Mechanism of Action - The Sugar Spillers
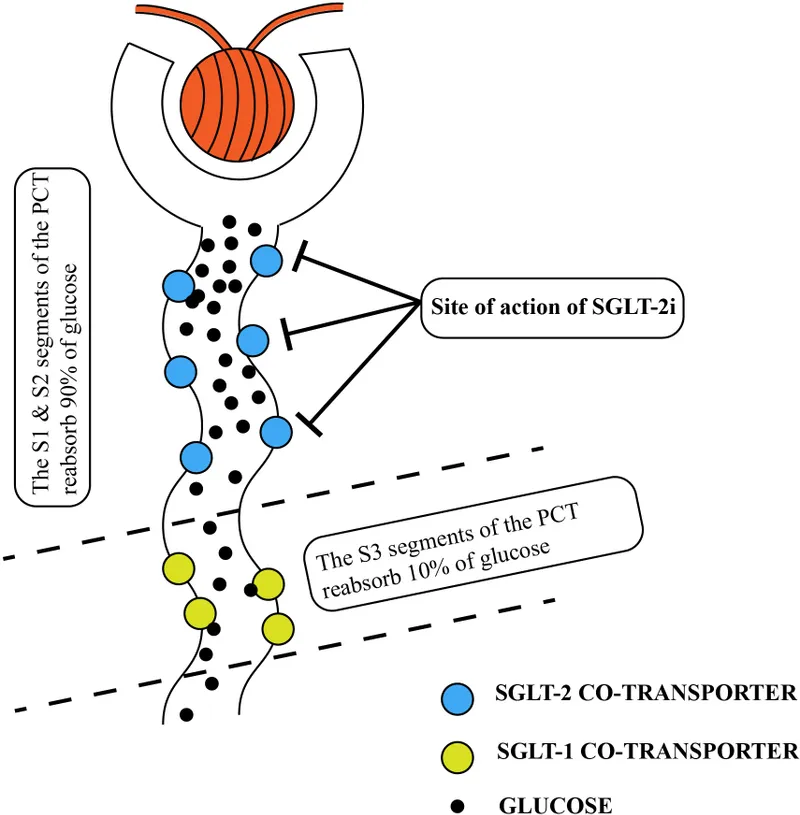
- Primary Site: Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) of the nephron.
- Action: Selectively inhibit the Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2).
- SGLT-2 is responsible for reabsorbing ~90% of filtered glucose.
- Inhibition blocks this reabsorption, leading to the excretion of glucose ($C_6H_{12}O_6$) in the urine.
- Key Effects:
- Glycosuria: "Spilling" sugar into the urine.
- Osmotic Diuresis: Water follows the excreted glucose, leading to increased urine output.
- Natriuresis: Mild sodium loss as SGLT-2 is a sodium-glucose cotransporter.
⭐ Insulin Independent: SGLT-2 inhibitors lower blood glucose without relying on β-cell function or insulin sensitivity, making them effective at various stages of type 2 diabetes.
The Agents - Meet the '-gliflozins'
This class of oral hypoglycemics is easily identified by the common suffix '-gliflozin'. They are crucial not just for diabetes management but also for their significant cardiorenal benefits.
- Canagliflozin
- Dapagliflozin
- Empagliflozin
📌 Mnemonic: These agents make glucose 'flow' out in the 'zin' (urine).
⭐ Beyond glycemic control, Empagliflozin and Canagliflozin are proven to reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and hospitalizations for heart failure in patients with established cardiovascular disease.
Clinical Uses - Cardio-Renal Superpowers
SGLT-2 inhibitors are indicated for Type 2 Diabetes, Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF), and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), offering significant cardio-renal protection.
| Indication | Benefit | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Type 2 DM | ↓ HbA1c, ↓ Weight, ↓ BP | Modest glucose lowering |
| Heart Failure (HFrEF) | ↓ CV Death & HF Hospitalizations | Benefit is independent of diabetes |
| CKD | ↓ Progression of renal disease | Benefit is independent of diabetes |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||
| flowchart TD |
SGLT2["💊 SGLT-2 Inhibition
• Target proximal tubule• Block glucose uptake"]
GLUC["📋 Glucosuria & Natriuresis
• Sugar in urine• Sodium excretion"]
OSM["🔬 Osmotic Diuresis
• Water loss via urine• Lowers fluid volume"]
IGP["🔬 ⬇️ Intraglomerular P
• Tubuloglomerular FB• Afferent constriction"]
PRE["📋 ⬇️ Pre/Afterload
• Lower wall stress• Reduced BP/volume"]
RENAL["✅ Renal Protection
• Slower eGFR decline• Lower proteinuria"]
CV["✅ CV Protection
• ⬇️ HF admissions• CV mortality benefit"]
SGLT2 --> GLUC GLUC --> OSM GLUC --> IGP OSM --> PRE PRE --> CV IGP --> RENAL
style SGLT2 fill:#F1FCF5,stroke:#BEF4D8,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#166534 style GLUC fill:#FEF8EC,stroke:#FBECCA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#854D0E style OSM fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C style IGP fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C style PRE fill:#FEF8EC,stroke:#FBECCA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#854D0E style RENAL fill:#F6F5F5,stroke:#E7E6E6,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#525252 style CV fill:#F6F5F5,stroke:#E7E6E6,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#525252
> ⭐ **High-Yield:** In HFrEF patients, SGLT-2 inhibitors reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure, even in those **without** diabetes.
## Adverse Effects - The Flozin Foes
* **Genitourinary Infections:** Increased urinary glucose promotes the growth of bacteria and fungi, leading to:
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
* **Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis (eDKA):** A critical, life-threatening state of ketoacidosis *without* marked hyperglycemia (blood glucose often < **250** mg/dL).
* **Hypotension:** Osmotic diuresis causes volume depletion, posing a risk for dizziness and falls, especially in the elderly.
* **Fournier's Gangrene:** A rare but severe necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum requiring urgent intervention.
* **Bone Fractures:** An increased risk has been associated specifically with Canagliflozin.
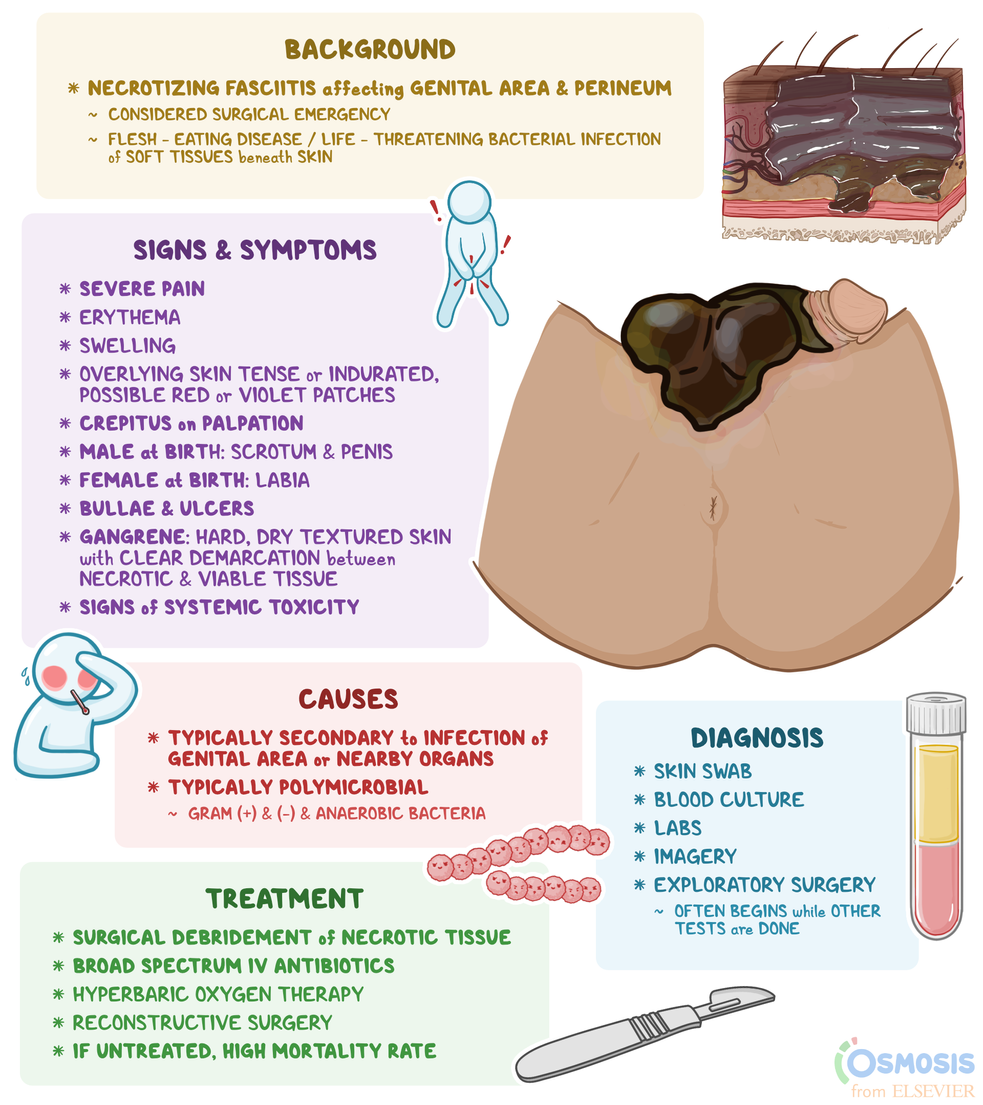
> ⭐ **High-Yield:** Always consider **eDKA** in a patient on an SGLT-2i presenting with nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain, even with near-normal blood glucose levels.
## High-Yield Points - ⚡ Biggest Takeaways
> * SGLT-2 inhibitors, ending in **"-gliflozin,"** block glucose reabsorption in the **proximal convoluted tubule**.
> * They promote **glucosuria**, leading to modest **weight loss** and a low risk of **hypoglycemia**.
> * Offer significant **cardiovascular and renal benefits**, reducing MACE and slowing diabetic kidney disease progression.
> * Major side effects include **genitourinary infections** (e.g., UTIs, vulvovaginal candidiasis) from glucosuria.
> * Be aware of the risk for **euglycemic DKA** and **dehydration**.

