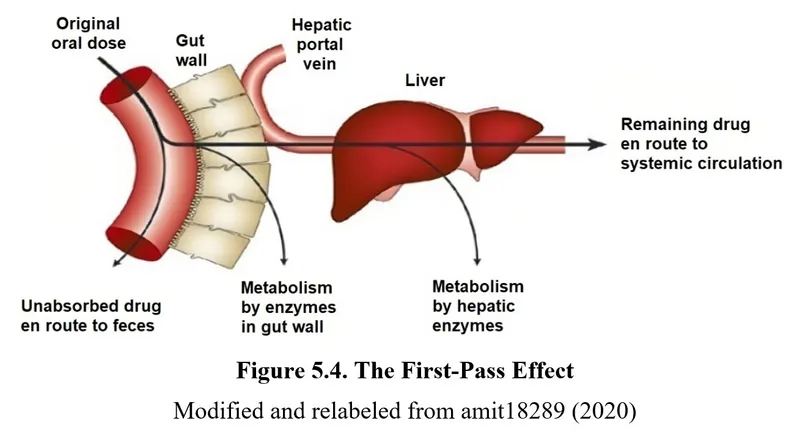
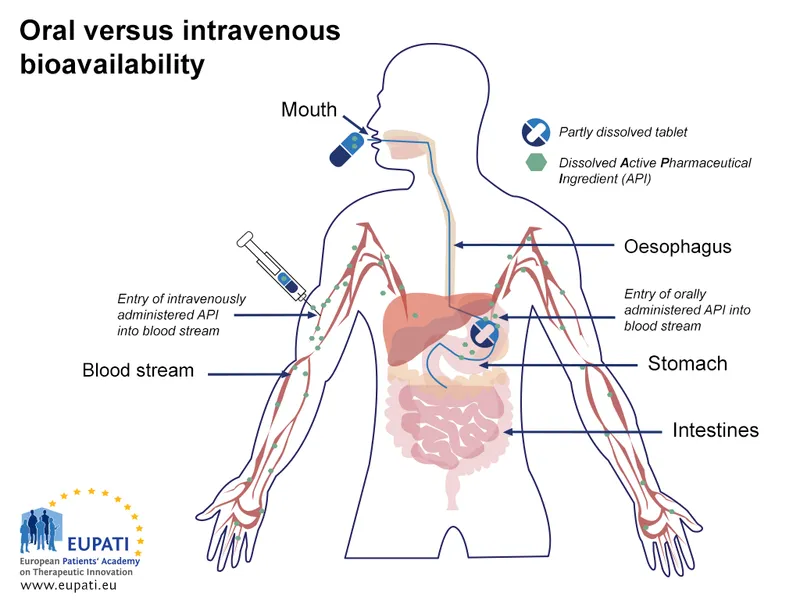
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for First-pass metabolism. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 1 hour history of bruising and bleeding. He says that he fell and scraped his knee on the ground. Since then, he has been unable to stop the bleeding and has developed extensive bruising around the area. He has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation for which he is taking an oral medication. He says that he recently started taking omeprazole for reflux. Which of the following processes is most likely inhibited in this patient?
- A. Sulfation
- B. Oxidation (Correct Answer)
- C. Filtration
- D. Acetylation
- E. Glucuronidation
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Oxidation***
- The patient is taking **omeprazole**, a proton pump inhibitor, which is a known **CYP450 inhibitor**.
- Since the patient is also on an **oral anticoagulant** for atrial fibrillation, inhibition of CYP450 enzymes can reduce the metabolism of the anticoagulant, leading to **increased anticoagulant effect** and subsequent bleeding and bruising.
*Sulfation*
- **Sulfation** is a phase II metabolic reaction that converts compounds into more polar and excretable forms, but omeprazole primarily affects phase I metabolism involving CYP450 enzymes.
- While sulfation can be important for the metabolism of some drugs, it is not the primary process inhibited by omeprazole to cause increased bleeding with oral anticoagulants.
*Filtration*
- **Filtration** is a renal process and not a metabolic enzyme pathway affected by omeprazole.
- Omeprazole's interaction with anticoagulants mainly occurs through hepatic metabolism, not renal filtration.
*Acetylation*
- **Acetylation** is a phase II metabolic reaction, primarily carried out by **N-acetyltransferases**.
- Omeprazole is primarily known to interact with **CYP450 enzymes** (phase I metabolism) rather than N-acetyltransferases.
*Glucuronidation*
- **Glucuronidation** is a phase II metabolic reaction involving **UGT enzymes** that typically inactivates and increases the excretion of drugs.
- While important for drug metabolism, omeprazole's primary drug interactions leading to increased anticoagulant effects are via **CYP450 inhibition** (phase I metabolism), not directly through glucuronidation.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 2: An experimental infusable drug, X729, is currently being studied to determine its pharmacokinetics. The drug was found to have a half life of 1.5 hours and is eliminated by first order kinetics. What is the minimum number of hours required to reach a steady state concentration of >90%?
- A. 6 (Correct Answer)
- B. 3
- C. 7.5
- D. 1.5
- E. 4.5
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***6***
- For a drug eliminated by **first-order kinetics**, approximately **4 to 5 half-lives** are required to reach **steady-state concentration**.
- To reach >90% of steady-state, at least **4 half-lives** are needed, where **93.75%** of the steady state is achieved.
- The time taken would be **4 half-lives × 1.5 hours/half-life = 6 hours**, making this the **minimum time** to exceed 90%.
*3*
- This represents only **2 half-lives** (2 × 1.5 hours = 3 hours), which would achieve roughly **75%** of the steady-state concentration.
- This is insufficient to reach >90% of the steady-state concentration.
*7.5*
- This time point represents **5 half-lives** (5 × 1.5 hours = 7.5 hours), which would achieve approximately **97%** of the steady-state concentration.
- While this does exceed 90%, the question asks for the **minimum** number of hours required, and 90% is already exceeded at 6 hours (4 half-lives).
*1.5*
- This is only **1 half-life**, which would achieve approximately **50%** of the steady-state concentration.
- This is far too early to reach a >90% steady-state concentration.
*4.5*
- This represents **3 half-lives** (3 × 1.5 hours = 4.5 hours), achieving approximately **87.5%** of the steady-state concentration.
- While close to 90%, it does not quite reach "greater than 90%".
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 3: A scientist is trying to design a drug to modulate cellular metabolism in the treatment of obesity. Specifically, he is interested in understanding how fats are processed in adipocytes in response to different energy states. His target is a protein within these cells that catalyzes catabolism of an energy source. The products of this reaction are subsequently used in gluconeogenesis or β-oxidation. Which of the following is true of the most likely protein that is being studied by this scientist?
- A. It is stimulated by epinephrine (Correct Answer)
- B. It is inhibited by glucagon
- C. It is inhibited by acetylcholine
- D. It is inhibited by cortisol
- E. It is stimulated by insulin
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***It is stimulated by epinephrine***
- The protein described is likely **hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL)**, which catabolizes **triglycerides** in adipocytes to **glycerol** and **fatty acids**.
- **Epinephrine** (and norepinephrine) stimulates HSL activity via a **cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)** pathway, leading to increased fatty acid release for energy.
*It is inhibited by glucagon*
- **Glucagon primarily acts on the liver** to promote gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, but it does **not directly inhibit HSL** in adipocytes.
- While glucagon has a lipolytic effect, it doesn't inhibit the enzyme that releases fatty acids.
*It is inhibited by acetylcholine*
- **Acetylcholine** is a neurotransmitter involved in the **parasympathetic nervous system**, which generally promotes energy storage.
- It does **not directly inhibit HSL**; its effects on lipid metabolism are indirect and typically involve other pathways.
*It is inhibited by cortisol*
- **Cortisol**, a glucocorticoid, generally **promotes lipolysis** (breakdown of fats) in certain contexts, particularly during stress to provide energy substrates.
- Therefore, it would **not inhibit HSL**; rather, it often enhances its activity or provides a permissive effect for other lipolytic hormones.
*It is stimulated by insulin*
- **Insulin** is an **anabolic hormone** that promotes energy storage, including **lipogenesis** (fat synthesis) and inhibits lipolysis.
- Insulin **inhibits HSL activity** by activating phosphodiesterase, which reduces cAMP levels, thus deactivating PKA and preventing HSL phosphorylation.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 4: A 56-year-old man with coronary artery disease agrees to participate in a pharmacological study. He takes an oral medication that leads to dephosphorylation of myosin light chains in venous smooth muscle cells. An investigator measures the plasma concentration of the drug over time after intravenous and then after oral administration. There is no statistically significant difference in the dose-corrected area under the curve for the 2 routes of administration. The patient most likely ingested which of the following drugs?
- A. Isosorbide mononitrate (Correct Answer)
- B. Nitroglycerine
- C. Nimodipine
- D. Nifedipine
- E. Nitroprusside
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Isosorbide mononitrate***
- **Isosorbide mononitrate** has nearly **100% oral bioavailability** due to minimal first-pass metabolism, which explains the comparable AUC between intravenous and oral administration.
- This drug acts by releasing **nitric oxide**, leading to dephosphorylation of myosin light chains and subsequent **venous smooth muscle relaxation**, a mechanism consistent with the question stem.
*Nitroglycerine*
- **Nitroglycerine** undergoes extensive **first-pass metabolism** when taken orally, resulting in very low oral bioavailability and a significantly smaller AUC compared to intravenous administration.
- It is typically administered sublingually or transdermally to avoid hepatic metabolism and achieve therapeutic effects.
*Nimodipine*
- **Nimodipine** is a **dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** used for cerebral vasospasm, not primarily as a venous dilator acting via myosin light chain dephosphorylation.
- While it can be given orally, its mechanism of action and primary clinical use are different from the description.
*Nifedipine*
- **Nifedipine** is another **dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** primarily affecting arterial smooth muscle, not venous smooth muscle via myosin light chain dephosphorylation.
- It undergoes significant first-pass metabolism, leading to variable oral bioavailability, which would likely result in a noticeable difference in AUC compared to IV administration.
*Nitroprusside*
- **Nitroprusside** is an **intravenously administered agent** that directly releases nitric oxide, but it has no oral formulation due to rapid degradation and toxicity.
- Its use is limited to acute hypertensive emergencies and it does not fit the description of an orally administered drug with high bioavailability.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 5: A 28-year-old woman presents to a psychiatrist with a 10-year history of unexplained anxiety symptoms. To date, she has not visited any psychiatrist, because she believes that she should not take medicines to change her emotions or thoughts. However, after explaining the nature of her disorder, the psychiatrist prescribes daily alprazolam. When she comes for her first follow-up, she reports excellent relief from her symptoms without any side-effects. The psychiatrist encourages her to continue her medication for the next 3 months and then return for a follow-up visit. After 3 months, she tells her psychiatrist that she has been experiencing excessive sedation and drowsiness over the last few weeks. The psychiatrist finds that she is taking alprazolam in the correct dosage, and she is not taking any other medication that causes sedation. Upon asking her about any recent changes in her lifestyle, she mentions that for the last 2 months, she has made a diet change. The psychiatrist tells her that diet change may be the reason why she is experiencing excessive sedation and drowsiness. Which of the following is the most likely diet change the psychiatrist is talking about?
- A. Daily consumption of tomatoes
- B. Daily consumption of St. John's wort
- C. Daily consumption of cruciferous vegetables
- D. Daily consumption of grapefruit juice (Correct Answer)
- E. Daily consumption of charcoal-broiled foods
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Daily consumption of grapefruit juice***
- **Grapefruit juice** is a potent inhibitor of the **CYP3A4 enzyme**, which is responsible for the metabolism of **alprazolam**.
- Inhibition of CYP3A4 leads to **increased plasma concentrations of alprazolam**, enhancing its sedative effects and causing drowsiness.
*Daily consumption of tomatoes*
- **Tomatoes** do not significantly interact with the metabolism of **alprazolam** or other benzodiazepines.
- They are a healthy food item with no known common drug interactions relevant to alprazolam's side effects.
*Daily consumption of St. John's wort*
- **St. John's wort** is a known **CYP3A4 inducer**, meaning it would *decrease* alprazolam levels, potentially leading to reduced efficacy.
- It would not cause increased sedation or drowsiness due to higher alprazolam concentrations.
*Daily consumption of cruciferous vegetables*
- **Cruciferous vegetables** (e.g., broccoli, cabbage) can induce certain CYP enzymes but generally do not significantly interfere with **alprazolam metabolism** to cause increased sedation.
- Their effects on drug metabolism are usually less pronounced or specific to other enzyme systems.
*Daily consumption of charcoal-broiled foods*
- **Charcoal-broiled foods** can induce **CYP1A2 enzymes**, but **alprazolam** is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4.
- Therefore, this dietary change is unlikely to significantly impact alprazolam metabolism or lead to increased sedation.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for his first appointment. He recently was released from prison. The patient wants a checkup before he goes out and finds a job. He states that lately he has felt very fatigued and has had a cough. He has lost roughly 15 pounds over the past 3 weeks. He attributes this to intravenous drug use in prison. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 127/68 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 18/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient is started on appropriate treatment. Which of the following is the most likely indication to discontinue this patient's treatment?
- A. Optic neuritis
- B. Peripheral neuropathy
- C. Hyperuricemia
- D. Elevated liver enzymes (Correct Answer)
- E. Red body excretions
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Elevated liver enzymes***
- The patient's presentation (fatigue, cough, weight loss, history of IV drug use, prison exposure) is highly suggestive of **active tuberculosis (TB)**, which is typically treated with a multi-drug regimen including **isoniazid** and **rifampin**.
- Both isoniazid and rifampin are associated with **hepatotoxicity**; significant elevation of liver enzymes (e.g., >5 times the upper limit of normal) is a strong indication to discontinue or modify the treatment regimen to prevent severe liver damage.
*Optic neuritis*
- **Ethambutol**, another first-line anti-TB drug, can cause **optic neuritis** (inflammation of the optic nerve) leading to vision changes or loss.
- While a serious side effect requiring discontinuation of ethambutol, it is specific to that drug and not a general indication to stop all anti-TB treatment as would be the case with widespread hepatotoxicity.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- **Isoniazid** can cause **peripheral neuropathy** due to interference with pyridoxine (vitamin B6) metabolism.
- This side effect can often be prevented or managed by co-administration of **pyridoxine** and does not typically necessitate discontinuation of isoniazid unless severe and unmanageable.
*Hyperuricemia*
- **Pyrazinamide**, another first-line TB drug, can cause **hyperuricemia** (elevated uric acid levels) by inhibiting urate excretion.
- While it can precipitate **gouty arthritis**, hyperuricemia alone is generally not an indication to discontinue pyrazinamide unless symptoms are severe or progress to acute gout.
*Red body excretions*
- **Rifampin** commonly causes **red-orange discoloration of urine, sweat, tears, and other body fluids**, which is a harmless side effect.
- This is an expected and benign pharmacological effect of the drug and does not warrant discontinuation of treatment.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 7: A 45-year-old Caucasian man is given nitroglycerin for the management of his stable angina. Nitroglycerin given for the rapid relief of acute angina would most likely be given through what route of administration?
- A. Subcutaneous injection
- B. Intramuscular injection
- C. Intravenous injection
- D. Sublingual (Correct Answer)
- E. Oral
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Sublingual***
- **Sublingual** administration provides rapid absorption into the bloodstream through the oral mucosa, bypassing first-pass metabolism, which is crucial for quick relief of acute angina.
- This route allows the medication to exert its vasodilatory effects within 1-3 minutes, alleviating chest pain efficiently.
- It is the **standard of care** for outpatient management of acute angina episodes due to ease of self-administration.
*Subcutaneous injection*
- **Subcutaneous injection** has a slower onset of action compared to sublingual administration, making it unsuitable for rapid relief of acute angina.
- While it avoids first-pass metabolism, the absorption rate is not fast enough for emergency situations.
*Intramuscular injection*
- **Intramuscular injection** also has a relatively slower onset of action and is less predictable for rapid relief compared to sublingual routes.
- It is not a standard route for acute angina management due to the need for immediate action.
*Intravenous injection*
- **Intravenous administration** provides immediate systemic availability and is used for continuous infusion in unstable angina or acute coronary syndromes in hospital settings.
- However, it is **not practical for outpatient or self-administered rapid relief** due to the need for IV access, medical personnel, and monitoring.
- While highly effective in critical care, it is not the route for typical acute angina episodes outside the hospital.
*Oral*
- **Oral administration** undergoes significant **first-pass metabolism** in the liver, which delays the onset of action and reduces bioavailability, rendering it ineffective for rapid relief of acute angina.
- The delayed absorption (typically 30-60 minutes) makes it impractical for emergency situations where immediate vasodilation is needed.
- Oral nitrates are used for prophylaxis, not acute relief.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 8: Which of the following is correct about the EMLA patch shown in the image below?
- A. Adverse effect is methemoglobinemia
- B. Contains bupivacaine & lignocaine
- C. Eutectic mixture is used (Correct Answer)
- D. 0.5% concentration of lignocaine has 50 mg in 1 gm is used
- E. Requires application for at least 15 minutes for adequate anesthesia
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Eutectic mixture is used***
- EMLA stands for **Eutectic Mixture of Local Anesthetics**, indicating that it uses a mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine to lower their melting points, allowing them to remain liquid at room temperature.
- This liquid form enhances skin penetration, providing more effective topical anesthesia compared to individual agents.
*Adverse effect is methemoglobinemia*
- While methemoglobinemia is a potential side effect of **prilocaine**, which is part of the EMLA cream, it is usually only seen with **excessive doses** or in susceptible individuals (e.g., infants).
- Given its topical application and typical dosing, it is not the most common or direct feature associated with correct use of the EMLA patch.
*Contains bupivacaine & lignocaine*
- The EMLA patch contains **lidocaine (lignocaine)** and **prilocaine**, not bupivacaine.
- Bupivacaine is another local anesthetic, but it is not a component of the EMLA formulation.
*0.5% concentration of lignocaine has 50 mg in 1 gm is used*
- The EMLA patch typically contains a 2.5% concentration of **lidocaine** and 2.5% of **prilocaine**, meaning 25 mg of each per gram of cream.
- A 0.5% concentration would be 5 mg per gram, so the stated concentration and amount are incorrect for the EMLA formulation.
*Requires application for at least 15 minutes for adequate anesthesia*
- EMLA requires a **minimum of 60 minutes** of application time for adequate dermal anesthesia, not 15 minutes.
- For procedures on intact skin, the recommended application time is **60-120 minutes** to achieve optimal anesthetic effect.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 9: Serum studies show a troponin T concentration of 6.73 ng/mL (N < 0.01), and fingerstick blood glucose concentration of 145 mg/dL. The cardiac catheterization team is activated. Treatment with unfractionated heparin, aspirin, ticagrelor, and sublingual nitroglycerin is begun, and the patient's pain subsides. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 65/min, respirations are 23/min, and blood pressure is 91/60 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 96%. Which of the following is the most appropriate additional pharmacotherapy?
- A. Intravenous morphine
- B. Intravenous furosemide
- C. Intravenous insulin
- D. Oral atorvastatin (Correct Answer)
- E. Intravenous nitroglycerin
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Oral atorvastatin***
- All patients with **acute coronary syndrome (ACS)** should receive high-intensity statin therapy, such as **atorvastatin 80 mg daily**, as early as possible.
- Statins stabilize plaques, reduce inflammation, and improve endothelial function, which are crucial in the acute setting of a myocardial infarction.
*Intravenous morphine*
- Morphine can be used for persistent chest pain refractory to nitroglycerin, but its routine use is now questioned due to potential adverse effects like hypotension and delayed antiplatelet absorption.
- The patient's pain has already subsided with initial treatment, and his blood pressure is already low (91/60 mm Hg), making morphine less appropriate.
*Intravenous furosemide*
- Furosemide is a loop diuretic primarily used for treating **fluid overload** and **pulmonary edema**, which are not indicated by the patient's current presentation (oxygen saturation 96%, no mention of crackles or dyspnea).
- Its use in a patient with **borderline hypotension** could worsen hemodynamic stability.
*Intravenous insulin*
- While the patient has elevated fingerstick glucose (145 mg/dL), this level does not immediately require intravenous insulin unless there is evidence of **diabetic ketoacidosis** or **hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state**, or persistent severe hyperglycemia.
- More moderate hyperglycemia can often be managed with subcutaneous insulin or diet in the acute phase, and focuses remain on cardiac stabilization.
*Intravenous nitroglycerin*
- Intravenous nitroglycerin is indicated for ongoing ischemic chest pain or uncontrolled hypertension in ACS, but the patient's pain has subsided and he is **hypotensive** (91/60 mm Hg).
- Administering more nitroglycerin would likely worsen his hypotension and could compromise coronary perfusion.
First-pass metabolism US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old woman is transferred to the intensive care unit after she underwent coronary stenting for a posterior-inferior STEMI. She is known to have allergies to amiodarone and captopril. A few hours after the transfer, she suddenly loses consciousness. The monitor shows ventricular fibrillation. CPR is initiated. After 3 consecutive shocks with a defibrillator, the monitor shows ventricular fibrillation. Which of the following medications should be administered next?
- A. Adrenaline and lidocaine (Correct Answer)
- B. Lidocaine and sotalol
- C. Adrenaline and verapamil
- D. Adrenaline and amiodarone
- E. Amiodarone and lidocaine
First-pass metabolism Explanation: ***Adrenaline and lidocaine***
- **Adrenaline (epinephrine)** is the standard vasopressor in ACLS for cardiac arrest, given at 1 mg IV/IO every 3-5 minutes to increase coronary and cerebral perfusion pressures, improving the chances of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
- **Lidocaine** is the recommended alternative antiarrhythmic for refractory ventricular fibrillation when **amiodarone is contraindicated** (as in this patient with documented amiodarone allergy).
- Per **ACLS guidelines**, after failed defibrillation attempts, continue CPR, administer epinephrine, and give an antiarrhythmic agent (lidocaine 1-1.5 mg/kg when amiodarone cannot be used).
*Lidocaine and sotalol*
- **Lidocaine** is appropriate as an antiarrhythmic in refractory VF when amiodarone is contraindicated.
- However, this option omits **epinephrine (adrenaline)**, which is a critical vasopressor required during cardiac arrest per ACLS protocols.
- **Sotalol** is a beta-blocker with Class III antiarrhythmic properties, but it is not recommended for acute management of refractory VF in cardiac arrest.
*Adrenaline and verapamil*
- **Adrenaline** is indicated as the vasopressor for cardiac arrest.
- **Verapamil** is a calcium channel blocker used for supraventricular arrhythmias; it is **contraindicated in ventricular fibrillation** due to negative inotropic effects and peripheral vasodilation that can worsen hemodynamic collapse during cardiac arrest.
*Adrenaline and amiodarone*
- While **adrenaline** is indicated and **amiodarone** would typically be the preferred antiarrhythmic for refractory VF, this patient has a **documented allergy to amiodarone**, making it contraindicated.
- Lidocaine must be used as the alternative antiarrhythmic agent.
*Amiodarone and lidocaine*
- **Lidocaine** is appropriate in this scenario.
- However, **amiodarone is contraindicated** due to the patient's known allergy.
- This combination would be dangerous and violates basic principles of avoiding known allergens.
More First-pass metabolism US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.