Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Immunosuppressant drug monitoring. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 1: A 31-year-old female receives a kidney transplant for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Three weeks later, the patient experiences acute, T-cell mediated rejection of the allograft and is given sirolimus. Which of the following are side effects of this medication?
- A. Nephrotoxicity, hypertension
- B. Hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia (Correct Answer)
- C. Nephrotoxicity, gingival hyperplasia
- D. Pancreatitis
- E. Cytokine release syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia***
- **Sirolimus** (rapamycin) is an **mTOR inhibitor** commonly used in transplant immunology, which frequently causes **hyperlipidemia** (elevated cholesterol and triglycerides) and **thrombocytopenia** (low platelet count).
- Other common side effects include **myelosuppression** (leukopenia, anemia), **mouth ulcers**, and **impaired wound healing**.
*Nephrotoxicity, hypertension*
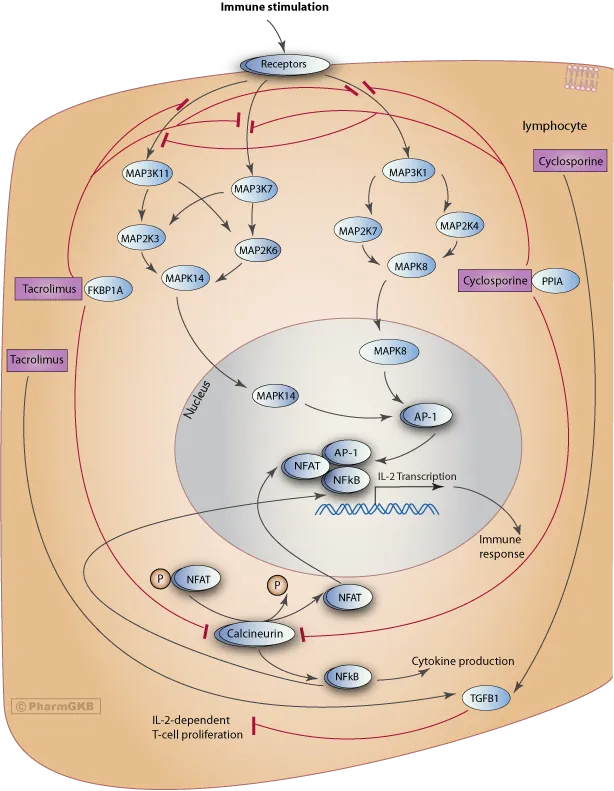
- **Nephrotoxicity** and **hypertension** are more characteristic side effects of **calcineurin inhibitors** like **tacrolimus** and **cyclosporine**, which are also used in transplant immunosuppression but have a different mechanism of action than sirolimus.
- While sirolimus can indirectly affect kidney function, it is generally considered less nephrotoxic than calcineurin inhibitors.
*Nephrotoxicity, gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** is a hallmark side effect of **cyclosporine**, a calcineurin inhibitor, along with **hirsutism** and **nephrotoxicity**.
- Sirolimus does not typically cause gingival hyperplasia.
*Pancreatitis*
- While some immunosuppressants can rarely cause pancreatitis, it is not a common or characteristic side effect of **sirolimus**.
- **Azathioprine** is more frequently associated with pancreatitis among immunosuppressive agents.
*Cytokine release syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction*
- **Cytokine release syndrome** and acute **hypersensitivity reactions** are more often associated with **monoclonal antibodies** (e.g., **basiliximab**, **daclizumab**) used for induction therapy or treatment of acute rejection, particularly within hours or days of administration.
- Sirolimus is less likely to cause these immediate severe reactions.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is conducting a study to identify potential risk factors for post-transplant hypertension. The investigator selects post-transplant patients with hypertension and gathers detailed information regarding their age, gender, preoperative blood pressure readings, and current medications. The results of the study reveal that some of the patients had been treated with cyclosporine. This study is best described as which of the following?
- A. Cross-sectional study
- B. Retrospective cohort study
- C. Prospective cohort study
- D. Case series
- E. Case-control study (Correct Answer)
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Case-control study***
- A **case-control study** compares individuals with a disease (cases) to individuals without the disease (controls) to identify risk factors retrospectively.
- In this study, the investigator selects post-transplant patients **with hypertension** (the cases) and looks backward at their exposures, including cyclosporine use, to identify potential risk factors.
- The analytical goal of "identifying risk factors" and the observation that **some patients had been treated with cyclosporine** (implying comparison with those who were not) indicates a case-control design.
- Even if controls are not explicitly mentioned, the study design involves analyzing exposure patterns among cases to identify associations with risk factors.
*Case series*
- A **case series** is purely descriptive and involves collecting detailed information on a group of patients with a common condition without any comparison or analytical hypothesis testing.
- While this study does describe patients with post-transplant hypertension, the key difference is the **analytical intent** to identify risk factors, which goes beyond simple description.
- A true case series would simply report clinical characteristics without attempting to establish associations between exposures and outcomes.
*Cross-sectional study*
- A **cross-sectional study** assesses both exposure and outcome simultaneously at a single point in time to determine prevalence.
- This approach would involve surveying a population of post-transplant patients to determine the prevalence of hypertension and associated factors at that moment.
- The study described has already selected patients with the outcome (hypertension), making it retrospective rather than cross-sectional.
*Retrospective cohort study*
- A **retrospective cohort study** examines past data by first classifying patients based on **exposure status** (e.g., cyclosporine use vs. no cyclosporine), then following them forward in time to see who developed the outcome.
- The key difference is that cohort studies **start with exposure** and move to outcome, whereas this study **starts with outcome** (hypertension) and looks back at exposures.
- If the investigator had selected all transplant patients, divided them by cyclosporine exposure, and then determined hypertension rates in each group, it would be a retrospective cohort study.
*Prospective cohort study*
- A **prospective cohort study** identifies a cohort at baseline (before the outcome) and follows them forward in time to observe who develops the outcome.
- This study has already selected patients **with the outcome present**, making it retrospective rather than prospective.
- A prospective design would require identifying transplant patients at the time of transplant and following them over time to see who develops hypertension.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 3: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 4: A 60-year-old female presents to her primary care physician complaining of bloating and fatigue over the past year. On examination, she has abdominal distension and ascites. Abdominal imaging reveals a mass-like lesion affecting the left ovary. A biopsy of the lesion demonstrates serous cystadenocarcinoma. She is subsequently started on a chemotherapeutic medication known to stabilize polymerized microtubules. Which of the following complications should this patient be monitored for following initiation of this medication?
- A. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- B. Pulmonary fibrosis
- C. Acoustic nerve damage
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Cardiotoxicity
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- The chemotherapeutic medication described, which stabilizes **polymerized microtubules**, is likely a **taxane** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel), often used for ovarian cancer.
- Taxanes are well-known to cause **dose-dependent peripheral neuropathy** due to their effects on microtubule dynamics in neuronal axons.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a significant side effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **bleomycin** or **busulfan**, but not typically with taxanes.
- Monitoring for this would involve assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and potentially imaging for interstitial changes.
*Acoustic nerve damage*
- **Acoustic nerve damage** and ototoxicity are characteristic side effects of **platinum-based chemotherapy agents** (e.g., cisplatin), which are also used in ovarian cancer but have a different mechanism of action than microtubule stabilizers.
- This typically manifests as **tinnitus** or **hearing loss**.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a common and severe side effect of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, alkylating agents, due to the accumulation of their metabolite **acrolein** in the bladder.
- It is not associated with microtubule-stabilizing agents like taxanes.
*Cardiotoxicity*
- **Cardiotoxicity**, including dilated cardiomyopathy, is a serious side effect primarily associated with **anthracyclines** (e.g., doxorubicin), which generate free radicals and damage cardiac myocytes.
- While some taxanes can cause cardiovascular effects, severe cardiotoxicity like that seen with anthracyclines is not their primary or most concerning side effect.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 5: A researcher is trying to determine whether a newly discovered substance X can be useful in promoting wound healing after surgery. She conducts this study by enrolling the next 100 patients that will be undergoing this surgery and separating them into 2 groups. She decides which patient will be in which group by using a random number generator. Subsequently, she prepares 1 set of syringes with the novel substance X and 1 set of syringes with a saline control. Both of these sets of syringes are unlabeled and the substances inside cannot be distinguished. She gives the surgeon performing the surgery 1 of the syringes and does not inform him nor the patient which syringe was used. After the study is complete, she analyzes all the data that was collected and performs statistical analysis. This study most likely provides which level of evidence for use of substance X?
- A. Level 3
- B. Level 1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 4
- D. Level 5
- E. Level 2
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Level 1***
- The study design described is a **randomized controlled trial (RCT)**, which is considered the **highest level of evidence (Level 1)** in the hierarchy of medical evidence.
- Key features like **randomization**, **control group**, and **blinding (double-blind)** help minimize bias and strengthen the validity of the findings.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence typically comprises **well-designed controlled trials without randomization** (non-randomized controlled trials) or **high-quality cohort studies**.
- While strong, they do not possess the same level of internal validity as randomized controlled trials.
*Level 3*
- Level 3 evidence typically includes **case-control studies** or **cohort studies**, which are observational designs and carry a higher risk of bias compared to RCTs.
- These studies generally do not involve randomization or intervention assignment by the researchers.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence is usually derived from **case series** or **poor quality cohort and case-control studies**.
- These studies provide descriptive information or investigate associations without strong control for confounding factors.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, consisting of **expert opinion** or **animal research/bench research**.
- This level lacks human clinical data or systematic investigative rigor needed for higher evidence levels.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 6: A 67-year-old woman who was recently diagnosed with Crohn disease comes to the physician for evaluation of her immunosuppressive therapy. She has had recurrent flares since her diagnosis. Physical examination shows two shallow ulcers on her oral mucosa. The physician considers adding azathioprine to her medication regimen. A deficiency of which of the following enzymes would diminish the therapeutic effect of this drug?
- A. Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase
- B. Dihydrofolate reductase
- C. Thymidylate synthase
- D. Xanthine oxidase
- E. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (Correct Answer)
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase***
- **Azathioprine** is a prodrug converted to **6-mercaptopurine (6-MP)**, which is then activated to **thioguanine nucleotides** (active metabolites) via the purine salvage pathway.
- **Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT)** is essential for converting 6-MP into its active thiopurine metabolites that inhibit purine synthesis and suppress the immune system.
- A deficiency in **HGPRT** (as seen in **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**) would lead to reduced formation of active drug metabolites, thereby **diminishing therapeutic efficacy** in treating Crohn disease.
*Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase*
- This enzyme synthesizes **phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP)**, a precursor for de novo **purine and pyrimidine synthesis**.
- While important for nucleotide metabolism, a deficiency would not directly reduce the activation of azathioprine through the salvage pathway.
*Dihydrofolate reductase*
- **Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)** is the target of **methotrexate**, which blocks the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate, inhibiting DNA synthesis.
- It is not involved in the metabolism or activation of azathioprine.
*Thymidylate synthase*
- **Thymidylate synthase** converts deoxyuridylate to deoxythymidylate, a critical step in DNA synthesis.
- This enzyme is targeted by drugs like **5-fluorouracil (5-FU)** but is not related to azathioprine's mechanism of action.
*Xanthine oxidase*
- **Xanthine oxidase** catabolizes azathioprine and 6-MP into **inactive metabolites**, thereby **reducing drug levels and toxicity**.
- **Inhibition** of xanthine oxidase (e.g., by **allopurinol**) increases active thiopurine metabolites, enhancing both therapeutic effect and toxicity risk.
- Xanthine oxidase deficiency would **increase** rather than diminish therapeutic effect.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 7: A 14-year-old boy has undergone kidney transplantation due to stage V chronic kidney disease. A pre-transplantation serologic assessment showed that he is negative for past or present HIV infection, viral hepatitis, EBV, and CMV infection. He has a known allergy for macrolides. The patient has no complaints 1 day after transplantation. His vital signs include: blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg, heart rate 89/min, respiratory rate 17/min, and temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F). On physical examination, the patient appears to be pale, his lungs are clear on auscultation, heart sounds are normal, and his abdomen is non-tender on palpation. His creatinine is 0.65 mg/dL (57.5 µmol/L), GFR is 71.3 mL/min/1.73 m2, and urine output is 0.9 mL/kg/h. Which of the following drugs should be used in the immunosuppressive regimen in this patient?
- A. Belatacept
- B. Sirolimus
- C. Omalizumab
- D. Daclizumab
- E. Basiliximab (Correct Answer)
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: **Basiliximab**
- **Basiliximab** is a **monoclonal antibody** that targets the **IL-2 receptor (CD25)** on activated T cells, preventing their proliferation and inducing immunosuppression.
- It is commonly used as **induction therapy** in kidney transplant recipients due to its good safety profile, especially in pediatric patients, without the nephrotoxicity associated with calcineurin inhibitors, minimizing acute rejection risks immediately post-transplant.
*Belatacept*
- **Belatacept** works by co-stimulation blockade, binding to **CD80 and CD86** on antigen-presenting cells to prevent T-cell activation.
- It is typically reserved for patients who cannot tolerate calcineurin inhibitors due to **nephrotoxicity** or require a steroid-sparing regimen, which is not indicated as an immediate need in this patient.
*Sirolimus*
- **Sirolimus** is an **mTOR inhibitor** that works by blocking T-cell proliferation and B-cell differentiation.
- It is associated with several side effects, including **delayed wound healing**, **thrombocytopenia**, and **hyperlipidemia**, which are undesirable in the immediate post-transplant period, especially in a growing adolescent.
*Omalizumab*
- **Omalizumab** is an **anti-IgE monoclonal antibody** primarily used for allergic asthma and chronic spontaneous urticaria.
- It has no role in **immunosuppression for organ transplantation** as its mechanism of action is unrelated to preventing graft rejection.
*Daclizumab*
- **Daclizumab** is another **monoclonal antibody** that also targets the **IL-2 receptor (CD25)**, similar to basiliximab.
- However, daclizumab has been **withdrawn from the market** due to serious adverse effects including severe liver injury and autoimmune encephalitis, making it unavailable for clinical use in transplantation.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 8: A 68-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. Three months ago, she underwent heart transplantation for restrictive cardiomyopathy and was started on transplant rejection prophylaxis. Her pulse is 76/min and blood pressure is 148/82 mm Hg. Physical examination shows enlargement of the gum tissue. There is a well-healed scar on her chest. Serum studies show hyperlipidemia. The physician recommends removing a drug that decreases T cell activation by inhibiting the transcription of interleukin-2 from the patient's treatment regimen and replacing it with a different medication. Which of the following drugs is the most likely cause of the adverse effects seen in this patient?
- A. Mycophenolate mofetil
- B. Azathioprine
- C. Tacrolimus
- D. Cyclosporine (Correct Answer)
- E. Prednisolone
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Cyclosporine***
- The patient's symptoms of **gingival hyperplasia**, **hypertension**, and **hyperlipidemia** are classic side effects associated with cyclosporine.
- Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that **decreases T-cell activation** by inhibiting IL-2 transcription, matching the drug description.
*Mycophenolate mofetil*
- Mycophenolate mofetil is an **antiproliferative agent** that inhibits purine synthesis, primarily affecting lymphocytes.
- Its common side effects are mainly **hematologic** (leukopenia, anemia) and **gastrointestinal** (diarrhea, nausea), not gingival hyperplasia or hypertension.
*Azathioprine*
- Azathioprine is a **purine analog** that impairs DNA synthesis and inhibits lymphocyte proliferation.
- Key side effects include **myelosuppression** (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) and **hepatotoxicity**, which are not present here.
*Tacrolimus*
- Tacrolimus is also a **calcineurin inhibitor** that inhibits IL-2 transcription, similar to cyclosporine.
- While it can cause **hypertension** and **hyperlipidemia**, it is less commonly associated with **gingival hyperplasia** than cyclosporine.
*Prednisolone*
- Prednisolone is a **corticosteroid** used for immunosuppression, acting broadly on the immune system.
- Common side effects include **hyperglycemia**, **osteoporosis**, and **cataracts**, not specific gingival overgrowth.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 9: A 63-year-old HIV-positive man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. Four years ago, he was diagnosed with HIV and was started on cART therapy. He tells the physician that he has been having difficulty adhering to his medication regimen. He has been unemployed for the past couple of years and relies on unemployment benefits to cover the costs of daily living. His father died of lymphoma at the age of 60 years. He wants more information about his risk of developing DLBCL. Which of the following is the greatest risk factor for the development of DLBCL in HIV-positive patients?
- A. Poor adherence to cART (Correct Answer)
- B. Income below $30,000 per year
- C. Male sex
- D. Positive family history of cancer
- E. Age over 55 years
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: **Poor adherence to cART**
- **Poor adherence** to cART leads to **uncontrolled HIV replication** and persistent **immunosuppression**, which significantly increases the risk of developing **DLBCL**.
- **Immune dysregulation** caused by HIV directly contributes to a higher incidence of **AIDS-defining malignancies**, including DLBCL.
*Income below $30,000 per year*
- While **socioeconomic factors** can impact access to care and medication adherence, low income itself is not a direct biological risk factor for DLBCL.
- Its influence is secondary to its effect on adherence and overall health status, rather than a primary risk factor for the malignancy.
*Positive family history of cancer*
- Although a family history of cancer can increase the risk for some malignancies, it is generally **not a significant risk factor** for **HIV-associated DLBCL**.
- The primary drivers of HIV-associated DLBCL are linked to HIV-induced immunodeficiency, not specific inherited genetic predispositions for lymphoma.
*Age over 55 years*
- While the incidence of many cancers increases with **age**, for **HIV-associated DLBCL**, age is less prominent than the degree of **immunodeficiency** caused by HIV.
- The stronger prognostic factor remains the state of the immune system, particularly a **low CD4 count**, which is often exacerbated by poor cART adherence.
*Male sex*
- While there are minor differences in cancer incidence between sexes, **male sex** is not a primary or significant independent risk factor for **HIV-associated DLBCL**.
- The risk is predominantly driven by factors related to HIV infection itself and the resulting immune dysfunction.
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG Question 10: A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. Two years ago, she was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. Three weeks ago, she was admitted and treated for right lower leg weakness with high-dose methylprednisone for 5 days. She has had 4 exacerbations over the past 6 months. Current medications include interferon beta and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 116/74 mm Hg. Examination shows pallor of the right optic disk. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. She is anxious about the number of exacerbations and repeated hospitalizations. She is counseled about the second-line treatment options available to her. She consents to treatment with natalizumab. However, she has read online about its adverse effects and is concerned. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
- A. Tuberculosis
- B. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
- C. Parkinsonism
- D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (Correct Answer)
- E. Aplastic anemia
Immunosuppressant drug monitoring Explanation: ***Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy***
- **Natalizumab** is a monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of leukocytes to endothelial cells, preventing their entry into the central nervous system. This immunosuppressive effect increases the risk of **progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)**, especially in patients who are positive for the **JC virus**.
- PML is a serious and often fatal opportunistic infection of the brain caused by the **JC virus**, which demyelinates axons and leads to severe neurological deficits.
*Tuberculosis*
- While some immunosuppressants can reactivate **latent tuberculosis**, natalizumab is not typically associated with an increased risk of TB compared to other immunomodulatory drugs like TNF-alpha inhibitors.
- The mechanism of action of natalizumab (alpha-4 integrin blocker) does not directly impede the immune response responsible for containing mycobacterial infections to the same extent as other treatments.
*Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone*
- **SIADH** is not a known adverse effect of natalizumab.
- SIADH is characterized by excessive secretion of **antidiuretic hormone**, leading to hyponatremia, and is often associated with certain medications (e.g., SSRIs, carbamazepine) or underlying conditions like malignancy or pulmonary disease.
*Parkinsonism*
- Parkinsonism involves symptoms like **bradykinesia**, rigidity, and tremor, and is a neurodegenerative disorder.
- There is **no evidence** suggesting a causal link between natalizumab treatment and the development of Parkinsonism.
*Aplastic anemia*
- **Aplastic anemia** is a rare but severe condition where the bone marrow fails to produce blood cells.
- This adverse effect is not associated with natalizumab; it is more commonly linked to certain **chemotherapeutic agents**, radiation, or specific antimicrobial drugs like chloramphenicol.
More Immunosuppressant drug monitoring US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.