Compliance

On this page
🫁 The Pulmonary Elasticity Engine: Mastering Compliance Mechanics
Compliance-the lung's willingness to expand-determines whether each breath comes easily or demands exhausting effort, and mastering it unlocks the mechanical logic behind breathlessness, ventilator settings, and life-threatening conditions from ARDS to emphysema. You'll learn to interpret pressure-volume relationships, recognize high- and low-compliance states at the bedside, distinguish restrictive from obstructive patterns, and apply evidence-based interventions that restore respiratory mechanics. By integrating compliance with resistance, gas exchange, and multi-system physiology, you'll transform abstract curves into clinical decisions that guide oxygen therapy, PEEP titration, and critical care management with precision and confidence.

The respiratory system operates as a sophisticated elastic engine where compliance-the lung's ability to stretch and recoil-determines the work of breathing and gas exchange efficiency. Master these compliance principles, and you unlock the logic behind every respiratory disorder pattern.
🫁 The Pulmonary Elasticity Engine: Mastering Compliance Mechanics
🔧 The Compliance Command Center: Defining Pulmonary Elasticity
Compliance Fundamentals
- Static Compliance: Measured during zero airflow conditions
- Normal value: 200 mL/cmH₂O in healthy adults
- Formula: C = ΔV/ΔP (volume change/pressure change)
- Reflects pure elastic properties without airway resistance
- Dynamic Compliance: Measured during active airflow
- Normal value: 100-150 mL/cmH₂O (lower than static)
- Includes both elastic and resistive components
- More clinically relevant for ventilated patients
📌 Remember: SPEC - Static measures Pure Elasticity, Compliance without airflow interference
| Parameter | Normal Value | Clinical Significance | Measurement Timing | Pathological Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static Compliance | 200 mL/cmH₂O | Pure lung elasticity | Zero flow pause | <100 mL/cmH₂O |
| Dynamic Compliance | 100-150 mL/cmH₂O | Real-time breathing | Active ventilation | <80 mL/cmH₂O |
| Specific Compliance | 0.05-0.1 /cmH₂O | Size-adjusted measure | Per lung volume | <0.03 /cmH₂O |
| Chest Wall Compliance | 200 mL/cmH₂O | Thoracic elasticity | Relaxed state | <100 mL/cmH₂O |
| Total Compliance | 100 mL/cmH₂O | Combined system | Breathing cycle | <50 mL/cmH₂O |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: A 50% reduction in compliance doubles the work of breathing, explaining why patients with restrictive disease develop rapid, shallow breathing patterns
Elastic Recoil Mechanisms
- Tissue Elasticity (30% of total recoil)
- Elastin and collagen fiber networks
- Provides structural framework for alveolar expansion
- Degrades with age, reducing compliance by 20-30% after age 65
- Surface Tension Forces (70% of total recoil)
- Air-liquid interface at alveolar surface
- Creates inward collapsing pressure of 50-70 cmH₂O
- Modulated by surfactant to prevent alveolar collapse
💡 Master This: Surface tension contributes 70% of lung recoil-understanding surfactant function predicts compliance changes in respiratory distress syndrome
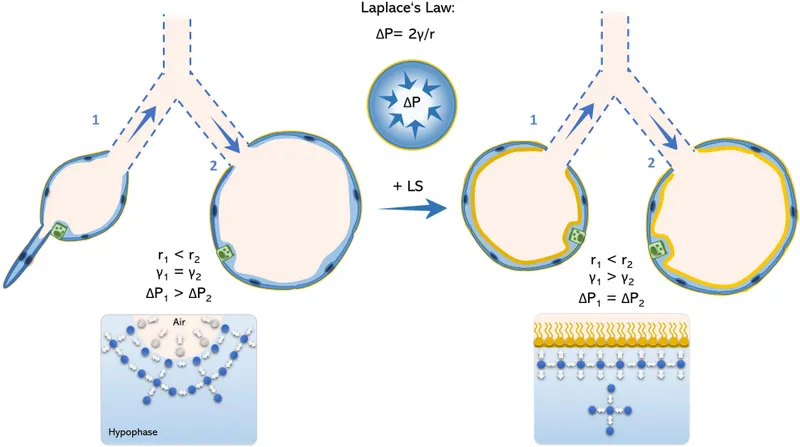
The compliance command center integrates multiple elastic components to maintain optimal breathing mechanics. Connect these foundational principles through pressure-volume relationships to understand how compliance changes manifest in clinical practice.
🔧 The Compliance Command Center: Defining Pulmonary Elasticity
📊 The Pressure-Volume Landscape: Mapping Compliance Curves
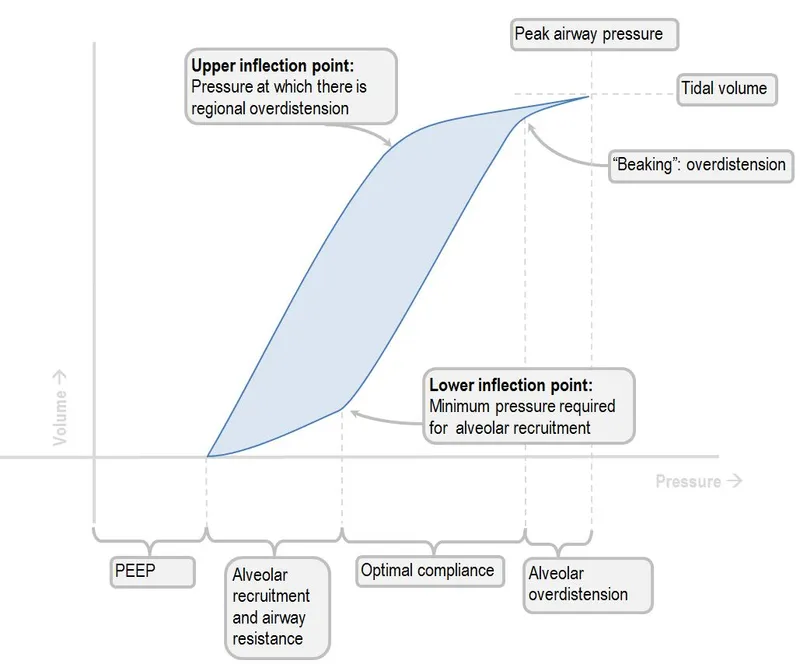
P-V Curve Architecture
- Inspiration Limb (Inflation curve)
- Lower inflection point: 6-10 cmH₂O (alveolar recruitment)
- Linear zone: 10-20 cmH₂O (optimal compliance)
- Upper inflection point: 25-30 cmH₂O (overdistension begins)
- Expiration Limb (Deflation curve)
- Hysteresis loop: Area between curves represents energy loss
- Closing pressure: 2-4 cmH₂O (alveolar collapse threshold)
- Functional residual capacity: Equilibrium point at 5 cmH₂O
📌 Remember: HILO - Hysteresis shows energy loss, Inflection points mark Lung limits, Optimal zone lies between
| Curve Feature | Normal Value | Clinical Significance | Pathological Change | Ventilator Implication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Inflection | 6-10 cmH₂O | Recruitment pressure | ↑15-20 cmH₂O in ARDS | PEEP setting guide |
| Linear Slope | 200 mL/cmH₂O | True compliance | ↓<100 mL/cmH₂O restriction | Tidal volume limit |
| Upper Inflection | 25-30 cmH₂O | Overdistension risk | ↓15-20 cmH₂O in fibrosis | Peak pressure alarm |
| Hysteresis Area | 20-30% | Energy efficiency | ↑50%+ in disease | Work of breathing |
| Closing Pressure | 2-4 cmH₂O | Collapse threshold | ↑8-12 cmH₂O in ARDS | Minimum PEEP |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The slope of the linear portion equals compliance-a steeper slope indicates higher compliance (easier inflation), while a flatter slope suggests reduced compliance (stiffer lungs)
Pathological P-V Patterns
- Restrictive Pattern
- Rightward shift: Higher pressures needed for same volume
- Reduced slope: Compliance decreased by 50-80%
- Narrow hysteresis: Less energy storage capacity
- Examples: Pulmonary fibrosis, ARDS, chest wall restriction
- Obstructive Pattern
- Leftward shift: Easier inflation but impaired deflation
- Increased hysteresis: 40-60% energy loss during expiration
- Elevated closing pressure: Premature airway collapse
- Examples: Emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma
💡 Master This: P-V curve shape changes predict optimal ventilator settings-restrictive lungs need lower tidal volumes (6 mL/kg), while obstructive lungs require longer expiratory times (I:E ratio 1:3-4)
The pressure-volume landscape reveals the mechanical fingerprint of respiratory disease. Connect these curve patterns through compliance calculations to understand how different pathologies alter breathing mechanics and guide therapeutic interventions.
📊 The Pressure-Volume Landscape: Mapping Compliance Curves
🎯 The Compliance Recognition Matrix: Clinical Pattern Mastery
Compliance Assessment Framework
- Physical Examination Clues
- Chest wall movement: Reduced excursion suggests ↓compliance
- Breathing pattern: Rapid, shallow breaths indicate stiff lungs
- Accessory muscle use: Increased work of breathing
- Percussion: Dullness suggests consolidation/fibrosis
- Pulmonary Function Patterns
- Total lung capacity: ↓20-50% in restrictive disease
- Vital capacity: ↓30-60% with reduced compliance
- FEV₁/FVC ratio: >80% in pure restrictive patterns
- DLCO: ↓40-70% in parenchymal disease
📌 Remember: RAPID - Reduced excursion, Accessory muscles, Pattern shallow, Increased work, Dullness on percussion
| Clinical Finding | Normal Range | Reduced Compliance | Increased Compliance | Diagnostic Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest Excursion | 5-8 cm | <3 cm | >10 cm | Restrictive vs obstructive |
| Respiratory Rate | 12-20 /min | 25-35 /min | 8-12 /min | Work of breathing |
| Tidal Volume | 500 mL | 300-400 mL | 600-800 mL | Compensation pattern |
| I:E Ratio | 1:2 | 1:1 | 1:3-4 | Expiratory limitation |
| Peak Pressure | <30 cmH₂O | >40 cmH₂O | <20 cmH₂O | Ventilator mechanics |
- ARDS Pattern
- Compliance: 20-40 mL/cmH₂O (↓70-80% from normal)
- P-V curve: Prominent lower inflection point at 15-20 cmH₂O
- Clinical: Bilateral infiltrates, refractory hypoxemia
- Ventilator: High peak pressures, poor oxygenation
- Pulmonary Fibrosis Pattern
- Compliance: 50-100 mL/cmH₂O (↓50-75% from normal)
- P-V curve: Steep, narrow curve with minimal hysteresis
- Clinical: Progressive dyspnea, dry cough, clubbing
- PFTs: ↓TLC, ↓DLCO, normal FEV₁/FVC ratio
⭐ Clinical Pearl: When compliance drops below 100 mL/cmH₂O, consider restrictive pathology-values <50 mL/cmH₂O indicate severe disease requiring aggressive intervention
Ventilator-Derived Compliance Monitoring
- Real-time Calculations
- Static compliance = Tidal volume / (Plateau pressure - PEEP)
- Dynamic compliance = Tidal volume / (Peak pressure - PEEP)
- Compliance ratio = Dynamic/Static (>0.8 suggests minimal airway resistance)
- Trending Parameters
- Daily compliance measurements track disease progression
- Compliance improvement indicates therapeutic response
- Sudden compliance drop suggests complications (pneumothorax, mucus plugging)
💡 Master This: Serial compliance monitoring predicts extubation readiness-improving compliance to >150 mL/cmH₂O with stable gas exchange suggests successful weaning potential
The compliance recognition matrix enables rapid pattern identification and therapeutic decision-making. Connect these clinical signatures through systematic assessment frameworks to distinguish between different causes of altered lung mechanics.
🎯 The Compliance Recognition Matrix: Clinical Pattern Mastery
⚖️ The Compliance Discrimination Engine: Differential Diagnosis Mastery

Quantitative Discrimination Matrix
| Disease Category | Compliance (mL/cmH₂O) | TLC (% predicted) | DLCO (% predicted) | FEV₁/FVC | Key Discriminator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary Fibrosis | 50-100 | 60-80% | 40-60% | >80% | Progressive DLCO decline |
| ARDS | 20-40 | 70-85% | 50-70% | >80% | Acute onset, bilateral infiltrates |
| Pleural Effusion | 80-120 | 70-90% | 80-100% | >80% | Blunted costophrenic angles |
| Chest Wall Disease | 60-100 | 60-80% | 90-110% | >80% | Normal DLCO, skeletal deformity |
| Emphysema | 250-400 | 110-130% | 40-70% | <70% | Increased compliance, air trapping |
- Parenchymal Restrictive Diseases
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Compliance 50-80 mL/cmH₂O, DLCO ↓40-60%
- ARDS: Compliance 20-40 mL/cmH₂O, acute onset <7 days
- Pneumoconiosis: Compliance 60-100 mL/cmH₂O, occupational exposure history
- Sarcoidosis: Compliance 70-120 mL/cmH₂O, hilar lymphadenopathy
- Extraparenchymal Restrictive Diseases
- Pleural Effusion: Compliance 80-120 mL/cmH₂O, preserved DLCO
- Pneumothorax: Compliance 60-100 mL/cmH₂O, sudden onset
- Kyphoscoliosis: Compliance 60-100 mL/cmH₂O, normal DLCO
- Obesity: Compliance 80-120 mL/cmH₂O, BMI >35 kg/m²
📌 Remember: PAID - Parenchymal diseases affect DLCO, Acute onset suggests ARDS, Infiltrates bilateral in ARDS, DLCO normal in extraparenchymal disease
Advanced Discrimination Techniques
- High-Resolution CT Patterns
- Honeycombing: End-stage fibrosis, compliance <50 mL/cmH₂O
- Ground-glass opacities: Early inflammation, compliance 100-150 mL/cmH₂O
- Reticular patterns: Progressive fibrosis, compliance 60-100 mL/cmH₂O
- Consolidation: Acute process, compliance 40-80 mL/cmH₂O
- Biomarker Integration
- KL-6: Elevated >1000 U/mL in pulmonary fibrosis
- SP-D: Correlates with disease severity in ILD
- Pro-BNP: Elevated >300 pg/mL suggests cor pulmonale
- LDH: Elevated >500 U/L in acute lung injury
⭐ Clinical Pearl: DLCO preservation with reduced compliance strongly suggests extraparenchymal restriction-look for pleural disease, chest wall abnormalities, or neuromuscular weakness
💡 Master This: The compliance-to-DLCO ratio provides powerful discrimination-ratios <2 suggest parenchymal disease, while ratios >3 indicate extraparenchymal restriction
The compliance discrimination engine enables precise differential diagnosis through systematic pattern analysis. Connect these quantitative discriminators through evidence-based algorithms to optimize diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic targeting.
⚖️ The Compliance Discrimination Engine: Differential Diagnosis Mastery
🔬 The Therapeutic Compliance Optimizer: Evidence-Based Management
Ventilator Optimization Strategies
| Compliance Range | Tidal Volume | PEEP Strategy | I:E Ratio | Peak Pressure Limit | Outcome Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <50 mL/cmH₂O | 4-6 mL/kg PBW | High PEEP 12-18 | 1:1 to 1:2 | <30 cmH₂O | Recruitment |
| 50-100 mL/cmH₂O | 6-8 mL/kg PBW | Moderate PEEP 8-12 | 1:2 | <35 cmH₂O | Lung protection |
| 100-200 mL/cmH₂O | 8-10 mL/kg PBW | Low PEEP 5-8 | 1:2 to 1:3 | <40 cmH₂O | Comfort |
| >200 mL/cmH₂O | 6-8 mL/kg PBW | Minimal PEEP 3-5 | 1:3 to 1:4 | Variable | Expiratory flow |
- Decremental PEEP Trial
- Start at 20 cmH₂O, decrease by 2 cmH₂O every 15 minutes
- Monitor compliance, oxygenation, and hemodynamics
- Optimal PEEP: 2 cmH₂O above lower inflection point
- Target: Best compliance with PaO₂/FiO₂ >200
- Recruitment Maneuvers
- Sustained inflation: 40 cmH₂O for 40 seconds
- Incremental PEEP: Increase to 25-30 cmH₂O for 2 minutes
- Success criteria: Compliance improvement >20%
- Contraindications: Hemodynamic instability, pneumothorax risk
📌 Remember: PEEP - Prevents collapse, Enhances recruitment, Elevates compliance, Protects from injury
Pharmacological Compliance Enhancement
- Bronchodilator Therapy
- Albuterol: 2.5-5 mg nebulized every 4-6 hours
- Ipratropium: 500 mcg nebulized every 6 hours
- Combination therapy: Synergistic effect in mixed disease
- Response monitoring: >15% improvement in dynamic compliance
- Anti-inflammatory Agents
- Methylprednisolone: 1-2 mg/kg/day in ARDS
- Timing: Most effective in proliferative phase (days 7-14)
- Duration: 7-14 days with gradual taper
- Monitoring: Compliance improvement >25% within 48-72 hours
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Compliance-guided steroid therapy in ARDS-if compliance doesn't improve by 25% within 72 hours, consider discontinuation to avoid complications
Advanced Therapeutic Interventions
- Prone Positioning
- Indication: P/F ratio <150 with compliance <40 mL/cmH₂O
- Duration: 16-18 hours daily for ≥3 days
- Response: Compliance improvement 30-50% within 2 hours
- Mechanism: Recruits dorsal lung regions, improves V/Q matching
- Extracorporeal Support
- ECMO criteria: Compliance <20 mL/cmH₂O with refractory hypoxemia
- VV-ECMO: Allows ultra-protective ventilation (TV 3-4 mL/kg)
- Weaning criteria: Compliance recovery to >100 mL/cmH₂O
- Outcomes: 60-70% survival in appropriate candidates
💡 Master This: Serial compliance monitoring guides therapy escalation-failure to improve compliance by 20% within 48 hours indicates need for advanced interventions
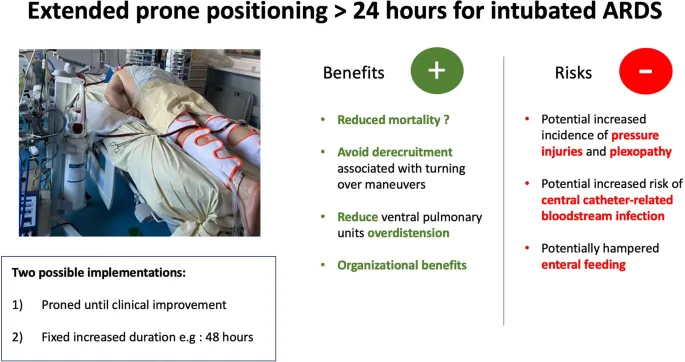
The therapeutic compliance optimizer provides evidence-based protocols for restoring lung elasticity and optimizing ventilatory support. Connect these intervention strategies through systematic monitoring frameworks to achieve optimal patient outcomes while minimizing complications.
🔬 The Therapeutic Compliance Optimizer: Evidence-Based Management
🌐 The Compliance Integration Network: Multi-System Mastery
Cardiopulmonary Compliance Interactions
- Heart-Lung Interdependence
- Venous return: ↓Compliance increases intrathoracic pressure, ↓venous return by 20-30%
- Cardiac output: High PEEP with stiff lungs ↓CO by 15-25%
- Right heart function: ↓Compliance increases pulmonary vascular resistance
- Optimal balance: Compliance >80 mL/cmH₂O maintains hemodynamic stability
- Fluid Management Integration
- Conservative strategy: Target CVP <8 mmHg when compliance <100 mL/cmH₂O
- Diuretic response: 1 kg fluid removal improves compliance by 10-15 mL/cmH₂O
- Albumin therapy: 25 g daily may improve compliance in hypoproteinemic patients
- Monitoring: Daily weights correlate with compliance trends
📌 Remember: FLUID - Fluid overload worsens compliance, Lung water increases stiffness, Ultrafiltration helps, Intrathoracic pressure affects heart, Diuresis improves mechanics
| System Interaction | Normal Response | Impaired Compliance | Clinical Implication | Therapeutic Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Output | Stable with PEEP <10 | ↓15-25% with PEEP >15 | Hemodynamic compromise | Optimize PEEP/compliance ratio |
| Venous Return | Minimal PEEP effect | ↓20-30% with stiff lungs | Preload reduction | Fluid optimization |
| Pulmonary Vascular Resistance | Normal <2 Wood units | ↑3-5 Wood units | Right heart strain | Vasodilator therapy |
| Renal Function | Stable GFR | ↓20% with high pressures | Kidney injury risk | Pressure limitation |
| Cerebral Perfusion | Normal ICP | ↑ICP with high PEEP | Neurological compromise | ICP monitoring |
- Respiratory Drive Modulation
- Chemoreceptor sensitivity: ↓Compliance increases CO₂ retention, ↑respiratory drive
- Work of breathing: Stiff lungs increase neural respiratory output by 50-100%
- Fatigue threshold: Compliance <60 mL/cmH₂O predisposes to respiratory failure
- Sedation requirements: ↑30-50% with severe compliance reduction
- Autonomic Integration
- Sympathetic activation: ↓Compliance triggers stress response
- Heart rate variability: Reduced in patients with stiff lungs
- Sleep quality: Compliance <100 mL/cmH₂O disrupts sleep architecture
- Weaning success: Requires compliance >120 mL/cmH₂O for spontaneous breathing
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Compliance-guided sedation protocols-patients with compliance <80 mL/cmH₂O require deeper sedation to prevent ventilator dyssynchrony and self-inflicted lung injury
Metabolic-Respiratory Integration
- Energy Expenditure
- Work of breathing: Increases exponentially as compliance decreases below 100 mL/cmH₂O
- Caloric requirements: ↑20-40% in patients with severe compliance reduction
- Protein needs: ↑1.5-2.0 g/kg/day to support respiratory muscle function
- Micronutrient demands: ↑Vitamin C, E, selenium for antioxidant protection
- Acid-Base Integration
- CO₂ retention: ↓Compliance impairs ventilation, causes respiratory acidosis
- Metabolic compensation: Renal bicarbonate retention within 24-48 hours
- pH targets: Maintain 7.30-7.45 to optimize cellular function
- Buffer systems: Compliance <50 mL/cmH₂O overwhelms compensation
💡 Master This: Compliance-metabolic coupling-every 50 mL/cmH₂O decrease in compliance increases energy expenditure by 15-20%, requiring adjusted nutritional support
Cutting-Edge Integration Strategies
- Personalized PEEP Titration
- Electrical impedance tomography: Real-time regional compliance mapping
- Transpulmonary pressure monitoring: Esophageal balloon guidance
- Machine learning algorithms: Predict optimal PEEP from multiple variables
- Outcome improvement: 20-30% reduction in ventilator days
- Biomarker-Guided Therapy
- Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE): Epithelial injury marker
- Surfactant protein-D: Correlates with compliance changes
- Club cell protein-16: Early indicator of lung injury
- Therapeutic targeting: Personalized anti-inflammatory protocols
The compliance integration network reveals how respiratory mechanics influence entire physiological systems. Connect these multi-system interactions through advanced monitoring and personalized therapeutic approaches to optimize patient outcomes across all organ systems.
🌐 The Compliance Integration Network: Multi-System Mastery
🎯 The Compliance Mastery Arsenal: Clinical Command Tools
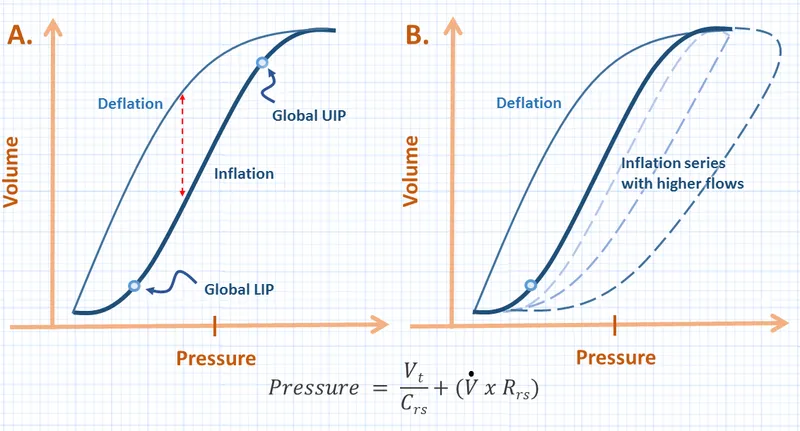
Rapid Assessment Protocol
- 30-Second Compliance Check
- Visual: Chest excursion <3 cm = ↓compliance
- Palpation: Reduced tactile fremitus suggests stiffness
- Auscultation: Fine crackles indicate ↓compliance
- Ventilator: Peak pressure >35 cmH₂O with normal TV
- Emergency Thresholds
- Critical: Compliance <40 mL/cmH₂O requires immediate intervention
- Severe: Compliance 40-80 mL/cmH₂O needs close monitoring
- Moderate: Compliance 80-120 mL/cmH₂O allows standard care
- Normal: Compliance >150 mL/cmH₂O suggests good prognosis
📌 Remember: FAST - Feel for excursion, Auscultate for crackles, See ventilator pressures, Think compliance
| Clinical Scenario | Compliance Range | Immediate Action | Monitoring Frequency | Escalation Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDS Acute Phase | 20-40 mL/cmH₂O | Lung protective ventilation | Every 4 hours | No improvement 48h |
| Post-operative | 80-120 mL/cmH₂O | Standard ventilation | Every 8 hours | Compliance drop >20% |
| Weaning Trial | >120 mL/cmH₂O | Spontaneous breathing | Every 2 hours | Compliance <100 |
| Chronic Ventilation | 60-100 mL/cmH₂O | Comfort ventilation | Daily | Acute deterioration |
| Emergency Intubation | Variable | Assess within 1 hour | Continuous | Pressure >40 cmH₂O |
- Compliance Formulas
- Static: C = TV / (Pplat - PEEP)
- Dynamic: C = TV / (Ppeak - PEEP)
- Specific: C = Compliance / FRC
- Effective: C = TV / (Pmean - PEEP)
- Predictive Equations
- Work of breathing: WOB = 0.35 × (Ppeak - PEEP)²
- Optimal PEEP: PEEP = LIP + 2 cmH₂O
- Weaning readiness: C × f/TV ratio <105
- Mortality risk: Compliance <30 mL/cmH₂O = >80% mortality
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The compliance × respiratory rate product predicts weaning success-values <2000 suggest readiness for spontaneous breathing trials
Master Clinician Decision Tree
💡 Master This: Compliance trending over 24-48 hours predicts therapeutic response better than single measurements-improving compliance indicates effective treatment, while declining values suggest disease progression or complications
The compliance mastery arsenal provides immediate access to evidence-based assessment and management tools. These clinical command resources enable rapid decision-making, optimal therapeutic interventions, and improved patient outcomes across diverse respiratory pathologies.
🎯 The Compliance Mastery Arsenal: Clinical Command Tools
Practice Questions: Compliance
Test your understanding with these related questions
A previously healthy 35-year-old woman is brought into the emergency department after being found unresponsive by her husband. Her husband finds an empty bottle of diazepam tablets in her pocket. She is stuporous. At the hospital, her blood pressure is 90/40 mm Hg, the pulse is 58/min, and the respirations are 6/min. The examination of the pupils shows normal size and reactivity to light. Deep tendon reflexes are 1+ bilaterally. Babinski sign is absent. All 4 extremities are hypotonic. The patient is intubated and taken to the critical care unit for mechanical ventilation and treatment. Regarding the prevention of pneumonia in this patient, which of the following strategies is most likely to achieve this goal?













