Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 1: A 31-year-old male presents to the emergency room following an altercation with patrons at a local grocery store. He is acting aggressively toward hospital staff and appears to be speaking to non-existent individuals. On examination he is tachycardic and diaphoretic. Horizontal and vertical nystagmus is noted. The patient eventually admits to taking an illegal substance earlier in the evening. Which of the following mechanisms of action is most consistent with the substance this patient took?
- A. Mu receptor agonist
- B. GABA agonist
- C. Biogenic amine reuptake inhibitor
- D. NMDA receptor antagonist (Correct Answer)
- E. Adenosine antagonist
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***NMDA receptor antagonist***
- The patient's presentation with **aggressiveness**, **psychosis** (speaking to non-existent individuals), **tachycardia**, **diaphoresis**, and particularly **horizontal and vertical nystagmus**, is highly consistent with **phencyclidine (PCP) intoxication**.
- PCP primarily acts as an **NMDA receptor antagonist**, blocking the activity of glutamate, which leads to its dissociative and psychotomimetic effects.
*Mu receptor agonist*
- **Mu receptor agonists** (e.g., opioids like heroin, morphine) typically cause central nervous system **depression**, miosis (pinpoint pupils), respiratory depression, and euphoria.
- The patient's **aggressiveness**, nystagmus, and tachycardia are **not characteristic of opioid intoxication**.
*GABA agonist*
- **GABA agonists** (e.g., benzodiazepines, barbiturates, alcohol) typically cause central nervous system **depression**, sedation, anxiolysis, and ataxia, and can lead to respiratory depression in overdose.
- The patient's agitation, psychosis, and nystagmus (especially vertical) are **not typical effects of GABAergic drugs**.
*Biogenic amine reuptake inhibitor*
- **Biogenic amine reuptake inhibitors** (e.g., cocaine, amphetamines) increase levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, leading to stimulant effects such as euphoria, agitation, paranoia, tachycardia, and hypertension.
- While some symptoms like tachycardia and agitation are consistent, the prominent **vertical nystagmus** and dissociative psychosis are generally **not hallmarks of stimulant intoxication**.
*Adenosine antagonist*
- **Adenosine antagonists** (e.g., caffeine) cause central nervous system stimulation, leading to increased alertness, restlessness, and mild tachycardia.
- The severe psychomotor agitation, prominent psychosis, and nystagmus seen in this patient are **far beyond the effects of typical adenosine antagonists**.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of spells of unresponsiveness and upward rolling of the eyes for 2 months. The episodes start abruptly and last a few seconds. During that time he does not hear anyone’s voice or make any purposeful movements. When the episodes end, he continues what he was doing before the spell. He does not lose his posture or fall to the ground. Episodes occur multiple times during the day. Physical examination shows no abnormal findings. An EEG following hyperventilation shows 3 Hz spike-and-slow-wave discharges. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy at this time?
- A. No pharmacotherapy at this time
- B. Ethosuximide (Correct Answer)
- C. Sodium valproate
- D. Oxcarbazepine
- E. Lamotrigine
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Ethosuximide***
- The described clinical picture (brief unresponsiveness, eye-rolling, continuing activity afterward, frequent daily episodes, normal physical exam, and 3-Hz spike-and-slow-wave discharges on EEG during hyperventilation) is classic for **childhood absence epilepsy**.
- **Ethosuximide** is the first-line and most effective treatment specifically for absence seizures due to its selective action on T-type calcium channels in the thalamus, which are implicated in the generation of absence seizures.
*No pharmacotherapy at this time*
- Leaving childhood absence epilepsy untreated can lead to significant impairments in learning, attention, and cognitive development due to the frequent, brief interruptions in consciousness.
- Given the clear diagnostic criteria including characteristic EEG findings and frequent episodes, initiating appropriate pharmacotherapy is medically indicated and crucial for the child's well-being.
*Sodium valproate*
- While **sodium valproate** is effective against absence seizures and has a broader spectrum of action against other seizure types, it is often considered a second-line agent for absence epilepsy due to potential side effects.
- Its use may be preferred if there are co-occurring generalized tonic-clonic seizures or if ethosuximide is not tolerated or effective, but for isolated absence seizures, ethosuximide has a better side effect profile.
*Oxcarbazepine*
- **Oxcarbazepine** is a sodium channel blocker primarily used for focal (partial onset) seizures and secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
- It is generally ineffective and can sometimes *worsen* absence seizures, making it an inappropriate choice for this diagnosis.
*Lamotrigine*
- **Lamotrigine** is a broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug effective for various seizure types, including focal, generalized tonic-clonic, and some forms of atypical absence seizures.
- While it can be used for absence seizures, it is generally considered a second-line or add-on therapy, especially when ethosuximide or valproate are ineffective or not tolerated, or if there are co-existing seizure types. It is not the most appropriate first-line choice for classic childhood absence epilepsy.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 3: A 56-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. One month ago, he was diagnosed with a focal seizure and treatment with a drug that blocks voltage-gated sodium channels was begun. Today, he reports that he has not had any abnormal body movements, but he has noticed occasional double vision. His serum sodium is 132 mEq/L, alanine aminotransferase is 49 U/L, and aspartate aminotransferase is 46 U/L. This patient has most likely been taking which of the following drugs?
- A. Carbamazepine (Correct Answer)
- B. Topiramate
- C. Lamotrigine
- D. Gabapentin
- E. Levetiracetam
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Carbamazepine***
- This patient's symptoms of **double vision (diplopia)**, **hyponatremia** (serum sodium 132 mEq/L), and mild elevation in **liver enzymes** (ALT 49 U/L, AST 46 U/L) are classic side effects of carbamazepine.
- Carbamazepine blocks **voltage-gated sodium channels**, which is consistent with the initial treatment description for focal seizures.
- Hyponatremia occurs due to **SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion)**, a well-known adverse effect.
*Topiramate*
- Common side effects include **cognitive slowing**, **paresthesias**, and **kidney stones**, which are not reported by the patient.
- While it can cause weight loss and metabolic acidosis, **diplopia** and **hyponatremia** are not typical adverse effects.
*Lamotrigine*
- Also blocks voltage-gated sodium channels but has a different side effect profile.
- The most significant and potentially life-threatening side effect is a severe skin rash known as **Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)** or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
- It does not commonly cause **diplopia** or significant **hyponatremia**.
*Gabapentin*
- Primarily acts by binding to the **α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels** and is NOT a sodium channel blocker.
- Side effects typically include **dizziness**, **somnolence**, and peripheral edema, not the constellation of symptoms presented.
*Levetiracetam*
- Its mechanism of action involves binding to the **synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A)**, a unique target, and it is NOT a voltage-gated sodium channel blocker.
- Common side effects include behavioral changes (**irritability**, **aggression**) and **somnolence**, but not diplopia or hyponatremia.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of violent jerky movements of his arms and legs that began 30 minutes ago. His father reports that the patient has a history of epilepsy. He is not responsive. Physical examination shows alternating tonic jerks and clonic episodes. There is blood in the mouth. Administration of intravenous lorazepam is begun. In addition, treatment with a second drug is started that alters the flow of sodium ions across neuronal membranes. The second agent administered was most likely which of the following drugs?
- A. Lamotrigine
- B. Phenobarbital
- C. Topiramate
- D. Carbamazepine
- E. Fosphenytoin (Correct Answer)
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Fosphenytoin***
- This patient is experiencing **status epilepticus** as evidenced by prolonged tonic-clonic seizures. **Lorazepam** is the first-line short-acting benzodiazepine for acute seizure termination, but a second, longer-acting antiepileptic drug is needed for maintenance.
- **Fosphenytoin** is a prodrug of **phenytoin** that can be administered intravenously; **phenytoin** works by blocking **voltage-sensitive sodium channels**, thereby altering the flow of sodium ions and stabilizing neuronal membranes.
*Lamotrigine*
- While **lamotrigine** does block voltage-gated sodium channels, it is primarily used for **partial seizures** and **generalized tonic-clonic seizures** as a maintenance therapy, not typically as an acute treatment for status epilepticus.
- It requires **slow titration** due to the risk of severe skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome), making it unsuitable for immediate use in status epilepticus.
*Phenobarbital*
- **Phenobarbital** is an antiepileptic drug that enhances **GABAergic neurotransmission**, leading to neuronal hyperpolarization and reduced excitability. It is a very effective and older anticonvulsant.
- Although it can be used for status epilepticus, it acts primarily on GABA receptors, not directly on **sodium ion channels** as described in the question.
*Topiramate*
- **Topiramate** has multiple mechanisms of action, including blocking voltage-gated sodium channels and enhancing GABA activity, but it is typically used as a **maintenance therapy** for various seizure types.
- It is not a first-line agent for acute management of **status epilepticus** and its primary mechanism mentioned isn't restricted to sodium channel modulation as explicitly as phenytoin.
*Carbamazepine*
- **Carbamazepine** is a sodium channel blocker, similar to phenytoin, and is effective for **partial** and **tonic-clonic seizures**.
- However, it is primarily an **oral medication** and its slow absorption makes it inappropriate for acute intravenous treatment of status epilepticus.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 5: A 36-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his girlfriend because of increasing confusion for the past 6 hours. He drinks large amounts of alcohol daily and occasionally uses illicit drugs. He is lethargic and oriented only to person. Physical examination shows jaundice, hepatomegaly, and scattered petechiae over the trunk and back. Neurologic examination shows normal, reactive pupils and a flapping tremor when the wrists are extended. A drug with which of the following mechanism of action would be most appropriate for this patient's condition?
- A. Production of NH3
- B. Activation of GABA receptors
- C. Excretion of free iron
- D. Inhibition of D2 receptors
- E. Excretion of NH4 (Correct Answer)
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Excretion of NH4***
- The patient presents with **hepatic encephalopathy**, characterized by **confusion**, **jaundice**, **hepatomegaly**, **petechiae**, and a **flapping tremor (asterixis)**, stemming from chronic alcohol abuse and liver damage. The main pathophysiology in hepatic encephalopathy is the accumulation of **ammonia (NH3)**, which is neurotoxic.
- Excretion of **NH4** (ammonium) through drug mechanisms such as **lactulose** (which acidifies the colon, trapping ammonia as ammonium for excretion) is the primary therapeutic target to reduce ammonia levels and improve neurological symptoms.
*Production of NH3*
- This mechanism would exacerbate the patient's condition by increasing the toxic load of **ammonia (NH3)**, which is already elevated in hepatic encephalopathy.
- Therapeutic interventions aim to decrease, not increase, ammonia production or absorption.
*Activation of GABA receptors*
- While **GABA receptor activation** is involved in the neurological effects of some substances that contribute to confusion, it is not the primary target for treating the underlying pathophysiology of **hepatic encephalopathy**.
- Medications that activate GABA receptors (e.g., benzodiazepines) can worsen encephalopathy by further depressing CNS function.
*Excretion of free iron*
- **Iron overload** can cause liver damage, but the acute confusion and flapping tremor are more indicative of **hepatic encephalopathy** due to ammonia toxicity, not primarily iron accumulation.
- Excreting free iron (e.g., with chelation therapy) is for conditions like hemochromatosis and would not address the immediate, life-threatening neurological symptoms in this patient.
*Inhibition of D2 receptors*
- This mechanism is characteristic of some **antipsychotic medications**. While dopamine imbalances can play a role in some neurological disorders, inhibiting D2 receptors is not a primary therapeutic target for **hepatic encephalopathy**.
- Such medications could have side effects that might complicate the clinical picture in a patient with acute liver failure.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 6: A 34-year-old woman presents with acute onset loss of vision and visual disturbances. She says that, several hours ago, her vision began to get dim, and she sees halos around light sources. This was immediately followed by a severe frontal headache. Past medical history is significant for epilepsy. The patient says her anticonvulsant medication was changed recently but she doesn’t remember the name. Slit-lamp examination reveals mild chemosis, injection, and ciliary flush with diffuse stromal haze, along with very shallow peripheral anterior chambers with areas of iridocorneal touch in both eyes. Gonioscopy showed closed angles bilaterally. Which of the following antiepileptic drugs is most likely responsible for this patient’s condition?
- A. Tiagabine
- B. Zonisamide
- C. Lamotrigine
- D. Gabapentin
- E. Topiramate (Correct Answer)
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Topiramate***
- **Topiramate** is strongly associated with acute angle-closure glaucoma, often presenting with **myopic shift** and **ciliary body edema**, leading to closure of the anterior chamber angle.
- The patient's symptoms of **acute vision loss**, **halos around lights**, **severe frontal headache**, and findings of **shallow anterior chambers** with **closed angles bilaterally** are classic for topiramate-induced angle closure.
- Topiramate is a **sulfonamide derivative** that causes ciliochoroidal effusion, leading to anterior rotation of the ciliary body and forward displacement of the lens-iris diaphragm.
*Tiagabine*
- **Tiagabine** is associated with central nervous system side effects such as dizziness, somnolence, and confusion.
- It is not typically linked to ophthalmological side effects involving acute angle-closure glaucoma.
*Zonisamide*
- **Zonisamide** is also a **sulfonamide derivative** and can rarely cause acute angle-closure glaucoma through a similar mechanism to topiramate.
- However, **topiramate** is more commonly and strongly associated with this adverse effect.
- Zonisamide is also known for other side effects like kidney stones and metabolic acidosis.
*Lamotrigine*
- **Lamotrigine** is primarily known for skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
- Ocular side effects are generally mild and do not include acute angle-closure glaucoma.
*Gabapentin*
- **Gabapentin** common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and peripheral edema.
- It is not associated with acute angle-closure glaucoma or the specific constellation of ocular symptoms described.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 7: A neuroscientist is delivering a lecture on the electrophysiology of the brain. He talks about neuroreceptors which act as ion channels in the neurons. He mentions a specific receptor, which is both voltage-gated and ligand-gated ion channel. Which of the following receptors is most likely to be the one mentioned by the neuroscientist?
- A. NMDA receptor (Correct Answer)
- B. GABAA receptor
- C. AMPA receptor
- D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
- E. Glycine receptor
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***NMDA receptor***
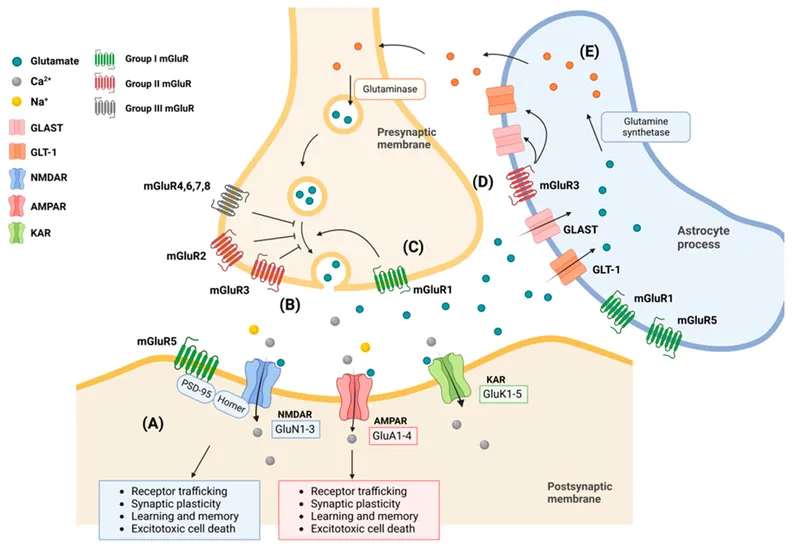
- The **NMDA receptor** is unique among ionotropic glutamate receptors as it functions as both a **ligand-gated** and **voltage-gated** ion channel.
- It requires both the binding of an excitatory neurotransmitter (like **glutamate**) and a sufficient **depolarization** of the postsynaptic membrane to remove a **magnesium ion (Mg2+) block** from its pore.
*GABAA receptor*
- The **GABAA receptor** is a **ligand-gated ion channel** that opens upon binding of the neurotransmitter **GABA**, leading to an influx of chloride ions and neuronal hyperpolarization.
- It is primarily responsible for **inhibitory synaptic transmission** in the central nervous system.
*AMPA receptor*
- The **AMPA receptor** is an ionotropic glutamate receptor that is primarily **ligand-gated**, opening swiftly upon binding of **glutamate** to allow sodium and potassium ion flow.
- While it contributes to depolarization, it is generally not considered to have a significant **voltage-gating** mechanism like the NMDA receptor.
*Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor*
- The **nicotinic acetylcholine receptor** is a **ligand-gated ion channel** that opens in response to the binding of **acetylcholine**, initiating fast excitatory synaptic transmission.
- It is **not voltage-gated** in the same manner as the NMDA receptor; its opening is primarily dependent on neurotransmitter binding.
*Glycine receptor*
- The **glycine receptor** is a **ligand-gated chloride channel** that mediates fast inhibitory synaptic transmission in the spinal cord and brainstem.
- Its activation by **glycine** leads to an influx of chloride ions, causing hyperpolarization, and it does not exhibit significant voltage-gating properties.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 8: A 20-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with painful abdominal cramping. She states she has missed her menstrual period for 5 months, which her primary care physician attributes to her obesity. She has a history of a seizure disorder treated with valproic acid; however, she has not had a seizure in over 10 years and is no longer taking medications for her condition. She has also been diagnosed with pseudoseizures for which she takes fluoxetine and clonazepam. Her temperature is 98.0°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 174/104 mmHg, pulse is 88/min, respirations are 19/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Neurologic exam is unremarkable. Abdominal exam is notable for a morbidly obese and distended abdomen that is nontender. Laboratory studies are ordered as seen below.
Serum:
hCG: 100,000 mIU/mL
Urine:
Color: Amber
hCG: Positive
Protein: Positive
During the patient's evaluation, she experiences 1 episode of tonic-clonic motions which persist for 5 minutes. Which of the following treatments is most appropriate for this patient?
- A. Phenobarbital
- B. Magnesium (Correct Answer)
- C. Phenytoin
- D. Propofol
- E. Lorazepam
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Magnesium***
- The patient's presentation with **painful abdominal cramping**, **elevated blood pressure (174/104 mmHg)**, **proteinuria**, a **positive hCG** (100,000 mIU/mL), and a **new-onset tonic-clonic seizure** strongly indicates **eclampsia**.
- **Magnesium sulfate** is the first-line treatment for seizure prophylaxis and management in patients with preeclampsia and eclampsia.
*Phenobarbital*
- While effective for seizure control, **phenobarbital** is a less preferred agent for eclampsia compared to magnesium sulfate.
- Its use in eclampsia is typically reserved for cases refractory to magnesium sulfate.
*Phenytoin*
- **Phenytoin** is not recommended as a first-line agent for eclamptic seizures, as magnesium sulfate has demonstrated superior efficacy.
- It carries a risk of adverse effects such as **cardiac arrhythmias** and **hypotension**, especially with rapid administration.
*Propofol*
- **Propofol** is an anesthetic and sedative used for continuous seizure control, often in status epilepticus, but is not the primary treatment for eclampsia.
- Its use can lead to significant **respiratory depression** and **hypotension**, requiring close monitoring and intubation.
*Lorazepam*
- Although **lorazepam** is a benzodiazepine used to acutely stop seizures, it is not the preferred agent for eclampsia.
- Benzodiazepines may cause **sedation** and **respiratory depression**, and their efficacy in eclampsia is inferior to magnesium sulfate.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 9: A 75-year-old man with a seizure disorder is brought to the emergency department by a friend because of progressive confusion over the past two weeks. He is unable to provide any history. His vital signs are within normal limits. He appears lethargic and is only oriented to person. Oral mucosa is moist. There is no jugular venous distention. A basic metabolic panel shows a serum sodium concentration of 115 mEq/L but is otherwise normal. Serum osmolality is low and antidiuretic hormone level is elevated. X-ray of the chest shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s hyponatremia?
- A. Aldosterone deficiency
- B. Medication effect (Correct Answer)
- C. Low cardiac output
- D. Insulin deficiency
- E. Excess cortisol
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Medication effect***
- This patient's **hyponatremia** with **appropriately low serum osmolality** and **elevated antidiuretic hormone (ADH)** levels, in the absence of signs of hypovolemia or fluid overload, points to the **syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH)**.
- Many medications, including anti-epileptic drugs like carbamazepine or oxcarbazepine (commonly used for seizure disorders), as well as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can cause SIADH.
*Aldosterone deficiency*
- **Aldosterone deficiency** would likely lead to **hyperkalemia** and metabolic acidosis, which are not mentioned in the basic metabolic panel as being abnormal.
- While it can cause hyponatremia due to inability to retain sodium, the elevated ADH level with normal volume status points away from primary aldosterone deficiency.
*Low cardiac output*
- **Low cardiac output** can lead to hyponatremia by decreased renal perfusion and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and ADH release.
- However, this patient has **normal vital signs** and **no jugular venous distention**, making significant low cardiac output and resultant hypovolemia less likely.
*Insulin deficiency*
- **Insulin deficiency** (as seen in uncontrolled diabetes) typically leads to **hyperglycemia** and can cause a **pseudohyponatremia** due to osmotic effects, or true hyponatremia due to polyuria and volume depletion.
- The basic metabolic panel is otherwise normal, suggesting no significant hyperglycemia or electrolyte abnormalities consistent with insulin deficiency.
*Excess cortisol*
- **Excess cortisol** (Cushing's syndrome) typically leads to **hyperglycemia**, hypertension, and features of fat redistribution, muscular weakness, and thin skin, none of which are detailed here.
- It does not directly cause hyponatremia; conversely, cortisol has some mineralocorticoid effects and typically opposes ADH action, so severe excess would more likely cause hypernatremia or normal sodium levels.
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG Question 10: A 42-year-old man is brought in to the emergency department by his daughter. She reports that her father drank heavily for the last 16 years, but he stopped 4 days ago after he decided to quit drinking on his birthday. She also reports that he has been talking about seeing cats running in his room since this morning, although there were no cats. There is no history of any known medical problems or any other substance use. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.4ºC (101.2ºF), heart rate is 116/min, blood pressure is 160/94 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 22/min. He is severely agitated and is not oriented to his name, time, or place. On physical examination, profuse perspiration and tremors are present. Which of the following best describes the pathophysiologic mechanism underlying his condition?
- A. Increased influx of chloride ions
- B. Increased inhibition of norepinephrine
- C. Functional increase in GABA
- D. Increased activity of NMDA receptors (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased inhibition of glutamate
Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics Explanation: ***Increased activity of NMDA receptors***
- Chronic alcohol use leads to **downregulation of GABA receptors** and **upregulation of NMDA receptors** to compensate for alcohol's inhibitory effects.
- When alcohol is withdrawn, the unopposed upregulation of NMDA receptors (and decreased GABA activity) causes a state of **neuronal hyperexcitability**, leading to symptoms like agitation, hallucinations, and autonomic hyperactivity seen in **delirium tremens**.
*Increased influx of chloride ions*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **GABA-A agonists** (like benzodiazepines), which enhance GABA's inhibitory effects by increasing chloride influx and hyperpolarizing neurons.
- In alcohol withdrawal, there is a **functional decrease in GABAergic activity**, not an increase in chloride ion influx.
*Increased inhibition of norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** is a neurotransmitter associated with wakefulness, alertness, and autonomic responses; increased activity is seen in alcohol withdrawal, contributing to sympathetic overdrive.
- Increased inhibition of norepinephrine would lead to sedation and reduced autonomic activity, which is the opposite of the patient's presentation.
*Functional increase in GABA*
- **GABA** (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain; alcohol enhances GABAergic activity.
- In alcohol withdrawal, there is a **functional decrease in GABAergic activity**, contributing to neuronal hyperexcitability and withdrawal symptoms.
*Increased inhibition of glutamate*
- **Glutamate** is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter, and its receptors (like NMDA) are implicated in alcohol withdrawal.
- Alcohol withdrawal is characterized by **increased excitatory activity**, including increased glutamate release and NMDA receptor activation, not increased inhibition of glutamate.
More Glutamate antagonist antiepileptics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.