not selective areas of ventilation-perfusion imbalance.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 7: A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after being involved in a motor vehicle collision in which he was a restrained passenger. The patient is confused. His pulse is 140/min and blood pressure is 85/60 mm Hg. Examination shows a hand-sized hematoma on the anterior chest wall. An ECG shows sinus tachycardia. Which of the following structures is most likely injured in this patient?
- A. Papillary muscle
- B. Left main coronary artery
- C. Inferior vena cava
- D. Aortic isthmus (Correct Answer)
- E. Aortic valve
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***Aortic isthmus***
- The **aortic isthmus** is the most common site of blunt **aortic injury** due to its relative immobility compared to the more mobile ascending aorta and arch. The deceleration forces experienced in a motor vehicle collision can cause a shearing injury at this location.
- The patient's **hypotension** and **tachycardia** are signs of significant hemorrhage, which is a common presentation of aortic injury. The chest wall hematoma also suggests significant trauma to the chest.
*Papillary muscle*
- Injury to the **papillary muscles** typically leads to severe **mitral regurgitation**, presenting with acute heart failure symptoms like pulmonary edema rather than primarily hypovolemic shock.
- While possible in trauma, the primary symptoms would involve a new significant murmur and rapid deterioration of cardiac function due to valve incompetence.
*Left main coronary artery*
- A **left main coronary artery** injury would likely lead to acute **myocardial ischemia** or infarction, manifesting as severe chest pain, ECG changes indicative of ischemia, and potentially cardiogenic shock, not hypovolemic shock.
- While trauma to the chest can cause coronary artery dissection, it is less common for blunt force to directly injure this artery without other, more widespread myocardial damage.
*Inferior vena cava*
- An injury to the **inferior vena cava (IVC)** would primarily cause severe internal bleeding, leading to hypovolemic shock. However, while possible, blunt force trauma to the chest is less likely to directly injure the retroperitoneal IVC without significant associated abdominal or lumbar spine injuries.
- The chest wall hematoma and focus on the chest suggests damage within the thoracic cavity, making an aortic injury more probable given the mechanism.
*Aortic valve*
- An injury to the **aortic valve** could cause acute **aortic regurgitation**, leading to acute heart failure and potentially cardiogenic shock with a new diastolic murmur.
- While possible, pure aortic valve injury from blunt trauma alone, without rupture of the aorta itself, is less common than aortic tear from shearing forces.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 8: A 24-year-old male is brought in by ambulance to the emergency department after he was found unresponsive at home for an unknown length of time. Upon arrival, he is found to be severely altered and unable to answer questions about his medical history. Based on clinical suspicion, a panel of basic blood tests are obtained including an arterial blood gas, which shows a pH of 7.32, a pCO2 of 70, and a bicarbonate level of 30 mEq/L. Which of the following is most likely the primary disturbance leading to the values found in the ABG?
- A. Respiratory acidosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Metabolic alkalosis
- C. Respiratory alkalosis
- D. Metabolic acidosis
- E. Mixed alkalosis
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***Respiratory acidosis***
- The **pH (7.32)** is acidic (normal 7.35-7.45), and the **pCO2 (70 mmHg)** is significantly elevated (normal 35-45 mmHg), indicating **primary respiratory acidosis** due to hypoventilation.
- The **bicarbonate (30 mEq/L)** is elevated above normal (22-26 mEq/L), indicating **partial metabolic compensation** by the kidneys retaining bicarbonate to buffer the acidosis.
- This pattern suggests **chronic respiratory acidosis** (e.g., from COPD, CNS depression, neuromuscular disease) with renal compensation.
*Metabolic alkalosis*
- This would present with **elevated pH** (>7.45) and **elevated bicarbonate** as the primary disturbance, often with compensatory elevation in pCO2.
- The patient's **pH is acidic (7.32)**, not alkalotic, ruling out metabolic alkalosis as the primary process.
*Respiratory alkalosis*
- This would present with **elevated pH** (>7.45) and **decreased pCO2** (<35 mmHg) due to hyperventilation.
- The patient has the opposite: **acidic pH and elevated pCO2**, ruling out respiratory alkalosis.
*Metabolic acidosis*
- This would present with **decreased pH** and **decreased bicarbonate** (<22 mEq/L) as the primary disturbance.
- While the pH is low, the **bicarbonate is elevated (30 mEq/L)**, not decreased, ruling out metabolic acidosis as the primary disorder.
*Mixed alkalosis*
- A mixed alkalosis would involve simultaneous respiratory and metabolic processes causing **elevated pH**.
- The patient's **pH is acidic (7.32)**, making any form of alkalosis impossible as the primary disturbance.
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 9: A 38-year-old woman presents to the physician’s clinic with a 6-month history of generalized weakness that usually worsens as the day progresses. She also complains of the drooping of her eyelids and double vision that is worse in the evening. Physical examination reveals bilateral ptosis after a sustained upward gaze and loss of eye convergence which improves upon placing ice packs over the eyes and after the administration of edrophonium. Which of the following is an intrinsic property of the muscle group affected in this patient?
- A. A small mass per motor unit
- B. High ATPase activity (Correct Answer)
- C. High myoglobin content
- D. High density of mitochondria
- E. Increased amount of ATP generated per molecule of glucose
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***High ATPase activity***
- This patient presents with **myasthenia gravis (MG)**, an autoimmune disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction through antibodies against acetylcholine receptors.
- **Extraocular muscles** and other muscles affected early in MG contain a high proportion of **fast-twitch (Type II) muscle fibers**, which are characterized by **high ATPase activity**.
- **Type II fibers** with high ATPase activity generate rapid, powerful contractions but are **more susceptible to neuromuscular junction dysfunction** due to their higher firing rates and greater dependence on efficient neuromuscular transmission.
- This intrinsic property (high ATPase activity) is why these muscles are preferentially affected in myasthenia gravis.
*A small mass per motor unit*
- While extraocular muscles do have **small motor units** (allowing for precise eye movements), this describes the **innervation pattern** rather than an intrinsic biochemical property of the muscle fibers themselves.
- The question specifically asks about an intrinsic property of the muscle group, referring to the metabolic and contractile characteristics of the muscle fibers.
*High myoglobin content*
- **High myoglobin content** is characteristic of **Type I (slow-twitch) oxidative fibers**, which rely on sustained oxygen delivery for prolonged, fatigue-resistant contractions.
- Muscles preferentially affected in MG have a higher proportion of **Type II fibers**, which have lower myoglobin content compared to Type I fibers.
*High density of mitochondria*
- **High mitochondrial density** is characteristic of **Type I (slow-twitch) oxidative fibers** that depend on aerobic metabolism for sustained energy production.
- While extraocular muscles do have oxidative capacity, the **Type II fibers** preferentially affected in MG have relatively lower mitochondrial density compared to Type I fibers and rely more on glycolytic metabolism for rapid energy needs.
*Increased amount of ATP generated per molecule of glucose*
- **Aerobic respiration** in Type I fibers generates approximately 32 ATP molecules per glucose through oxidative phosphorylation.
- **Type II fibers** rely more heavily on **anaerobic glycolysis**, which produces only 2 ATP per glucose molecule, making them less efficient in ATP generation per glucose.
- The muscles affected in MG have higher proportions of Type II fibers with lower ATP efficiency per glucose molecule.
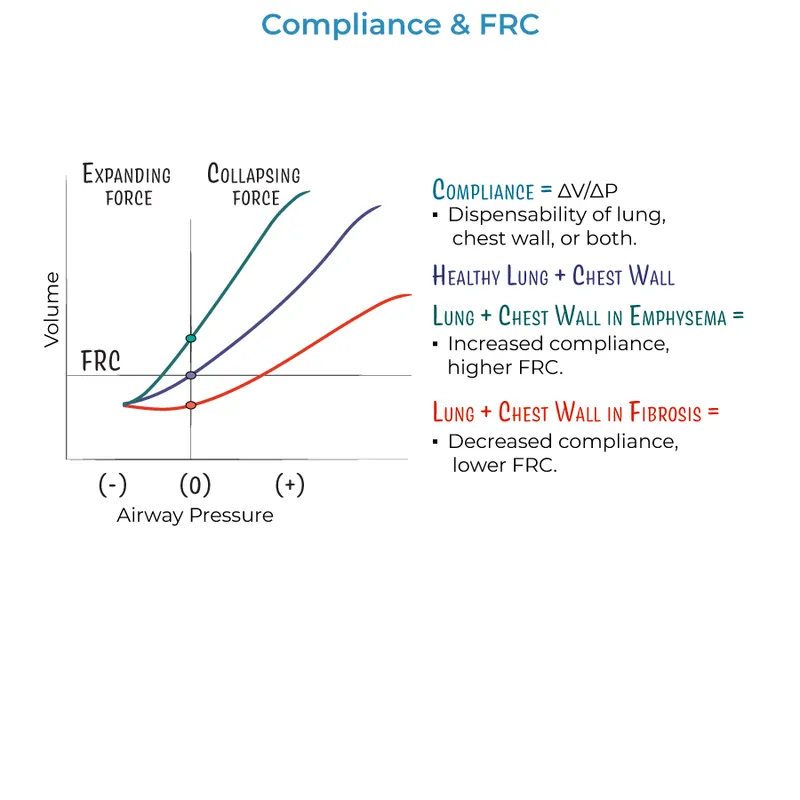
Chest wall compliance US Medical PG Question 10: A 68-year-old man with both severe COPD (emphysema) and newly diagnosed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis presents with worsening dyspnea. His pressure-volume curve shows a complex pattern with features of both diseases. Static compliance measured at mid-lung volumes is 120 mL/cm H2O. His pulmonologist must decide on optimal management. Synthesizing the pathophysiology of both conditions, what represents the most significant clinical challenge in managing his combined disease?
- A. Pulmonary rehabilitation cannot address the opposing mechanical derangements
- B. The increased compliance from emphysema completely negates decreased compliance from fibrosis
- C. The opposing effects on compliance create a pseudonormal total respiratory compliance masking disease severity (Correct Answer)
- D. Emphysema treatment with bronchodilators will worsen fibrosis progression
- E. Oxygen therapy beneficial for COPD will accelerate fibrotic changes
Chest wall compliance Explanation: ***The opposing effects on compliance create a pseudonormal total respiratory compliance masking disease severity***
- In **Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema (CPFE)**, the **increased lung compliance** from upper-lobe emphysema is offset by the **decreased compliance** from lower-lobe fibrosis.
- This results in a **pseudonormalization** of lung volumes (like FVC and TLC) and compliance measurements, which can lead to a significant **underestimation of disease severity** during clinical assessment.
*Pulmonary rehabilitation cannot address the opposing mechanical derangements*
- While mechanical derangements are complex, **pulmonary rehabilitation** remains a cornerstone of management to improve functional capacity and reduce dyspnea in both conditions.
- The challenge is not that rehabilitation is ineffective, but rather the **physiological monitoring** and objective assessment of progress are hampered by masked lung volumes.
*The increased compliance from emphysema completely negates decreased compliance from fibrosis*
- The two forces do not perfectly negate each other; rather, they coexist to produce a **paradoxical physiological profile** where static measurements appear mid-range while gas exchange is severely impaired.
- Patients often exhibit a **disproportionate reduction in DLCO** (diffusion capacity) despite relatively preserved lung volumes, indicating the negation is only superficial and numerical.
*Emphysema treatment with bronchodilators will worsen fibrosis progression*
- There is no clinical evidence suggesting that **bronchodilators** (beta-agonists or anticholinergics) used for COPD/emphysema accelerate the **pathological scarring** seen in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- Bronchodilators primarily target **airway smooth muscle** and do not interfere with the fibroblastic pathways driving interstitial lung disease.
*Oxygen therapy beneficial for COPD will accelerate fibrotic changes*
- **Long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT)** is used to treat chronic hypoxemia in both COPD and fibrosis and does not cause or accelerate **lung remodeling** or fibrosis.
- While high concentrations of inspired oxygen (FiO2) can cause **oxidative stress**, the flow rates used for clinical management do not contribute to the progression of pulmonary fibrosis.
More Chest wall compliance US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.