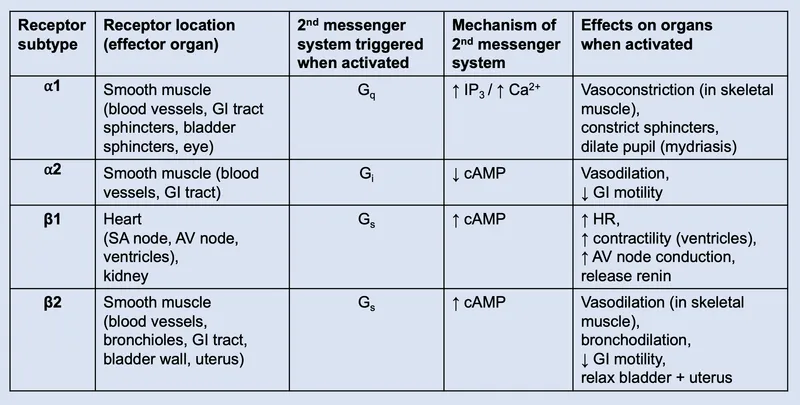
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Autonomic drug interactions. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 1: In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stimulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors results in an increase in mucus secretion, smooth muscle contraction and bronchoconstriction. The end result is an increase in airway resistance. Which of the following pharmacologic agents interferes directly with this pathway?
- A. Epinephrine
- B. Albuterol
- C. Theophylline
- D. Ipratropium (Correct Answer)
- E. Metoprolol
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Ipratropium***
- **Ipratropium** is an **anticholinergic** agent that blocks muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
- By blocking these receptors, it **reduces bronchoconstriction**, mucus secretion, and smooth muscle contraction, thus decreasing airway resistance.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is a non-selective **adrenergic agonist** that stimulates both alpha and beta receptors.
- Its effects in the airways are primarily mediated through **beta-2 agonism**, leading to bronchodilation, but it does not directly interfere with muscarinic pathways.
*Albuterol*
- **Albuterol** is a **short-acting beta-2 adrenergic agonist (SABA)**.
- It primarily causes bronchodilation by stimulating beta-2 receptors on airway smooth muscle, independent of the muscarinic pathway.
*Theophylline*
- **Theophylline** is a **methylxanthine** that primarily acts as a non-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor.
- This leads to increased intracellular **cAMP** and bronchodilation, but it does not directly block muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
*Metoprolol*
- **Metoprolol** is a **selective beta-1 adrenergic blocker** (beta-blocker).
- Its primary action is on the heart; it has minimal effect on airway beta-2 receptors at therapeutic doses due to its selectivity, and it does not interfere with the muscarinic pathway.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 2: A 43-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 45 minutes after his wife found him on the floor sweating profusely. On arrival, he is lethargic and unable to provide a history. He vomited multiple times on the way to the hospital. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 55/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 98/65 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 80%. Examination shows profuse diaphoresis and excessive salivation. He withdraws his extremities sluggishly to pain. The pupils are constricted and reactive. Scattered expiratory wheezing and rhonchi are heard throughout both lung fields. Cardiac examination shows no abnormalities. There are fine fasciculations in the lower extremities bilaterally. Muscle strength is reduced and deep tendon reflexes are 1+ bilaterally. His clothes are soaked with urine and feces. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the most appropriate initial pharmacotherapy?
- A. Non-selective α-adrenergic antagonism
- B. Competitive antagonism of mACh receptors (Correct Answer)
- C. Alkaloid emesis-induction
- D. Enteral binding
- E. Urine alkalization
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Competitive antagonism of mACh receptors***
- The patient's symptoms, including **profuse sweating, salivation, constricted pupils, wheezing, bradycardia, hypotension, fasciculations**, and incontinence, are classic signs of **cholinergic crisis** due to **organophosphate poisoning**.
- **Atropine**, a competitive antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine (mACh) receptors, is the primary initial pharmacotherapy for organophosphate poisoning, counteracting the excessive parasympathetic stimulation.
*Non-selective α-adrenergic antagonism*
- This mechanism would typically be used to treat conditions involving **excessive alpha-adrenergic activity**, such as a pheochromocytoma or severe hypertension.
- It would **worsen the hypotension** already present in this patient and does not address the underlying cholinergic overstimulation.
*Alkaloid emesis-induction*
- While vomiting occurred, inducing further emesis with an alkaloid is **contraindicated** in cases of organophosphate poisoning due to the risk of **aspiration pneumonitis** and the patient's altered mental status.
- Furthermore, modern management of poisoning rarely recommends routine emesis induction.
*Enteral binding*
- **Activated charcoal** acts by enteral binding to prevent absorption of toxins from the gastrointestinal tract.
- While it may be considered in some poisonings, the rapid onset of severe symptoms and the potential for aspiration in a lethargic patient makes **airway protection** and **antidote administration** the immediate priorities.
*Urine alkalization*
- Urine alkalization is a technique used to enhance the renal excretion of certain acidic drugs by increasing their ionization in the urine, preventing reabsorption.
- It is **not relevant** for the initial management of organophosphate poisoning, which primarily requires anticholinergic agents and cholinesterase reactivators.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 3: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of episodic retrosternal chest pain and shortness of breath for the past 6 months. His symptoms occur when he takes long walks or climbs stairs but resolve promptly with rest. He has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, for which he takes ipratropium bromide. His pulse is 81/min and blood pressure is 153/82 mm Hg. Physical examination shows mild expiratory wheezing over both lungs. Additional treatment with a beta blocker is considered. Which of the following agents should be avoided in this patient?
- A. Betaxolol
- B. Esmolol
- C. Bisoprolol
- D. Atenolol
- E. Labetalol (Correct Answer)
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Labetalol***
- **Labetalol** is a **non-selective beta-blocker** with additional **alpha-1 blocking activity**.
- Its **non-selective beta-blocking** effects can exacerbate **bronchoconstriction** in patients with **COPD**, leading to worsening respiratory symptoms.
*Betaxolol*
- **Betaxolol** is a **beta-1 selective blocker (cardioselective)**, meaning it primarily targets the heart.
- While no beta-blocker is entirely safe in **COPD**, cardioselective agents are generally preferred due to their reduced risk of **bronchospasm**.
*Esmolol*
- **Esmolol** is an **ultra-short-acting**, **beta-1 selective blocker** often used for acute cardiac conditions.
- Its **cardioselective nature** and rapid metabolism make it relatively safer in patients with **COPD** compared to non-selective agents.
*Bisoprolol*
- **Bisoprolol** is a **highly beta-1 selective blocker** commonly used for chronic cardiac conditions.
- Its high **cardioselectivity** minimizes its impact on **bronchial beta-2 receptors**, making it a safer option for patients with **COPD**.
*Atenolol*
- **Atenolol** is a **beta-1 selective blocker** used for conditions like hypertension and angina.
- Like other cardioselective beta-blockers, it has a lower risk of causing **bronchoconstriction** in patients with **COPD** compared to non-selective agents.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old male with a history of CHF presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath, lower leg edema, and fatigue. He is diagnosed with acute decompensated congestive heart failure, was admitted to the CCU, and treated with a medication that targets beta-1 adrenergic receptors preferentially over beta-2 adrenergic receptors. The prescribing physician explained that this medication would only be used temporarily as its efficacy decreases within 2-3 days due to receptor downregulation. Which of the following was prescribed?
- A. Epinephrine
- B. Norepinephrine
- C. Milrinone
- D. Isoproterenol
- E. Dobutamine (Correct Answer)
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Dobutamine***
- **Dobutamine** is a beta-1 adrenergic agonist preferentially acting on beta-1 receptors in the heart, increasing contractility and heart rate during acute decompensated heart failure.
- Its efficacy reduces over time due to **receptor downregulation**, making it effective for only short-term use, typically less than 72 hours.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is a non-selective adrenergic agonist acting on both alpha and beta receptors, causing vasoconstriction and bronchodilation in addition to cardiac stimulation.
- It is typically used in emergency situations like **cardiac arrest** and **anaphylaxis**, not primarily for acute CHF exacerbation in this manner.
*Norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** primarily acts on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing significant vasoconstriction, and has some beta-1 agonistic effects.
- It is mainly used as a **vasopressor** in septic shock or severe hypotension to increase systemic vascular resistance, rather than directly improving cardiac output in decompensated CHF.
*Milrinone*
- **Milrinone** is a phosphodiesterase-3 inhibitor, increasing intracellular cAMP levels and leading to positive inotropy and vasodilation.
- While used in acute heart failure, its mechanism is distinct from adrenergic agonists, and its efficacy is not limited by a rapid receptor downregulation mechanism as described.
*Isoproterenol*
- **Isoproterenol** is a non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist, stimulating both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, leading to increased heart rate and contractility, as well as bronchodilation and vasodilation.
- Due to its strong chronotropic effects and potential for severe arrhythmias and hypotension, it is rarely used in CHF and is primarily reserved for conditions like **bradycardia** or **torsades de pointes**.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 5: A 75-year-old male arrives by ambulance to the emergency room severely confused. His vitals are T 40 C, HR 120 bpm, BP 80/55 mmHg, RR 25. His wife explains that he injured himself about a week ago while cooking, and several days later his finger became infected, oozing with pus. He ignored her warning to see a doctor and even refused after he developed fever, chills, and severe fatigue yesterday. After being seen by the emergency physician, he was given antibiotics and IV fluids. Following initial resuscitation with IV fluids, he remains hypotensive. The ED physicians place a central venous catheter and begin infusing norepinephrine. Which of the following receptors are activated by norepinephrine?
- A. Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1, Beta 2
- B. Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Alpha 2
- D. Alpha 1, Beta 1, Dopamine 1
- E. Alpha 1, Beta 1
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1***
- **Norepinephrine** primarily activates **alpha-1** (peripheral vasoconstriction), **alpha-2** (presynaptic inhibition and some vasoconstriction), and **beta-1** (increased heart rate and contractility) adrenergic receptors.
- These are the **primary receptors** responsible for norepinephrine's clinical effects: vasoconstriction (alpha-1, alpha-2) and positive inotropic/chronotropic effects (beta-1).
- This receptor profile makes norepinephrine an ideal **vasopressor** in septic shock, as seen in this patient.
*Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1, Beta 2*
- While **norepinephrine** does activate alpha-1, alpha-2, and beta-1 receptors, it has **negligible affinity for beta-2 receptors**.
- **Epinephrine** (not norepinephrine) is the catecholamine with significant **beta-2 activity**, causing bronchodilation and vasodilation in skeletal muscle.
- Including beta-2 is a common mistake when confusing norepinephrine with epinephrine.
*Alpha 2*
- This option is far too incomplete as **norepinephrine** has significant action on **alpha-1** and **beta-1** receptors, which are crucial for its vasoconstrictive and inotropic effects.
- Activating only alpha-2 receptors would primarily lead to presynaptic inhibition and limited vasoconstriction, not the broad cardiovascular support required in septic shock.
*Alpha 1, Beta 1, Dopamine 1*
- While **norepinephrine** does activate **alpha-1** and **beta-1** receptors, it does **not** activate **dopamine 1 (D1) receptors**.
- Only **dopamine** itself or specific **dopamine agonists** stimulate D1 receptors, leading to renal and mesenteric vasodilation.
- This option incorrectly attributes dopaminergic activity to norepinephrine.
*Alpha 1, Beta 1*
- This option correctly identifies two of the main receptors activated by **norepinephrine**: alpha-1 (vasoconstriction) and beta-1 (positive inotropy and chronotropy).
- However, it **omits alpha-2 receptors**, which norepinephrine also activates, contributing to both presynaptic feedback inhibition and additional vasoconstriction.
- While not completely wrong, this is an incomplete answer.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 32 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital for the management of elevated blood pressures. On admission, her pulse is 81/min, and blood pressure is 165/89 mm Hg. Treatment with an intravenous drug is initiated. Two days after admission, she has a headache and palpitations. Her pulse is 116/min and regular, and blood pressure is 124/80 mm Hg. Physical examination shows pitting edema of both lower extremities that was not present on admission. This patient most likely was given a drug that predominantly acts by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Inhibition of β1, β2, and α1 receptors
- B. Inhibition of angiotensin II production
- C. Activation of α2 adrenergic receptors
- D. Inhibition of sodium reabsorption
- E. Direct dilation of the arterioles (Correct Answer)
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Direct dilation of the arterioles***
- The development of **headache**, **palpitations**, and **tachycardia** (pulse 116), along with a reduction in blood pressure (124/80 mm Hg) and new-onset **pitting edema**, suggests a direct arterial vasodilator like **hydralazine**.
- **Hydralazine reduces peripheral vascular resistance** by directly relaxing vascular smooth muscle, primarily in arterioles, leading to reflex tachycardia and fluid retention as compensatory mechanisms.
*Inhibition of β1, β2, and α1 receptors*
- Labetaolol, which is commonly used in pre-eclampsia and acts by inhibiting β1, β2, and α1 receptors, would typically lead to a **decrease in heart rate and sympathetic compensation**, not palpitations and increased pulse.
- While it lowers blood pressure, it would not typically cause **reflex tachycardia and new-onset edema** to this extent unless there is an underlying cardiac issue or overdose.
*Inhibition of angiotensin II production*
- Inhibitors of angiotensin II production (like ACE inhibitors or ARBs) are **contraindicated in pregnancy** due to their teratogenic effects, especially in the second and third trimesters.
- They typically do not cause **reflex tachycardia and palpitations** as primary side effects, but rather dry cough (ACE inhibitors) or hyperkalemia.
*Activation of α2 adrenergic receptors*
- **Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists** (e.g., methyldopa, clonidine) reduce sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system, leading to a **decrease in heart rate and blood pressure**.
- While effective for hypertension in pregnancy, they are more associated with **sedation and dry mouth** rather than palpitations and reflex tachycardia, and they do not typically cause significant peripheral edema.
*Inhibition of sodium reabsorption*
- Medications that inhibit sodium reabsorption are **diuretics**. While diuretics can help manage edema, they primarily lower blood pressure by reducing blood volume, and are not typically the immediate go-to for acute severe hypertension in pregnancy.
- Diuretics would **reduce edema**, not cause new-onset pitting edema, and would not typically cause reflex tachycardia as seen in this patient unless there is profound hypovolemia leading to a compensatory increase in heart rate.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 7: A researcher is studying receptors that respond to epinephrine in the body and discovers a particular subset that is expressed in presynaptic adrenergic nerve terminals. She discovers that upon activation, these receptors will lead to decreased sympathetic nervous system activity. She then studies the intracellular second messenger changes that occur when this receptor is activated. She records these changes and begins searching for analogous receptor pathways. Which of the following receptors would cause the most similar set of intracellular second messenger changes?
- A. Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract
- B. Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system
- C. Vasopressin receptors in the kidney
- D. Dopamine receptors in the brain (Correct Answer)
- E. Aldosterone receptors in the kidney
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Dopamine receptors in the brain***
- The described presynaptic receptors for epinephrine that decrease sympathetic activity are **alpha-2 adrenergic receptors**, which are **G inhibitory protein (Gi)-coupled receptors**.
- Gi-coupled receptors **inhibit adenylyl cyclase**, leading to a **decrease in intracellular cAMP**, a signaling pathway shared by **D2 dopamine receptors**.
*Muscarinic cholinoreceptors in the gastrointestinal tract*
- Most muscarinic receptors (M1 and M3) in the GI tract are **Gq-coupled**, leading to an **increase in phospholipase C (PLC) activity**, ultimately increasing intracellular **IP3 and DAG** and promoting smooth muscle contraction.
- This mechanism is distinct from the **Gi-mediated inhibition of cAMP** described for the presynaptic adrenergic receptor.
*Growth hormone receptors in the musculoskeletal system*
- Growth hormone receptors are **tyrosine kinase-associated receptors** (specifically, they are linked to **JAK/STAT pathways**), not G protein-coupled receptors.
- Their intracellular signaling involves **protein phosphorylation cascades**, which are fundamentally different from second messenger changes involving cAMP.
*Vasopressin receptors in the kidney*
- Vasopressin (ADH) acts on **V2 receptors** in the kidney, which are **G stimulatory protein (Gs)-coupled receptors**.
- Activation of V2 receptors leads to an **increase in adenylyl cyclase activity** and thus an **increase in intracellular cAMP**, the opposite effect of the described Gi-coupled receptor.
*Aldosterone receptors in the kidney*
- Aldosterone receptors are **intracellular steroid hormone receptors** that directly bind to DNA and regulate gene transcription.
- They do not engage in rapid intracellular second messenger changes like G protein-coupled receptors, but rather alter **protein synthesis** over hours to days.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 8: Which neurotransmitter is primarily responsible for parasympathetic effects on heart rate?
- A. Norepinephrine
- B. Dopamine
- C. Acetylcholine (Correct Answer)
- D. Epinephrine
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Acetylcholine***
- **Acetylcholine** is the primary neurotransmitter released by postganglionic parasympathetic neurons.
- It acts on **muscarinic receptors** (M2 receptors) in the heart to decrease heart rate.
*Norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** is primarily associated with the **sympathetic nervous system**, increasing heart rate and contractility.
- It acts on **beta-1 adrenergic receptors** in the heart.
*Dopamine*
- **Dopamine** is a precursor to norepinephrine and epinephrine, and primarily functions as a neurotransmitter in the **central nervous system** and in regulating renal blood flow.
- While it can have cardiac effects, it is not the primary neurotransmitter for parasympathetic actions on heart rate.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** (adrenaline) is a hormone released by the adrenal medulla and a neurotransmitter in the sympathetic nervous system, causing an **increase in heart rate** and contractility.
- It works through **beta-1 adrenergic receptors**, antagonistic to parasympathetic effects.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 9: A 64-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife with a 2-hour history of diarrhea and vomiting. He says that he felt fine in the morning, but noticed that he was salivating, sweating, and feeling nauseated on the way home from his work as a landscaper. The diarrhea and vomiting then started about 10 minutes after he got home. His past medical history is significant for depression and drug abuse. His wife says that he has also been more confused lately and is afraid he may have ingested something unusual. Physical exam reveals miosis, rhinorrhea, wheezing, and tongue fasciculations. Which of the following treatments would most likely be effective for this patient?
- A. Sodium bicarbonate
- B. Naloxone
- C. Atropine (Correct Answer)
- D. Fomepizole
- E. Ammonium chloride
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Atropine***
- This patient displays classic signs of **organophosphate poisoning**, characterized by **cholinergic crisis** (salivation, sweating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, miosis, rhinorrhea, wheezing, fasciculations). **Atropine** is a competitive antagonist of acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors and is the primary antidote, reversing most of these symptoms.
- The patient's profession as a **landscaper** increases his exposure risk, and the acute onset of symptoms supports a toxic exposure rather than an infection.
*Sodium bicarbonate*
- **Sodium bicarbonate** is primarily used to treat **metabolic acidosis**, such as in aspirin overdose or tricyclic antidepressant poisoning, or to alkalinize urine in certain toxic exposures.
- While metabolic acidosis can occur in severe organophosphate poisoning, it is not the primary treatment for the **cholinergic symptoms** themselves.
*Naloxone*
- **Naloxone** is an opioid antagonist used to reverse the effects of **opioid overdose**, characterized by respiratory depression, miosis, and central nervous system depression.
- The patient's symptoms of excessive secretions, gastrointestinal distress, and muscle fasciculations are inconsistent with opioid overdose.
*Fomepizole*
- **Fomepizole** is an alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor used to treat **methanol and ethylene glycol poisoning**.
- These poisonings present with severe metabolic acidosis, visual disturbances (methanol), or renal failure (ethylene glycol), which are not the primary features described in this patient.
*Ammonium chloride*
- **Ammonium chloride** is an acidifying agent used to treat severe **metabolic alkalosis** or to increase the excretion of basic drugs.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of organophosphate poisoning and would likely exacerbate any existing acidosis.
Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old woman presents to her physician complaining of a headache in the occipital region for 1 week. Past medical history is significant for essential hypertension, managed with lifestyle modifications and 2 antihypertensives for the previous 6 months. Her blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg. Neurological examination is normal. A third antihypertensive drug is added that acts as a selective α2 adrenergic receptor agonist. On follow-up, she reports that she does not have any symptoms and her blood pressure is 124/82 mm Hg. Which of the following mechanisms best explains the therapeutic effect of this new drug in this patient?
- A. Vasodilation of peripheral arteries
- B. Vasodilation of peripheral arteries and peripheral veins
- C. Decreased peripheral sympathetic outflow (Correct Answer)
- D. Negative inotropic effect on the heart
- E. Vasodilation of peripheral veins
Autonomic drug interactions Explanation: ***Decreased peripheral sympathetic outflow***
- Selective **α2 adrenergic receptor agonists** (e.g., clonidine, guanfacine, methyldopa) act **centrally in the brainstem** (nucleus tractus solitarius and rostral ventrolateral medulla) to reduce **sympathetic nervous system activity**.
- This **central action** leads to a **decrease in peripheral sympathetic outflow**, resulting in reduced heart rate, decreased cardiac output, and peripheral vasodilation, all contributing to lower blood pressure.
- This is the **primary mechanism** of antihypertensive action for central α2 agonists.
*Vasodilation of peripheral arteries*
- While central α2 agonists do cause some peripheral vasodilation, this is an **indirect effect** of **reduced sympathetic tone**, not a primary direct action on peripheral arteries.
- Their main mechanism of action is **central**, decreasing the overall sympathetic drive to the vasculature.
*Vasodilation of peripheral arteries and peripheral veins*
- This option describes a broader effect, and while some vasodilation occurs, it doesn't pinpoint the **primary mechanism of action** of central α2 agonists.
- Drugs like alpha-1 blockers (prazosin, doxazosin) or direct vasodilators (hydralazine, minoxidil) would have a more pronounced direct effect on both arterial and venous smooth muscle.
*Negative inotropic effect on the heart*
- While central α2 agonists can **reduce heart rate** (bradycardia) and cardiac output due to decreased sympathetic stimulation, a **negative inotropic effect** (decreased myocardial contractility) is not their primary or most significant mechanism.
- **Beta-blockers** are primarily known for their negative inotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart.
*Vasodilation of peripheral veins*
- Similar to arterial vasodilation, this is an **indirect effect** of **reduced sympathetic tone**, not the primary mechanism of action of central α2 agonists.
- Direct venodilators like **nitrates** would primarily target peripheral veins to reduce preload.
More Autonomic drug interactions US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.