B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for B-cell depleting antibodies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 1: A researcher is studying the effects of various substances on mature B-cells. She observes that while most substances are only able to promote the production of antibodies when the B-cells are co-cultured with T-cells, a small subset of substances are able to trigger antibody production even in the absence of T-cells. She decides to test these substances that stimulate B-cells alone by injecting them into model organisms. She then analyzes the characteristics of the response that is triggered by these substances. Which of the following correctly describes how the immune response triggered by the B-cell-alone-substances compares with that triggered by substances that also require T-cells?
- A. Is T-dependent
- B. Is T-independent (Correct Answer)
- C. Requires MHC class II presentation
- D. Requires cognate interaction
- E. Requires B7-CD28 interaction
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Is T-independent***
- The scenario describes substances that activate B-cells and induce antibody production **without the need for T-cells**, which is the defining characteristic of a T-independent immune response.
- T-independent activation typically involves **polysaccharide antigens** or other repetitive structures that can cross-link multiple B-cell receptors, providing a strong enough signal for activation without T-cell help.
*Is T-dependent*
- This option is incorrect because the question explicitly states that the substances can trigger antibody production **in the absence of T-cells**.
- A T-dependent response requires **CD4+ T-helper cells** to activate B-cells through co-stimulation and cytokine signaling.
*Requires MHC class II presentation*
- While B-cells can present antigens via **MHC class II** to T-cells in T-dependent responses, T-independent activation of B-cells does not necessarily require antigen presentation on MHC class II molecules.
- T-independent antigens often directly activate B-cells through **toll-like receptors (TLRs)** or extensive cross-linking of B-cell receptors.
*Requires cognate interaction*
- **Cognate interaction** refers to the specific recognition between an antigen-presenting B-cell and a helper T-cell, which is a hallmark of T-dependent responses.
- Since the B-cells are producing antibodies in the absence of T-cells, cognate interaction is not required in this specific scenario.
*Requires B7-CD28 interaction*
- The **B7-CD28 interaction** is a crucial co-stimulatory signal provided by antigen-presenting cells (like B-cells) to T-cells, and from T-cells back to B-cells, in a T-dependent immune response.
- As the scenario involves T-cell independent activation, this co-stimulatory pathway between T-cells and B-cells is not essential for antibody production.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 2: A 33-year-old woman with a history of multiple sclerosis is brought to the physician because of dizziness, urinary incontinence, loss of vision in her right eye, and numbness and weakness of the left leg. She has had recurrent episodes of neurological symptoms despite several changes in her medication regimen. An MRI of the brain shows several new enhancing lesions in the periventricular white matter and the brainstem. Treatment with a drug that binds to CD52 is initiated. Which of the following agents was most likely prescribed?
- A. Alemtuzumab (Correct Answer)
- B. Eculizumab
- C. Abciximab
- D. Rituximab
- E. Bevacizumab
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Alemtuzumab***
- **Alemtuzumab** is a monoclonal antibody that targets **CD52**, a glycoprotein found on the surface of mature lymphocytes (T and B cells), monocytes, and macrophages, leading to their depletion.
- It is used in **highly active relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS)**, especially when other disease-modifying therapies have failed, which aligns with the patient's history of recurrent neurological symptoms and new enhancing lesions.
*Eculizumab*
- **Eculizumab** targets the **C5 complement protein** and is used for conditions like **paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria** and **atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome**, not multiple sclerosis.
- It works by inhibiting the complement cascade, which is not the primary mechanism of action for MS treatment involving lymphocyte depletion.
*Abciximab*
- **Abciximab** is a **glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor** that prevents platelet aggregation and is used as an antiplatelet agent in acute coronary syndromes and percutaneous coronary intervention.
- Its mechanism of action and primary indication are unrelated to the immunological processes involved in multiple sclerosis.
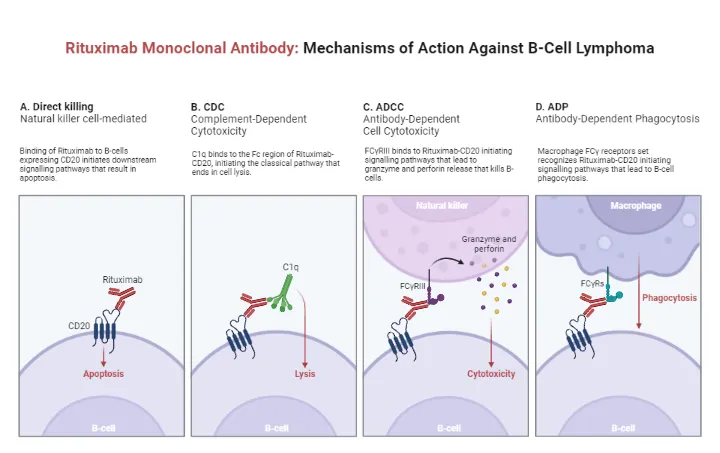
*Rituximab*
- **Rituximab** targets **CD20** on B cells and is used in conditions like **non-Hodgkin lymphoma**, **chronic lymphocytic leukemia**, and certain autoimmune diseases like **rheumatoid arthritis** and **vasculitis**.
- While it's a B-cell depleting agent and has shown efficacy in MS, the question specifically asks for a drug that binds to **CD52**, not CD20.
*Bevacizumab*
- **Bevacizumab** is an anti-VEGF antibody that inhibits **angiogenesis** and is primarily used in the treatment of various cancers, such as colorectal, lung, and renal cell carcinoma.
- Its mechanism of action involving inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is not indicated for the management of multiple sclerosis.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 3: A 61-year-old man presents to the emergency department with new-onset dizziness. He reports associated symptoms of confusion, headaches, and loss of coordination. The patient’s wife also mentions he has had recent frequent nosebleeds. Physical examination demonstrates a double vision. Routine blood work is significant for a slightly reduced platelet count. A noncontrast CT of the head is normal. A serum protein electrophoresis is performed and shows an elevated IgM spike. The consulting hematologist strongly suspects Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Which of the following is the best course of treatment for this patient?
- A. Plasmapheresis (Correct Answer)
- B. Vincristine
- C. Cyclophosphamide
- D. Rituximab
- E. Prednisone
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Plasmapheresis***
- This patient presents with symptoms of **hyperviscosity syndrome** (dizziness, confusion, headaches, loss of coordination, double vision, nosebleeds) due to high levels of IgM, which is characteristic of Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.
- **Plasmapheresis** is the most effective initial treatment to rapidly reduce the IgM level and relieve these acute neurological and hemorrhagic symptoms by removing the excess globulins from the plasma.
*Vincristine*
- **Vincristine** is a chemotherapy agent used in the treatment of Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, but it is typically used as part of a multi-drug regimen for long-term disease control, not for acute management of hyperviscosity.
- Its mechanism involves inhibiting microtubule formation, which is a slower process and would not provide immediate relief for the crisis.
*Cyclophosphamide*
- **Cyclophosphamide** is an alkylating agent, often part of chemotherapy regimens for Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, especially for long-term disease control to reduce IgM production.
- Like vincristine, it works by damaging DNA in cancer cells, a process that is too slow to address the immediate, life-threatening symptoms of hyperviscosity syndrome.
*Rituximab*
- **Rituximab** is an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that targets B-cells, often used in Waldenström's macroglobulinemia to reduce the malignant B-cell clone and subsequent IgM production.
- While effective for disease control, its therapeutic effects take weeks to materialize and would not provide rapid relief for acute hyperviscosity.
*Prednisone*
- **Prednisone** is a corticosteroid that can be used in some hematologic malignancies to reduce inflammation or induce apoptosis in certain cell types.
- However, in Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, corticosteroids alone are not effective in rapidly reducing the large IgM burden causing hyperviscosity, and their role is often supportive or part of combination chemotherapy.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 4: A 44-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his daughter for a 1-week history of right leg weakness, unsteady gait, and multiple falls. During the past 6 months, he has become more forgetful and has sometimes lost his way along familiar routes. He has been having difficulties operating simple kitchen appliances such as the dishwasher and the coffee maker. He has recently become increasingly paranoid, agitated, and restless. He has HIV, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. His last visit to a physician was more than 2 years ago, and he has been noncompliant with his medications. His temperature is 37.2 °C (99.0 °F), blood pressure is 152/68 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 14/min. He is somnolent and slightly confused. He is oriented to person, but not place or time. There is mild lymphadenopathy in the cervical, axillary, and inguinal areas. Neurological examination shows right lower extremity weakness with normal tone and no other focal deficits. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 9.2 g/dL
Leukocyte count 3600/mm3
Platelet count 140,000/mm3
CD4+ count 56/μL
HIV viral load > 100,000 copies/mL
Serum
Cryptococcal antigen negative
Toxoplasma gondii IgG positive
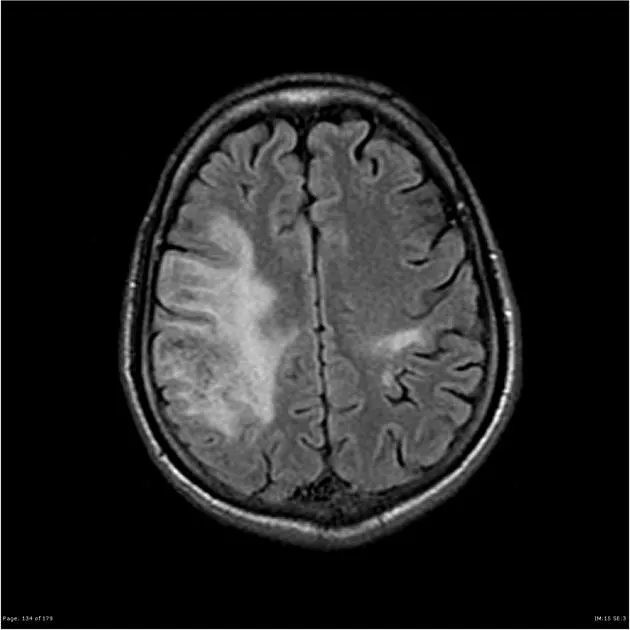
An MRI of the brain shows disseminated, nonenhancing white matter lesions with no mass effect. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Vascular dementia
- B. Primary CNS lymphoma
- C. Neurocysticercosis
- D. Cerebral toxoplasmosis
- E. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (Correct Answer)
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy***
- The patient's severe **immunosuppression** (CD4 count 56/μL) and **non-enhancing white matter lesions** disseminated throughout the brain are highly characteristic of **PML**, caused by the **JC virus**.
- **Progressive neurological deficits** including cognitive decline, motor weakness, and personality changes are typical presentations of PML in advanced HIV.
*Vascular dementia*
- While the patient has **hypertension** and a history of falls, the MRI findings of **disseminated non-enhancing white matter lesions** are not classic for vascular dementia, which typically shows lacunar infarcts or larger areas of ischemic damage.
- The rapid progression of symptoms and severe immunosuppression also point away from typical vascular dementia as the primary cause.
*Primary CNS lymphoma*
- **Primary CNS lymphoma** in HIV patients usually presents as **solitary or multiple mass lesions** that are typically **ring-enhancing** on MRI, which contradicts the described non-enhancing lesions.
- While it can cause neurological deficits, the MRI findings are a strong differentiating factor.
*Neurocysticercosis*
- **Neurocysticercosis** is caused by the parasite *Taenia solium* and is more common in endemic areas; MRI typically shows **cysts, calcifications, or enhancing lesions**, often with associated edema.
- The patient's non-enhancing white matter lesions and high HIV viral load make this diagnosis less likely, despite the global prevalence of the infection.
*Cerebral toxoplasmosis*
- **Cerebral toxoplasmosis** is common in HIV patients with low CD4 counts and positive *Toxoplasma gondii* IgG, but it typically presents with **multiple ring-enhancing lesions** on MRI, often with **mass effect**.
- The absence of enhancement and mass effect on MRI makes toxoplasmosis less probable despite the positive IgG serology.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 5: A 71-year-old man comes to the physician for routine health maintenance examination. He feels well. He has hypertension and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Current medications include metoprolol and pantoprazole. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. Temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 75/min, and blood pressure 135/87 mm Hg. Examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hematocrit 43%
Leukocyte count 32,000/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 22%
Basophils 1%
Eosinophils 2%
Lymphocytes 74%
Monocytes 1%
Platelet count 190,000/mm3
Blood smear shows small, mature lymphocytes and several smudge cells. Immunophenotypic analysis with flow cytometry shows B-cells that express CD19, CD20 and CD23. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Stem cell transplantation
- B. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab
- C. All-trans retinoic acid
- D. Imatinib
- E. Observation and follow-up (Correct Answer)
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Observation and follow-up***
- The patient's presentation, including marked **lymphocytosis** (leukocyte count 32,000/mm³ with 74% lymphocytes), **small mature lymphocytes** and **smudge cells** on blood smear, and **CD19, CD20, CD23 expression** on B-cells, is highly suggestive of **Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)**.
- Given the patient is **asymptomatic** and has **no signs of end-organ damage** or disease progression, the most appropriate initial management for CLL is "watch and wait" or observation. Treatment is typically initiated only when symptoms develop or there are signs of advanced disease.
*Stem cell transplantation*
- **Stem cell transplantation** is a highly intensive treatment, usually reserved for young, fit patients with **high-risk CLL refractory to conventional chemotherapy** or for those with transformation to aggressive lymphoma.
- It is not indicated for an asymptomatic 71-year-old man with newly diagnosed, likely early-stage CLL.
*Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab*
- This combination, known as **FCR regimen**, is a common and effective first-line chemotherapy for **symptomatic CLL** patients who require treatment.
- However, for asymptomatic patients fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for CLL but without indications for treatment (e.g., progressive lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, B symptoms), initiating chemotherapy is not recommended.
*All-trans retinoic acid*
- **All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)** is a specific differentiating agent used primarily in the treatment of **Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL)**, a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia.
- It has no role in the management of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL).
*Imatinib*
- **Imatinib** is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used primarily in the treatment of **Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)**, which is characterized by the Philadelphia chromosome (BCR-ABL fusion gene).
- While sometimes used in other malignancies with specific kinase mutations, it is not indicated for CLL.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 6: A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. Two years ago, she was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. Three weeks ago, she was admitted and treated for right lower leg weakness with high-dose methylprednisone for 5 days. She has had 4 exacerbations over the past 6 months. Current medications include interferon beta and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 116/74 mm Hg. Examination shows pallor of the right optic disk. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. She is anxious about the number of exacerbations and repeated hospitalizations. She is counseled about the second-line treatment options available to her. She consents to treatment with natalizumab. However, she has read online about its adverse effects and is concerned. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
- A. Tuberculosis
- B. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
- C. Parkinsonism
- D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (Correct Answer)
- E. Aplastic anemia
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy***
- **Natalizumab** is a monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of leukocytes to endothelial cells, preventing their entry into the central nervous system. This immunosuppressive effect increases the risk of **progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)**, especially in patients who are positive for the **JC virus**.
- PML is a serious and often fatal opportunistic infection of the brain caused by the **JC virus**, which demyelinates axons and leads to severe neurological deficits.
*Tuberculosis*
- While some immunosuppressants can reactivate **latent tuberculosis**, natalizumab is not typically associated with an increased risk of TB compared to other immunomodulatory drugs like TNF-alpha inhibitors.
- The mechanism of action of natalizumab (alpha-4 integrin blocker) does not directly impede the immune response responsible for containing mycobacterial infections to the same extent as other treatments.
*Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone*
- **SIADH** is not a known adverse effect of natalizumab.
- SIADH is characterized by excessive secretion of **antidiuretic hormone**, leading to hyponatremia, and is often associated with certain medications (e.g., SSRIs, carbamazepine) or underlying conditions like malignancy or pulmonary disease.
*Parkinsonism*
- Parkinsonism involves symptoms like **bradykinesia**, rigidity, and tremor, and is a neurodegenerative disorder.
- There is **no evidence** suggesting a causal link between natalizumab treatment and the development of Parkinsonism.
*Aplastic anemia*
- **Aplastic anemia** is a rare but severe condition where the bone marrow fails to produce blood cells.
- This adverse effect is not associated with natalizumab; it is more commonly linked to certain **chemotherapeutic agents**, radiation, or specific antimicrobial drugs like chloramphenicol.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old woman has a follow-up visit with her physician. She was diagnosed with allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma at 11 years of age. Her regular controller medications include daily high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and montelukast, but she still needs to use a rescue inhaler 3–4 times a week following exercise. She also becomes breathless with moderate exertion. After a thorough evaluation, the physician explains that her medication dosages need to be increased. She declines taking oral corticosteroids daily due to concerns about side effects. The physician prescribes omalizumab, which is administered subcutaneously every 3 weeks. Which of the following best explains the mechanism of action of the new medication that has been added to the controller medications?
- A. Prevention of binding of IgE antibodies to mast cell receptors (Correct Answer)
- B. Inhibition of synthesis of interleukin-4 (IL-4)
- C. Inhibition of synthesis of IgE antibodies
- D. Selective binding to interleukin-3 (IL-3) and inhibition of its actions
- E. Prevention of binding of interleukin-5 (IL-5) to its receptors
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Prevention of binding of IgE antibodies to mast cell receptors***
- **Omalizumab** is a **monoclonal antibody** that specifically targets and binds to **free IgE** in the bloodstream, preventing it from attaching to high-affinity IgE receptors on **mast cells** and **basophils**.
- By reducing surface IgE, omalizumab **downregulates IgE receptors** on these cells, thereby reducing the release of inflammatory mediators upon allergen exposure, which is beneficial in **allergic asthma** uncontrolled by standard therapies.
*Inhibition of synthesis of interleukin-4 (IL-4)*
- **IL-4** is a cytokine primarily involved in **Th2 differentiation** and **IgE class switching**, but omalizumab's action is not directly blocking its synthesis.
- While *omalizumab* indirectly reduces IgE levels, its primary mechanism isn't to inhibit the production of IL-4 itself, but rather to prevent the effects of existing IgE.
*Inhibition of synthesis of IgE antibodies*
- **Omalizumab** does not inhibit the *synthesis* of IgE antibodies; instead, it binds to already synthesized **free IgE** circulating in the blood.
- This binding effectively neutralizes IgE, preventing it from contributing to the allergic cascade, but it doesn't stop B cells from producing more IgE.
*Selective binding to interleukin-3 (IL-3) and inhibition of its actions*
- **IL-3** is a cytokine involved in the growth and differentiation of various **hematopoietic cells**, including mast cells and basophils, but it is not the target of omalizumab.
- Omalizumab specifically targets **IgE** and has no known direct action on IL-3 signaling pathways.
*Prevention of binding of interleukin-5 (IL-5) to its receptors*
- **IL-5** is a key cytokine in the **eosinophilic inflammatory pathway** and is targeted by other therapies (e.g., mepolizumab, reslizumab) used for severe eosinophilic asthma.
- Omalizumab's mechanism is distinct, focusing on **IgE-mediated inflammation** rather than direct eosinophil control.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 8: A biology student is studying apoptosis pathways. One of the experiments conducted involves the binding of a ligand to a CD95 receptor. A defect of this pathway will most likely cause which of the conditions listed below?
- A. Chronic granulomatous disease
- B. Chédiak-Higashi syndrome
- C. Follicular lymphoma
- D. Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome***
- A defect in the **CD95 (Fas) receptor pathway** impairs the normal **apoptotic deletion of self-reactive lymphocytes**, leading to their accumulation.
- This accumulation results in **lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and autoimmune manifestations** due to uncontrolled lymphocyte proliferation.
*Chronic granulomatous disease*
- This condition is characterized by a defect in **NADPH oxidase**, leading to recurrent infections and granuloma formation due to the inability of phagocytes to produce **reactive oxygen species**.
- It does not primarily involve the CD95 apoptosis pathway.
*Chédiak-Higashi syndrome*
- This is an **autosomal recessive disorder** involving a defect in lysosomal trafficking, leading to impaired function of phagocytes, melanocytes, and platelets.
- Symptoms include **recurrent pyogenic infections, partial albinism, and neurological abnormalities**, not directly linked to the CD95 pathway.
*Follicular lymphoma*
- This is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma characterized by a **t(14;18) translocation**, which causes overexpression of the **BCL2 gene**, an anti-apoptotic protein.
- While it involves impaired apoptosis, the primary defect is not in the CD95 receptor itself but rather in the regulation of apoptosis through BCL2.
*Leukocyte adhesion deficiency*
- This is a rare **immunodeficiency disorder** characterized by defects in **leukocyte adhesion molecules (integrins)**, impairing the ability of white blood cells to adhere to endothelial surfaces and migrate to sites of infection.
- It results in **recurrent bacterial infections and impaired wound healing**, unrelated to the CD95 apoptosis pathway.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 9: A patient is infected with a pathogen and produces many antibodies to many antigens associated with that pathogen via Th cell-activated B cells. This takes place in the germinal center of the lymphoid tissues. If the same patient is later re-infected with the same pathogen, the immune system will respond with a much stronger response, producing antibodies with greater specificity for that pathogen in a shorter amount of time. What is the term for this process that allows the B cells to produce antibodies specific to that antigen?
- A. Affinity maturation (Correct Answer)
- B. Avidity
- C. Immunoglobulin class switching
- D. T cell negative selection
- E. T cell positive selection
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Affinity maturation***
- **Affinity maturation** is the process by which B cells produce antibodies with progressively higher affinity for an antigen over the course of an immune response, allowing for a more specific and potent response upon re-exposure.
- This process occurs primarily in the **germinal centers** of lymphoid organs, driven by somatic hypermutation of antibody genes and subsequent selection of B cells exhibiting increased binding affinity.
*Avidity*
- **Avidity** refers to the overall strength of binding between a multivalent antibody and a multivalent antigen, taking into account the combined strength of multiple binding sites.
- While high avidity is a characteristic of effective antibody responses, it describes the strength of binding rather than the *process* of improving specificity and affinity over time.
*Immunoglobulin class switching*
- **Immunoglobulin class switching** (or isotype switching) is the process by which B cells change the class of antibody they produce (e.g., from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE), while retaining the same antigen specificity.
- This process diversifies the effector functions of antibodies but does not directly describe the *improvement in antigen binding affinity* or specificity.
*T cell negative selection*
- **T cell negative selection** is a critical process in the thymus where T cells that react too strongly to self-antigens are eliminated or inactivated to prevent autoimmunity.
- This process is fundamental for establishing central tolerance in T cells and is separate from the B cell-mediated improvement in antibody specificity described.
*T cell positive selection*
- **T cell positive selection** also occurs in the thymus, ensuring that only T cells capable of recognizing self-MHC molecules survive and mature.
- This process is essential for T cell function (MHC restriction) but is distinct from the described mechanism of B cell antibody refinement.
B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG Question 10: A scientist is studying the process of thymus-dependent B cell activation in humans. He observes that, after bacterial infections, the germinal centers of secondary lymphoid organs become highly metabolically active. After subsequent reinfection with the same pathogen, the organism is able to produce immunoglobulins at a much faster pace. Which of the following processes is likely taking place in the germinal centers at the beginning of an infection?
- A. T cell positive selection
- B. T cell negative selection
- C. Development of early pro-B cells
- D. Development of immature B cells
- E. Affinity maturation (Correct Answer)
B-cell depleting antibodies Explanation: ***Affinity maturation***
- This process involves **somatic hypermutation** in the germinal centers, leading to B cells with receptors having higher affinity for the antigen.
- Coupled with **clonal selection**, this ensures that subsequent immune responses are faster and more effective due to the improved binding of antibodies to the pathogen.
*T cell positive selection*
- This process occurs in the **thymic cortex** and selects T cells capable of recognizing self-MHC molecules.
- It is crucial for the development of the T cell repertoire and does not occur in germinal centers during B cell activation.
*T cell negative selection*
- This process takes place primarily in the **thymic medulla** and eliminates T cells that bind too strongly to self-peptide/MHC complexes, preventing autoimmunity.
- It is a central tolerance mechanism and is not related to B cell responses in germinal centers.
*Development of early pro-B cells*
- The development of pro-B cells, and indeed all early stages of B cell development (pro-B, pre-B, immature B), occurs primarily in the **bone marrow**.
- These are early developmental stages, distinct from the antigen-driven processes occurring in secondary lymphoid organs during an infection.
*Development of immature B cells*
- Immature B cells develop from pre-B cells in the **bone marrow** and then migrate to secondary lymphoid organs to complete maturation.
- This step occurs prior to encountering an antigen in the germinal centers and is part of initial B cell development rather than the refinement of the immune response to an infection.
More B-cell depleting antibodies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.