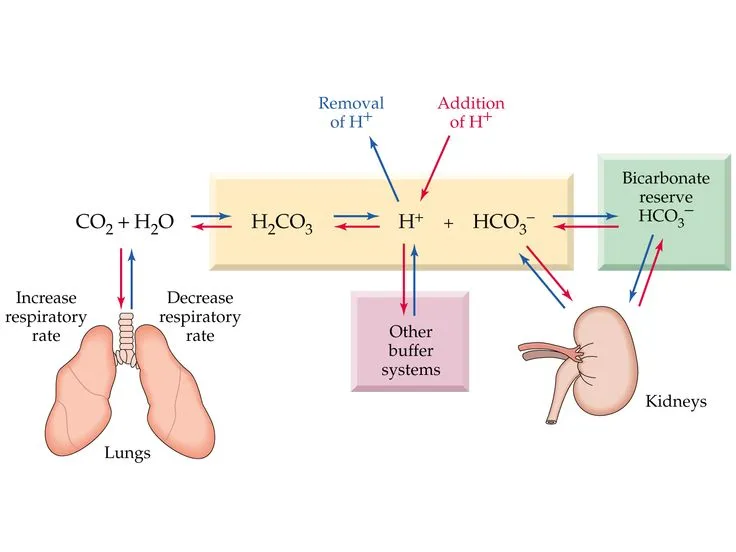
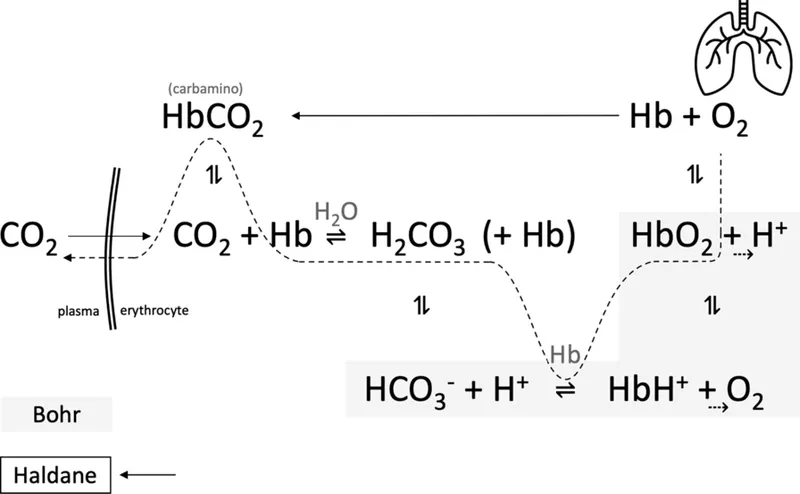
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 1: Which factor most strongly influences protein filtration at the glomerulus?
- A. Electrical charge
- B. Molecular size (Correct Answer)
- C. Shape
- D. Temperature
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Molecular size***
- The glomerular filtration barrier, particularly the **slit diaphragms** between podocytes, acts as a size-selective filter, restricting the passage of larger molecules.
- Proteins like **albumin** (molecular radius ~36 Å, molecular weight ~69 kDa) are significantly large, making them difficult to pass through the filtration barrier.
- Size selectivity is the **primary and most important** factor in protein filtration.
*Electrical charge*
- The glomerular basement membrane contains **negatively charged proteoglycans** (heparan sulfate), which repel negatively charged proteins like albumin, contributing to their retention.
- While important, the role of electrical charge is **secondary** to molecular size in preventing the bulk passage of most proteins.
*Shape*
- While abnormal protein shapes (e.g., **amyloid fibrils**) can impact filtration in specific disease states, the typical physiological filtration of most proteins is primarily governed by size and charge.
- The inherent shape of normal globular proteins plays a less direct role compared to their overall size.
*Temperature*
- **Physiological temperature** is relatively constant in the body and does not directly influence the molecular interactions and physical properties of the glomerular filtration barrier in a way that significantly alters protein filtration.
- Temperature changes would lead to denaturation or aggregation, which are not the primary determinants of normal protein filtration.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator studying epigenetic mechanisms isolates histone proteins, the structural motifs involved in DNA binding and regulation of transcription. The peptide bonds of histone proteins are hydrolyzed and one type of amino acid is isolated. At normal body pH, this amino acid has a net charge of +1 . The investigator performs titration of this amino acid and obtains the graph shown. The isolated amino acid is most likely which of the following?
- A. Proline
- B. Lysine (Correct Answer)
- C. Aspartate
- D. Serine
- E. Histidine
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Lysine***
- Histones are **positively charged** proteins rich in **basic amino acids** like lysine and arginine, which allows them to bind tightly to the negatively charged DNA.
- The titration curve shown with three distinct pKa values and a net charge of +1 at normal body pH (around 7.4) is characteristic of **lysine**, which has both an alpha-amino group (pKa ~9-10) and a basic side chain (pKa ~10.5).
*Proline*
- **Proline is a nonpolar** amino acid that does not contribute significantly to the positive charge of histones required for DNA binding.
- Furthermore, its unique cyclic structure incorporates its amino group into the ring, impacting its pKa relative to other primary amino acids but not making it a primary basic residue in the histone context.
*Aspartate*
- **Aspartate is an acidic amino acid** with a negatively charged side chain at physiological pH, which would repel DNA rather than bind to it.
- Its titration curve would show a net negative charge at normal body pH, not a positive one.
*Serine*
- **Serine is a polar, uncharged** amino acid and would not contribute the necessary positive charge for histone-DNA interaction.
- Its side chain lacks an ionizable group within the physiological pH range, so its titration curve would only show two pKa values (for the carboxyl and amino groups) and a net charge of 0 at neutral pH.
*Histidine*
- While **histidine is a basic amino acid**, its side chain pKa is around 6.0, meaning it is only partially protonated and positively charged at physiological pH.
- A protein rich in **histidine** would not consistently carry a strong positive charge across the typical physiological pH range as effectively as one rich in lysine or arginine.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 3: Which transport mechanism is primarily responsible for calcium reabsorption in the proximal tubule?
- A. Paracellular transport (Correct Answer)
- B. Facilitated diffusion
- C. Active transport
- D. Antiport with sodium
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Paracellular transport***
- In the **proximal tubule**, approximately 60-70% of filtered calcium is reabsorbed primarily through the **paracellular pathway**, driven by the electrochemical gradient and solvent drag.
- This transport occurs between cells, moving through the **tight junctions**, and is passive, following the reabsorption of water.
*Facilitated diffusion*
- While a type of passive transport, **facilitated diffusion** typically involves membrane proteins and occurs across the cell membrane, not primarily between cells in the proximal tubule for calcium.
- This mechanism is prominent for calcium reabsorption in other nephron segments like the **distal convoluted tubule** via **TRPV5/6 channels**, but not the main route in the proximal tubule.
*Active transport*
- **Active transport** of calcium, mainly via **calcium ATPase** and the **Na+/Ca2+ exchanger**, occurs across the luminal and basolateral membranes, respectively, in specific nephron segments.
- However, in the **proximal tubule**, the bulk of calcium reabsorption is passive and paracellular, not ATP-dependent active transport across cell membranes.
*Antiport with sodium*
- The **Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX)** is an antiport mechanism that plays a crucial role in extruding calcium from the cell into the interstitium, particularly in the basolateral membrane of the distal tubule.
- However, it is not the primary mechanism for overall tubular reabsorption of calcium in the **proximal tubule**, where paracellular movement dominates.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old male is brought in by ambulance to the emergency department after he was found unresponsive at home for an unknown length of time. Upon arrival, he is found to be severely altered and unable to answer questions about his medical history. Based on clinical suspicion, a panel of basic blood tests are obtained including an arterial blood gas, which shows a pH of 7.32, a pCO2 of 70, and a bicarbonate level of 30 mEq/L. Which of the following is most likely the primary disturbance leading to the values found in the ABG?
- A. Respiratory acidosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Metabolic alkalosis
- C. Respiratory alkalosis
- D. Metabolic acidosis
- E. Mixed alkalosis
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Respiratory acidosis***
- The **pH (7.32)** is acidic (normal 7.35-7.45), and the **pCO2 (70 mmHg)** is significantly elevated (normal 35-45 mmHg), indicating **primary respiratory acidosis** due to hypoventilation.
- The **bicarbonate (30 mEq/L)** is elevated above normal (22-26 mEq/L), indicating **partial metabolic compensation** by the kidneys retaining bicarbonate to buffer the acidosis.
- This pattern suggests **chronic respiratory acidosis** (e.g., from COPD, CNS depression, neuromuscular disease) with renal compensation.
*Metabolic alkalosis*
- This would present with **elevated pH** (>7.45) and **elevated bicarbonate** as the primary disturbance, often with compensatory elevation in pCO2.
- The patient's **pH is acidic (7.32)**, not alkalotic, ruling out metabolic alkalosis as the primary process.
*Respiratory alkalosis*
- This would present with **elevated pH** (>7.45) and **decreased pCO2** (<35 mmHg) due to hyperventilation.
- The patient has the opposite: **acidic pH and elevated pCO2**, ruling out respiratory alkalosis.
*Metabolic acidosis*
- This would present with **decreased pH** and **decreased bicarbonate** (<22 mEq/L) as the primary disturbance.
- While the pH is low, the **bicarbonate is elevated (30 mEq/L)**, not decreased, ruling out metabolic acidosis as the primary disorder.
*Mixed alkalosis*
- A mixed alkalosis would involve simultaneous respiratory and metabolic processes causing **elevated pH**.
- The patient's **pH is acidic (7.32)**, making any form of alkalosis impossible as the primary disturbance.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 5: A 25-year-old woman with an extensive psychiatric history is suspected of having metabolic acidosis after ingesting a large amount of aspirin in a suicide attempt. Labs are drawn and the values from the ABG are found to be: PCO2: 25, and HCO3: 15, but the pH value is smeared on the print-out and illegible. The medical student is given the task of calculating the pH using the pCO2 and HCO3 concentrations. He recalls from his first-year physiology course that the pKa of relevance for the bicarbonate buffering system is approximately 6.1. Which of the following is the correct formula the student should use, using the given values from the incomplete ABG?
- A. 15/6.1 + log[10/(0.03*25)]
- B. 6.1 + log[15/(0.03*25)] (Correct Answer)
- C. 10^6.1 + 15/0.03*25
- D. 6.1 + log[0.03/15*25]
- E. 6.1 + log[25/(15*0.03)]
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***6.1 + log[15/(0.03*25)]***
- This formula correctly represents the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for the bicarbonate buffer system: **pH = pKa + log([HCO3-]/[0.03 * PCO2])**.
- Here, **pKa is 6.1**, **[HCO3-] is 15**, and **[0.03 * PCO2] is 0.03 * 25**, making this the appropriate calculation for pH.
*15/6.1 + log[10/(0.03*25)]*
- This formula incorrectly places the pKa in the denominator of the first term and introduces an arbitrary '10' in the numerator of the logarithmic term.
- The **Henderson-Hasselbalch equation** dictates that pKa is added, not divided into, another component, and the logarithmic term should reflect the ratio of bicarbonate to carbonic acid.
*10^6.1 + 15/0.03*25*
- This option incorrectly uses an exponentiation of pKa and adds it to an unrelated fractional term, which does not correspond to the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation structure.
- The formula for pH calculation is a sum of pKa and a logarithmic term, not an exponentiation and a simple fraction.
*6.1 + log[0.03/15*25]*
- This option incorrectly inverts the ratio within the logarithm, placing the carbonic acid component (0.03 * PCO2) in the numerator and bicarbonate in the denominator.
- The correct Henderson-Hasselbalch equation requires the **bicarbonate concentration in the numerator** and the carbonic acid concentration in the denominator.
*6.1 + log [25/(15*0.03)]*
- This option incorrectly places the PCO2 (25) in the numerator of the logarithmic term and the product of HCO3- and 0.03 in the denominator.
- The correct ratio for the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is **[HCO3-] / [0.03 * PCO2]**.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 6: A 39-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of fever, chills, dyspnea, and a non-bloody productive cough. He was diagnosed with HIV infection 4 years ago and has been on highly active antiretroviral therapy since then. His temperature is 38.8°C (101.8°F). Examination shows crackles over the left lower lung base. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 520/mm3 (N ≥ 500). An x-ray of the chest shows an infiltrate in the left lower lobe. Sputum cultures grow colonies with a narrow zone of green hemolysis without clearing on blood agar. The most likely causal pathogen of this patient's condition produces which of the following virulence factors?
- A. Protein A
- B. M protein
- C. Polysaccharide capsule (Correct Answer)
- D. Type III secretion system
- E. Lipopolysaccharide
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Polysaccharide capsule***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, chills, dyspnea, productive cough, crackles, left lower lobe infiltrate) are consistent with **bacterial pneumonia**. The sputum culture showing colonies with a **narrow zone of green hemolysis (alpha-hemolysis)** without clearing on blood agar is characteristic of *Streptococcus pneumoniae*.
- *Streptococcus pneumoniae* is encased in a **polysaccharide capsule**, which is its primary virulence factor. This capsule helps the bacteria evade phagocytosis by preventing the attachment of antibodies and complement proteins, allowing it to survive and proliferate in the host.
*Protein A*
- **Protein A** is a major virulence factor associated with *Staphylococcus aureus*, not *Streptococcus pneumoniae*.
- It binds to the Fc region of antibodies, particularly IgG, interfering with opsonization and phagocytosis.
*M protein*
- **M protein** is a key virulence factor found in *Streptococcus pyogenes* (Group A Streptococcus), which typically causes pharyngitis, scarlet fever, and rheumatic fever.
- While *Streptococcus pyogenes* also causes hemolysis, it exhibits **beta-hemolysis** (complete clearing) on blood agar, unlike the alpha-hemolysis seen in this patient's culture.
*Type III secretion system*
- **Type III secretion systems** are complex protein machines that inject bacterial effector proteins directly into host cells, commonly found in gram-negative bacteria such as *Salmonella*, *Shigella*, and *Pseudomonas*.
- *Streptococcus pneumoniae* is a **gram-positive bacterium** and does not possess a Type III secretion system.
*Lipopolysaccharide*
- **Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)**, also known as **endotoxin**, is a major component of the outer membrane of **gram-negative bacteria**.
- *Streptococcus pneumoniae* is a **gram-positive bacterium** and therefore lacks LPS.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 7: A 44-year-old Caucasian male complains of carpopedal spasms, peri-oral numbness, and paresthesias of the hands and feet. His wife also mentions that he had a seizure not too long ago. His past surgical history is significant for total thyroidectomy due to papillary thyroid carcinoma. They then realized all of the symptoms occurred after the surgery. Which of the following would be present in this patient?
- A. Chvostek sign, QT prolongation, increased PTH, decreased serum calcium, decreased serum phosphate
- B. Chvostek sign, QT prolongation, decreased PTH, decreased serum calcium, increased serum phosphate (Correct Answer)
- C. Chvostek sign, QT shortening, increased PTH, increased serum calcium, increased serum phosphate
- D. Chvostek sign, QT shortening, decreased PTH, decreased serum calcium, increased serum phosphate
- E. Chvostek sign, QT prolongation, decreased PTH, increased serum calcium, decreased serum phosphate
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Chvostek sign, QT prolongation, decreased PTH, decreased serum calcium, increased serum phosphate***
- The patient's symptoms of carpopedal spasms, peri-oral numbness, paresthesias, and seizures following a **total thyroidectomy** are classic signs of **hypocalcemia** due to **hypoparathyroidism**. This would lead to a **decreased PTH** level, which in turn causes **decreased serum calcium** and **increased serum phosphate** due to impaired renal phosphate excretion.
- **Hypocalcemia** characteristically causes **QT prolongation** on EKG and can manifest as the **Chvostek sign** (facial muscle twitching when tapping the facial nerve).
*Chvostek sign, QT prolongation, increased PTH, decreased serum calcium, decreased serum phosphate*
- This option incorrectly states **increased PTH**. The symptoms are due to iatrogenic hypoparathyroidism following thyroidectomy, which results in **decreased PTH** production.
- While **decreased serum calcium** and **Chvostek sign** are consistent, the PTH and phosphate levels described here are characteristic of **pseudohypoparathyroidism** or vitamin D deficiency, not post-surgical hypoparathyroidism.
*Chvostek sign, QT shortening, increased PTH, increased serum calcium, increased serum phosphate*
- **QT shortening** is typically associated with **hypercalcemia**, not hypocalcemia, and the patient's symptoms are indicative of hypocalcemia.
- **Increased serum calcium** and **increased PTH** would point towards primary hyperparathyroidism, which is the opposite of the clinical picture presented.
*Chvostek sign, QT shortening, decreased PTH, decreased serum calcium, increased serum phosphate*
- This option incorrectly states **QT shortening**. **Hypocalcemia** is known to cause **QT prolongation**, not shortening.
- While other findings like **decreased PTH**, **decreased serum calcium**, and **increased serum phosphate** are consistent with post-thyroidectomy hypoparathyroidism, the erroneous QT interval change makes this option incorrect.
*Chvostek sign, QT prolongation, decreased PTH, increased serum calcium, decreased serum phosphate*
- This option incorrectly states **increased serum calcium**. The symptoms of carpopedal spasms and paresthesias are classic manifestations of **hypocalcemia**.
- Additionally, **decreased serum phosphate** in the setting of decreased PTH would be unusual; **hypoparathyroidism** typically leads to **hyperphosphatemia** due to reduced renal phosphate excretion.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 8: A 41-year-old man presents to urgent care with a 1-week history of severe diarrhea. He says that he has been having watery stools every 2-3 hours. The stools do not contain blood and do not float. On presentation, he is observed to have significant facial flushing, and laboratory tests reveal the following:
Serum:
Na+: 137 mEq/L
K+: 2.7 mEq/L
Cl-: 113 mEq/L
HCO3-: 14 mEq/L
A computed tomography scan reveals a small intra-abdominal mass. Staining of this mass would most likely reveal production of which of the following?
- A. Insulin
- B. Glucagon
- C. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (Correct Answer)
- D. Somatostatin
- E. Gastrin
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Vasoactive intestinal peptide***
- The patient's presentation with **severe watery diarrhea**, **hypokalemia**, **metabolic acidosis** (low HCO3-), and **facial flushing** in the presence of an **intra-abdominal mass** is highly indicative of a **VIPoma**.
- VIPomas are neuroendocrine tumors that secrete large amounts of **vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)**, which stimulates intestinal fluid secretion and inhibits absorption, leading to characteristic symptoms.
*Insulin*
- **Insulinomas** typically cause symptoms related to **hypoglycemia** (e.g., sweating, palpitations, confusion), which are not described in this patient.
- While insulinomas can be associated with an intra-abdominal mass, the patient's symptoms are inconsistent with excessive insulin production.
*Glucagon*
- **Glucagonomas** classically present with a syndrome including **necrolytic migratory erythema**, **diabetes mellitus**, and weight loss, along with diarrhea in some cases.
- The distinct skin rash and hyperglycemia are absent in this patient's presentation.
*Somatostatin*
- **Somatostatinomas** are often associated with a triad of **diabetes mellitus**, **cholelithiasis**, and **steatorrhea**, and sometimes hypochlorhydria.
- The patient's symptoms of severe watery diarrhea and flushing are not typical of somatostatin overproduction.
*Gastrin*
- **Gastrinomas** (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome) cause severe **peptic ulcer disease** due to excessive gastric acid secretion, often leading to abdominal pain and chronic diarrhea.
- While diarrhea can occur, the prominent hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis, and flushing point away from a gastrinoma as the primary diagnosis.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 9: A 67-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department complaining of weakness and fatigue. She says she caught a “stomach bug” and has not been able to eat anything without vomiting for three days. Past medical history is significant for hyperlipidemia. She takes atorvastatin and a multivitamin daily, except for the last two days due to nausea. Today her heart rate is 106/min, respiratory rate is 16/min, temperature is 37.6°C (99.7°F) and blood pressure of 110/70 mm Hg. On physical examination, her oral mucosa is dry and she looks pale and uncomfortable. She is admitted for care and administered ondansetron. An intravenous infusion of normal saline is also initiated. An arterial blood gas is collected. Which of the following results is expected to be seen in this patient?
- A. pH: 7.48, pCO2: 44 mm Hg, HCO3-: 29 mEq/L (Correct Answer)
- B. pH: 7.49, pCO2: 33 mm Hg, HCO3-: 18 mEq/L
- C. pH: 7.31, pCO2: 62 mm Hg, HCO3-: 27 mEq/L
- D. pH: 7.30, pCO2: 36 mm Hg, HCO3-: 17 mEq/L
- E. pH: 7.36, pCO2: 42 mm Hg, HCO3-: 22 mEq/L
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***pH: 7.48, pCO2: 44 mm Hg, HCO3-: 29 mEq/L***
- The patient's prolonged vomiting leads to a loss of **gastric acid (HCl)**, resulting in an increase in serum bicarbonate (**metabolic alkalosis**), which is reflected by the elevated pH (7.48) and HCO3- (29 mEq/L).
- The pCO2 (44 mm Hg) is slightly elevated above normal (40 mm Hg), indicating the expected **respiratory compensation** for metabolic alkalosis (hypoventilation to retain CO2 and normalize pH).
*pH: 7.49, pCO2: 33 mm Hg, HCO3-: 18 mEq/L*
- This option indicates a **respiratory alkalosis** with partial metabolic compensation, characterized by a high pH, low pCO2, and low HCO3-.
- The patient's condition of prolonged vomiting would not lead to an acidic (low HCO3-) or hyperventilatory (low pCO2) state.
*pH: 7.31, pCO2: 62 mm Hg, HCO3-: 27 mEq/L*
- This result suggests **respiratory acidosis** with partial metabolic compensation, indicated by a low pH, high pCO2, and slightly elevated HCO3-.
- Vomiting primarily causes metabolic alkalosis due to loss of acid, not respiratory acidosis.
*pH: 7.30, pCO2: 36 mm Hg, HCO3-: 17 mEq/L*
- This option points to **metabolic acidosis** with a low pH and low HCO3-, and a near-normal pCO2, indicating minimal respiratory compensation.
- While dehydration can occur, the primary acid-base disturbance from prolonged vomiting is a loss of acid, leading to alkalosis, not acidosis.
*pH: 7.36, pCO2: 42 mm Hg, HCO3-: 22 mEq/L*
- These values fall within the **normal range**, implying no significant acid-base disturbance.
- The patient's symptoms of prolonged vomiting and dehydration would inevitably lead to an acid-base imbalance.
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG Question 10: A 22-year-old woman presents to the physician due to lightheadedness. Earlier in the day, she had her first job interview since graduating from college 3 months ago. While waiting outside the interviewer’s office, she began to feel nervous and started breathing really fast. She then felt as if she was going to faint. She excused herself from the interview, and requested a friend to drive her to the clinic. Which of the following is responsible for her symptoms?
- A. Increased arterial pO2
- B. Decreased arterial pH
- C. Decreased arterial pCO2 (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased plasma lactic acid
- E. Vagus nerve stimulation
Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) Explanation: ***Decreased arterial pCO2***
- The patient's **lightheadedness** and sensation of fainting, coupled with **rapid breathing** during a stressful situation, are classic signs of **hyperventilation syndrome**.
- Rapid breathing leads to excessive elimination of carbon dioxide, causing **respiratory alkalosis** and a decrease in arterial pCO2.
- Low pCO2 causes **cerebral vasoconstriction**, reducing cerebral blood flow and leading to **lightheadedness and presyncope**.
*Increased arterial pO2*
- While hyperventilation can slightly increase arterial pO2, this increase generally has **minimal physiological impact** and does not cause lightheadedness or syncope.
- The primary physiological consequence in this scenario is due to the **alteration of CO2 levels**, not O2.
*Decreased arterial pH*
- This symptom describes **acidosis**, which would typically result from conditions like hypoventilation (leading to CO2 retention) or metabolic disturbances.
- The patient's rapid breathing indicates **respiratory alkalosis**, which involves an **increased arterial pH**, not decreased.
*Increased plasma lactic acid*
- While stress can induce some **anaerobic metabolism**, leading to lactic acid production, the primary and most immediate cause of symptoms in acute hyperventilation is not lactic acidosis.
- **Lactic acidosis** is associated with more severe metabolic disturbances or sustained intense physical exertion, not acute anxiety-related hyperventilation.
*Vagus nerve stimulation*
- **Vagal stimulation** can lead to symptoms like lightheadedness and fainting by causing **bradycardia** and **vasodilation** (vasovagal syncope).
- However, this is typically associated with specific triggers and leads to a direct cardiovascular response rather than the **rapid breathing** pattern seen in this patient, which points to a respiratory cause.
More Buffer systems (bicarbonate, phosphate, protein) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.