Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Sympathomimetics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 1: A 17-year-old high school student is brought to the emergency department because of irritability and rapid breathing. He appears agitated and is diaphoretic. His temperature is 38.3°C (101°F), pulse is 129/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 158/95 mmHg. His pupils are dilated. An ECG shows sinus tachycardia. Which of the following substances is used to make the drug this patient has most likely taken?
- A. Ergotamine
- B. Codeine
- C. Sodium oxybate
- D. Homatropine
- E. Pseudoephedrine (Correct Answer)
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Pseudoephedrine***
- This patient's symptoms (irritability, agitation, rapid breathing, tachycardia, hypertension, dilated pupils, and diaphoresis) are consistent with **sympathomimetic toxicity**, often seen with stimulants like **methamphetamine**.
- **Pseudoephedrine** is a common over-the-counter decongestant that can be chemically converted into methamphetamine through a process called **reduction**.
*Ergotamine*
- **Ergotamine** is an ergot alkaloid used to treat migraines; it causes vasoconstriction and can lead to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and peripheral ischemia, which do not fully align with the patient's presentation.
- While it can cause elevated blood pressure, the widespread stimulant effects and agitation are less typical, and it's not a common precursor for illicit stimulant synthesis.
*Codeine*
- **Codeine** is an opioid; overdose would present with central nervous system depression, respiratory depression, and miosis (pinpoint pupils), which is the opposite of this patient's dilated pupils and agitated state.
- It is a precursor to certain other opioids (e.g., desomorphine or "krokodil"), but not to the type of stimulant producing these symptoms.
*Sodium oxybate*
- **Sodium oxybate** (GHB) is a central nervous system depressant and would cause sedation, bradycardia, and respiratory depression, not the stimulant toxidrome observed.
- It is not commonly used as a precursor for illicit stimulants causing sympathomimetic effects.
*Homatropine*
- **Homatropine** is an anticholinergic agent, which can cause dilated pupils, tachycardia, and a dry mouth, but typically not severe diaphoresis with agitation to this degree; also less common for illicit drug manufacturing.
- While it fits some anticholinergic toxidrome features, it is not a direct precursor for street drugs causing such profound sympathomimetic effects.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 2: A 24-year-old graduate student is brought to the emergency department by her boyfriend because of chest pain that started 90 minutes ago. Her boyfriend says she has been taking medication to help her study for an important exam and has not slept in several days. On examination, she is diaphoretic, agitated, and attempts to remove her IV lines and ECG leads. Her temperature is 37.6°C (99.7°F), pulse is 128/min, and blood pressure is 163/97 mmHg. Her pupils are dilated. The most appropriate next step in management is the administration of which of the following?
- A. Lorazepam (Correct Answer)
- B. Ketamine
- C. Haloperidol
- D. Activated charcoal
- E. Dantrolene
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Lorazepam***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **sympathomimetic toxicity** (agitation, tachycardia, hypertension, dilated pupils, diaphoresis) likely due to stimulant abuse for studying. **Benzodiazepines** like lorazepam are the first-line treatment to manage agitation, tachycardia, and hypertension in this setting.
- Lorazepam helps by **calming the central nervous system** and reducing the sympathetic overdrive, thereby mitigating the cardiovascular and neurological effects of stimulant toxicity.
*Ketamine*
- Ketamine is a **dissociative anesthetic** that typically increases heart rate and blood pressure, which would exacerbate the patient's existing sympathetic hyperactivity and cardiovascular instability.
- It is not indicated for the management of stimulant-induced agitation or catecholamine surge.
*Haloperidol*
- Haloperidol is an **antipsychotic** that can prolong the **QT interval** and potentially lower the seizure threshold, effects that can be dangerous in stimulant toxicity.
- It does not directly address the underlying sympathetic overdrive and can worsen hyperthermia with its anticholinergic properties.
*Activated charcoal*
- Activated charcoal is used to **prevent absorption** of toxins from the gastrointestinal tract, but it is typically only effective if given within 1-2 hours of ingestion. This patient's symptoms started 90 minutes ago, implying some absorption has already occurred, and her agitated state makes oral administration risky if airway protection is not ensured.
- It is also contraindicated in patients with an unprotected airway due to the risk of aspiration, and benzodiazepines are needed first to control agitation and protect the airway.
*Dantrolene*
- Dantrolene is a **skeletal muscle relaxant** used primarily to treat **malignant hyperthermia** and **neuroleptic malignant syndrome**.
- While this patient has some signs of hyperthermia, dantrolene is not the first-line treatment for stimulant-induced hyperthermia, which is primarily managed by controlling agitation and sympathetic overdrive with benzodiazepines and external cooling.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 3: A 43-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 45 minutes after his wife found him on the floor sweating profusely. On arrival, he is lethargic and unable to provide a history. He vomited multiple times on the way to the hospital. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 55/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 98/65 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 80%. Examination shows profuse diaphoresis and excessive salivation. He withdraws his extremities sluggishly to pain. The pupils are constricted and reactive. Scattered expiratory wheezing and rhonchi are heard throughout both lung fields. Cardiac examination shows no abnormalities. There are fine fasciculations in the lower extremities bilaterally. Muscle strength is reduced and deep tendon reflexes are 1+ bilaterally. His clothes are soaked with urine and feces. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the most appropriate initial pharmacotherapy?
- A. Non-selective α-adrenergic antagonism
- B. Competitive antagonism of mACh receptors (Correct Answer)
- C. Alkaloid emesis-induction
- D. Enteral binding
- E. Urine alkalization
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Competitive antagonism of mACh receptors***
- The patient's symptoms, including **profuse sweating, salivation, constricted pupils, wheezing, bradycardia, hypotension, fasciculations**, and incontinence, are classic signs of **cholinergic crisis** due to **organophosphate poisoning**.
- **Atropine**, a competitive antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine (mACh) receptors, is the primary initial pharmacotherapy for organophosphate poisoning, counteracting the excessive parasympathetic stimulation.
*Non-selective α-adrenergic antagonism*
- This mechanism would typically be used to treat conditions involving **excessive alpha-adrenergic activity**, such as a pheochromocytoma or severe hypertension.
- It would **worsen the hypotension** already present in this patient and does not address the underlying cholinergic overstimulation.
*Alkaloid emesis-induction*
- While vomiting occurred, inducing further emesis with an alkaloid is **contraindicated** in cases of organophosphate poisoning due to the risk of **aspiration pneumonitis** and the patient's altered mental status.
- Furthermore, modern management of poisoning rarely recommends routine emesis induction.
*Enteral binding*
- **Activated charcoal** acts by enteral binding to prevent absorption of toxins from the gastrointestinal tract.
- While it may be considered in some poisonings, the rapid onset of severe symptoms and the potential for aspiration in a lethargic patient makes **airway protection** and **antidote administration** the immediate priorities.
*Urine alkalization*
- Urine alkalization is a technique used to enhance the renal excretion of certain acidic drugs by increasing their ionization in the urine, preventing reabsorption.
- It is **not relevant** for the initial management of organophosphate poisoning, which primarily requires anticholinergic agents and cholinesterase reactivators.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 4: A 55-year-old woman comes to the physician because of involuntary hand movements that improve with alcohol consumption. Physical examination shows bilateral hand tremors that worsen when the patient is asked to extend her arms out in front of her. The physician prescribes a medication that is associated with an increased risk of bronchospasms. This drug has which of the following immediate effects on the cardiovascular system?
Stroke volume | Heart rate | Peripheral vascular resistance
- A. ↓ ↓ ↓
- B. ↓ ↓ ↑ (Correct Answer)
- C. ↓ ↑ ↑
- D. ↑ ↑ ↑
- E. ↑ ↑ ↓
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***↓ ↓ ↑***
- This patient likely has **essential tremor**, which is characterized by **bilateral hand tremors** that improve with alcohol and worsen with intention (postural tremor). The prescribed medication is a **beta-blocker** (e.g., propranolol), which is associated with an increased risk of bronchospasms due to blocking **beta-2 receptors** in the airways.
- Beta-blockers **decrease heart rate** (negative chronotropic effect) and **stroke volume** (negative inotropic effect) by blocking beta-1 receptors in the heart, reducing cardiac output.
- **Peripheral vascular resistance increases** acutely due to: (1) **unopposed alpha-1 adrenergic tone** in blood vessels (loss of beta-2 mediated vasodilation), and (2) baroreceptor-mediated reflex vasoconstriction in response to decreased cardiac output. This helps maintain blood pressure despite reduced cardiac output.
*↓ ↓ ↓*
- While beta-blockers decrease **heart rate** and **stroke volume**, peripheral vascular resistance does not decrease acutely. A decrease in all three parameters would cause severe hypotension.
- The loss of beta-2 receptor-mediated vasodilation and baroreceptor reflexes lead to increased, not decreased, peripheral vascular resistance.
*↓ ↑ ↑*
- Beta-blockers **decrease heart rate** through beta-1 blockade, not increase it. This is their primary cardiac mechanism of action.
- An increase in heart rate would be expected with sympathomimetic drugs or anticholinergics, not beta-blockers.
*↑ ↑ ↑*
- This combination indicates increased cardiovascular activity, which is the opposite effect of **beta-blockers**.
- Beta-blockers reduce heart rate and stroke volume by blocking beta-1 receptors; they do not increase these parameters.
- This pattern would suggest sympathetic activation or administration of an adrenergic agonist.
*↑ ↑ ↓*
- Beta-blockers **decrease** (not increase) both heart rate and stroke volume through beta-1 receptor blockade.
- While decreased peripheral vascular resistance occurs with vasodilators, beta-blockers acutely **increase** PVR due to unopposed alpha-adrenergic tone.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 5: A 44-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by fire and rescue after he was the unrestrained driver in a motor vehicle accident. His wife notes that the patient’s only past medical history is recent development of severe episodes of headache accompanied by sweating and palpitations. She says that these episodes were diagnosed as atypical panic attacks by the patient’s primary care provider, and the patient was started on sertraline and alprazolam. In the trauma bay, the patient’s temperature is 97.6°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 81/56 mmHg, pulse is 127/min, and respirations are 14/min. He has a Glascow Coma Score (GCS) of 10. He is extremely tender to palpation in the abdomen with rebound and guarding. His skin is cool and clammy, and he has thready peripheral pulses. The patient's Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) exam reveals bleeding in the perisplenic space, and he is taken for emergency laparotomy. He is found to have a ruptured spleen, and his spleen is removed. During manipulation of the bowel, the patient’s temperature is 97.8°F (36.6°C), blood pressure is 246/124 mmHg, and pulse is 104/min. The patient is administered intravenous labetalol, but his blood pressure continues to worsen. The patient dies during the surgery.
Which of the following medications would most likely have prevented this outcome?
- A. Lorazepam
- B. Propylthiouracil
- C. Phenoxybenzamine (Correct Answer)
- D. Dantrolene
- E. Phentolamine
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Phenoxybenzamine***
- This patient likely had an undiagnosed **pheochromocytoma**, which is a **catecholamine-secreting tumor**. The severe labile hypertension during surgery, unresponsive to labetalol, is a classic sign of a catecholamine surge.
- **Phenoxybenzamine** is an **irreversible alpha-adrenergic blocker** that would have been used pre-operatively to control blood pressure and prevent such a hypertensive crisis by blocking the effects of excess catecholamines.
*Lorazepam*
- **Lorazepam** is a **benzodiazepine** used for anxiety and seizure control. While it might have helped to calm the patient or manage panic, it would not address the underlying physiological cause of the hypertensive crisis associated with an endocrine tumor.
- Its effects on blood pressure are generally mild and would not counteract the massive catecholamine release seen in a pheochromocytoma.
*Propylthiouracil*
- **Propylthiouracil** is an **antithyroid medication** used to treat **hyperthyroidism**. There is no indication of thyroid dysfunction in this patient's presentation.
- The symptoms of palpitations and sweating are common to both pheochromocytoma and hyperthyroidism, but the rapid, extreme hypertensive crisis points away from thyroid storm and towards a catecholamine-secreting tumor.
*Dantrolene*
- **Dantrolene** is a **skeletal muscle relaxant** primarily used to treat and prevent **malignant hyperthermia**.
- There is no evidence in the clinical presentation to suggest malignant hyperthermia as the cause of this patient's deterioration; the extreme hypertension is the primary issue.
*Phentolamine*
- **Phentolamine** is a **reversible alpha-adrenergic blocker** used to manage hypertensive crises, particularly those due to pheochromocytoma or monoamine oxidase inhibitor interactions.
- While phentolamine could be used during a crisis, **phenoxybenzamine** is preferred for *pre-operative preparation* due to its longer-acting and irreversible blockade, preventing the crisis more effectively when surgery is anticipated for pheochromocytoma.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 6: A 75-year-old male arrives by ambulance to the emergency room severely confused. His vitals are T 40 C, HR 120 bpm, BP 80/55 mmHg, RR 25. His wife explains that he injured himself about a week ago while cooking, and several days later his finger became infected, oozing with pus. He ignored her warning to see a doctor and even refused after he developed fever, chills, and severe fatigue yesterday. After being seen by the emergency physician, he was given antibiotics and IV fluids. Following initial resuscitation with IV fluids, he remains hypotensive. The ED physicians place a central venous catheter and begin infusing norepinephrine. Which of the following receptors are activated by norepinephrine?
- A. Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1, Beta 2
- B. Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Alpha 2
- D. Alpha 1, Beta 1, Dopamine 1
- E. Alpha 1, Beta 1
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1***
- **Norepinephrine** primarily activates **alpha-1** (peripheral vasoconstriction), **alpha-2** (presynaptic inhibition and some vasoconstriction), and **beta-1** (increased heart rate and contractility) adrenergic receptors.
- These are the **primary receptors** responsible for norepinephrine's clinical effects: vasoconstriction (alpha-1, alpha-2) and positive inotropic/chronotropic effects (beta-1).
- This receptor profile makes norepinephrine an ideal **vasopressor** in septic shock, as seen in this patient.
*Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1, Beta 2*
- While **norepinephrine** does activate alpha-1, alpha-2, and beta-1 receptors, it has **negligible affinity for beta-2 receptors**.
- **Epinephrine** (not norepinephrine) is the catecholamine with significant **beta-2 activity**, causing bronchodilation and vasodilation in skeletal muscle.
- Including beta-2 is a common mistake when confusing norepinephrine with epinephrine.
*Alpha 2*
- This option is far too incomplete as **norepinephrine** has significant action on **alpha-1** and **beta-1** receptors, which are crucial for its vasoconstrictive and inotropic effects.
- Activating only alpha-2 receptors would primarily lead to presynaptic inhibition and limited vasoconstriction, not the broad cardiovascular support required in septic shock.
*Alpha 1, Beta 1, Dopamine 1*
- While **norepinephrine** does activate **alpha-1** and **beta-1** receptors, it does **not** activate **dopamine 1 (D1) receptors**.
- Only **dopamine** itself or specific **dopamine agonists** stimulate D1 receptors, leading to renal and mesenteric vasodilation.
- This option incorrectly attributes dopaminergic activity to norepinephrine.
*Alpha 1, Beta 1*
- This option correctly identifies two of the main receptors activated by **norepinephrine**: alpha-1 (vasoconstriction) and beta-1 (positive inotropy and chronotropy).
- However, it **omits alpha-2 receptors**, which norepinephrine also activates, contributing to both presynaptic feedback inhibition and additional vasoconstriction.
- While not completely wrong, this is an incomplete answer.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 7: An investigator is studying the effects of different drugs on the contraction of cardiomyocytes. The myocytes are able to achieve maximal contractility with the administration of drug A. The subsequent administration of drug B produces the response depicted in the graph shown. Which of the following drugs is most likely to produce a response similar to that of drug B?
- A. Albuterol
- B. Phenoxybenzamine
- C. Pindolol (Correct Answer)
- D. Isoproterenol
- E. Propranolol
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Pindolol***
- The graph shows drug B reducing the maximal contractility achieved by drug A, suggesting it is a **partial agonist** or a **competitive antagonist** that can exert some intrinsic activity. Pindolol is a **beta-blocker** with **intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA)**, meaning it can partially stimulate beta-receptors while blocking full agonists.
- This **partial agonism** allows pindolol to reduce the effect of a stronger agonist (like drug A, if it's a full beta-agonist) but still provide some baseline stimulation, thus decreasing the maximal response rather than completely abolishing it.
*Albuterol*
- Albuterol is a **selective beta-2 adrenergic agonist** primarily used as a bronchodilator.
- It would increase contractility if beta-2 receptors were present and acted upon, but it would not reduce the maximal contraction from an existing strong agonist.
*Phenoxybenzamine*
- Phenoxybenzamine is an **irreversible alpha-adrenergic antagonist**.
- It would not directly affect cardiac contractility which is primarily mediated by beta-adrenergic receptors, nor would it produce the depicted effect on contractility.
*Isoproterenol*
- Isoproterenol is a **non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist**.
- As a full agonist, it would increase contractility and could even be drug A if drug A is a beta-agonist, but it would not reduce the maximal response of an established agonist.
*Propranolol*
- Propranolol is a **non-selective beta-adrenergic antagonist** without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA).
- It would act as a **full competitive antagonist**, completely blocking the effects of drug A if drug A is a beta-agonist, thus reducing contractility much more significantly than depicted, potentially to baseline or below.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is studying receptors that respond to epinephrine in the body and discovers a particular subset that is expressed in presynaptic adrenergic nerve terminals. She discovers that upon activation, these receptors will lead to decreased sympathetic nervous system activity. She then studies the intracellular second messenger changes that occur when this receptor is activated. She records these changes and begins searching for analogous receptor pathways. Which of the following receptors would cause the most similar set of intracellular second messenger changes?
- A. Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract
- B. Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system
- C. Vasopressin receptors in the kidney
- D. Dopamine receptors in the brain (Correct Answer)
- E. Aldosterone receptors in the kidney
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Dopamine receptors in the brain***
- The described presynaptic receptors for epinephrine that decrease sympathetic activity are **alpha-2 adrenergic receptors**, which are **G inhibitory protein (Gi)-coupled receptors**.
- Gi-coupled receptors **inhibit adenylyl cyclase**, leading to a **decrease in intracellular cAMP**, a signaling pathway shared by **D2 dopamine receptors**.
*Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract*
- Most muscarinic receptors (M1 and M3) in the GI tract are **Gq-coupled**, leading to an **increase in phospholipase C (PLC) activity**, ultimately increasing intracellular **IP3 and DAG** and promoting smooth muscle contraction.
- This mechanism is distinct from the **Gi-mediated inhibition of cAMP** described for the presynaptic adrenergic receptor.
*Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system*
- Growth hormone receptors are **tyrosine kinase-associated receptors** (specifically, they are linked to **JAK/STAT pathways**), not G protein-coupled receptors.
- Their intracellular signaling involves **protein phosphorylation cascades**, which are fundamentally different from second messenger changes involving cAMP.
*Vasopressin receptors in the kidney*
- Vasopressin (ADH) acts on **V2 receptors** in the kidney, which are **G stimulatory protein (Gs)-coupled receptors**.
- Activation of V2 receptors leads to an **increase in adenylyl cyclase activity** and thus an **increase in intracellular cAMP**, the opposite effect of the described Gi-coupled receptor.
*Aldosterone receptors in the kidney*
- Aldosterone receptors are **intracellular steroid hormone receptors** that directly bind to DNA and regulate gene transcription.
- They do not engage in rapid intracellular second messenger changes like G protein-coupled receptors, but rather alter **protein synthesis** over hours to days.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 9: A 22-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her roommate for unusual behavior. They were at a party where alcohol and recreational drugs were consumed, but her roommate is unsure of what she may have taken or had to drink. She is otherwise healthy and does not take any medications. The patient appears anxious. Her temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 110/min, respiratory rate is 16/min, and blood pressure is 145/82 mmHg. Examination shows dry mucous membranes and bilateral conjunctival injection. Breath sounds are normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Further evaluation will most likely reveal which of the following?
- A. Decreased appetite
- B. Impaired reaction time (Correct Answer)
- C. Respiratory depression
- D. Pupillary constriction
- E. Increased libido
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Impaired reaction time***
- The patient's presentation with **anxiety**, **tachycardia**, **hypertension**, **dry mucous membranes**, and **conjunctival injection** are consistent with acute **cannabis intoxication**.
- **Cannabis use** is known to cause dose-dependent **psychomotor impairment** including **slowed reaction time**, impaired judgment, and decreased coordination, making tasks like driving dangerous.
- This is the most clinically significant finding that would be revealed upon further evaluation (e.g., through psychomotor testing or assessment).
*Decreased appetite*
- While chronic cannabis use can increase appetite (the "munchies"), acute intoxication does not typically lead to decreased appetite.
- Cannabis is more commonly associated with increased appetite rather than decreased appetite, making this option incorrect.
*Respiratory depression*
- **Opioid overdose** or severe sedative intoxication would typically present with **respiratory depression**, which is not seen in this patient (respiratory rate is normal at 16/min).
- Cannabis intoxication generally causes either no significant change in respiratory rate or, less commonly, slight bronchodilation, not respiratory depression.
*Pupillary constriction*
- **Pupillary constriction** (miosis) is a classic sign of **opioid intoxication** or organophosphate poisoning.
- Cannabis intoxication more commonly causes **pupillary dilation** (mydriasis) or no significant change, not constriction.
*Increased libido*
- While some individuals may report altered sexual experiences under the influence of cannabis, it is not a consistent or clinically significant feature of acute intoxication in an emergency setting.
- This is not an objective finding that would likely be revealed upon further evaluation in the emergency department.
Sympathomimetics US Medical PG Question 10: Two 19-year-old men are referred by their professor and mentor to a psychiatrist for substance abuse management. The two friends have both used different stimulants for 3 years—Drug A and Drug B, respectively. Both use these substances cyclically. Use of Drug A usually lasts for about 12 hours. The cycle for Drug B lasts several days. A month ago, both men visited the emergency room (ER) due to acute intoxication. Clinical features in the emergency department included hypotension, bradycardia, sweating, chills, mydriasis, nausea, and psychomotor agitation. After a urine drug screen, the psychiatrist identifies both the drugs and informs the professor that although both Drug A and Drug B are stimulants, their mechanisms of action are different. Drug A is an alkaloid that is naturally present in the leaves of the coca plant, while it is possible to make Drug B from over-the-counter nasal decongestant products. Which of the following options best describes the mechanism of action of both drugs?
- A. Drug A increases norepinephrine activity, while Drug B does not.
- B. Drug A increases serotonin activity, while Drug B does not.
- C. Drug A predominantly acts by increasing the release of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) into the synapse, while Drug B does not.
- D. Drug A transiently increases the extracellular concentration of dopamine in the reward circuit, while Drug B does not.
- E. Drug A predominantly acts by inhibiting the reuptake of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) at the synapse, while Drug B predominantly acts by promoting their release from presynaptic terminals. (Correct Answer)
Sympathomimetics Explanation: ***Drug A predominantly acts by inhibiting the reuptake of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) at the synapse, while Drug B predominantly acts by promoting their release from presynaptic terminals.***
- Drug A is **cocaine**, an alkaloid from the coca plant, which primarily acts by **blocking the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin**, leading to their accumulation in the synaptic cleft.
- Drug B is likely **methamphetamine**, derivable from nasal decongestants, which primarily works by **promoting the release of monoamines** from presynaptic terminals, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine.
*Drug A increases norepinephrine activity, while Drug B does not.*
- While Drug A (cocaine) does increase norepinephrine activity by inhibiting its reuptake, Drug B (methamphetamine) also significantly increases norepinephrine activity by promoting its release.
- This option incorrectly states that Drug B does not increase norepinephrine activity.
*Drug A increases serotonin activity, while Drug B does not.*
- Both Drug A (cocaine) and Drug B (methamphetamine) increase serotonin activity, albeit through different mechanisms. Cocaine inhibits serotonin reuptake, while methamphetamine promotes its release.
- The premise that Drug B does not affect serotonin activity is incorrect.
*Drug A predominantly acts by increasing the release of monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine) into the synapse, while Drug B does not.*
- This statement misrepresents the primary mechanism of Drug A (cocaine), which is to **inhibit reuptake**, not primarily increase release.
- It also incorrectly implies that Drug B does not significantly affect the monoamine neurotransmitter release.
*Drug A transiently increases the extracellular concentration of dopamine in the reward circuit, while Drug B does not.*
- Both cocaine (Drug A) and methamphetamine (Drug B) **increase extracellular dopamine** in the reward circuit, which is central to their addictive properties.
- This option is incorrect because Drug B also significantly increases dopamine concentrations.
More Sympathomimetics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.
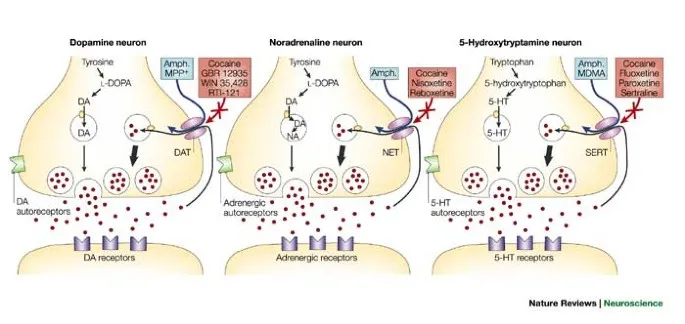 , and sites of action for amphetamine and cocaine)
, and sites of action for amphetamine and cocaine)
