SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for SV2A modulating antiepileptics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 1: A 59-year-old male presents to his primary care physician complaining of a tremor. He developed a tremor in his left hand approximately three months ago. It appears to be worse at rest and diminishes if he points to something or uses the hand to hold an object. His past medical history is notable for emphysema and myasthenia gravis. He has a 40 pack-year smoking history. Physical examination reveals slowed movements. The patient takes several seconds to rise from his chair for a gait analysis which reveals a shuffling gait. The physician decides to start the patient on a medication that prevents the degradation of a neurotransmitter. This medication is also indicated for use in which of the following conditions?
- A. Hyperprolactinemia
- B. Seasonal allergies
- C. Influenza
- D. Major depressive disorder (Correct Answer)
- E. Restless leg syndrome
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Major depressive disorder***
- The patient's symptoms (resting tremor worse at rest, bradykinesia, shuffling gait) are classic for **Parkinson's disease**, caused by dopamine deficiency in the substantia nigra
- The medication that **prevents neurotransmitter degradation** refers to **MAO-B inhibitors** (e.g., selegiline, rasagiline), which inhibit monoamine oxidase type B, preventing the breakdown of dopamine
- **MAO inhibitors** as a class prevent the degradation of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin)
- **Non-selective MAO inhibitors** (phenelzine, tranylcypromine) and **MAO-A inhibitors** (moclobemide) are used to treat **major depressive disorder**, particularly treatment-resistant depression
- Both MAO-B inhibitors (for Parkinson's) and MAO-A inhibitors (for depression) work by preventing enzymatic degradation of neurotransmitters
*Hyperprolactinemia*
- Treated with **dopamine agonists** (bromocriptine, cabergoline) that directly stimulate dopamine D2 receptors to suppress prolactin secretion
- These are not degradation inhibitors but receptor agonists
*Seasonal allergies*
- Treated with antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, or leukotriene inhibitors
- No role for medications that prevent neurotransmitter degradation
*Influenza*
- Treated with antiviral medications (oseltamivir, zanamivir) that inhibit neuraminidase
- Note: While oseltamivir inhibits viral neuraminidase (an enzyme), this is unrelated to neurotransmitter degradation in the CNS
*Restless leg syndrome*
- Primarily treated with **dopamine agonists** (pramipexole, ropinirole) that stimulate dopamine receptors
- While dopamine is involved, the mechanism is receptor stimulation, not prevention of degradation
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because his teachers have noticed him staring blankly on multiple occasions over the past month. These episodes last for several seconds and occasionally his eyelids flutter. He was born at term and has no history of serious illness. He has met all his developmental milestones. He appears healthy. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. Hyperventilation for 30 seconds precipitates an episode of unresponsiveness and eyelid fluttering that lasts for 7 seconds. He regains consciousness immediately afterward. An electroencephalogram shows 3-Hz spikes and waves. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
- A. Phenytoin
- B. Clonazepam
- C. Levetiracetam
- D. Carbamazepine
- E. Ethosuximide (Correct Answer)
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Ethosuximide***
- This patient presents with classic features of **absence seizures**, including brief staring spells with eyelid fluttering, precipitation by hyperventilation, and a characteristic **3-Hz spike-and-wave pattern on EEG**. **Ethosuximide** is the first-line pharmacotherapy for typical absence seizures due to its high efficacy and favorable side effect profile.
- It works by blocking **T-type calcium channels** in the thalamic neurons, which are crucial in generating the 3-Hz spike-and-wave discharges characteristic of absence seizures.
*Phenytoin*
- **Phenytoin** is a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant primarily used for **tonic-clonic seizures** and **focal seizures**.
- It is generally **ineffective** and can sometimes exacerbate absence seizures, making it an inappropriate choice for this patient.
*Clonazepam*
- **Clonazepam** is a benzodiazepine that can be used as an adjunct in some epilepsy syndromes, particularly for myoclonic or atypical absence seizures.
- While it has broad anti-seizure properties, it is not the **first-line drug of choice** for typical absence seizures, and its use is often limited by sedative side effects and the potential for tolerance and dependence.
*Levetiracetam*
- **Levetiracetam** is a broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug effective for focal, generalized tonic-clonic, and myoclonic seizures.
- While it can be used for absence seizures, **ethosuximide** or valproic acid are generally considered more effective as monotherapy options for typical absence seizures due to their specific mechanism of action.
*Carbamazepine*
- **Carbamazepine** is primarily used for **focal seizures** and **tonic-clonic seizures**.
- Like phenytoin, **carbamazepine** is known to **exacerbate absence seizures**, making it an unsuitable and potentially harmful treatment choice for this patient.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 3: A 19-year-old male presents to the ER with generalized tonic-clonic seizures. He does not have a prior history of seizures and has not taken any drugs except for his daily asthma medication. Which of the following is associated with seizures?
- A. Albuterol
- B. Prednisone
- C. Cromolyn
- D. Theophylline (Correct Answer)
- E. Ipratropium
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Theophylline***
- **Theophylline** has a narrow therapeutic index, and its toxicity can manifest as **seizures** and cardiac arrhythmias, especially in a patient with no prior seizure history.
- While used for asthma, uncontrolled or high doses can lead to systemic effects including neurological complications like **seizures**.
*Albuterol*
- **Albuterol** is a beta-2 agonist and is generally well-tolerated at therapeutic doses, with common side effects being **tremor** and **tachycardia**.
- While overdose can cause cardiotoxicity, it is less commonly associated with **seizures** as a primary side effect compared to theophylline.
*Prednisone*
- **Prednisone**, a corticosteroid, can have psychiatric side effects like mood changes and psychosis, but **generalized tonic-clonic seizures** are a rare complication.
- Seizures are more likely to be associated with steroid withdrawal or very high doses in susceptible individuals, which is not clearly indicated here.
*Cromolyn*
- **Cromolyn** is a mast cell stabilizer used for asthma prevention and is known for its excellent safety profile, with very few systemic side effects.
- It is not associated with **seizures** or other severe neurological complications.
*Ipratropium*
- **Ipratropium** is an anticholinergic bronchodilator primarily used for asthma and COPD. Systemic absorption is minimal, so systemic side effects are rare.
- While high doses can cause anticholinergic effects, **seizures** are not a typical or common adverse event associated with its use.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 4: A 56-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. One month ago, he was diagnosed with a focal seizure and treatment with a drug that blocks voltage-gated sodium channels was begun. Today, he reports that he has not had any abnormal body movements, but he has noticed occasional double vision. His serum sodium is 132 mEq/L, alanine aminotransferase is 49 U/L, and aspartate aminotransferase is 46 U/L. This patient has most likely been taking which of the following drugs?
- A. Carbamazepine (Correct Answer)
- B. Topiramate
- C. Lamotrigine
- D. Gabapentin
- E. Levetiracetam
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Carbamazepine***
- This patient's symptoms of **double vision (diplopia)**, **hyponatremia** (serum sodium 132 mEq/L), and mild elevation in **liver enzymes** (ALT 49 U/L, AST 46 U/L) are classic side effects of carbamazepine.
- Carbamazepine blocks **voltage-gated sodium channels**, which is consistent with the initial treatment description for focal seizures.
- Hyponatremia occurs due to **SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion)**, a well-known adverse effect.
*Topiramate*
- Common side effects include **cognitive slowing**, **paresthesias**, and **kidney stones**, which are not reported by the patient.
- While it can cause weight loss and metabolic acidosis, **diplopia** and **hyponatremia** are not typical adverse effects.
*Lamotrigine*
- Also blocks voltage-gated sodium channels but has a different side effect profile.
- The most significant and potentially life-threatening side effect is a severe skin rash known as **Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)** or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
- It does not commonly cause **diplopia** or significant **hyponatremia**.
*Gabapentin*
- Primarily acts by binding to the **α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels** and is NOT a sodium channel blocker.
- Side effects typically include **dizziness**, **somnolence**, and peripheral edema, not the constellation of symptoms presented.
*Levetiracetam*
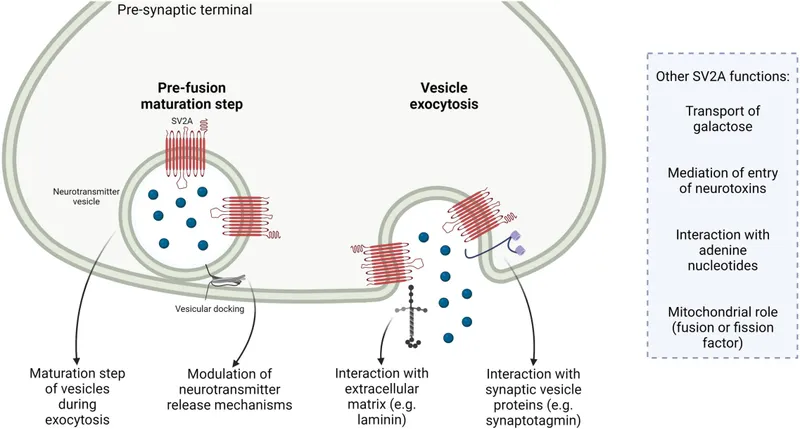
- Its mechanism of action involves binding to the **synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A)**, a unique target, and it is NOT a voltage-gated sodium channel blocker.
- Common side effects include behavioral changes (**irritability**, **aggression**) and **somnolence**, but not diplopia or hyponatremia.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 5: A 35-year-old woman comes to the physician accompanied by her husband after he started noticing strange behavior. He first noticed her talking to herself 8 months ago. For the past 6 months, she has refused to eat any packaged foods out of fear that the government is trying to poison her. She has no significant past medical history. She smoked marijuana in college but has not smoked any since. She appears restless. Mental status examination shows a flat affect. Her speech is clear, but her thought process is disorganized with many loose associations. The patient is diagnosed with schizophrenia and started on olanzapine. This patient is most likely to experience which of the following adverse effects?
- A. Dyslipidemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Diabetes insipidus
- C. Agranulocytosis
- D. Myoglobinuria
- E. Seizures
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Dyslipidemia***
- **Olanzapine** is a **second-generation antipsychotic** commonly associated with significant **metabolic side effects**, including **weight gain**, **dyslipidemia**, and **insulin resistance**.
- These metabolic disturbances increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
*Diabetes insipidus*
- This is a rare side effect, not typically associated with **olanzapine** or other **second-generation antipsychotics**.
- **Lithium** is an antimanic agent that can cause **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus**, but it is not relevant here.
*Agranulocytosis*
- While a serious side effect of some antipsychotics, **agranulocytosis** is most notably associated with **clozapine**,
- **Olanzapine** has a much lower risk of causing **agranulocytosis** compared to clozapine.
*Myoglobinuria*
- **Myoglobinuria** is associated with conditions like significant muscle damage (e.g., rhabdomyolysis).
- It is not a direct or common adverse effect of **olanzapine** therapy.
*Seizures*
- While some antipsychotics can lower the **seizure threshold**, **olanzapine** generally has a relatively low risk of inducing seizures.
- The risk is higher with certain other antipsychotics, particularly at high doses, or in patients with pre-existing seizure disorders.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 6: A 24-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of violent jerky movements of his arms and legs that began 30 minutes ago. His father reports that the patient has a history of epilepsy. He is not responsive. Physical examination shows alternating tonic jerks and clonic episodes. There is blood in the mouth. Administration of intravenous lorazepam is begun. In addition, treatment with a second drug is started that alters the flow of sodium ions across neuronal membranes. The second agent administered was most likely which of the following drugs?
- A. Lamotrigine
- B. Phenobarbital
- C. Topiramate
- D. Carbamazepine
- E. Fosphenytoin (Correct Answer)
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Fosphenytoin***
- This patient is experiencing **status epilepticus** as evidenced by prolonged tonic-clonic seizures. **Lorazepam** is the first-line short-acting benzodiazepine for acute seizure termination, but a second, longer-acting antiepileptic drug is needed for maintenance.
- **Fosphenytoin** is a prodrug of **phenytoin** that can be administered intravenously; **phenytoin** works by blocking **voltage-sensitive sodium channels**, thereby altering the flow of sodium ions and stabilizing neuronal membranes.
*Lamotrigine*
- While **lamotrigine** does block voltage-gated sodium channels, it is primarily used for **partial seizures** and **generalized tonic-clonic seizures** as a maintenance therapy, not typically as an acute treatment for status epilepticus.
- It requires **slow titration** due to the risk of severe skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome), making it unsuitable for immediate use in status epilepticus.
*Phenobarbital*
- **Phenobarbital** is an antiepileptic drug that enhances **GABAergic neurotransmission**, leading to neuronal hyperpolarization and reduced excitability. It is a very effective and older anticonvulsant.
- Although it can be used for status epilepticus, it acts primarily on GABA receptors, not directly on **sodium ion channels** as described in the question.
*Topiramate*
- **Topiramate** has multiple mechanisms of action, including blocking voltage-gated sodium channels and enhancing GABA activity, but it is typically used as a **maintenance therapy** for various seizure types.
- It is not a first-line agent for acute management of **status epilepticus** and its primary mechanism mentioned isn't restricted to sodium channel modulation as explicitly as phenytoin.
*Carbamazepine*
- **Carbamazepine** is a sodium channel blocker, similar to phenytoin, and is effective for **partial** and **tonic-clonic seizures**.
- However, it is primarily an **oral medication** and its slow absorption makes it inappropriate for acute intravenous treatment of status epilepticus.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 7: A neurophysiologist describes the mechanism of a specific type of synaptic transmission to his students. While illustrating this, he points out that when the action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a chemical synapse, the voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open. Ca2+ ions trigger the release of neurotransmitters from vesicles in the presynaptic terminal. In this type of synaptic transmission, increased cytosolic Ca2+ levels cause the release of a neurotransmitter from small vesicles with dense cores. Which of the following neurotransmitters is most likely to be the one that is released into the synaptic cleft in this type of synapse?
- A. Epinephrine
- B. Glutamate
- C. Glycine
- D. GABA (γ-amino butyric acid)
- E. Norepinephrine (Correct Answer)
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Norepinephrine***
- **Norepinephrine** is the primary catecholamine neurotransmitter stored in **small vesicles with dense cores** (dense-core vesicles).
- It is released from **sympathetic postganglionic neurons** and central nervous system neurons, particularly from the **locus coeruleus**.
- Dense-core vesicles are the hallmark of catecholaminergic neurons, and norepinephrine is the most abundant neuronal catecholamine.
- The description perfectly matches noradrenergic synaptic transmission.
*Epinephrine*
- While epinephrine is also a catecholamine stored in dense-core vesicles, it functions primarily as a **hormone** released from the **adrenal medulla** (not a neurotransmitter).
- Only a **very small number** of CNS neurons use epinephrine as a neurotransmitter (mainly in medullary regions).
- In the context of synaptic transmission, norepinephrine is far more common.
*Glutamate*
- **Glutamate** is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS but is stored in **small, clear synaptic vesicles**, not dense-core vesicles.
- It does not fit the description of dense-core vesicle storage.
*Glycine*
- **Glycine** is an inhibitory neurotransmitter stored in **small, clear synaptic vesicles**.
- Found predominantly in the **spinal cord** and brainstem, not in dense-core vesicles.
*GABA (γ-amino butyric acid)*
- **GABA** is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter stored in **small, clear synaptic vesicles**.
- Not associated with dense-core vesicle storage.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 8: A 58-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of difficulty walking, clumsiness of her arms and legs, and slurred speech. Physical examination shows masked facies and a slow, shuffling gait. When her ankles are passively flexed, there is involuntary, jerky resistance. Treatment is initiated with a combination of levodopa and carbidopa. The addition of carbidopa is most likely to decrease the risk of which of the following potential adverse drug effects?
- A. Visual hallucinations
- B. Dyskinesia
- C. Urinary retention
- D. Orthostatic hypotension (Correct Answer)
- E. Resting tremor
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Orthostatic hypotension***
- Carbidopa inhibits **peripheral DOPA decarboxylase**, preventing the conversion of levodopa to dopamine in the systemic circulation.
- This reduces systemic dopamine levels, thereby decreasing adverse effects such as **nausea, vomiting**, and **orthostatic hypotension** caused by peripheral dopamine action.
*Visual hallucinations*
- **Visual hallucinations** are a central dopaminergic side effect of levodopa and are not directly prevented by carbidopa.
- Carbidopa increases the amount of levodopa reaching the brain, which can potentially worsen central side effects if not managed with dosage adjustments.
*Dyskinesia*
- **Dyskinesia** is a common long-term motor complication of levodopa therapy, resulting from pulsating dopamine stimulation in the brain.
- Carbidopa itself, by increasing the availability of levodopa to the brain, does not reduce the risk of dyskinesia and may even contribute to it.
*Urinary retention*
- **Urinary retention** is not a characteristic immediate side effect of levodopa-carbidopa therapy; instead, anticholinergic medications may cause this.
- Levodopa's primary effects are on the dopamine system, and its association with urinary retention is not prominent.
*Resting tremor*
- **Resting tremor** is a cardinal symptom of Parkinson's disease and is typically *improved* by levodopa, not caused or worsened by it.
- Carbidopa enhances the therapeutic effect of levodopa, thereby helping to reduce the tremor.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 9: A 31-year-old woman makes an appointment with a fertility specialist because she has not been able to conceive despite trying for over a year with her husband. She is concerned because her husband has 2 children from a previous marriage whereas she has no children. After obtaining a detailed history as well as lab tests, the specialist prescribes a certain drug. Interestingly, this drug is able to stimulate receptors in the presence of low hormone levels and inhibit the same receptors in the presence of high hormone levels. The drug that is most likely being prescribed in this case is associated with which of the following adverse events?
- A. Hirsutism
- B. Deep venous thrombosis
- C. Thrombophilia
- D. Osteoporosis
- E. Visual disturbances (Correct Answer)
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Visual disturbances***
- The description of the drug activating receptors in low hormone states and inhibiting them in high hormone states, coupled with its use for infertility, strongly suggests **clomiphene citrate**, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM).
- **Visual disturbances** such as blurred vision, scotomas, or photopsia are a relatively common adverse effect of clomiphene due to its effect on estrogen receptors in the retina.
*Hirsutism*
- **Hirsutism** (excessive hair growth) is typically associated with conditions causing androgen excess, like **polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)**, and is not a direct common adverse effect of clomiphene.
- While clomiphene aims to induce ovulation, it does not directly cause an increase in androgens leading to hirsutism.
*Deep venous thrombosis*
- Although some hormonal treatments can increase the risk of **DVT**, clomiphene's association with DVT is **not as primary or common** as other adverse effects, and it's less direct compared to estrogen-containing medications.
- The mechanism of action of clomiphene as a SERM modulating estrogen receptors does not typically lead to a significant procoagulant state comparable to exogenous estrogen.
*Thrombophilia*
- **Thrombophilia** refers to an increased tendency to form blood clots; while some hormonal medications can exacerbate thrombophilia, clomiphene is **not generally recognized** for causing thrombophilia or significantly increasing its risk.
- Its mechanism of action primarily involves stimulating gonadotropin release rather than directly altering coagulation factors to induce thrombophilia.
*Osteoporosis*
- While **estrogen deficiency** can lead to osteoporosis, clomiphene's role is to modulate estrogen receptors; it can cause some anti-estrogenic effects, but **osteoporosis is not a common acute or direct adverse event** of its short-term use for fertility.
- Long-term use of anti-estrogenic drugs like tamoxifen can increase osteoporosis risk, but clomiphene is typically used for a limited duration, making osteoporosis less relevant as an immediate adverse event.
SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 10: Two 19-year-old men are referred by their professor and mentor to a psychiatrist for substance abuse management. The two friends have both used different stimulants for 3 years—Drug A and Drug B, respectively. Both use these substances cyclically. Use of Drug A usually lasts for about 12 hours. The cycle for Drug B lasts several days. A month ago, both men visited the emergency room (ER) due to acute intoxication. Clinical features in the emergency department included hypotension, bradycardia, sweating, chills, mydriasis, nausea, and psychomotor agitation. After a urine drug screen, the psychiatrist identifies both the drugs and informs the professor that although both Drug A and Drug B are stimulants, their mechanisms of action are different. Drug A is an alkaloid that is naturally present in the leaves of the coca plant, while it is possible to make Drug B from over-the-counter nasal decongestant products. Which of the following options best describes the mechanism of action of both drugs?
- A. Drug A increases norepinephrine activity, while Drug B does not.
- B. Drug A increases serotonin activity, while Drug B does not.
- C. Drug A predominantly acts by increasing the release of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) into the synapse, while Drug B does not.
- D. Drug A transiently increases the extracellular concentration of dopamine in the reward circuit, while Drug B does not.
- E. Drug A predominantly acts by inhibiting the reuptake of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) at the synapse, while Drug B predominantly acts by promoting their release from presynaptic terminals. (Correct Answer)
SV2A modulating antiepileptics Explanation: ***Drug A predominantly acts by inhibiting the reuptake of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) at the synapse, while Drug B predominantly acts by promoting their release from presynaptic terminals.***
- Drug A is **cocaine**, an alkaloid from the coca plant, which primarily acts by **blocking the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin**, leading to their accumulation in the synaptic cleft.
- Drug B is likely **methamphetamine**, derivable from nasal decongestants, which primarily works by **promoting the release of monoamines** from presynaptic terminals, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine.
*Drug A increases norepinephrine activity, while Drug B does not.*
- While Drug A (cocaine) does increase norepinephrine activity by inhibiting its reuptake, Drug B (methamphetamine) also significantly increases norepinephrine activity by promoting its release.
- This option incorrectly states that Drug B does not increase norepinephrine activity.
*Drug A increases serotonin activity, while Drug B does not.*
- Both Drug A (cocaine) and Drug B (methamphetamine) increase serotonin activity, albeit through different mechanisms. Cocaine inhibits serotonin reuptake, while methamphetamine promotes its release.
- The premise that Drug B does not affect serotonin activity is incorrect.
*Drug A predominantly acts by increasing the release of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) into the synapse, while Drug B does not.*
- This statement misrepresents the primary mechanism of Drug A (cocaine), which is to **inhibit reuptake**, not primarily increase release.
- It also incorrectly implies that Drug B does not significantly affect the monoamine neurotransmitter release.
*Drug A transiently increases the extracellular concentration of dopamine in the reward circuit, while Drug B does not.*
- Both cocaine (Drug A) and methamphetamine (Drug B) **increase extracellular dopamine** in the reward circuit, which is central to their addictive properties.
- This option is incorrect because Drug B also significantly increases dopamine concentrations.
More SV2A modulating antiepileptics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.