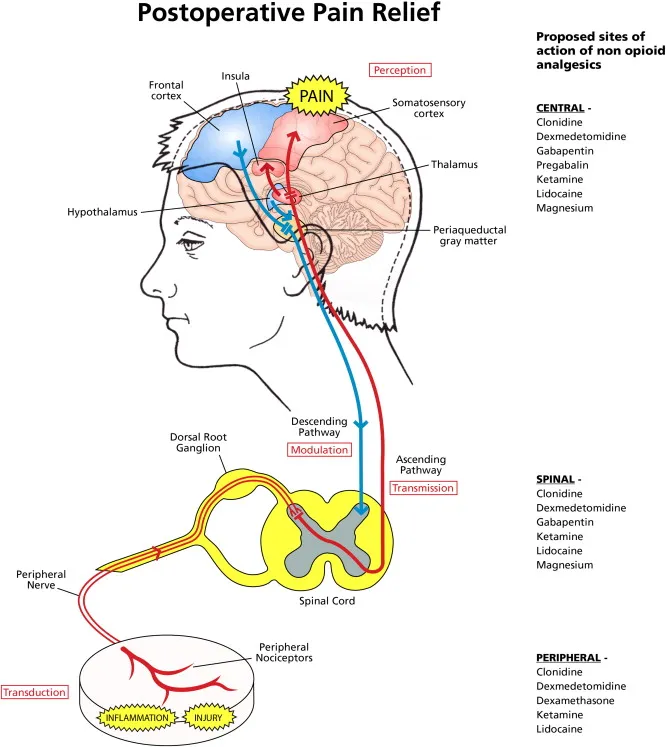
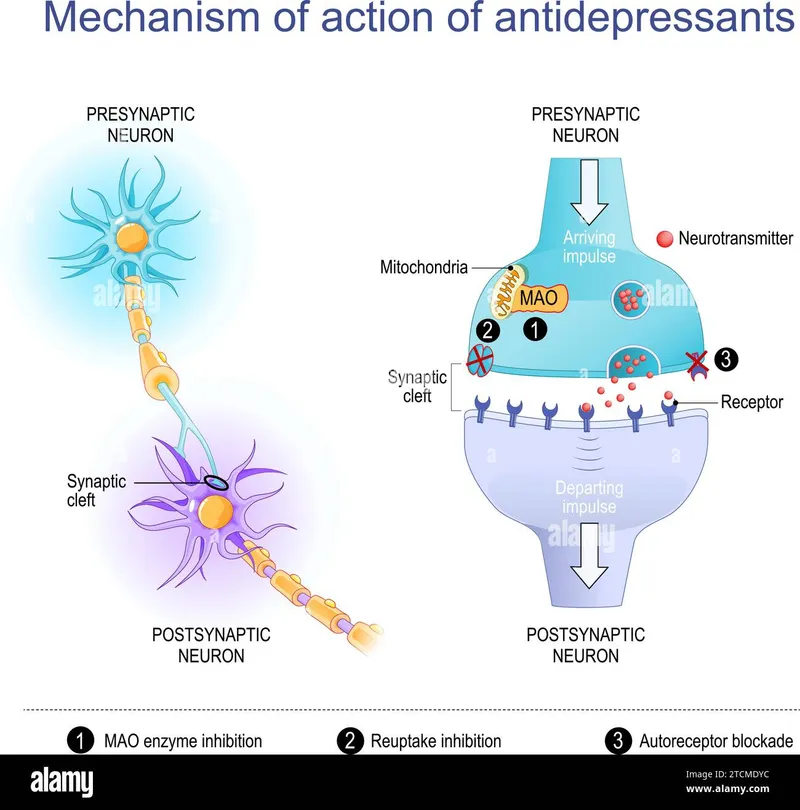
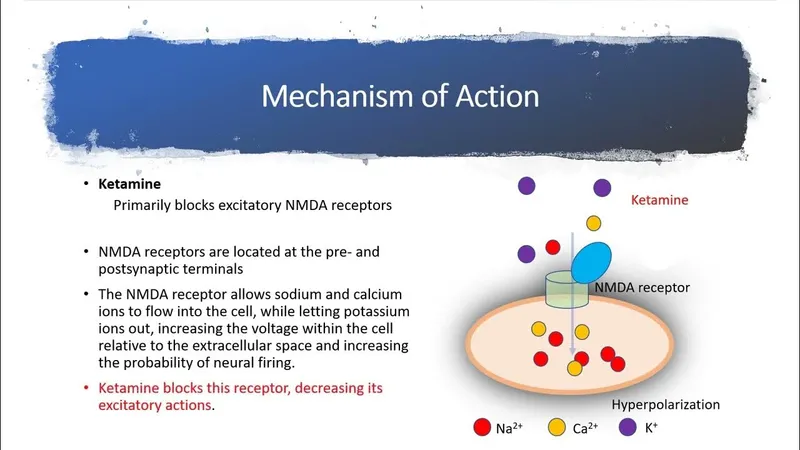
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Adjuvant analgesics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 1: A 59-year-old female presents to the emergency department after a fall. She reports severe pain in her right hip and an inability to move her right leg. Her past medical history is notable for osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and has never undergone surgery before. The patient was adopted, and her family history is unknown. She has never smoked and drinks alcohol socially. Her temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Her right leg is shortened, abducted, and externally rotated. A radiograph demonstrates a displaced femoral neck fracture. She is admitted and eventually brought to the operating room to undergo right hip arthroplasty. While undergoing induction anesthesia with inhaled sevoflurane, she develops severe muscle contractions. Her temperature is 103.4°F (39.7°C). A medication with which of the following mechanisms of action is indicated in the acute management of this patient’s condition?
- A. Ryanodine receptor antagonist (Correct Answer)
- B. Acetylcholine receptor agonist
- C. Serotonin 1B/1D agonist
- D. NMDA receptor antagonist
- E. GABA agonist
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Ryanodine receptor antagonist***
- The patient's presentation with **high fever**, **muscle rigidity**, and **tachycardia** shortly after induction with **sevoflurane** is highly suggestive of **malignant hyperthermia (MH)**.
- **Dantrolene**, a **ryanodine receptor antagonist**, is the specific treatment for MH, as it blocks the excessive release of **calcium** from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells.
*Acetylcholine receptor agonist*
- **Acetylcholine receptor agonists** (e.g., succinylcholine) stimulate muscle contraction and would worsen the muscle rigidity seen in malignant hyperthermia.
- These agents are often triggers for malignant hyperthermia when combined with volatile anesthetics.
*Serotonin 1B/1D agonist*
- **Serotonin 1B/1D agonists** (e.g., triptans) are primarily used in the acute treatment of migraines.
- They have no role in the management of malignant hyperthermia and would not address the underlying pathophysiology.
*NMDA receptor antagonist*
- **NMDA receptor antagonists** (e.g., ketamine) are dissociative anesthetics and analgesics.
- They do not directly affect the calcium release channels in skeletal muscle responsible for malignant hyperthermia.
*GABA agonist*
- **GABA agonists** (e.g., benzodiazepines, propofol) are central nervous system depressants used for sedation and anesthesia.
- While they can have muscle relaxant properties, they do not specifically target the **ryanodine receptor** pathway involved in malignant hyperthermia.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 2: A 65-year-old male who is being treated for depression visits your emergency room complaining of being unable to urinate. In addition, the patient complains of tachycardia and dry mouth. He has no history of benign prostatic hyperplasia and reports of only being on one psychiatric medication. What type of psychiatric medication would cause such a side effect profile?
- A. Tricyclic antidepressant (Correct Answer)
- B. Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
- C. Monoamine oxidase inhibitor
- D. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
- E. Aminoketone
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Tricyclic antidepressant***
- The patient's symptoms of **urinary retention**, dry mouth, and tachycardia are characteristic **anticholinergic side effects**, frequently seen with TCAs.
- TCAs block muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, leading to these peripheral effects.
*Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor*
- SNRIs primarily affect serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake and are less likely to cause severe anticholinergic effects like urinary retention.
- While they can cause some dry mouth or tachycardia due to noradrenergic effects, the combination with significant urinary retention points away from SNRIs.
*Monoamine oxidase inhibitor*
- MAOIs are generally associated with side effects such as **hypertensive crisis** (with tyramine-rich foods), orthostatic hypotension, and insomnia.
- They do not typically cause the prominent anticholinergic syndrome described.
*Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor*
- SSRIs primarily affect serotonin reuptake and are known for side effects such as **gastrointestinal upset**, sexual dysfunction, and anxiety.
- They have a low affinity for muscarinic receptors and are less likely to cause significant anticholinergic effects like urinary retention.
*Aminoketone*
- Aminoketones (e.g., bupropion) typically act by inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine.
- Common side effects include **insomnia**, agitation, and **seizure risk** at high doses; they do not typically produce the anticholinergic profile seen here.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 3: A 40-year-old man presents with multiple episodes of sudden-onset severe pain in his right side of the face lasting for only a few seconds. He describes the pain as lancinating, giving the sensation of an electrical shock. He says the episodes are precipitated by chewing or touching the face. Which of the following side effects is characteristic of the drug recommended for treatment of this patient’s most likely condition?
- A. Syndrome of inappropriate ADH (Correct Answer)
- B. Hirsutism
- C. Pinpoint pupils
- D. Gingival hyperplasia
- E. Alopecia
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Syndrome of inappropriate ADH***
- The patient's symptoms (sudden-onset severe lancinating facial pain, precipitated by chewing/touching the face) are classic for **trigeminal neuralgia**.
- The first-line treatment for trigeminal neuralgia is **carbamazepine**, which can cause a serious side effect of **Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)** leading to hyponatremia.
*Hirsutism*
- **Hirsutism** (excessive hair growth) is a common side effect associated with the anticonvulsant medication **phenytoin**, not carbamazepine.
- Phenytoin is used for seizures and status epilepticus, not typically first-line for trigeminal neuralgia.
*Pinpoint pupils*
- **Pinpoint pupils** are characteristic of **opioid overdose** or organophosphate poisoning, and are not a typical side effect of carbamazepine.
- Opioids are generally not effective for trigeminal neuralgia.
*Gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** (overgrowth of gum tissue) is a well-known side effect of chronic **phenytoin** use.
- This is not associated with carbamazepine.
*Alopecia*
- **Alopecia** (hair loss) can be a side effect of several medications, including some chemotherapy agents and anticonvulsants like **valproic acid**, but it is not a hallmark side effect of carbamazepine.
- Valproic acid is primarily used for seizures and bipolar disorder.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 4: A 43-year-old woman walks into the clinic for an annual check-up appointment with her family physician. When asked about any changes in her life, she states that she lost her job about 6 months ago. Since then, she has lived with her boyfriend who is also unemployed. She frequently uses laxatives and takes some over the counter medications to help her sleep. Her blood pressure is 129/87 mm Hg, respirations are 12/min, pulse is 58/min, and temperature is 36.7°C (98.1°F). Her physical exam is mostly benign. Her pupils appear mildly constricted and she appears drowsy and subdued. The physician suspects that the physical findings in this patient are caused by a substance she is likely abusing. Which of the following is the substance?
- A. Cocaine
- B. Alprazolam
- C. Codeine (Correct Answer)
- D. Clonazepam
- E. Ketamine
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Codeine***
- **Miosis** (constricted pupils), **drowsiness**, **bradycardia** (pulse 58/min), and **reduced respiratory rate** (12/min) represent the classic **opioid toxidrome**.
- The patient's use of **laxatives** suggests chronic opioid use to manage opioid-induced constipation, a common side effect.
- Codeine is available in many over-the-counter preparations and is commonly abused.
*Cocaine*
- Cocaine is a **sympathomimetic stimulant** that causes **mydriasis** (pupil dilation), tachycardia, hypertension, and increased alertness or agitation.
- The patient's presentation of miosis, bradycardia, and sedation is completely opposite to cocaine intoxication.
*Alprazolam*
- While alprazolam (a benzodiazepine) can cause drowsiness and sedation, it does **not typically cause miosis**.
- Benzodiazepines may cause respiratory depression at high doses but are not associated with the pronounced **miosis** and **bradycardia** seen in this patient.
- The opioid toxidrome is more specific to this clinical presentation.
*Clonazepam*
- Clonazepam, another benzodiazepine, shares similar effects with alprazolam, causing **sedation** and potential respiratory depression at high doses.
- However, like other benzodiazepines, it does **not cause miosis** or bradycardia, which are hallmark features of opioid intoxication.
*Ketamine*
- Ketamine causes a **dissociative state** with **nystagmus**, and typically produces **hypertension and tachycardia** (not bradycardia).
- It does not cause the **miosis**, bradycardia, or classic sedated presentation characteristic of opioid intoxication.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 5: A 67-year-old man comes to the physician because of progressive burning pain and intermittent "electrical shocks" in his right chest for 3 months. Over the last 2 weeks, the pain has increased to an extent that he can no longer tolerate clothing on the affected area. Three months ago, he had a rash around his right nipple and axilla that resolved a week later. The patient had a myocardial infarction 2 years ago. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 47 years. Current medications include aspirin, simvastatin, metoprolol, and ramipril. His temperature is 36.9°C (97.9°F), pulse is 92/min, and blood pressure is 150/95 mm Hg. Examination shows increased sensation to light touch over the right chest. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Sublingual nitrates
- B. Oral famciclovir
- C. Intrathecal glucocorticoids
- D. Oral tricyclic antidepressants
- E. Oral gabapentin (Correct Answer)
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Oral gabapentin***
- The patient's presentation with a history of a unilateral vesicular rash followed by persistent, burning pain, "electrical shocks," and **allodynia** (increased sensation to light touch) in the same dermatomal distribution is highly characteristic of **postherpetic neuralgia (PHN)**.
- **Gabapentin** (and pregabalin) are first-line medications for neuropathic pain conditions like PHN as they modulate calcium channels in the central nervous system, reducing neurotransmitter release.
*Sublingual nitrates*
- Sublingual nitrates are used for immediate relief of **anginal chest pain**, which is typically described as pressure or heaviness, often radiating to the arm or jaw, and relieved by rest or nitrates.
- The described pain is neuropathic (burning, electrical shocks, allodynia) and does not fit the pattern of angina, despite the patient's history of MI.
*Oral famciclovir*
- **Famciclovir** (and acyclovir, valacyclovir) are antiviral medications used to treat acute **herpes zoster (shingles)** to shorten the duration of the rash and reduce the risk of PHN if given within 72 hours of rash onset.
- The patient's rash resolved 3 months ago, meaning the acute viral phase is over, and antiviral therapy at this stage would not be effective for PHN.
*Intrathecal glucocorticoids*
- **Intrathecal glucocorticoids** are rarely used for PHN and are generally reserved for severe, refractory cases as a last resort due to potential side effects and invasiveness.
- They are not a first-line treatment for PHN, especially before trying oral neuropathic pain medications.
*Oral tricyclic antidepressants*
- **Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)** like amitriptyline are effective for neuropathic pain, including PHN, and are considered first-line agents alongside gabapentinoids.
- However, in elderly patients with a history of cardiac disease (MI, hypertension, on metoprolol and ramipril), TCAs carry a higher risk of **cardiac side effects** (e.g., arrhythmias, orthostatic hypotension) and anticholinergic side effects compared to gabapentin.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 6: A 53-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician due to her "feet feeling painful." She reports initially having decreased sensation on both of her feet and recently her hands. She now experiences paresthesias, numbness, and a "burning pain." She is recovering from a recent myocardial infarction. Approximately 1.5 weeks ago, she experienced mild watery diarrhea and an atypical pneumonia. For the past 3 weeks, she has been experiencing fatigue, trouble with concentration, and mild weight gain. Beyond this she has no other acute concerns. Her past medical history is significant for type II diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and coronary artery disease. She is currently taking metformin, aspirin, atorvastatin, metoprolol, and lisinopril. Her temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 155/98 mmHg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 14/min. On physical exam, there is a loss of vibratory sensation and altered proprioception in the bilateral feet. She has impaired pain, light touch, and temperature sensation starting from her feet to mid-calf and hands. She has normal strength and muscle tone throughout her upper and lower extremities, as well as absent bilateral ankle reflexes. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Amitriptyline
- B. Lidocaine patch
- C. Gabapentin (Correct Answer)
- D. Venlafaxine
- E. Intravenous immunoglobulin
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Gabapentin***
- The patient's symptoms (paresthesias, numbness, burning pain, loss of vibratory sensation, impaired pain/light touch/temperature, absent ankle reflexes) are highly suggestive of **neuropathic pain**, likely from a **peripheral neuropathy**.
- **Gabapentin** is a first-line agent for the treatment of neuropathic pain, working by modulating voltage-gated calcium channels to reduce neurotransmitter release, effectively alleviating symptoms like burning and tingling.
*Amitriptyline*
- **Amitriptyline** is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that can be used for neuropathic pain. However, it is generally considered a second-line agent due to its significant **anticholinergic side effects** (e.g., dry mouth, constipation, sedation) as well as cardiac side effects, which might be problematic for a patient with a history of coronary artery disease and recent MI.
*Lidocaine patch*
- **Lidocaine patches** provide topical analgesia and are primarily used for **localized neuropathic pain**, such as postherpetic neuralgia or localized diabetic neuropathy. The patient's symptoms are described as bilateral and diffuse, affecting both feet and hands, making a topical treatment less suitable as a sole initial therapeutic approach.
*Venlafaxine*
- **Venlafaxine** is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) that is also used for neuropathic pain. While it is an effective option, especially when co-occurring depression is present, current guidelines often favor gabapentin or pregabalin as first-line agents due to a generally more favorable side effect profile and ease of titration, particularly in a patient with cardiovascular history.
*Intravenous immunoglobulin*
- **Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)** is a treatment reserved for serious autoimmune neuropathies such as **Guillain-Barré Syndrome** or severe chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). While the patient's symptoms could suggest an underlying neuropathy, there is no evidence of rapid progression or severe motor weakness that would indicate an acute inflammatory demyelinating process warranting IVIG.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of gradually worsening pain and burning in his feet that is impairing his ability to sleep. He also has a non-healing, painless ulcer on the bottom of his right toe, which has been progressively increasing in size despite the application of bandages and antiseptic creams at home. He has a 7-year history of type II diabetes mellitus treated with oral metformin. He also has narrow-angle glaucoma treated with timolol eye drops and chronic back pain due to a motorcycle accident a few years ago, which is treated with tramadol. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows a 3-cm, painless ulcer on the plantar surface of the right toe. The ulcer base is dry, with no associated erythema, edema, or purulent discharge. Neurological examination shows loss of touch, pinprick sensation, proprioception, and vibration sense of bilateral hands and feet. These sensations are preserved in the proximal portions of the limbs. Muscle strength is normal. Bilateral ankle reflexes are absent. A diabetic screening panel is done and shows a fasting blood sugar of 206 mg/dL. An ECG shows a left bundle branch block. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient's pain?
- A. Oxycodone
- B. Pregabalin (Correct Answer)
- C. Injectable insulin
- D. Amitriptyline
- E. Ulcer debridement
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Pregabalin***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **diabetic peripheral neuropathy**, including burning pain in the feet, a painless neuropathic ulcer, and loss of sensation in a stocking-glove distribution with absent ankle reflexes. **Pregabalin** is a first-line agent for neuropathic pain.
- It works by binding to the **α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels**, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters.
- Pregabalin is **preferred over amitriptyline** in this patient due to his cardiac conduction abnormality (LBBB) and age-related concerns with anticholinergic effects.
*Oxycodone*
- **Opioids like oxycodone** are generally not recommended as first-line treatment for chronic neuropathic pain due to concerns about tolerance, dependence, and side effects.
- While it may provide some pain relief, the **risks often outweigh the benefits** for long-term management of diabetic neuropathy.
*Injectable insulin*
- Poorly controlled **diabetes mellitus** is the underlying cause for the patient's neuropathy and ulcer, and optimizing glycemic control (e.g., with insulin) is crucial for preventing progression and complications.
- However, **injectable insulin** is not a direct treatment for the symptomatic **neuropathic pain or burning sensation** the patient is experiencing.
- While important for long-term management, it does not address the immediate complaint of pain.
*Amitriptyline*
- **Amitriptyline**, a tricyclic antidepressant, is another first-line medication for **neuropathic pain**.
- However, it is **relatively contraindicated** in this patient due to his **left bundle branch block (LBBB)**, as tricyclic antidepressants can worsen cardiac conduction abnormalities and increase the risk of arrhythmias.
- Additionally, as an **anticholinergic** agent, it is generally less preferred in older patients due to potential side effects like urinary retention, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness, and confusion.
*Ulcer debridement*
- **Ulcer debridement** is an important step in the management of the non-healing ulcer to promote healing and prevent infection.
- While crucial for ulcer management, it does not directly address the primary complaint of **burning neuropathic pain** in the feet.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 8: A 42-year-old man is brought in to the emergency department by his daughter. She reports that her father drank heavily for the last 16 years, but he stopped 4 days ago after he decided to quit drinking on his birthday. She also reports that he has been talking about seeing cats running in his room since this morning, although there were no cats. There is no history of any known medical problems or any other substance use. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.4ºC (101.2ºF), heart rate is 116/min, blood pressure is 160/94 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 22/min. He is severely agitated and is not oriented to his name, time, or place. On physical examination, profuse perspiration and tremors are present. Which of the following best describes the pathophysiologic mechanism underlying his condition?
- A. Increased influx of chloride ions
- B. Increased inhibition of norepinephrine
- C. Functional increase in GABA
- D. Increased activity of NMDA receptors (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased inhibition of glutamate
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Increased activity of NMDA receptors***
- Chronic alcohol use leads to **downregulation of GABA receptors** and **upregulation of NMDA receptors** to compensate for alcohol's inhibitory effects.
- When alcohol is withdrawn, the unopposed upregulation of NMDA receptors (and decreased GABA activity) causes a state of **neuronal hyperexcitability**, leading to symptoms like agitation, hallucinations, and autonomic hyperactivity seen in **delirium tremens**.
*Increased influx of chloride ions*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **GABA-A agonists** (like benzodiazepines), which enhance GABA's inhibitory effects by increasing chloride influx and hyperpolarizing neurons.
- In alcohol withdrawal, there is a **functional decrease in GABAergic activity**, not an increase in chloride ion influx.
*Increased inhibition of norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** is a neurotransmitter associated with wakefulness, alertness, and autonomic responses; increased activity is seen in alcohol withdrawal, contributing to sympathetic overdrive.
- Increased inhibition of norepinephrine would lead to sedation and reduced autonomic activity, which is the opposite of the patient's presentation.
*Functional increase in GABA*
- **GABA** (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain; alcohol enhances GABAergic activity.
- In alcohol withdrawal, there is a **functional decrease in GABAergic activity**, contributing to neuronal hyperexcitability and withdrawal symptoms.
*Increased inhibition of glutamate*
- **Glutamate** is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter, and its receptors (like NMDA) are implicated in alcohol withdrawal.
- Alcohol withdrawal is characterized by **increased excitatory activity**, including increased glutamate release and NMDA receptor activation, not increased inhibition of glutamate.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 9: A 71-year-old woman presents to her hematologist-oncologist for follow up after having begun doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide in addition to radiation therapy for the treatment of her stage 3 breast cancer. Her past medical history is significant for preeclampsia, hypertension, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and hypercholesterolemia. She currently smokes 1 pack of cigarettes per day, drinks a glass of wine per day, and denies any illicit drug use. The vital signs include: temperature 36.7°C (98.0°F), blood pressure 126/74 mm Hg, heart rate 111/min, and respiratory rate 23/min. On physical examination, the pulses are strong and irregular, she has a grade 3/6 holosystolic murmur heard best at the left upper sternal border, clear bilateral breath sounds, and erythema over her site of radiation. Which of the following statements regarding doxorubicin is true?
- A. Doxorubicin has a maximum lifetime dose, due to the risk of cardiac toxicity (Correct Answer)
- B. Doxorubicin has a maximum lifetime dose, due to the risk of pulmonary toxicity
- C. Doxorubicin will increase her risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE)
- D. Doxorubicin frequently causes an acneiform rash
- E. Doxorubicin frequently causes cystitis
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Doxorubicin has a maximum lifetime dose, due to the risk of cardiac toxicity***
- **Doxorubicin** is a potent chemotherapy agent (anthracycline) with a well-known risk of **cardiotoxicity**, which can lead to **dilated cardiomyopathy** and heart failure.
- To mitigate this severe side effect, a **cumulative lifetime dose limit** (usually 450-550 mg/m²) is established for doxorubicin.
*Doxorubicin has a maximum lifetime dose, due to the risk of pulmonary toxicity*
- While some chemotherapy agents can cause pulmonary toxicity, **doxorubicin** is not primarily associated with this as its main dose-limiting toxicity.
- The most significant and common dose-limiting toxicity of doxorubicin is **cardiotoxicity**, not pulmonary.
*Doxorubicin will increase her risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE)*
- Chemotherapy in general can increase the risk of **thromboembolic events**, but this is not a specific dose-limiting toxicity of **doxorubicin** that dictates a lifetime maximum dose.
- The concern for DVT/PE is a broader complication of cancer and its treatment, distinct from doxorubicin's specific cardiac risk.
*Doxorubicin frequently causes an acneiform rash*
- **Acneiform rash** is a common side effect of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors (e.g., cetuximab, erlotinib), not typically associated with **doxorubicin**.
- Doxorubicin's dermatologic side effects usually involve **alopecia**, hand-foot syndrome, and radiation recall, but not a predominant acneiform rash.
*Doxorubicin frequently causes cystitis*
- **Cystitis**, particularly hemorrhagic cystitis, is a well-known side effect of **cyclophosphamide** (another drug the patient is receiving), not **doxorubicin**.
- **Mesna** is often administered with cyclophosphamide to prevent this urological toxicity.
Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG Question 10: A 45-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with fever, cough, tonsillar enlargement, and bleeding lips. She has a diffuse blistering rash that encompasses the palms and soles of her feet, in total covering 55% of her total body surface area (TBSA). The upper epidermal layer easily slips away with slight rubbing. Within 24 hours the rash progresses to 88% TBSA involvement and the patient requires mechanical ventilation for respiratory distress. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s condition?
- A. Cytomegalovirus
- B. Deficiency of C-1 esterase inhibitor
- C. Exposure to carbamazepine (Correct Answer)
- D. Herpes simplex virus
- E. Molluscum contagiosum
Adjuvant analgesics Explanation: ***Exposure to carbamazepine***
- The rapid progression of a widespread blistering rash, **positive Nikolsky's sign** (skin slipping away), significant TBSA involvement (55% rapidly increasing to 88%), and systemic symptoms (fever, respiratory distress) are highly characteristic of **Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (SJS/TEN)**.
- **Carbamazepine** is a well-known medication trigger for SJS/TEN, a severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction.
*Cytomegalovirus*
- While CMV can cause a rash and systemic symptoms, it typically manifests as a **maculopapular rash** or purpura, not extensive blistering with a positive Nikolsky's sign.
- CMV infection usually presents with features like mononucleosis-like syndrome, hepatitis, or retinitis, which are not described here as the primary concern.
*Deficiency of C-1 esterase inhibitor*
- This deficiency causes **hereditary angioedema**, characterized by recurrent episodes of localized swelling, typically affecting the face, airways, and gastrointestinal tract.
- It does not cause a blistering rash or the extensive epidermal detachment seen in this patient.
*Herpes simplex virus*
- HSV can cause blistering lesions, but these are typically **localized vesicles** that progress to ulcers, such as cold sores or genital herpes.
- While widespread HSV infection can occur in immunocompromised patients, it does not typically present as a diffuse blistering rash with such extensive epidermal detachment and high TBSA involvement as described.
*Molluscum contagiosum*
- This is a viral skin infection that causes characteristic **dome-shaped, umbilicated papules**.
- It does not cause a widespread blistering rash, fever, or the severe systemic symptoms and epidermal detachment seen in this patient.
More Adjuvant analgesics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.