Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antithyroid medications. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 1: A 27-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of palpitations, diaphoresis, and a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss. Her pulse is 101/min and blood pressure is 141/84 mm Hg. Physical examination shows a fine tremor when the fingers are outstretched. After confirmation of the diagnosis, treatment is begun with an antithyroid medication. The physician emphasizes the need for adequate contraception because of the increased risk of severe fetal malformations associated with the use of this medication, which is why its use is discouraged in the first trimester of pregnancy. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of thyroid hormone release
- B. Inhibition of peripheral conversion of T4 to T3
- C. Decreased iodide uptake by follicular cells
- D. Suppression of thyroid-stimulating hormone release
- E. Inhibition of iodide ion oxidation (Correct Answer)
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Inhibition of iodide ion oxidation***
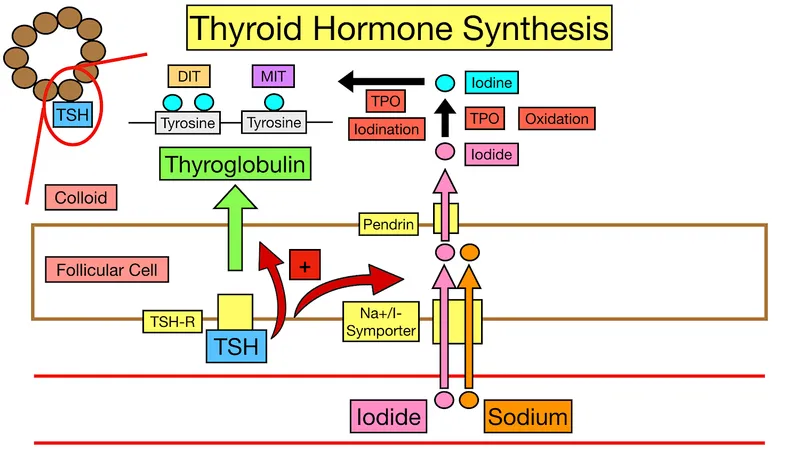
- The patient's symptoms (palpitations, diaphoresis, weight loss, tremor, tachycardia, hypertension) are classic for **hyperthyroidism**, likely **Graves' disease**.
- The antithyroid drug described, which is contraindicated in the first trimester due to teratogenicity, is **methimazole**. Methimazole (and propylthiouracil) primarily inhibits **thyroid peroxidase**, thereby preventing the **oxidation of iodide** and its subsequent organification into tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, blocking thyroid hormone synthesis.
*Inhibition of thyroid hormone release*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **iodides** (e.g., Lugol's solution, potassium iodide), which acutely inhibit the release of pre-formed thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland.
- While iodides can be used for rapid control of hyperthyroidism (e.g., before surgery or in thyroid storm), they are not the primary long-term antithyroid medications and do not carry the specific first-trimester teratogenicity risk described for PTU/methimazole.
*Inhibition of peripheral conversion of T4 to T3*
- This mechanism is primarily associated with **propylthiouracil (PTU)** (in addition to inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis) and **beta-blockers** (like propranolol), as well as **glucocorticoids** and **amiodarone**.
- While PTU also inhibits iodide oxidation, its unique ability to inhibit peripheral T4 to T3 conversion makes it the preferred antithyroid drug in the **first trimester of pregnancy** due to a lower teratogenic risk compared to methimazole, directly contrasting the drug described in the question.
*Decreased iodide uptake by follicular cells*
- This is the mechanism of action of **perchlorate** and **thiocyanate**, which are competitive inhibitors of the **sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)**, blocking iodide transport into follicular cells.
- These agents are rarely used clinically due to toxicity concerns and are not the first-line antithyroid drugs with the described teratogenic profile.
*Suppression of thyroid-stimulating hormone release*
- **TSH release** from the pituitary is primarily suppressed by **negative feedback** from high levels of circulating thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), or by direct intervention with agents like **somatostatin analogs** (e.g., octreotide) in rare cases of TSH-producing pituitary adenomas.
- Antithyroid drugs do not directly suppress TSH release; rather, by reducing thyroid hormone levels, they would eventually lead to an *increase* in TSH secretion if hyperthyroidism were adequately treated and feedback restored.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 2: A 21-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician at 10 weeks' gestation because of progressive fatigue for the past 3 weeks. She reports that she has had a 3.2-kg (7-lb) weight loss after conceiving despite an increase in appetite. She has become increasingly anxious and has trouble falling asleep. There is no personal or family history of serious illness. Medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. She is 165 cm (5 ft 5 in) tall and weighs 55 kg (120 lb); BMI is 20 kg/m2. Her temperature is 37.4°C (99.4°F), pulse is 120/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 150/70 mm Hg. The globes of the eyes are prominent. The thyroid gland is firm and diffusely enlarged. Neurologic examination shows a fine resting tremor of the hands. There is a midsystolic click at the apex and a grade 2/6 early systolic murmur at the upper left sternal border. Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone concentration is 0.1 μU/mL. An ECG is normal except for sinus tachycardia. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Radioactive iodine ablation
- B. Lugol's iodine
- C. Atenolol
- D. Propylthiouracil (Correct Answer)
- E. Thyroidectomy
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Propylthiouracil***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **hyperthyroidism** (**fatigue, weight loss despite increased appetite, anxiety, tachycardia, prominent globes, fine tremor, diffusely enlarged thyroid**, and a **TSH of 0.1 μU/mL**), likely **Graves' disease** given her age and presentation.
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)** is the preferred antithyroid drug during the **first trimester of pregnancy** due to a lower risk of teratogenicity compared to methimazole, especially preventing **embryopathy** (aplasia cutis).
*Radioactive iodine ablation*
- **Radioactive iodine (RAI) ablation** is **contraindicated in pregnancy** as it crosses the placenta and can cause **fetal hypothyroidism** and **cretinism** by destroying the fetal thyroid gland.
- It is typically used for definitive treatment of hyperthyroidism in non-pregnant individuals or post-pregnancy.
*Lugol's iodine*
- **Lugol's iodine (potassium iodide)** is used in the short term to acutely block thyroid hormone release, primarily as preparation for thyroidectomy or in **thyroid storm**.
- It is not a primary long-term treatment for hyperthyroidism and can be problematic in pregnancy due to potential for fetal goiter and hypothyroidism with prolonged use.
*Atenolol*
- **Atenolol**, a **beta-blocker**, can relieve adrenergic symptoms of hyperthyroidism like tachycardia, tremors, and anxiety.
- However, it does not address the underlying **excessive thyroid hormone production** and has been associated with **fetal growth restriction** and **bradycardia** in pregnancy. **Propranolol** is a safer beta-blocker if needed during pregnancy but should be used cautiously.
*Thyroidectomy*
- **Thyroidectomy** is a definitive treatment for hyperthyroidism but is usually reserved for patients who fail medical therapy or have large goiters causing compressive symptoms, and its preferred timing is during the **second trimester of pregnancy** if indicated, to minimize risks to both mother and fetus.
- It is not the most appropriate initial management step for an uncomplicated presentation of hyperthyroidism in early pregnancy.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 3: A 31-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with a 2-week history of diarrhea. She says that she has also noticed that she is losing weight, which makes her feel anxious since she has relatives who have suffered from anorexia. Finally, she says that she is worried she has a fever because she feels warm and has been sweating profusely. On physical examination she is found to have proptosis, fine tremor of her hands, and symmetrical, non-tender thyroid enlargement. Which of the following types of enzymes is targeted by a treatment for this disease?
- A. Peroxidase (Correct Answer)
- B. Kinase
- C. Catalase
- D. Cyclooxygenase
- E. Phosphatase
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Peroxidase***
- The patient's symptoms (diarrhea, weight loss, anxiety, sweating, proptosis, fine tremor, and symmetrical thyroid enlargement) are classic for **Graves' disease**, a form of **hyperthyroidism**.
- **Thionamides** (e.g., propylthiouracil, methimazole) are a primary treatment for Graves' disease, and they work by inhibiting **thyroid peroxidase (TPO)**, an enzyme crucial for thyroid hormone synthesis.
*Kinase*
- **Kinases** are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups, often involved in signaling pathways. While kinases are important drug targets, they are not directly involved in the primary treatment mechanism for Graves' disease.
- Examples of kinase inhibitors include those used in cancer therapy, but not for hyperthyroidism's specific pathophysiology.
*Catalase*
- **Catalase** is an enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- It has no direct role in the synthesis of thyroid hormones or as a target for hyperthyroidism treatment.
*Cyclooxygenase*
- **Cyclooxygenase (COX)** enzymes are involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes, key mediators of inflammation and pain.
- COX inhibitors (like NSAIDs) are used for pain and inflammation, not for managing the hyperactive thyroid gland in Graves' disease.
*Phosphatase*
- **Phosphatases** are enzymes that remove phosphate groups from molecules. They play a role in various cellular processes but are not the primary target for drugs treating Graves' disease.
- While important in metabolic regulation, they are not directly inhibited by thionamide drugs used in hyperthyroidism.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 4: A 54-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by a nurse 30 minutes after receiving scheduled radiation therapy for papillary thyroid cancer. After the radioisotope was ingested, the physician realized that a much larger fixed dose was given instead of the appropriate dose based on radiation dosimetry. Which of the following pharmacotherapies should be administered immediately to prevent complications from this exposure?
- A. Dexrazoxane
- B. Methimazole
- C. Propylthiouracil
- D. Potassium iodide (Correct Answer)
- E. Mercaptoethanesulfonate
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Potassium iodide***
- **Potassium iodide (KI)** is the immediate treatment for **radioactive iodine exposure** and works by saturating the thyroid gland with stable, non-radioactive iodine.
- This **competitive inhibition** prevents the uptake of radioactive iodine-131 by the thyroid, thereby reducing the risk of radiation-induced thyroid damage and cancer.
- **Timing is critical**: KI is most effective when given immediately (within hours) after exposure to radioactive iodine.
- The patient received an overdose of **radioactive iodine-131** (commonly used for papillary thyroid cancer treatment), making immediate KI administration the definitive thyroid protective measure.
*Dexrazoxane*
- **Dexrazoxane** is a **cardioprotective agent** used to reduce cardiotoxicity associated with **anthracycline chemotherapy** (e.g., doxorubicin).
- It chelates iron and prevents formation of anthracycline-iron complexes that generate free radicals.
- It has no role in preventing complications from radioactive iodine exposure.
*Methimazole*
- **Methimazole** is an **antithyroid drug** that inhibits thyroid peroxidase, thereby blocking the **iodination and coupling of tyrosyl residues** in thyroid hormone synthesis.
- While it reduces thyroid hormone production, it does **not prevent uptake** of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland.
- It is ineffective for acute radiation protection in this scenario.
*Propylthiouracil*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)** is another **antithyroid drug** that inhibits thyroid peroxidase and also blocks peripheral conversion of **T4 to T3**.
- Like methimazole, PTU does **not prevent radioactive iodine uptake** by the thyroid.
- It is not indicated for acute radioactive iodine exposure management.
*Mercaptoethanesulfonate*
- **Mercaptoethanesulfonate (MESNA)** is a **uroprotective agent** used to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis caused by **oxazaphosphorine chemotherapy agents** (cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide).
- MESNA binds to and detoxifies acrolein, the toxic metabolite responsible for bladder toxicity.
- It has no role in managing radioactive iodine exposure.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 5: A 29-year-old woman comes to the physician because of intermittent episodes of sharp chest pain and palpitations. She appears nervous. Her pulse is 115/min and irregularly irregular, and blood pressure is 139/86 mmHg. Examination shows a fine tremor on both hands and digital swelling; the extremities are warm. There is retraction of the right upper eyelid. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Amiodarone
- B. Propylthiouracil
- C. Warfarin
- D. Methimazole
- E. Propranolol (Correct Answer)
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Propranolol***
- This patient presents with symptoms suggestive of **hyperthyroidism** (tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, warm extremities, eyelid retraction, and nervousness). **Propranolol** is a non-selective beta-blocker that would help manage the sympathetic symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as tachycardia and tremor.
- While other treatments target the thyroid hormone production, propranolol provides **rapid symptomatic relief** and is often used as initial therapy alongside antithyroid medications or radioiodine.
*Amiodarone*
- **Amiodarone** is an antiarrhythmic medication and a known cause of both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism due to its high iodine content and direct thyroid effects.
- It would not be appropriate for treating existing hyperthyroidism and could potentially worsen the condition if it's the underlying cause or if the hyperthyroidism is related to iodine excess.
*Propylthiouracil*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)** is an antithyroid medication that inhibits thyroid hormone synthesis and the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3.
- While PTU is a definitive treatment for hyperthyroidism, it has a slower onset of action compared to beta-blockers for symptomatic relief and carries a risk of severe **hepatotoxicity**, making methimazole often preferred unless in specific situations like pregnancy or thyroid storm.
*Warfarin*
- **Warfarin** is an anticoagulant used to prevent blood clots. While patients with atrial fibrillation (which can be caused by hyperthyroidism and presents as an irregularly irregular pulse) may require anticoagulation, it is not the most immediate step for managing the acute symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
- The patient's pulse is 115/min and irregularly irregular, suggesting possible atrial fibrillation, but addressing the hyperadrenergic state with a beta-blocker is the primary immediate intervention.
*Methimazole*
- **Methimazole** is an antithyroid medication that inhibits thyroid hormone synthesis. It is a common first-line treatment for hyperthyroidism.
- Similar to PTU, methimazole has a slower onset of action for symptomatic relief and does not immediately address the acute adrenergic symptoms as effectively as a beta-blocker.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 6: A 50-year-old woman comes to the physician because of palpitations and irritability. Over the past 4 months, she has had several episodes of heart racing and skipping beats that lasted between 30 seconds and several hours. She has also been arguing with her husband more, often about the temperature being too warm. The patient has also lost 8.8-kg (19.4-lb) over the past 4 months, despite being less strict with her diet. She has mild asthma treated with inhaled bronchodilators. Her pulse is 102/min and blood pressure is 148/98 mm Hg. On physical examination, the skin is warm and moist. A mass is palpated in the anterior neck area. On laboratory studies, thyroid stimulating hormone is undetectable and there are antibodies against the thyrotropin-receptor. Thyroid scintigraphy shows diffusely increased iodine uptake. Two weeks later, a single oral dose of radioactive iodine is administered. This patient will most likely require which of the following in the long-term?
- A. Propranolol therapy
- B. Near-total thyroidectomy
- C. L-thyroxine therapy (Correct Answer)
- D. Methimazole therapy
- E. Estrogen replacement therapy
Antithyroid medications Explanation: * ***L-thyroxine therapy***
* Radioactive iodine ablation for **Graves' disease** often leads to **permanent hypothyroidism**, necessitating **lifelong thyroid hormone replacement** with levothyroxine.
* The patient presents with classic **hyperthyroidism** symptoms (palpitations, irritability, weight loss, heat intolerance, warm/moist skin, goiter, undetectable TSH, positive **TSH receptor antibodies**, diffuse uptake on scintigraphy), treated with radioactive iodine.
* *Propranolol therapy*
* Propranolol is a **beta-blocker** used for symptomatic relief of hyperthyroidism, particularly palpitations and tremors.
* It does **not treat the underlying cause** of hyperthyroidism or subsequent hypothyroidism, and therefore is not a long-term solution after successful radioactive iodine therapy.
* *Near-total thyroidectomy*
* A near-total thyroidectomy is a surgical option for hyperthyroidism, especially in cases of very large goiters, contraindications to radioactive iodine, or malignancy.
* While it also often leads to **hypothyroidism** requiring long-term L-thyroxine, it was **not the chosen treatment modality** in this scenario (radioactive iodine was administered).
* *Methimazole therapy*
* Methimazole is an **antithyroid drug** used to decrease thyroid hormone synthesis in hyperthyroidism.
* It is used as a **primary treatment for hyperthyroidism** or as preparation for definitive therapy like radioactive iodine or surgery; it is not a long-term treatment after successful radioactive iodine ablation has induced hypothyroidism.
* *Estrogen replacement therapy*
* Estrogen replacement therapy is used for symptoms of **menopause** or to prevent osteoporosis, but it has no direct role in the management of thyroid disorders.
* The patient's symptoms are clearly indicative of a **thyroid pathology**, not primarily menopausal symptoms.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 7: A 44-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of fatigue, constipation, and a 7-kg (15.4-lb) weight gain. Menses occur irregularly in intervals of 40–50 days. Her pulse is 51/min, and blood pressure is 145/86 mm Hg. Examination shows conjunctival pallor and cool, dry skin. There is mild, nonpitting periorbital edema. Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone concentration is 8.1 μU/mL. Treatment with the appropriate pharmacotherapy is initiated. After several weeks of therapy with this drug, which of the following hormonal changes is expected?
- A. Increased TRH
- B. Increased T3
- C. Decreased T4
- D. Increased T4
- E. Decreased TSH (Correct Answer)
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Decreased TSH***
- The patient has **primary hypothyroidism** (elevated TSH 8.1 μU/mL, symptoms of fatigue, constipation, bradycardia, weight gain, cool dry skin) and is treated with **levothyroxine (synthetic T4)**.
- The phrase **"after several weeks of therapy"** is key: while T4 levels rise within days of starting levothyroxine, **TSH takes 6-8 weeks to normalize** due to the negative feedback loop.
- As circulating thyroid hormone levels are restored, the **hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis** re-establishes negative feedback, leading to **decreased TSH secretion** from the pituitary.
- **Decreased TSH is the primary clinical marker** used to assess adequacy of thyroid hormone replacement after several weeks of therapy.
*Increased T4*
- While T4 levels do increase with levothyroxine therapy, this occurs **rapidly (within days)**, not over "several weeks."
- The question's timeframe of "several weeks" directs attention to the **delayed TSH response**, which is what clinicians monitor at 6-8 weeks to adjust dosing.
- T4 elevation is immediate; TSH normalization takes weeks and is the endpoint being tested.
*Increased T3*
- T3 levels will increase as **T4 is peripherally converted to the active form T3**, but this is not the primary hormonal change being monitored after several weeks.
- The question asks about expected hormonal changes in the context of treatment monitoring, where **TSH is the gold standard**.
*Increased TRH*
- **Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)** from the hypothalamus stimulates TSH release. In primary hypothyroidism, both TRH and TSH are elevated.
- With thyroid hormone replacement, negative feedback would lead to **decreased TRH**, not increased.
*Decreased T4*
- This is the opposite of what occurs with levothyroxine therapy.
- The goal of treatment is to **increase** deficient T4 levels to the physiological range.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 8: A patient with Graves' disease is treated with thiocyanate (a historical antithyroid agent). Thiocyanate helps reduce thyroid hormone production by:
- A. Inhibiting thyroid peroxidase
- B. Inhibiting 5'-deiodinase
- C. Inhibiting iodide follicular uptake (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibiting beta-adrenergic receptors
- E. Inhibiting thyroid deiodinase
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Inhibiting iodide follicular uptake***
- Thiocyanate is a competitive inhibitor of the **sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)** on thyroid follicular cells, blocking the uptake of iodide into the thyroid gland.
- By preventing iodide entry, thiocyanate reduces the raw material needed for thyroid hormone synthesis, thereby mitigating the **hyperthyroidism** seen in Graves' disease.
*Inhibiting thyroid peroxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **thionamide drugs** (e.g., methimazole, propylthiouracil), which block the oxidation of iodide and its organification.
- While effective in Graves' disease, thiocyanate does not directly inhibit thyroid peroxidase activity.
*Inhibiting 5'-deiodinase*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)**, but not thiocyanate, inhibits the peripheral conversion of T4 to the more active T3 by blocking 5'-deiodinase enzymes.
- This action helps to reduce the overall effect of thyroid hormones in the body.
*Inhibiting beta-adrenergic receptors*
- **Beta-blockers** (e.g., propranolol) are used to manage the symptomatic effects of hyperthyroidism, such as palpitations, tremor, and anxiety.
- They do not affect thyroid hormone synthesis or release, but rather block the peripheral actions of thyroid hormones on adrenergic receptors.
*Inhibiting thyroid deiodinase*
- This option refers to the enzymes responsible for removing iodine from thyroid hormones, which is part of the normal catabolism of these hormones or for converting T4 to T3.
- Thiocyanate does not primarily act by inhibiting these deiodinase enzymes within the thyroid gland or peripherally; its main action is on iodide uptake.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 9: A 19-year-old woman, accompanied by her parents, presents after a one-week history of abnormal behavior, delusions, and unusual aggression. She denies fever, seizures or illicit drug use. Family history is negative for psychiatric illnesses. She was started on risperidone and sent home with her parents. Three days later, she is brought to the emergency department with fever and confusion. She is not verbally responsive. At the hospital, her temperature is 39.8°C (103.6°F), the blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, the pulse rate is 102/min, and the respiratory rate is 16/min. She is extremely diaphoretic and appears stiff. She has spontaneous eye-opening but she is not verbally responsive and she is not following commands. Laboratory studies show:
Sodium 142 mmol/L
Potassium 5.0 mmol/L
Creatinine 1.8 mg/dl
Calcium 10.4 mg/dl
Creatine kinase 9800 U/L
White blood cells 14,500/mm3
Hemoglobin 12.9 g/dl
Platelets 175,000/mm3
Urinalysis shows protein 1+, hemoglobin 3+ with occasional leukocytes and no red blood casts. What is the best first step in the management of this condition?
- A. Paracetamol
- B. Dantrolene
- C. Intravenous hydration
- D. Switch risperidone to clozapine
- E. Stop risperidone (Correct Answer)
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Stop risperidone***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, altered mental status, muscle rigidity**, and elevated **creatine kinase** after starting risperidone is highly suggestive of **neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)**.
- The **first and most critical step** in managing NMS is to **immediately discontinue the offending antipsychotic medication**, as continuation can worsen the severe symptoms and increase mortality.
*Paracetamol*
- While the patient has a high fever (39.8°C), **paracetamol** (acetaminophen) alone is **insufficient** to address the underlying severe hyperthermia and other systemic effects of NMS.
- The fever in NMS is due to **muscle rigidity** and **dysregulation of the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center**, which requires more comprehensive management than antipyretics.
*Dantrolene*
- **Dantrolene** is a **muscle relaxant** often used in NMS to reduce muscle rigidity and hyperthermia by inhibiting calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- However, the **withdrawal of the causative agent** (risperidone) is always the **initial and most crucial management step** before or in conjunction with supportive medications like dantrolene or bromocriptine.
*Intravenous hydration*
- **Intravenous hydration** is an important **supportive measure** in NMS to manage dehydration, support renal function (due to potential **rhabdomyolysis** from elevated CK), and help with temperature regulation.
- While critical, it is **not the *first* step**; discontinuing the causative drug is paramount.
*Switch risperidone to clozapine*
- Switching to another antipsychotic, even clozapine, is **inappropriate** at this stage because the patient is experiencing a severe adverse reaction to an antipsychotic.
- Reintroducing another antipsychotic could **exacerbate NMS** or trigger a similar reaction, and the immediate priority is to stabilize the patient by removing the trigger.
Antithyroid medications US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old female with a history of childhood asthma presents to clinic complaining of a three month history of frequent, loose stools. She currently has three to four bowel movements per day, and she believes that these episodes have been getting worse and are associated with mild abdominal pain. She also endorses seeing red blood on the toilet tissue. On further questioning, she also endorses occasional palpitations over the past few months. She denies fevers, chills, headache, blurry vision, cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, nausea, or vomiting. She describes her mood as slightly irritable and she has been sleeping poorly. A review of her medical chart reveals a six pound weight loss since her visit six months ago, but she says her appetite has been normal. The patient denies any recent illness or travel. She is a non-smoker. Her only current medication is an oral contraceptive pill.
Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 104/min, blood pressure is 95/65 mmHg, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. On physical exam, the physician notes that her thyroid gland appears symmetrically enlarged but is non-tender to palpation. Upon auscultation there is an audible thyroid bruit. Her cranial nerve is normal and ocular exam reveals exophthalmos. Her abdomen is soft and non-tender to palpation. Deep tendon reflexes are 3+ throughout. Lab results are as follows:
Serum:
Na+: 140 mEq/L
K+: 4.1 mEq/L
Cl-: 104 mEq/L
HCO3-: 26 mEq/L
BUN: 18 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
Hemoglobin: 14.0 g/dL
Leukocyte count: 7,400/mm^3
Platelet count 450,000/mm^3
TSH & Free T4: pending
A pregnancy test is negative. The patient is started on propranolol for symptomatic relief. What is the most likely best next step in management for this patient?
- A. Thyroid scintigraphy with I-123
- B. Surgical thyroidectomy
- C. IV hydrocortisone
- D. Adalimumab
- E. Methimazole (Correct Answer)
Antithyroid medications Explanation: ***Methimazole***
- The patient's symptoms (tachycardia, weight loss despite normal appetite, irritability, insomnia, diarrhea, exophthalmos, goiter with bruit, hyperreflexia) are classic for **hyperthyroidism**, most likely **Graves' disease**.
- **Methimazole** is an antithyroid drug that inhibits thyroid hormone synthesis and is a primary treatment for hyperthyroidism.
*Thyroid scintigraphy with I-123*
- While thyroid scintigraphy is useful for differentiating causes of hyperthyroidism, it is typically performed **after initial laboratory confirmation** of hyperthyroidism (TSH and T4 levels) to guide long-term treatment.
- Given the strong clinical picture, immediate treatment to control symptoms (propranolol) and reduce hormone synthesis (methimazole) is a more pressing next step.
*Surgical thyroidectomy*
- **Thyroidectomy** is a definitive treatment for hyperthyroidism but is usually reserved for cases that fail medical therapy, have very large goiters, or suspicion of malignancy.
- It also requires the patient to be **euthyroid** before surgery to minimize operative risks.
*IV hydrocortisone*
- **IV hydrocortisone** is used for the treatment of **thyroid storm**, a severe, life-threatening manifestation of hyperthyroidism, or in cases of adrenal crisis.
- While the patient is symptomatic, her vital signs and lack of severe multi-organ dysfunction do not suggest thyroid storm.
*Adalimumab*
- **Adalimumab** is a TNF-alpha inhibitor used to treat autoimmune conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis), rheumatoid arthritis, or psoriasis.
- Although the patient has GI symptoms, **inflammatory bowel disease** is less likely given the constellation of other symptoms pointing to hyperthyroidism, and adalimumab is not a treatment for thyroid disease.
More Antithyroid medications US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.