Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Dosing in hepatic impairment. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 1: Two months after giving birth to a boy, a 27-year-old woman comes to the physician with her infant for a well-child examination. She was not seen by a physician during her pregnancy. Physical examination of the mother and the boy shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show elevated titers of hepatitis B surface antigen in both the mother and the boy. Which of the following statements regarding the infant's condition is most accurate?
- A. Hepatitis B e antigen titer is likely undetectable
- B. Chronic infection is unlikely
- C. Lifetime risk of hepatocellular carcinoma is low
- D. Significant elevation of transaminases is not expected (Correct Answer)
- E. The viral replication rate is low
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: **Significant elevation of transaminases is not expected**
- Infants infected with HBV vertically are often **immunologically tolerant** to the virus, leading to low or normal levels of **alanine aminotransferase (ALT)** and **aspartate aminotransferase (AST)** despite high viral loads.
- This **immune tolerance** means their immune system does not actively attack infected hepatocytes, preventing inflammation and liver damage in the early stages.
*Hepatitis B e antigen titer is likely undetectable*
- In infants with **vertical transmission** of HBV, especially when not treated, the **HBeAg titer** is typically **HIGH** and detectable, indicating active viral replication.
- A detectable HBeAg in this scenario signifies a **highly infectious state** and is a marker of high viral load.
*Chronic infection is unlikely*
- Perinatal transmission of HBV has a very high — 70-90% — likelihood of leading to **chronic HBV infection** if the infant is not properly immunized at birth.
- The presence of **HBsAg in both mother and child** and lack of prenatal care strongly suggest chronic infection in the infant.
*Lifetime risk of hepatocellular carcinoma is low*
- Infants who acquire HBV perinatally and develop **chronic infection** have a significantly **increased lifetime risk** of developing **cirrhosis** and **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**.
- The immune tolerance and persistent viral replication in early life contribute to long-term liver disease progression.
*The viral replication rate is low*
- In infants with vertically transmitted HBV who are in the **immune-tolerant phase**, the **viral replication rate is high**, often characterized by very high HBV DNA levels.
- This high replication without significant immune response is why they are often asymptomatic but highly infectious.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old woman is started on a new experimental intravenous drug X. In order to make sure that she is able to take this drug safely, the physician in charge of her care calculates the appropriate doses to give to this patient. Data on the properties of drug X from a subject with a similar body composition to the patient is provided below:
Weight: 100 kg
Dose provided: 1500 mg
Serum concentration 15 mg/dL
Bioavailability: 1
If the patient has a weight of 60 kg and the target serum concentration is 10 mg/dL, which of the following best represents the loading dose of drug X that should be given to this patient?
- A. 300 mg
- B. 450 mg
- C. 150 mg
- D. 1000 mg
- E. 600 mg (Correct Answer)
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***600 mg***
- First, calculate the **volume of distribution (Vd)** using the provided data: **Vd = Total Dose / Serum Concentration**. Converting units: 15 mg/dL = 150 mg/L. Therefore, Vd = 1500 mg / 150 mg/L = **10 L** (for the 100 kg subject).
- Since the Vd value is for a 100 kg person, Vd per kg = 10 L / 100 kg = **0.1 L/kg**. For the 60 kg patient, the Vd = 0.1 L/kg × 60 kg = **6 L**.
- The **loading dose = Target Serum Concentration × Vd / Bioavailability**. Converting target concentration: 10 mg/dL = 100 mg/L. Therefore: (100 mg/L × 6 L) / 1 = **600 mg**.
*300 mg*
- This value is obtained if an incorrect **Vd** or target concentration was used, potentially through miscalculation or incorrect unit conversion.
- For instance, if the **Vd** was inaccurately calculated at 3 L (instead of 6 L), this could lead to the incorrect answer.
*450 mg*
- This result might occur if the **Vd calculation** was flawed or if the target concentration was incorrectly interpreted.
- A potential error could involve using a Vd of 4.5 L which would result in 450 mg, or if the drug amount was simply prorated by weight without properly considering the Vd per kg.
*150 mg*
- This value suggests a significant error in the calculation of the **volume of distribution** or the target concentration.
- It might be obtained if the **Vd** was mistakenly taken as 1.5 L or if the dose was divided by the original serum concentration without accounting for the new patient's weight and desired concentration.
*1000 mg*
- This value is significantly higher than the correct answer, indicating an overestimation of the **Vd** or target concentration.
- It could result from using the original dose (1500 mg) and attempting to scale it incorrectly by weight alone (1500 mg × 60/100 = 900 mg, close to 1000), or if unit conversions were mishandled during the Vd determination.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 3: A 5-year-old boy undergoes MRI neuroimaging for the evaluation of worsening headaches and intermittent nausea upon awakening. He receives a bolus of intravenous thiopental for sedation during the procedure. Ten minutes after the MRI, the patient is awake and responsive. Which of the following pharmacological properties is most likely responsible for this patient's rapid recovery from this anesthetic agent?
- A. First-pass metabolism
- B. Redistribution (Correct Answer)
- C. Zero-order elimination
- D. Ion trapping
- E. Cytochrome P450 oxidation
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***Redistribution***
- Thiopental is a highly **lipid-soluble** drug that rapidly crosses the **blood-brain barrier**, leading to quick onset of action.
- The drug then rapidly **redistributes** from the brain to other highly perfused tissues (e.g., muscle, fat) and then less perfused tissues, causing a rapid decrease in drug concentration at the site of action and thus termination of the anesthetic effect.
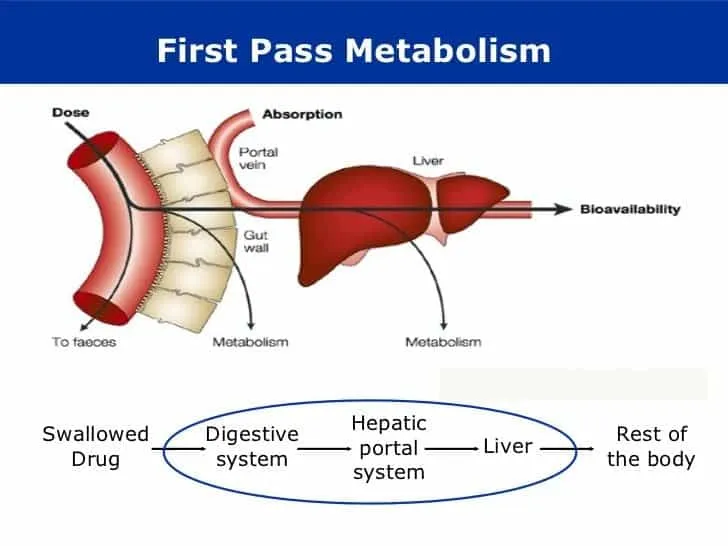
*First-pass metabolism*
- This refers to the **metabolism of a drug** before it reaches systemic circulation, typically after oral administration, and does not explain the termination of action for an intravenously administered drug like thiopental.
- While thiopental is ultimately metabolized by the liver, this process is slower than redistribution and does not account for the **rapid awakening**.
*Zero-order elimination*
- **Zero-order elimination** occurs when a constant amount of drug is eliminated per unit of time, regardless of the drug's concentration, often seen with drug saturation of elimination pathways.
- Thiopental elimination follows **first-order kinetics** at therapeutic doses, meaning a constant fraction of the drug is eliminated per unit time, and this describes slower, overall elimination, not rapid recovery.
*Ion trapping*
- **Ion trapping** occurs when a drug accumulates in a compartment due to differences in pH across a membrane and the drug's pKa, leading to ionization and reduced ability to diffuse back.
- This mechanism is important for drug excretion or distribution into specific compartments (e.g., accumulation of basic drugs in acidic urine) but does not explain the **rapid termination of CNS effects** via redistribution.
*Cytochrome P450 oxidation*
- **Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) oxidation** is a major pathway for drug metabolism in the liver, which is responsible for the eventual elimination of thiopental from the body.
- While important for overall drug clearance, the rate of CYP450 oxidation is too slow to account for the **rapid awakening** seen after a single bolus dose of thiopental; redistribution is the primary factor for rapid recovery.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 4: A 28-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for a 1-week history of jaundice and nausea. She recalls eating some seafood last weekend at a cookout. She lives at home with her 2-year-old son who attends a daycare center. The child's immunizations are up-to-date, and his last hepatitis A vaccine was administered 6 weeks ago. The woman's temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 82/min, and blood pressure is 134/84 mm Hg. Examination shows scleral icterus. The liver is palpated 2-cm below the right costal margin and is tender. Her serum studies show:
Total bilirubin 3.4 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 89 U/L
AST 185 U/L
ALT 723 U/L
Hepatitis A IgM antibody positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody positive
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Hepatitis B core IgM antibody negative
Hepatitis C antibody negative
Which of the following health maintenance recommendations is most appropriate for the child at this time?
- A. Isolate the child
- B. Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin and hepatitis B vaccine
- C. No additional steps are needed (Correct Answer)
- D. Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin only
- E. Administer hepatitis A vaccine and hepatitis A immunoglobulin
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***No additional steps are needed***
- The child received his **last hepatitis A vaccine 6 weeks ago**, which provides adequate protection against hepatitis A infection.
- According to **CDC/ACIP guidelines**, children who have received **at least one dose** of hepatitis A vaccine do **not require post-exposure prophylaxis** (neither additional vaccine nor immunoglobulin) after exposure to hepatitis A.
- One dose of hepatitis A vaccine provides protection within **2-4 weeks**, and since 6 weeks have elapsed, the child is already immune.
- The child's **immunizations are up-to-date**, confirming he is on the appropriate hepatitis A vaccination schedule (2-dose series).
*Administer hepatitis A vaccine and hepatitis A immunoglobulin*
- This would be appropriate for **previously unvaccinated** individuals exposed to hepatitis A, immunocompromised patients, or infants under 12 months.
- However, this child has **already been vaccinated** 6 weeks ago and therefore has adequate protection.
- Administering both vaccine and immunoglobulin is **unnecessary** and not indicated per current guidelines when prior vaccination has occurred.
*Isolate the child*
- Isolation is not the primary recommendation for hepatitis A post-exposure management in household contacts.
- The focus should be on **prevention through immunization**, but this child is already protected by prior vaccination.
- Standard hygiene measures (handwashing) are recommended but formal isolation is not necessary.
*Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin and hepatitis B vaccine*
- The mother's serology shows **HBsAg negative** and **HBsAb positive**, indicating she is **immune to hepatitis B** (likely from prior vaccination) and not currently infected.
- There is **no risk of hepatitis B transmission** from the mother to the child.
- This intervention addresses the wrong infection entirely.
*Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin only*
- This is inappropriate because the mother does **not have active hepatitis B infection** (HBsAg negative).
- This option does not address the **hepatitis A exposure**, which is the relevant concern in this scenario.
- Hepatitis B immunoglobulin is indicated only for exposure to hepatitis B, not hepatitis A.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 5: A drug discovery team is conducting research to observe the characteristics of a novel drug under different experimental conditions. The drug is converted into the inactive metabolites by an action of an enzyme E. After multiple experiments, the team concludes that as compared to physiologic pH, the affinity of the enzyme E for the drug decreases markedly in acidic pH. Co-administration of an antioxidant A increases the value of Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) for the enzyme reaction, while co-administration of a drug B decreases the value of Km. Assume the metabolism of the novel drug follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics at the therapeutic dose, and that the effects of different factors on the metabolism of the drug are first-order linear. For which of the following conditions will the metabolism of the drug be the slowest?
- A. Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A and of drug B
- B. Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B (Correct Answer)
- C. Physiologic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B
- D. Acidic pH, co-administration of drug B, no administration of antioxidant A
- E. Acidic pH, without administration of antioxidant A or drug B
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B***
- **Decreased affinity** at acidic pH reduces the enzyme's ability to bind the drug, slowing metabolism.
- Co-administration of **antioxidant A increases Km**, indicating a further reduction in enzyme affinity and thus slower metabolism.
*Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A and of drug B*
- While acidic pH and antioxidant A slow metabolism, co-administration of **drug B decreases Km**, which would increase enzyme affinity and counteract the slowing effect to some extent.
- The combination would result in a slower metabolism than baseline, but likely not the slowest possible due to the partially opposing effects of A and B.
*Physiologic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B*
- At **physiologic pH**, the enzyme's affinity for the drug is higher than at acidic pH, promoting faster metabolism.
- Although antioxidant A increases Km, the favorable pH for enzyme activity means metabolism will not be as slow as under acidic conditions.
*Acidic pH, co-administration of drug B, no administration of antioxidant A*
- **Acidic pH** reduces enzyme affinity, slowing metabolism.
- However, the co-administration of **drug B decreases Km**, which increases enzyme affinity and would partially offset the reduced affinity caused by the acidic pH, leading to a faster metabolism compared to when antioxidant A is present.
*Acidic pH, without administration of antioxidant A or drug B*
- At **acidic pH**, the enzyme's affinity for the drug decreases, which slows metabolism.
- However, in this condition, there are no additional factors (like antioxidant A) further increasing Km, nor factors (like drug B) decreasing Km, so the metabolic rate would be slower than physiologic pH but not as slow as when antioxidant A is also present.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 6: A 76-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. One week ago, he was prescribed azithromycin for acute bacterial sinusitis. He has a history of atrial fibrillation treated with warfarin and metoprolol. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Compared to one month ago, laboratory studies show a mild increase in INR. Which of the following best explains this patient's laboratory finding?
- A. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity
- B. Depletion of intestinal flora
- C. Inhibition of cytochrome p450 (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased gastrointestinal absorption of warfarin
- E. Increased non-protein bound warfarin fraction
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***Inhibition of cytochrome p450***
- **Azithromycin**, while a weaker inhibitor compared to erythromycin and clarithromycin, **does inhibit CYP3A4 and other cytochrome P450 enzymes** to a clinically significant degree.
- This inhibition **reduces warfarin metabolism**, leading to increased warfarin levels and **enhanced anticoagulant effect**, manifesting as an **increased INR**.
- This pharmacokinetic interaction is well-documented and is the **primary mechanism** for azithromycin-warfarin interaction.
*Depletion of intestinal flora*
- The theory that antibiotics deplete **vitamin K-producing gut bacteria** leading to increased warfarin effect is a **common misconception**.
- Humans obtain vitamin K primarily from **dietary sources** (leafy greens, vegetable oils), not from gut bacterial synthesis; intestinal bacteria contribute minimally to vitamin K stores.
- This mechanism has been **debunked** in modern pharmacology literature and does not explain antibiotic-warfarin interactions.
*Drug-induced hepatotoxicity*
- While hepatotoxicity can impair **clotting factor synthesis** and increase INR, **azithromycin** rarely causes significant liver injury.
- The presentation shows only a **mild INR increase** one week after starting therapy, without other signs of liver dysfunction.
- This acute, mild change is more consistent with a **pharmacokinetic drug interaction** than hepatotoxicity.
*Increased gastrointestinal absorption of warfarin*
- **Warfarin** has high oral bioavailability (~100%) under normal conditions.
- **Azithromycin** does not enhance the **gastrointestinal absorption** of warfarin.
- This mechanism is not supported by pharmacological evidence for this drug interaction.
*Increased non-protein bound warfarin fraction*
- Displacement of warfarin from **plasma protein binding sites** can transiently increase free drug.
- However, **azithromycin** does not significantly displace warfarin from **albumin**.
- This mechanism does not explain the sustained INR elevation seen with azithromycin therapy.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 7: A 65-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He feels well. His most recent examination 2 years ago included purified protein derivative (PPD) skin testing and showed no abnormalities. He is a retired physician and recently came back from rural China where he completed a voluntary service at a local healthcare center. A PPD skin test is performed. Three days later, an induration of 12 mm is noted. An x-ray of the chest shows no abnormalities. He is started on a drug that inhibits the synthesis of mycolic acid. This patient is at greatest risk of developing which of the following adverse effects?
- A. Cytochrome P-450 induction
- B. Hyperuricemia
- C. Liver injury (Correct Answer)
- D. Optic neuropathy
- E. Nephrotoxicity
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***Liver injury***
- The drug described is **isoniazid**, which inhibits **mycolic acid synthesis** and is first-line treatment for **latent tuberculosis infection**.
- **Isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity** is the most significant adverse effect, with risk increasing dramatically in patients **>35 years old** (this patient is 65).
- Additional risk factors include alcohol use, pre-existing liver disease, and concurrent hepatotoxic medications.
- Patients should be monitored with baseline and periodic liver function tests.
*Cytochrome P-450 induction*
- **Rifampin**, not isoniazid, is a potent **CYP450 inducer** that decreases levels of many co-administered drugs.
- Isoniazid is actually a **CYP450 inhibitor** (inhibits CYP2C19, CYP3A4), which can increase levels of other drugs like phenytoin and warfarin.
*Hyperuricemia*
- **Pyrazinamide** is the anti-tuberculosis drug that causes **hyperuricemia** by inhibiting renal tubular secretion of uric acid.
- This can precipitate acute gout attacks in susceptible patients.
- Isoniazid does not affect uric acid metabolism.
*Optic neuropathy*
- **Ethambutol** causes dose-dependent **optic neuropathy**, presenting with decreased visual acuity and **red-green color blindness**.
- Patients on ethambutol require baseline and monthly visual assessments.
- Isoniazid is not associated with optic toxicity.
*Nephrotoxicity*
- **Aminoglycosides** (e.g., streptomycin) and some other antibiotics cause **nephrotoxicity** through tubular damage.
- Isoniazid is not significantly nephrotoxic and does not require renal dose adjustment.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 8: A 27-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for his first appointment. He recently was released from prison. The patient wants a checkup before he goes out and finds a job. He states that lately he has felt very fatigued and has had a cough. He has lost roughly 15 pounds over the past 3 weeks. He attributes this to intravenous drug use in prison. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 127/68 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 18/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient is started on appropriate treatment. Which of the following is the most likely indication to discontinue this patient's treatment?
- A. Optic neuritis
- B. Peripheral neuropathy
- C. Hyperuricemia
- D. Elevated liver enzymes (Correct Answer)
- E. Red body excretions
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***Elevated liver enzymes***
- The patient's presentation (fatigue, cough, weight loss, history of IV drug use, prison exposure) is highly suggestive of **active tuberculosis (TB)**, which is typically treated with a multi-drug regimen including **isoniazid** and **rifampin**.
- Both isoniazid and rifampin are associated with **hepatotoxicity**; significant elevation of liver enzymes (e.g., >5 times the upper limit of normal) is a strong indication to discontinue or modify the treatment regimen to prevent severe liver damage.
*Optic neuritis*
- **Ethambutol**, another first-line anti-TB drug, can cause **optic neuritis** (inflammation of the optic nerve) leading to vision changes or loss.
- While a serious side effect requiring discontinuation of ethambutol, it is specific to that drug and not a general indication to stop all anti-TB treatment as would be the case with widespread hepatotoxicity.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- **Isoniazid** can cause **peripheral neuropathy** due to interference with pyridoxine (vitamin B6) metabolism.
- This side effect can often be prevented or managed by co-administration of **pyridoxine** and does not typically necessitate discontinuation of isoniazid unless severe and unmanageable.
*Hyperuricemia*
- **Pyrazinamide**, another first-line TB drug, can cause **hyperuricemia** (elevated uric acid levels) by inhibiting urate excretion.
- While it can precipitate **gouty arthritis**, hyperuricemia alone is generally not an indication to discontinue pyrazinamide unless symptoms are severe or progress to acute gout.
*Red body excretions*
- **Rifampin** commonly causes **red-orange discoloration of urine, sweat, tears, and other body fluids**, which is a harmless side effect.
- This is an expected and benign pharmacological effect of the drug and does not warrant discontinuation of treatment.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 9: A 65-year-old female patient with a past medical history of diabetes mellitus and an allergy to penicillin develops an infected abscess positive for MRSA on the third day of her hospital stay. She is started on an IV infusion of vancomycin at a dose of 1000 mg every 12 hours. Vancomycin is eliminated by first-order kinetics and has a half life of 6 hours. The volume of distribution of vancomycin is 0.5 L/kg. Assuming no loading dose is given, how long will it take for the drug to reach 94% of its plasma steady state concentration?
- A. 30 hours
- B. 12 hours
- C. 6 hours
- D. 18 hours
- E. 24 hours (Correct Answer)
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***24 hours***
- For a drug eliminated by **first-order kinetics**, it takes approximately **4 half-lives** to reach **93.75%** of steady state concentration, which is conventionally rounded to **94%**.
- Since the half-life of vancomycin is **6 hours**, reaching 94% of steady state requires: 4 × 6 hours = **24 hours**.
- This follows the pharmacokinetic principle that each half-life brings the drug closer to steady state: 1 t½ = 50%, 2 t½ = 75%, 3 t½ = 87.5%, 4 t½ = 93.75%.
*30 hours*
- This duration represents **five half-lives** (5 × 6 hours), at which point approximately **96.875%** (often rounded to 97%) of steady state would be reached.
- This exceeds the 94% target specified in the question.
*18 hours*
- This duration represents **three half-lives** (3 × 6 hours), at which point approximately **87.5%** of steady state concentration would be reached.
- This falls short of the 94% target.
*12 hours*
- This duration represents **two half-lives** (2 × 6 hours), at which point approximately **75%** of steady state concentration would be reached.
- This is insufficient time to reach 94% of plasma steady state concentration.
*6 hours*
- This duration represents **one half-life**, at which point approximately **50%** of steady state concentration would be reached.
- This is far too short to achieve near-steady state levels.
Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG Question 10: A researcher is investigating the behavior of two novel chemotherapeutic drugs that he believes will be effective against certain forms of lymphoma. In order to evaluate the safety of these drugs, this researcher measures the concentration and rate of elimination of each drug over time. A partial set of the results is provided below.
Time 1:
Concentration of Drug A: 4 mg/dl
Concentration of Drug B: 3 mg/dl
Elimination of Drug A: 1 mg/minute
Elimination of Drug B: 4 mg/minute
Time 2:
Concentration of Drug A: 2 mg/dl
Concentration of Drug B: 15 mg/dl
Elimination of Drug A: 0.5 mg/minute
Elimination of Drug B: 4 mg/minute
Which of the following statements correctly identifies the most likely relationship between the half-life of these two drugs?
- A. The half-life of drug A is always longer than that of drug B
- B. The half-life of both drug A and drug B are constant
- C. The half-life of both drug A and drug B are variable
- D. The half-life of drug A is variable but that of drug B is constant
- E. The half-life of drug A is constant but that of drug B is variable (Correct Answer)
Dosing in hepatic impairment Explanation: ***The half-life of drug A is constant but that of drug B is variable***
- Drug A shows a **constant fraction** eliminated per unit time (1 mg/minute from 4 mg/dl, then 0.5 mg/minute from 2 mg/dl), indicating **first-order kinetics** and thus a constant half-life.
- Drug B's elimination rate remains constant (4 mg/minute) despite varying concentrations (3 mg/dl then 15 mg/dl), which suggests **zero-order kinetics** and a variable half-life dependent on concentration.
*The half-life of drug A is always longer than that of drug B*
- This statement is incorrect because Drug B exhibits **zero-order kinetics**, meaning its **half-life changes** with concentration, making a constant comparison invalid.
- At very high concentrations, Drug B's half-life could actually be longer than Drug A's if the elimination rate is slow relative to the large amount of drug.
*The half-life of both drug A and drug B are constant*
- This is incorrect because Drug B demonstrates **zero-order kinetics**, where the elimination rate is constant, but the **half-life is variable** and directly depends on the drug concentration.
- For zero-order kinetics, a constant amount of drug is eliminated per unit time, not a constant fraction, which causes the half-life to change.
*The half-life of both drug A and drug B are variable*
- This is incorrect because Drug A exhibits **first-order kinetics**, where a **constant proportion** of the drug is eliminated per unit time, resulting in a **constant half-life**.
- Its elimination rate is directly proportional to its concentration (1 mg/min from 4 mg/dl, 0.5 mg/min from 2 mg/dl), which defines first-order kinetics.
*The half-life of drug A is variable but that of drug B is constant*
- This statement is the opposite of what the data indicates for Drug A; Drug A's elimination is **proportional to its concentration**, signifying **first-order kinetics** and a constant half-life.
- Drug B's elimination rate is constant regardless of concentration, which points to **zero-order kinetics** and thus a variable half-life.
More Dosing in hepatic impairment US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.