CNS drugs (antiepileptics, anesthetics)

On this page
🧠 The Neural Command Center: Mastering CNS Drug Architecture
You'll master the pharmacology that controls consciousness itself-from preventing seizures to orchestrating safe anesthesia. This lesson builds your command of how antiepileptics stabilize hyperexcitable neurons and how anesthetics precisely modulate awareness across a spectrum from sedation to surgical depth. You'll learn to recognize clinical patterns, select appropriate agents based on mechanism and patient factors, and navigate the critical decision points that distinguish competent from exceptional neurotherapeutic care. By integrating molecular targets with multi-system effects, you'll develop the pattern recognition and therapeutic reasoning that transforms complex CNS pharmacology into confident clinical action.
The central nervous system operates through precisely balanced excitatory and inhibitory networks. GABA mediates 40% of all inhibitory neurotransmission, while glutamate drives 90% of excitatory signaling. This 4:9 ratio creates the foundation for understanding how antiepileptics restore balance and anesthetics suppress consciousness.
📌 Remember: GABA-GLUT - GABA Augmenters (benzodiazepines, barbiturates), Blockers of sodium channels, Antagonists of glutamate - Glutamate blockers, Levetiracetam (SV2A), Use-dependent sodium blockers, T-type calcium blockers
CNS Drug Classification Matrix
| Mechanism | Primary Targets | Seizure Types | Anesthetic Use | Onset Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABA Enhancement | GABA-A receptors | Generalized, status | Induction, maintenance | 30-60 seconds |
| Sodium Channel Block | Nav1.1, Nav1.2 | Focal, generalized | Local anesthesia | 2-5 minutes |
| Glutamate Antagonism | NMDA, AMPA | Refractory seizures | Dissociative anesthesia | 1-2 minutes |
| SV2A Modulation | Synaptic vesicles | Broad spectrum | Not used | 30-60 minutes |
| Calcium Channel Block | T-type, L-type | Absence seizures | Adjuvant only | 15-30 minutes |
- Antiepileptic Drug Hierarchy
- First-line agents: Levetiracetam (20-40 mg/kg loading dose)
- Broad spectrum efficacy: 85% seizure control
- Minimal drug interactions: <5% protein binding
- Second-line agents: Phenytoin (15-20 mg/kg loading dose)
- Narrow therapeutic index: 10-20 mcg/mL
- Zero-order kinetics above 10 mcg/mL
- Rescue agents: Midazolam (0.2 mg/kg IM/IV)
- Rapid onset: 2-3 minutes
- Duration: 30-60 minutes
- First-line agents: Levetiracetam (20-40 mg/kg loading dose)
💡 Master This: Use-dependent sodium channel blockade explains why phenytoin and carbamazepine preferentially block rapidly firing neurons during seizures while sparing normal neural activity. Higher firing frequencies (>10 Hz) create more inactivated channels available for drug binding.
- Anesthetic Agent Categories
- Intravenous induction agents: Propofol (1-2.5 mg/kg)
- Onset: 30-40 seconds
- Duration: 5-10 minutes
- Context-sensitive half-time: <40 minutes
- Inhalational maintenance: Sevoflurane (MAC 2.05%)
- Blood-gas partition coefficient: 0.65
- Emergence time: 8-12 minutes
- Dissociative agents: Ketamine (1-2 mg/kg IV)
- NMDA receptor antagonism: >80% blockade
- Preserves airway reflexes and respiratory drive
- Intravenous induction agents: Propofol (1-2.5 mg/kg)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Propofol infusion syndrome occurs with doses >4 mg/kg/hr for >48 hours, presenting with metabolic acidosis, rhabdomyolysis, and cardiac failure. Mortality approaches 30% once syndrome develops.
Understanding these foundational principles creates the framework for mastering specific drug mechanisms and their clinical applications in seizure management and anesthetic practice.
🧠 The Neural Command Center: Mastering CNS Drug Architecture
⚡ Synaptic Transmission Mastery: The Molecular Switches
Synaptic transmission operates through calcium-dependent vesicle fusion occurring within 200 microseconds of action potential arrival. SV2A proteins regulate this process by controlling vesicle priming, making them ideal targets for antiepileptic intervention without affecting normal neurotransmission.
📌 Remember: SNAP-25 - Synaptic vesicle Needs ATP, Priming requires SV2A - 25 milliseconds for complete vesicle recycling cycle
Neurotransmitter System Dynamics
| System | Synthesis Rate | Reuptake Efficiency | Receptor Subtypes | Clinical Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABA | 50 μmol/g/hr | 95% within 100ms | GABA-A, GABA-B | Benzodiazepines, barbiturates |
| Glutamate | 200 μmol/g/hr | 90% within 50ms | NMDA, AMPA, kainate | Ketamine, memantine |
| Glycine | 30 μmol/g/hr | 85% within 200ms | GlyR-α1, GlyR-α2 | Propofol enhancement |
| Acetylcholine | 15 μmol/g/hr | 99% via AChE | Nicotinic, muscarinic | Neuromuscular blockers |
- Pentameric structure: 2α, 2β, 1γ subunit composition
- 19 α-subunit variants determine regional specificity
- α1-subunits: 60% of all GABA-A receptors (sedation)
- α2/α3-subunits: 25% of receptors (anxiolysis)
- Chloride conductance: 10-30 pS per channel
- Benzodiazepine enhancement: 2-5x increased frequency
- Barbiturate enhancement: 10x increased duration
- Allosteric modulation sites:
- Benzodiazepine site: α1-6/γ2 interface
- Barbiturate site: β2/β3 transmembrane domain
- Propofol site: β2/β3 and α1/β2 interfaces
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Flumazenil (0.2 mg IV) reverses benzodiazepine effects within 1-2 minutes but has a half-life of 54 minutes versus diazepam's 36-hour half-life, requiring repeated dosing to prevent re-sedation.
- Glutamate Receptor Mechanisms
- NMDA receptors: Voltage and ligand-gated
- Mg2+ block removed at -40 mV
- Calcium permeability: 10x higher than Na+/K+
- Glycine co-agonist required for 100% activation
- AMPA receptors: Fast excitatory transmission
- Desensitization time: 2-10 milliseconds
- GluR2 subunit determines Ca2+ permeability
- Trafficking regulation via CaMKII phosphorylation
- NMDA receptors: Voltage and ligand-gated
💡 Master This: NMDA receptor hypofunction explains ketamine's dissociative effects. 40-60% NMDA blockade produces anesthesia while >80% blockade causes emergence phenomena and psychotomimetic effects.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Levetiracetam binds SV2A with Kd = 4.2 μM, reducing vesicle release probability by 30-40% without affecting baseline neurotransmission. This selectivity explains its broad-spectrum efficacy with minimal cognitive side effects.
Understanding synaptic transmission mechanisms reveals how antiepileptics restore excitatory-inhibitory balance while anesthetics progressively suppress consciousness through targeted receptor modulation.
⚡ Synaptic Transmission Mastery: The Molecular Switches
🎯 Clinical Pattern Recognition: The Diagnostic Framework
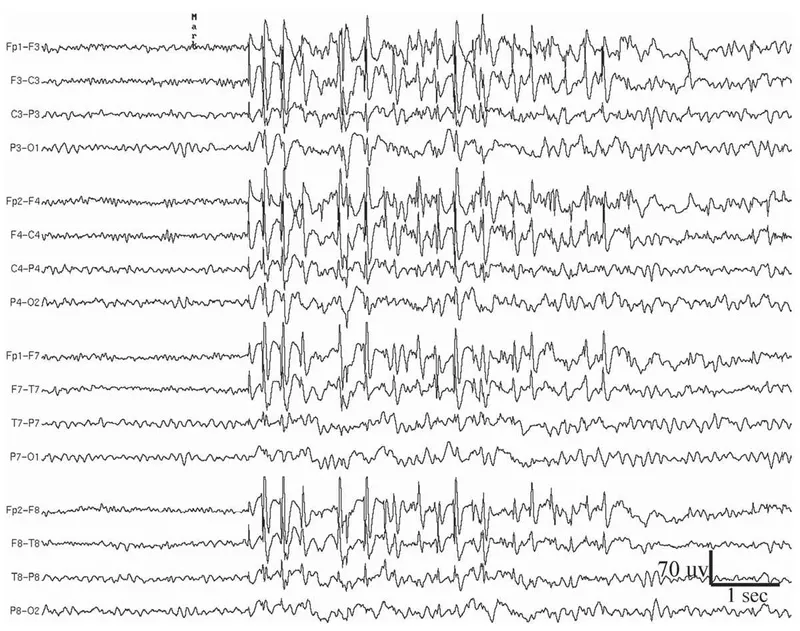
Clinical seizure recognition follows semiology-based classification where motor manifestations predict anatomical localization with 85% accuracy. Focal seizures with secondary generalization require different antiepileptic strategies than primary generalized seizures.
📌 Remember: FAST-SEIZURE - Focal starts one side, Absence has staring, Status needs IV drugs, Tonic-clonic shakes all - Secondary generalization spreads, Epileptic spasms in infants, Ictal confusion follows, Zone of onset matters, Unresponsive during event, Recovery takes time, EEG confirms diagnosis
Seizure Classification and Treatment Matrix
| Seizure Type | EEG Pattern | First-Line Drug | Loading Dose | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focal Aware | Unilateral spikes | Levetiracetam | 20 mg/kg IV | 1000-3000 mg/day |
| Focal Impaired | Regional slowing | Carbamazepine | 400 mg PO | 800-1200 mg/day |
| Generalized TC | Bilateral spikes | Valproate | 15-20 mg/kg IV | 1000-2000 mg/day |
| Absence | 3-Hz spike-wave | Ethosuximide | 15 mg/kg PO | 750-1500 mg/day |
| Status Epilepticus | Continuous activity | Lorazepam | 0.1 mg/kg IV | Phenytoin 20 mg/kg |
- Temporal lobe onset: Automatisms in 80% of cases
- Oroalimentary: Chewing, lip smacking, swallowing
- Manual: Picking, fumbling, repetitive movements
- Duration: 1-3 minutes with postictal confusion
- Frontal lobe onset: Bizarre behaviors with preserved awareness
- Hypermotor: Thrashing, cycling, sexual automatisms
- Duration: <60 seconds with rapid recovery
- Nocturnal clustering: 70% occur during sleep
- Parietal lobe onset: Sensory symptoms predominate
- Somatosensory: Tingling, numbness, pain
- Vertiginous: Spinning, floating sensations
- Visual: Simple hallucinations, distortions
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Todd's paralysis following focal motor seizures lasts <24 hours in 95% of cases. Persistent weakness >48 hours suggests structural lesion requiring urgent MRI and neurosurgical evaluation.
- Generalized Seizure Patterns
- Absence seizures: Sudden onset/offset with preserved posture
- Hyperventilation provocation: 90% sensitivity
- EEG: 3-Hz spike-and-wave complexes
- Duration: 5-20 seconds without postictal state
- Myoclonic seizures: Brief muscle jerks lasting <100 milliseconds
- Morning predominance: 80% occur within 2 hours of awakening
- Photosensitivity: 30% triggered by flashing lights
- Valproate response: 70% seizure reduction
- Tonic-clonic seizures: Biphasic pattern with distinct phases
- Tonic phase: 10-30 seconds of muscle rigidity
- Clonic phase: 1-3 minutes of rhythmic jerking
- Postictal period: 15-30 minutes of confusion
- Absence seizures: Sudden onset/offset with preserved posture
💡 Master This: Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy presents with morning myoclonus, photosensitivity, and sleep deprivation triggers. Valproate achieves seizure freedom in 85% of patients, but withdrawal leads to seizure recurrence in >90% within 6 months.
- Status Epilepticus Treatment Algorithm
- 0-5 minutes: Lorazepam 0.1 mg/kg IV (maximum 4 mg)
- Alternative: Midazolam 10 mg IM if no IV access
- Repeat once if seizures continue after 5 minutes
- 5-20 minutes: Phenytoin 20 mg/kg IV at ≤50 mg/min
- Alternative: Fosphenytoin 20 PE/kg at ≤150 PE/min
- Monitor: Cardiac rhythm and blood pressure
- 20-40 minutes: Valproate 40 mg/kg IV over 10 minutes
- Alternative: Levetiracetam 60 mg/kg IV over 15 minutes
- Consider: Anesthesia consultation for refractory cases
- 0-5 minutes: Lorazepam 0.1 mg/kg IV (maximum 4 mg)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Refractory status epilepticus (seizures >60 minutes) requires continuous EEG monitoring and anesthetic agents. Propofol 1-2 mg/kg bolus followed by 2-10 mg/kg/hr infusion achieves burst suppression in >90% of cases.
These recognition patterns enable rapid therapeutic decision-making, transforming seizure emergencies into manageable clinical scenarios with evidence-based treatment protocols.
🎯 Clinical Pattern Recognition: The Diagnostic Framework
🔬 Anesthetic Depth Mastery: The Consciousness Spectrum
Anesthetic Agent Comparison Matrix
| Agent | MAC (%) | Blood:Gas | Induction (min) | Emergence (min) | Metabolism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sevoflurane | 2.05 | 0.65 | 2-3 | 8-12 | 3-5% hepatic |
| Desflurane | 6.0 | 0.42 | 4-6 | 4-8 | 0.02% hepatic |
| Isoflurane | 1.15 | 1.4 | 6-8 | 10-15 | 0.2% hepatic |
| Propofol | N/A | N/A | 0.5-1 | 5-10 | 100% hepatic |
| Etomidate | N/A | N/A | 0.5-1 | 3-8 | 75% hepatic |
- Inhalational Anesthetic Mechanisms
- GABA-A receptor enhancement: Primary mechanism at 0.5-1.5 MAC
- α1-subunit binding: Sedation and amnesia
- β2/β3-subunit effects: Immobility and muscle relaxation
- Glycine receptor potentiation: Spinal cord depression
- NMDA receptor antagonism: Secondary mechanism at >1 MAC
- Glutamate suppression: Unconsciousness and analgesia
- Calcium channel blockade: Neuroprotection
- Two-pore potassium channels: Background conductance modulation
- TREK-1 activation: Neuronal hyperpolarization
- TASK-3 enhancement: Thalamic suppression
- GABA-A receptor enhancement: Primary mechanism at 0.5-1.5 MAC
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Sevoflurane has the lowest blood:gas partition coefficient (0.65) among volatile agents, enabling rapid induction and emergence. Desflurane (0.42) is even lower but requires heated vaporizer due to boiling point of 23.5°C.
- Intravenous Anesthetic Profiles
- Propofol: Phenolic compound with rapid onset/offset
- Mechanism: GABA-A receptor positive allosteric modulation
- Pharmacokinetics: Context-sensitive half-time <40 minutes
- Metabolism: Hepatic conjugation and extrahepatic clearance
- Side effects: Hypotension (20-30% decrease), apnea (30-60 seconds)
- Etomidate: Imidazole derivative with cardiovascular stability
- Mechanism: GABA-A β2/β3 subunit enhancement
- Advantages: Minimal hemodynamic effects in shock patients
- Limitations: Adrenal suppression for 6-24 hours
- Ketamine: NMDA antagonist with unique properties
- Mechanism: Non-competitive NMDA blockade at phencyclidine site
- Advantages: Preserved airway reflexes and respiratory drive
- Applications: Pediatric procedures, trauma, chronic pain
- Propofol: Phenolic compound with rapid onset/offset
💡 Master This: Context-sensitive half-time explains why propofol enables rapid emergence even after prolonged infusions. Unlike thiopental, which accumulates in fat with half-life >11 hours, propofol's rapid redistribution and high clearance maintain predictable recovery.
- Anesthetic Depth Monitoring
- Bispectral Index (BIS): EEG-derived parameter
- Awake: BIS 85-100
- Light sedation: BIS 70-85
- General anesthesia: BIS 40-60
- Deep anesthesia: BIS <40
- Clinical signs: Traditional monitoring parameters
- Heart rate variability: Decreases with deeper anesthesia
- Blood pressure response: Blunted to surgical stimulation
- Pupil size: Miotic at surgical depth
- Lacrimation: Absent during adequate anesthesia
- Bispectral Index (BIS): EEG-derived parameter
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Awareness under anesthesia occurs in 0.1-0.2% of general anesthetics but increases to 1-2% in cardiac surgery and trauma cases. BIS monitoring reduces awareness incidence by 80% when maintained between 40-60.
Understanding anesthetic depth principles enables precise titration of consciousness levels while maintaining patient safety and surgical conditions.
🔬 Anesthetic Depth Mastery: The Consciousness Spectrum
⚖️ Therapeutic Decision Algorithms: The Treatment Protocols
📌 Remember: STATUS-PROTOCOL - Stabilize airway, Thiamine + glucose, Anticonvulsant IV, Time is critical, Unresponsive needs intubation, Second-line if continues - Phenytoin loading, Refractory needs ICU, Ongoing EEG monitoring, Third-line anesthetics, Optimize electrolytes, Continuous infusions, Outcome depends on speed, Lorazepam first-line
Antiepileptic Drug Selection Matrix
| Clinical Scenario | First Choice | Efficacy Rate | Loading Protocol | Monitoring Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New-onset focal | Levetiracetam | 85% seizure-free | 500 mg BID | Renal function |
| Generalized epilepsy | Valproate | 80% seizure-free | 15 mg/kg/day | LFTs, CBC, ammonia |
| Absence seizures | Ethosuximide | 90% absence control | 250 mg BID | CBC, LFTs |
| Status epilepticus | Lorazepam | 70% termination | 0.1 mg/kg IV | Respiratory status |
| Pregnancy | Lamotrigine | 75% seizure-free | 25 mg BID | Folate levels |
- Phase 1 (0-5 minutes): Immediate stabilization
- Airway assessment: Position, suction, oxygen
- IV access: Large bore (18G or larger)
- Lorazepam 0.1 mg/kg IV (maximum 4 mg)
- Thiamine 100 mg IV + Dextrose 50 mL if hypoglycemic
- Phase 2 (5-20 minutes): Second-line therapy
- Phenytoin 20 mg/kg IV at ≤50 mg/min
- Cardiac monitoring: Risk of arrhythmias and hypotension
- Alternative: Fosphenytoin 20 PE/kg at ≤150 PE/min
- Phase 3 (20-60 minutes): Third-line options
- Valproate 40 mg/kg IV over 10 minutes
- Levetiracetam 60 mg/kg IV over 15 minutes
- Phenobarbital 20 mg/kg IV at ≤100 mg/min
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Refractory status epilepticus (failure of 2 appropriate AEDs) occurs in 23-43% of cases. Continuous midazolam infusion (0.2 mg/kg bolus, then 0.05-2 mg/kg/hr) achieves seizure control in 80% of refractory cases.
- Anesthetic Induction Protocols
- Rapid Sequence Induction (RSI):
- Preoxygenation: 3-5 minutes with 100% FiO2
- Induction: Propofol 1-2.5 mg/kg + Succinylcholine 1-1.5 mg/kg
- Intubation: Within 60 seconds of muscle relaxant
- Success rate: >95% first-attempt intubation
- Modified RSI for hemodynamic instability:
- Etomidate 0.2-0.3 mg/kg instead of propofol
- Rocuronium 1.2 mg/kg if succinylcholine contraindicated
- Ketamine 1-2 mg/kg for severe hypotension
- Awake fiberoptic intubation:
- Topical anesthesia: Lidocaine 4% spray
- Sedation: Dexmedetomidine 1 mcg/kg over 10 minutes
- Success rate: 98% in experienced hands
- Rapid Sequence Induction (RSI):
💡 Master This: Succinylcholine provides optimal intubating conditions within 60 seconds but is contraindicated in hyperkalemia, malignant hyperthermia susceptibility, and neuromuscular disorders. Rocuronium 1.2 mg/kg provides similar onset (90 seconds) with reversibility using sugammadex.
- Perioperative Anesthetic Management
- Maintenance anesthesia targets:
- MAC 0.7-1.3 for surgical anesthesia
- BIS 40-60 for adequate depth
- Mean arterial pressure >65 mmHg for organ perfusion
- End-tidal CO2 35-45 mmHg for normocarbia
- Emergence protocols:
- Volatile agent discontinuation at skin closure
- Neuromuscular blockade reversal: Sugammadex 2-4 mg/kg
- Extubation criteria: TOF ratio >0.9, sustained head lift
- Recovery time: 8-15 minutes with modern agents
- Maintenance anesthesia targets:
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Delayed emergence (failure to awaken within 30 minutes) occurs in <1% of cases. Differential diagnosis includes residual anesthetics, metabolic disorders, stroke, or seizures. Flumazenil 0.2 mg IV and naloxone 0.4 mg IV can reverse suspected benzodiazepine or opioid effects.
These evidence-based protocols ensure systematic approaches to complex clinical scenarios, optimizing patient outcomes through standardized care pathways.
⚖️ Therapeutic Decision Algorithms: The Treatment Protocols
🔗 Advanced Integration: The Multi-System Network
📌 Remember: NEURO-PROTECT - Neuroprotection needs hypothermia, EEG monitoring essential, Uncontrolled seizures worsen outcome, Reduce metabolic demand, Optimize perfusion pressure - Propofol decreases CMRO2, Reduce ICP with positioning, Osmotherapy with mannitol, Temperature control critical, Electrolyte balance, Cerebral perfusion >70 mmHg, Thiopental for refractory ICP
Neuroprotection and CNS Drug Matrix
| Agent | CMRO2 Reduction | ICP Effect | CPP Impact | Seizure Threshold | Neuroprotection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propofol | 45% decrease | ↓ 25-40% | ↓ 15-25% | Anticonvulsant | Antioxidant |
| Thiopental | 55% decrease | ↓ 50-60% | ↓ 30-40% | Anticonvulsant | Free radical scavenger |
| Isoflurane | 50% decrease | ↑ 15-25% | Variable | Proconvulsant >1.5 MAC | Preconditioning |
| Sevoflurane | 40% decrease | ↑ 10-15% | Minimal | Anticonvulsant <1 MAC | Minimal |
| Ketamine | Variable | ↑ 25-30% | ↑ 10-20% | Anticonvulsant | NMDA antagonism |
- Autoregulation preservation: Critical for brain-injured patients
- Normal range: MAP 50-150 mmHg maintains constant CBF
- Propofol: Preserves autoregulation at doses <4 mg/kg/hr
- Volatile agents: Impair autoregulation in dose-dependent manner
- Ketamine: Increases CBF and ICP through sympathetic stimulation
- Carbon dioxide reactivity: Maintained with most anesthetics
- Normal response: CBF changes 1-2 mL/100g/min per mmHg CO2
- Hyperventilation: Reduces ICP but risks cerebral ischemia
- Target PaCO2: 35-40 mmHg for optimal balance
- Oxygen consumption coupling: Flow-metabolism relationship
- Normal CMRO2: 3.5 mL O2/100g/min
- Anesthetic reduction: Proportional CBF decrease
- Seizures increase: CMRO2 by 200-300%
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Burst suppression with propofol or thiopental provides maximal neuroprotection by reducing CMRO2 to 15-20% of baseline. However, hypotension from high doses can compromise cerebral perfusion and negate benefits.
- Multi-Drug Interaction Networks
- Antiepileptic drug combinations: Synergistic mechanisms
- Valproate + Lamotrigine: Enhanced efficacy but increased rash risk
- Levetiracetam + Phenytoin: Additive effects without pharmacokinetic interactions
- Benzodiazepines + Barbiturates: Synergistic GABA enhancement
- Anesthetic drug interactions: Additive CNS depression
- Propofol + Midazolam: 50% dose reduction of each agent
- Volatile + Opioid: MAC reduction of 50-70% with fentanyl
- Ketamine + Propofol: "Ketofol" provides hemodynamic stability
- Antiepileptic drug combinations: Synergistic mechanisms
💡 Master This: Pharmacodynamic interactions between CNS drugs follow response surface models where combined effects exceed simple addition. Propofol EC50 for loss of consciousness decreases from 3.4 mcg/mL to 1.8 mcg/mL when combined with fentanyl 2 ng/mL.
- Systems-Based Monitoring Integration
- Neurological monitoring: Multi-modal assessment
- Continuous EEG: Seizure detection and anesthetic depth
- ICP monitoring: >20 mmHg requires intervention
- Cerebral oximetry: rSO2 >15% decrease from baseline
- Transcranial Doppler: Vasospasm detection and autoregulation
- Physiological parameter integration:
- Mean arterial pressure: CPP = MAP - ICP (target >70 mmHg)
- Temperature management: Normothermia or mild hypothermia (33-36°C)
- Glucose control: Target 140-180 mg/dL in critically ill
- Electrolyte balance: Sodium 135-145 mEq/L, avoid hyponatremia
- Neurological monitoring: Multi-modal assessment
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Multimodal monitoring in neurocritical care reduces mortality by 23% and improves functional outcomes by 35%. Goal-directed therapy using ICP, CPP, and brain tissue oxygenation optimizes individual patient management.
Understanding these complex interactions enables precision medicine approaches to CNS pharmacotherapy, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects across multiple organ systems.
🔗 Advanced Integration: The Multi-System Network
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Rapid Reference Framework
📌 Remember: MASTER-DOSES - Midazolam 0.2 mg/kg, Atropine 0.02 mg/kg, Succinylcholine 1-1.5 mg/kg, Thiopental 3-5 mg/kg, Ephedrine 0.1-0.2 mg/kg, Rocuronium 0.6-1.2 mg/kg - Dantrolene 2.5 mg/kg, Ondansetron 0.1 mg/kg, Sugammadex 2-4 mg/kg, Epinephrine 10 mcg/kg, Sodium bicarbonate 1-2 mEq/kg
Essential CNS Drug Arsenal
| Emergency | First-Line Drug | Dose | Onset | Duration | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status Epilepticus | Lorazepam | 0.1 mg/kg IV | 2-3 min | 6-8 hours | Max 4 mg, repeat once |
| Anesthesia Induction | Propofol | 1-2.5 mg/kg | 30-40 sec | 5-10 min | Avoid in shock |
| RSI Paralysis | Succinylcholine | 1-1.5 mg/kg | 45-60 sec | 5-10 min | Check K+, MH history |
| Emergence Agitation | Midazolam | 0.05 mg/kg | 2-5 min | 30-60 min | Titrate to effect |
| Local Anesthesia | Lidocaine | 4-7 mg/kg | 2-5 min | 60-120 min | Max dose with epi |
- Immediate assessment (<2 minutes)
- Airway patency: Position, suction, oxygen 15L/min
- IV access: 18G or larger, bilateral if possible
- Glucose check: Fingerstick, treat if <60 mg/dL
- Vital signs: Continuous monitoring, blood pressure q2min
- First-line intervention (2-5 minutes)
- Lorazepam 0.1 mg/kg IV (maximum 4 mg)
- Alternative: Midazolam 10 mg IM if no IV access
- Thiamine 100 mg IV before dextrose in adults
- Second-line therapy (5-20 minutes)
- Phenytoin 20 mg/kg IV at ≤50 mg/min
- Cardiac monitoring: Risk of bradycardia and hypotension
- Alternative: Levetiracetam 60 mg/kg IV over 15 minutes
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Benzodiazepine-refractory seizures occur in 30% of status epilepticus cases. Levetiracetam achieves seizure termination in 68% of refractory cases versus 47% with phenytoin (p<0.001).
- Anesthetic Emergency Management
- Malignant hyperthermia protocol:
- Discontinue triggers: Stop volatile agents and succinylcholine
- Dantrolene 2.5 mg/kg IV bolus, repeat q1-3min until control
- Cooling measures: Ice packs, cold saline, cooling blanket
- Hyperventilation: FiO2 100%, high fresh gas flows
- Laboratory monitoring: ABG, electrolytes, CK, myoglobin
- Cannot intubate, cannot ventilate:
- Call for help: Additional personnel and equipment
- Surgical airway: Cricothyrotomy within 3-4 minutes
- Jet ventilation: Temporary measure if available
- Success rate: >95% with trained personnel
- Local anesthetic systemic toxicity:
- Lipid emulsion 20%: 1.5 mL/kg bolus, then 0.25 mL/kg/min
- Seizure control: Benzodiazepines, avoid propofol
- Cardiac support: ACLS protocols, avoid lidocaine
- Continue lipid: Until hemodynamic stability achieved
- Malignant hyperthermia protocol:
💡 Master This: Lipid rescue therapy for local anesthetic toxicity works through lipid sink mechanism, sequestering lipophilic drugs from cardiac sodium channels. Success rate approaches 90% when initiated within 10 minutes of cardiovascular collapse.
- Critical Threshold Values
- Seizure management thresholds:
- Lorazepam level: >50 ng/mL for seizure control
- Phenytoin level: 10-20 mcg/mL therapeutic range
- Valproate level: 50-100 mcg/mL for status epilepticus
- Levetiracetam level: 12-46 mcg/mL therapeutic range
- Anesthetic monitoring targets:
- BIS: 40-60 for surgical anesthesia
- MAC: 0.7-1.3 for adequate depth
- Train-of-four: 1-2 twitches for surgical relaxation
- End-tidal CO2: 35-45 mmHg for normocarbia
- Seizure management thresholds:
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Propofol infusion syndrome risk increases exponentially with doses >4 mg/kg/hr for >48 hours. Early signs include metabolic acidosis (pH <7.35), elevated lactate (>2 mmol/L), and rhabdomyolysis (CK >1000 U/L).
This clinical arsenal provides immediate access to life-saving protocols, enabling rapid decision-making during high-stakes emergencies where seconds determine outcomes.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Rapid Reference Framework
Practice Questions: CNS drugs (antiepileptics, anesthetics)
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 24-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a persistent and low grade headache as well as trouble focusing. The patient was seen in the emergency department 3 days ago after hitting his head on a branch while biking under the influence of alcohol. His head CT at the time was normal, and the patient was sent home with follow up instructions. Since the event, he has experienced trouble focusing on his school work and feels confused at times while listening to lectures. He states that he can’t remember the lectures and also says he has experienced a sensation of vertigo at times. On review of systems, he states that he has felt depressed lately and has had trouble sleeping, though he denies any suicidal or homicidal ideation. His temperature is 98.2°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 122/65 mmHg, pulse is 70/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient’s neurological and cardiopulmonary exam are within normal limits. Which of the following is the best next step in management?













