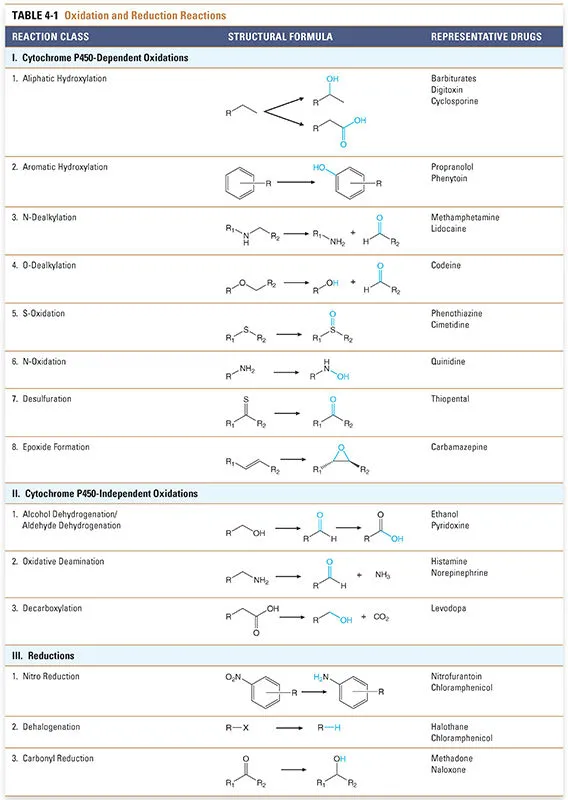
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 1 hour history of bruising and bleeding. He says that he fell and scraped his knee on the ground. Since then, he has been unable to stop the bleeding and has developed extensive bruising around the area. He has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation for which he is taking an oral medication. He says that he recently started taking omeprazole for reflux. Which of the following processes is most likely inhibited in this patient?
- A. Sulfation
- B. Oxidation (Correct Answer)
- C. Filtration
- D. Acetylation
- E. Glucuronidation
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Oxidation***
- The patient is taking **omeprazole**, a proton pump inhibitor, which is a known **CYP450 inhibitor**.
- Since the patient is also on an **oral anticoagulant** for atrial fibrillation, inhibition of CYP450 enzymes can reduce the metabolism of the anticoagulant, leading to **increased anticoagulant effect** and subsequent bleeding and bruising.
*Sulfation*
- **Sulfation** is a phase II metabolic reaction that converts compounds into more polar and excretable forms, but omeprazole primarily affects phase I metabolism involving CYP450 enzymes.
- While sulfation can be important for the metabolism of some drugs, it is not the primary process inhibited by omeprazole to cause increased bleeding with oral anticoagulants.
*Filtration*
- **Filtration** is a renal process and not a metabolic enzyme pathway affected by omeprazole.
- Omeprazole's interaction with anticoagulants mainly occurs through hepatic metabolism, not renal filtration.
*Acetylation*
- **Acetylation** is a phase II metabolic reaction, primarily carried out by **N-acetyltransferases**.
- Omeprazole is primarily known to interact with **CYP450 enzymes** (phase I metabolism) rather than N-acetyltransferases.
*Glucuronidation*
- **Glucuronidation** is a phase II metabolic reaction involving **UGT enzymes** that typically inactivates and increases the excretion of drugs.
- While important for drug metabolism, omeprazole's primary drug interactions leading to increased anticoagulant effects are via **CYP450 inhibition** (phase I metabolism), not directly through glucuronidation.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 2: An experimental infusable drug, X729, is currently being studied to determine its pharmacokinetics. The drug was found to have a half life of 1.5 hours and is eliminated by first order kinetics. What is the minimum number of hours required to reach a steady state concentration of >90%?
- A. 6 (Correct Answer)
- B. 3
- C. 7.5
- D. 1.5
- E. 4.5
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***6***
- For a drug eliminated by **first-order kinetics**, approximately **4 to 5 half-lives** are required to reach **steady-state concentration**.
- To reach >90% of steady-state, at least **4 half-lives** are needed, where **93.75%** of the steady state is achieved.
- The time taken would be **4 half-lives × 1.5 hours/half-life = 6 hours**, making this the **minimum time** to exceed 90%.
*3*
- This represents only **2 half-lives** (2 × 1.5 hours = 3 hours), which would achieve roughly **75%** of the steady-state concentration.
- This is insufficient to reach >90% of the steady-state concentration.
*7.5*
- This time point represents **5 half-lives** (5 × 1.5 hours = 7.5 hours), which would achieve approximately **97%** of the steady-state concentration.
- While this does exceed 90%, the question asks for the **minimum** number of hours required, and 90% is already exceeded at 6 hours (4 half-lives).
*1.5*
- This is only **1 half-life**, which would achieve approximately **50%** of the steady-state concentration.
- This is far too early to reach a >90% steady-state concentration.
*4.5*
- This represents **3 half-lives** (3 × 1.5 hours = 4.5 hours), achieving approximately **87.5%** of the steady-state concentration.
- While close to 90%, it does not quite reach "greater than 90%".
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 3: You are seeing a patient in clinic who recently started treatment for active tuberculosis. The patient is currently being treated with rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. The patient is not used to taking medicines and is very concerned about side effects. Specifically regarding the carbohydrate polymerization inhibiting medication, which of the following is a known side effect?
- A. Vision loss (Correct Answer)
- B. Paresthesias of the hands and feet
- C. Cutaneous flushing
- D. Arthralgias
- E. Elevated liver enzymes
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Vision loss***
- The "carbohydrate polymerization inhibiting medication" refers to **ethambutol**, which inhibits **arabinosyl transferase** (involved in mycobacterial cell wall arabinogalactan synthesis)
- **Ethambutol** causes **optic neuritis**, leading to **decreased visual acuity**, **red-green color blindness**, and potentially **irreversible vision loss**
- **Regular ophthalmologic monitoring** is essential during ethambutol therapy
*Paresthesias of the hands and feet*
- This describes **peripheral neuropathy** caused by **isoniazid**
- Isoniazid interferes with **pyridoxine (vitamin B6) metabolism**, leading to neurotoxicity
- Risk factors include malnutrition, diabetes, alcoholism, and pregnancy
- Prevented by **pyridoxine supplementation**
*Cutaneous flushing*
- Not a characteristic side effect of first-line anti-tuberculosis medications
- More commonly associated with niacin or certain allergic/vasodilatory reactions
*Arthralgias*
- Classic side effect of **pyrazinamide**, often affecting small joints
- Caused by **pyrazinamide-induced hyperuricemia** (inhibits renal uric acid excretion)
- May require dose adjustment or discontinuation if severe
*Elevated liver enzymes*
- **Hepatotoxicity** can occur with **rifampin**, **isoniazid**, and **pyrazinamide**
- Requires regular monitoring of liver function tests during TB treatment
- Most common serious adverse effect of combination TB therapy
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 4: A 17-year-old female is brought to the emergency room by her parents shortly after a suicide attempt by aspirin overdose. Which of the following acid/base changes will occur FIRST in this patient?
- A. Metabolic alkalosis
- B. Respiratory acidosis
- C. Anion gap metabolic acidosis
- D. Respiratory alkalosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Respiratory alkalosis***
- **Aspirin overdose** initially causes direct stimulation of the **respiratory center in the medulla**, leading to **hyperventilation**.
- This increased rate and depth of breathing blows off CO2, resulting in a primary **respiratory alkalosis**.
*Metabolic alkalosis*
- This is an unlikely primary event in aspirin overdose, which typically causes acidosis.
- While aspirin can cause electrolyte disturbances, a direct metabolic alkalosis as the *first* change is not characteristic.
*Respiratory acidosis*
- Respiratory depression, leading to respiratory acidosis, can occur in *severe* and *late-stage* aspirin overdose due to central nervous system depression.
- However, the initial effect is stimulation of respiration, causing alkalosis.
*Anion gap metabolic acidosis*
- This is a significant acid-base disturbance that *does* occur in aspirin overdose, but it develops *later*.
- Salicylates uncouple oxidative phosphorylation and impair cellular metabolism, leading to the accumulation of organic acids (e.g., lactic acid), causing a high anion gap metabolic acidosis.
*Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis*
- This type of acidosis is characterized by a preservation of the anion gap and is often associated with conditions like diarrhea or renal tubular acidosis.
- It is not the expected initial or primary acid-base disturbance in aspirin overdose.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 5: A research group wants to assess the safety and toxicity profile of a new drug. A clinical trial is conducted with 20 volunteers to estimate the maximum tolerated dose and monitor the apparent toxicity of the drug. The study design is best described as which of the following phases of a clinical trial?
- A. Phase 0
- B. Phase III
- C. Phase V
- D. Phase II
- E. Phase I (Correct Answer)
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Phase I***
- **Phase I clinical trials** involve a small group of healthy volunteers (typically 20-100) to primarily assess **drug safety**, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side effects.
- The main goal is to establish the **maximum tolerated dose (MTD)** and evaluate the drug's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory studies conducted in a very small number of subjects (10-15) to gather preliminary data on a drug's **pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics** in humans.
- They involve microdoses, not intended to have therapeutic effects, and thus cannot determine toxicity or MTD.
*Phase III*
- **Phase III trials** are large-scale studies involving hundreds to thousands of patients to confirm the drug's **efficacy**, monitor side effects, compare it to standard treatments, and collect information that will allow the drug to be used safely.
- These trials are conducted after safety and initial efficacy have been established in earlier phases.
*Phase V*
- "Phase V" is not a standard, recognized phase in the traditional clinical trial classification (Phase 0, I, II, III, IV).
- This term might be used in some non-standard research contexts or for post-marketing studies that go beyond Phase IV surveillance, but it is not a formal phase for initial drug development.
*Phase II*
- **Phase II trials** involve several hundred patients with the condition the drug is intended to treat, focusing on **drug efficacy** and further evaluating safety.
- While safety is still monitored, the primary objective shifts to determining if the drug works for its intended purpose and at what dose.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 6: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 7: A 76-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. One week ago, he was prescribed azithromycin for acute bacterial sinusitis. He has a history of atrial fibrillation treated with warfarin and metoprolol. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Compared to one month ago, laboratory studies show a mild increase in INR. Which of the following best explains this patient's laboratory finding?
- A. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity
- B. Depletion of intestinal flora
- C. Inhibition of cytochrome p450 (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased gastrointestinal absorption of warfarin
- E. Increased non-protein bound warfarin fraction
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Inhibition of cytochrome p450***
- **Azithromycin**, while a weaker inhibitor compared to erythromycin and clarithromycin, **does inhibit CYP3A4 and other cytochrome P450 enzymes** to a clinically significant degree.
- This inhibition **reduces warfarin metabolism**, leading to increased warfarin levels and **enhanced anticoagulant effect**, manifesting as an **increased INR**.
- This pharmacokinetic interaction is well-documented and is the **primary mechanism** for azithromycin-warfarin interaction.
*Depletion of intestinal flora*
- The theory that antibiotics deplete **vitamin K-producing gut bacteria** leading to increased warfarin effect is a **common misconception**.
- Humans obtain vitamin K primarily from **dietary sources** (leafy greens, vegetable oils), not from gut bacterial synthesis; intestinal bacteria contribute minimally to vitamin K stores.
- This mechanism has been **debunked** in modern pharmacology literature and does not explain antibiotic-warfarin interactions.
*Drug-induced hepatotoxicity*
- While hepatotoxicity can impair **clotting factor synthesis** and increase INR, **azithromycin** rarely causes significant liver injury.
- The presentation shows only a **mild INR increase** one week after starting therapy, without other signs of liver dysfunction.
- This acute, mild change is more consistent with a **pharmacokinetic drug interaction** than hepatotoxicity.
*Increased gastrointestinal absorption of warfarin*
- **Warfarin** has high oral bioavailability (~100%) under normal conditions.
- **Azithromycin** does not enhance the **gastrointestinal absorption** of warfarin.
- This mechanism is not supported by pharmacological evidence for this drug interaction.
*Increased non-protein bound warfarin fraction*
- Displacement of warfarin from **plasma protein binding sites** can transiently increase free drug.
- However, **azithromycin** does not significantly displace warfarin from **albumin**.
- This mechanism does not explain the sustained INR elevation seen with azithromycin therapy.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 8: After being warned by the locals not to consume the freshwater, a group of American backpackers set off on a week-long hike into a region of the Ecuadorean Amazon forest known for large gold mines. The group of hikers stopped near a small stream and used the water they filtered from the stream to make dinner. Within the next half hour, the hikers began to experience headaches, vertigo, visual disturbances, confusion, tachycardia, and altered levels of consciousness. Which of the following enzymes was most likely inhibited in this group of hikers?
- A. NADH dehydrogenase
- B. ATP synthase
- C. Cytochrome c oxidase (Correct Answer)
- D. Cytochrome bc1 complex
- E. Succinate dehydrogenase
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Cytochrome c oxidase***
- The symptoms described (headaches, vertigo, visual disturbances, confusion, tachycardia, altered consciousness occurring within 30 minutes) are characteristic of **acute cyanide poisoning**.
- **Cyanide** is commonly found in water near **gold mining operations**, where it is used in the gold extraction process and can contaminate local water sources.
- **Cyanide** is a potent inhibitor of **cytochrome c oxidase** (Complex IV) in the electron transport chain, binding to the heme iron (Fe³⁺) and preventing oxygen utilization, leading to **histotoxic hypoxia**.
- This results in cellular energy failure, particularly affecting high-energy-demand organs like the brain and heart, explaining the acute neurological and cardiovascular symptoms.
*NADH dehydrogenase*
- While NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) is a component of the electron transport chain, it is not the primary target of **cyanide poisoning**.
- Inhibitors of Complex I include rotenone and barbiturates, which cause different clinical presentations and do not produce the rapid onset of symptoms seen with cyanide.
*ATP synthase*
- **ATP synthase** (Complex V) synthesizes ATP using the proton gradient, but it is not directly inhibited by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of ATP synthase, such as oligomycin, prevent ATP synthesis by blocking the enzyme directly, whereas cyanide acts upstream at Complex IV.
*Cytochrome bc1 complex*
- The **cytochrome bc1 complex** (Complex III) is involved in electron transfer and proton pumping, but it is not the primary enzyme inhibited by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of Complex III include antimycin A, which would disrupt the electron transport chain but do not cause the characteristic rapid-onset symptoms of cyanide poisoning.
*Succinate dehydrogenase*
- **Succinate dehydrogenase** (Complex II) participates in both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain, but it is not targeted by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of Complex II, such as malonate, competitively block succinate oxidation but do not produce the acute systemic toxicity characteristic of cyanide poisoning.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for his first appointment. He recently was released from prison. The patient wants a checkup before he goes out and finds a job. He states that lately he has felt very fatigued and has had a cough. He has lost roughly 15 pounds over the past 3 weeks. He attributes this to intravenous drug use in prison. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 127/68 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 18/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient is started on appropriate treatment. Which of the following is the most likely indication to discontinue this patient's treatment?
- A. Optic neuritis
- B. Peripheral neuropathy
- C. Hyperuricemia
- D. Elevated liver enzymes (Correct Answer)
- E. Red body excretions
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Elevated liver enzymes***
- The patient's presentation (fatigue, cough, weight loss, history of IV drug use, prison exposure) is highly suggestive of **active tuberculosis (TB)**, which is typically treated with a multi-drug regimen including **isoniazid** and **rifampin**.
- Both isoniazid and rifampin are associated with **hepatotoxicity**; significant elevation of liver enzymes (e.g., >5 times the upper limit of normal) is a strong indication to discontinue or modify the treatment regimen to prevent severe liver damage.
*Optic neuritis*
- **Ethambutol**, another first-line anti-TB drug, can cause **optic neuritis** (inflammation of the optic nerve) leading to vision changes or loss.
- While a serious side effect requiring discontinuation of ethambutol, it is specific to that drug and not a general indication to stop all anti-TB treatment as would be the case with widespread hepatotoxicity.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- **Isoniazid** can cause **peripheral neuropathy** due to interference with pyridoxine (vitamin B6) metabolism.
- This side effect can often be prevented or managed by co-administration of **pyridoxine** and does not typically necessitate discontinuation of isoniazid unless severe and unmanageable.
*Hyperuricemia*
- **Pyrazinamide**, another first-line TB drug, can cause **hyperuricemia** (elevated uric acid levels) by inhibiting urate excretion.
- While it can precipitate **gouty arthritis**, hyperuricemia alone is generally not an indication to discontinue pyrazinamide unless symptoms are severe or progress to acute gout.
*Red body excretions*
- **Rifampin** commonly causes **red-orange discoloration of urine, sweat, tears, and other body fluids**, which is a harmless side effect.
- This is an expected and benign pharmacological effect of the drug and does not warrant discontinuation of treatment.
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG Question 10: You are currently employed as a clinical researcher working on clinical trials of a new drug to be used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Currently, you have already determined the safe clinical dose of the drug in a healthy patient. You are in the phase of drug development where the drug is studied in patients with the target disease to determine its efficacy. Which of the following phases is this new drug currently in?
- A. Phase 4
- B. Phase 1
- C. Phase 2 (Correct Answer)
- D. Phase 0
- E. Phase 3
Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) Explanation: ***Phase 2***
- **Phase 2 trials** involve studying the drug in patients with the target disease to assess its **efficacy** and further evaluate safety, typically involving a few hundred patients.
- The question describes a stage after safe dosing in healthy patients (Phase 1) and before large-scale efficacy confirmation (Phase 3), focusing on efficacy in the target population.
*Phase 4*
- **Phase 4 trials** occur **after a drug has been approved** and marketed, monitoring long-term effects, optimal use, and rare side effects in a diverse patient population.
- This phase is conducted post-market approval, whereas the question describes a drug still in development prior to approval.
*Phase 1*
- **Phase 1 trials** primarily focus on determining the **safety and dosage** of a new drug in a **small group of healthy volunteers** (or sometimes patients with advanced disease if the drug is highly toxic).
- The question states that the safe clinical dose in a healthy patient has already been determined, indicating that Phase 1 has been completed.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory, very early-stage studies designed to confirm that the drug reaches the target and acts as intended, typically involving a very small number of doses and participants.
- These trials are conducted much earlier in the development process, preceding the determination of safe clinical doses and large-scale efficacy studies.
*Phase 3*
- **Phase 3 trials** are large-scale studies involving hundreds to thousands of patients to confirm **efficacy**, monitor side effects, compare it to commonly used treatments, and collect information that will allow the drug to be used safely.
- While Phase 3 does assess efficacy, it follows Phase 2 and is typically conducted on a much larger scale before submitting for regulatory approval.
More Phase I metabolism (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.