Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Alpha-adrenergic agonists. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 1: A patient presents with periods of severe headaches and flushing however every time they have come to the physician they have not experienced any symptoms. The only abnormal finding is a blood pressure of 175 mmHg/100 mmHg. It is determined that the optimal treatment for this patient is surgical. Prior to surgery which of the following noncompetitive inhibitors should be administered?
- A. Phentolamine
- B. Isoproterenol
- C. Atropine
- D. Propranolol
- E. Phenoxybenzamine (Correct Answer)
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Phenoxybenzamine***
- This patient likely has a **pheochromocytoma**, which explains the episodic headaches, flushing, and hypertension. **Phenoxybenzamine** is a **non-competitive, irreversible alpha-adrenergic blocker** that is crucial for preoperative preparation to prevent a **hypertensive crisis** during surgery.
- Its **irreversible binding** provides sustained alpha blockade, essential to control blood pressure and avoid catecholamine-induced surges during tumor manipulation.
*Phentolamine*
- **Phentolamine** is a **competitive alpha-adrenergic blocker** used to manage acute hypertensive episodes, but it has a shorter duration of action.
- It is not preferred for sustained preoperative alpha blockade due to its **reversible nature** and potential for drug washout during surgery, which could lead to catecholamine surges.
*Isoproterenol*
- **Isoproterenol** is a **beta-adrenergic agonist** that increases heart rate and contractility, and causes bronchodilation.
- It would be contraindicated in a patient with pheochromocytoma as it could worsen hypertension and cardiac symptoms by stimulating beta receptors that are already overly sensitive to endogenous catecholamines.
*Atropine*
- **Atropine** is a **muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist** that blocks parasympathetic effects, like bradycardia and salivation.
- It has no role in managing hypertension or the catecholamine excess seen in pheochromocytoma.
*Propranolol*
- **Propranolol** is a **non-selective beta-adrenergic blocker** that can be used to control tachycardia and arrhythmias in pheochromocytoma, but only *after* adequate alpha-blockade has been established.
- Using **propranolol alone** or before alpha-blockade can lead to **unopposed alpha-adrenergic stimulation**, resulting in a severe, life-threatening hypertensive crisis.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 2: A 60-year-old man presents to the office for a scheduled follow-up visit. He has had hypertension for the past 30 years and his current anti-hypertensive medications include lisinopril (40 mg/day) and hydrochlorothiazide (50 mg/day). He follows most of the lifestyle modifications recommended by his physician, but is concerned about his occasional occipital headaches in the morning. His blood pressure is 160/98 mm Hg. The physician adds another drug to his regimen that acts centrally as an α2-adrenergic agonist. Which of the following second messengers is involved in the mechanism of action of this new drug?
- A. Calcium ions
- B. Inositol triphosphate
- C. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- D. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (Correct Answer)
- E. Diacylglycerol
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Cyclic adenosine monophosphate***
- The physician likely added **clonidine or methyldopa**, both of which are **central α2-adrenergic agonists** used to treat hypertension.
- Activation of **α2-adrenergic receptors** leads to the **inhibition of adenylyl cyclase** and a decrease in **intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels**, which is the second messenger.
*Calcium ions*
- While calcium ions are crucial second messengers in many cellular processes, they are primarily involved in the mechanism of action of **α1-adrenergic receptors** and **voltage-gated calcium channels**, not directly inhibited by α2-agonists.
- **α2-adrenergic agonism** primarily acts to *reduce* neuronal excitability, which can indirectly affect calcium flux but does not directly involve calcium as the primary second messenger.
*Inositol triphosphate*
- **Inositol triphosphate (IP3)** is a second messenger primarily associated with the activation of **Gq protein-coupled receptors**, leading to the release of intracellular calcium.
- This pathway is characteristic of **α1-adrenergic receptors**, which cause vasoconstriction, and is antagonistic to the α2-agonist mechanism.
*Cyclic guanosine monophosphate*
- **Cyclic GMP (cGMP)** is a key second messenger in processes such as **vasodilation mediated by nitric oxide** and the action of ANP/BNP.
- **α2-adrenergic agonists** do not directly modulate cGMP levels as their primary mechanism of action.
*Diacylglycerol*
- **Diacylglycerol (DAG)** is a second messenger, along with IP3, produced from the hydrolysis of **PIP2** by phospholipase C, following activation of **Gq protein-coupled receptors**.
- This pathway is associated with **α1-adrenergic receptor activation**, not the inhibitory pathway initiated by central α2-adrenergic agonists.
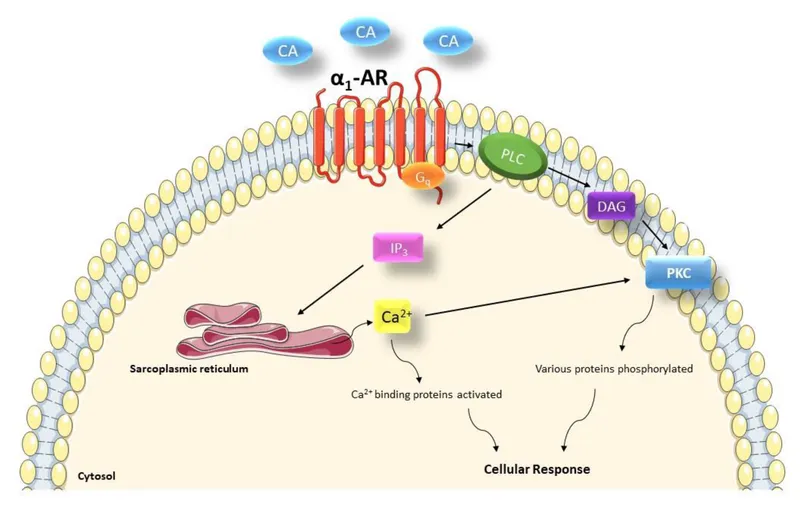
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 3: A drug research team has synthesized a novel oral drug that acts as an agonist at multiple adrenergic receptors. When administered in animals, it has been shown to produce urinary retention at therapeutic doses with the absence of other manifestations of adrenergic stimulation. The researchers are interested in understanding signal transduction and molecular mechanisms behind the action of the novel drug. Which of the following receptors would most likely transduce signals across the plasma membrane following the administration of this novel drug?
- A. GoPCRs (Go protein-coupled receptors)
- B. GsPCRs (Gs protein-coupled receptors)
- C. GqPCRs (Gq protein-coupled receptors) (Correct Answer)
- D. GtPCRs (Gt protein-coupled receptors)
- E. GiPCRs (Gi protein-coupled receptors)
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***GqPCRs (Gq protein-coupled receptors)***
- **Urinary retention** is primarily mediated by the activation of **alpha-1 adrenergic receptors** in the bladder neck and prostate, which are classically Gq-protein coupled receptors.
- Activation of **GqPCRs** leads to the activation of **phospholipase C**, increased **IP3 (inositol trisphosphate)** and **DAG (diacylglycerol)**, and subsequently, a rise in intracellular **calcium**, causing smooth muscle contraction.
*GoPCRs (Go protein-coupled receptors)*
- While Go proteins are a subtype of Gi/Go family, their direct primary role in mediating **urinary retention** via **adrenergic agonism** is not as well-established as Gq.
- Go signaling often involves modulation of **ion channels** and can be involved in neuronal signaling, not directly causing smooth muscle contraction in the bladder.
*GsPCRs (Gs protein-coupled receptors)*
- **GsPCRs** (e.g., beta-adrenergic receptors) activate **adenylate cyclase**, leading to increased **cAMP** levels, which typically causes smooth muscle relaxation.
- This effect would promote **urinary relaxation** and flow, not retention, and hence is contrary to the observed drug effect.
*GtPCRs (Gt protein-coupled receptors)*
- **GtPCRs** (transducin) are primarily involved in the **phototransduction** cascade in the retina, mediating vision.
- They have no known central role in mediating adrenergic effects on the **urinary tract smooth muscle**.
*GiPCRs (Gi protein-coupled receptors)*
- **GiPCRs** (e.g., alpha-2 adrenergic receptors) inhibit **adenylate cyclase**, leading to decreased **cAMP** levels, which generally causes smooth muscle contraction in some tissues, but also presynaptic inhibition.
- While Gi activation can lead to contraction in some contexts, the primary mechanism of **urinary retention** via bladder neck contraction is through alpha-1 receptors linked to Gq.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 4: A 34-year-old female presents to the emergency room with headache and palpitations. She is sweating profusely and appears tremulous on exam. Vital signs are as follows: HR 120, BP 190/110, RR 18, O2 99% on room air, and Temp 37C. Urinary metanephrines and catechols are positive. Which of the following medical regimens is contraindicated as a first-line therapy in this patient?
- A. Labetalol
- B. Propranolol (Correct Answer)
- C. Nitroprusside
- D. Lisinopril
- E. Phenoxybenzamine
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Propranolol***
- This patient's presentation with headache, palpitations, sweating, hypertension, and tachycardia, along with elevated urinary metanephrines and catechols, is highly suggestive of a **pheochromocytoma**.
- **Pure beta-blockers** (like propranolol) are **absolutely contraindicated** as first-line therapy because blocking $\beta_2$ receptors without initial $\alpha$-blockade leads to unopposed $\alpha$-adrenergic stimulation, causing severe **vasoconstriction** and a dangerous **hypertensive crisis**.
- This is the **most contraindicated** option among the choices listed.
*Labetalol*
- Labetalol is a **non-selective $\beta$-blocker with some $\alpha_1$-blocking activity** (β:α blockade ratio ~7:1).
- While **not recommended** as first-line monotherapy in pheochromocytoma due to predominant beta-blockade, it has **some alpha-blocking properties** that distinguish it from pure beta-blockers.
- In practice, it's typically avoided as initial therapy, but it carries **less risk** than pure beta-blockers because of its partial alpha-blockade.
- Some sources consider it relatively contraindicated, but propranolol (pure beta-blocker) is more definitively contraindicated.
*Nitroprusside*
- **Nitroprusside** is a potent **vasodilator** that acts on both arterial and venous beds, making it effective for **rapid blood pressure reduction** in hypertensive emergencies.
- It is **not contraindicated** and can be used in a pheochromocytoma crisis for acute blood pressure control, though it should ideally be combined with alpha-blockade.
- It does not directly address catecholamine effects but provides symptomatic BP control.
*Lisinopril*
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor**, which works by preventing the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, leading to vasodilation and reduced aldosterone secretion.
- It is **not contraindicated** but is **inappropriate** as first-line therapy in pheochromocytoma crisis because it does not directly counteract the massive catecholamine release.
- It would be ineffective for managing the acute hypertensive emergency.
*Phenoxybenzamine*
- **Phenoxybenzamine** is an **irreversible, non-selective $\alpha$-adrenergic blocker** that is the **gold standard first-line therapy** for pheochromocytoma.
- It effectively blocks the vasoconstrictive effects of catecholamines, allowing for adequate blood pressure control before any $\beta$-blockade is considered.
- This is the **correct first-line medication**, not contraindicated.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 5: A 53-year-old man presents to the office for a routine examination. The medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus, for which he is taking metformin. The medical records show blood pressure readings from three separate visits to fall in the 130–160 mm Hg range for systolic and 90–100 mm Hg range for diastolic. Prazosin is prescribed. Which of the following are effects of this drug?
- A. Vasodilation, decreased heart rate, bronchial constriction
- B. Vasodilation, increased peristalsis, bronchial dilation
- C. Vasoconstriction, bladder sphincter constriction, mydriasis
- D. Vasoconstriction, increase in AV conduction rate, bronchial dilation
- E. Vasodilation, bladder sphincter relaxation (Correct Answer)
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Vasodilation, bladder sphincter relaxation***
- **Prazosin** is an **alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist**, which blocks the effects of norepinephrine on vascular smooth muscle, leading to **vasodilation** and decreased blood pressure.
- Blocking alpha-1 receptors in the bladder neck and prostate causes **bladder sphincter relaxation**, which can improve urine flow and is also useful in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- These are the two primary clinically relevant effects of alpha-1 blockade with prazosin.
*Vasodilation, decreased heart rate, bronchial constriction*
- While prazosin causes **vasodilation**, it does not typically decrease heart rate directly; alpha-1 blockade can lead to **reflex tachycardia** due to decreased blood pressure.
- Prazosin has no significant effect on bronchial smooth muscle and does not cause **bronchial constriction**; bronchial effects are primarily mediated by beta-2 receptors or muscarinic (M3) receptors.
*Vasodilation, increased peristalsis, bronchial dilation*
- Prazosin does cause **vasodilation** but does not directly cause **increased peristalsis**; gastrointestinal motility is mainly regulated by the autonomic nervous system via muscarinic receptors and the enteric nervous system.
- Prazosin does not cause **bronchial dilation**; this effect is mediated by beta-2 adrenergic receptor stimulation.
*Vasoconstriction, bladder sphincter constriction, mydriasis*
- Prazosin is an alpha-1 antagonist, meaning it *blocks* **vasoconstriction** and instead causes vasodilation.
- Similarly, it causes **bladder sphincter relaxation**, not constriction.
- Prazosin has minimal effects on pupil size; mydriasis would be caused by alpha-1 agonists or muscarinic antagonists, not alpha-1 antagonists.
*Vasoconstriction, increase in AV conduction rate, bronchial dilation*
- Prazosin causes **vasodilation**, not vasoconstriction.
- It does not significantly affect **AV conduction rate** or directly cause **bronchial dilation**.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 6: A 65-year-old male with a history of CHF presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath, lower leg edema, and fatigue. He is diagnosed with acute decompensated congestive heart failure, was admitted to the CCU, and treated with a medication that targets beta-1 adrenergic receptors preferentially over beta-2 adrenergic receptors. The prescribing physician explained that this medication would only be used temporarily as its efficacy decreases within 2-3 days due to receptor downregulation. Which of the following was prescribed?
- A. Epinephrine
- B. Norepinephrine
- C. Milrinone
- D. Isoproterenol
- E. Dobutamine (Correct Answer)
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Dobutamine***
- **Dobutamine** is a beta-1 adrenergic agonist preferentially acting on beta-1 receptors in the heart, increasing contractility and heart rate during acute decompensated heart failure.
- Its efficacy reduces over time due to **receptor downregulation**, making it effective for only short-term use, typically less than 72 hours.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is a non-selective adrenergic agonist acting on both alpha and beta receptors, causing vasoconstriction and bronchodilation in addition to cardiac stimulation.
- It is typically used in emergency situations like **cardiac arrest** and **anaphylaxis**, not primarily for acute CHF exacerbation in this manner.
*Norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** primarily acts on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing significant vasoconstriction, and has some beta-1 agonistic effects.
- It is mainly used as a **vasopressor** in septic shock or severe hypotension to increase systemic vascular resistance, rather than directly improving cardiac output in decompensated CHF.
*Milrinone*
- **Milrinone** is a phosphodiesterase-3 inhibitor, increasing intracellular cAMP levels and leading to positive inotropy and vasodilation.
- While used in acute heart failure, its mechanism is distinct from adrenergic agonists, and its efficacy is not limited by a rapid receptor downregulation mechanism as described.
*Isoproterenol*
- **Isoproterenol** is a non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist, stimulating both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, leading to increased heart rate and contractility, as well as bronchodilation and vasodilation.
- Due to its strong chronotropic effects and potential for severe arrhythmias and hypotension, it is rarely used in CHF and is primarily reserved for conditions like **bradycardia** or **torsades de pointes**.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of intermittent palpitations that occur when he is stressed, exercising, or when he drinks alcohol. Physical examination shows an irregularly irregular pulse. An ECG shows irregular QRS complexes without any discrete P waves. Pharmacotherapy with carvedilol is initiated for his condition. Compared to treatment with propranolol, which of the following adverse effects is most likely?
- A. Bradycardia
- B. Bronchospasm
- C. Hyperkalemia
- D. Hypotension (Correct Answer)
- E. Hyperglycemia
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Hypotension***
- **Carvedilol** is a non-selective beta-blocker with additional **alpha-1 adrenergic receptor blocking activity**, which leads to peripheral vasodilation and a greater potential for **hypotension** compared to propranolol (a pure beta-blocker).
- The **alpha-1 blockade** causes a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance, leading to a more pronounced decrease in blood pressure.
*Bradycardia*
- Both carvedilol and propranolol are beta-blockers and can cause **bradycardia** by reducing heart rate.
- However, the question asks for an adverse effect **more likely** with carvedilol compared to propranolol, and while both can cause bradycardia, carvedilol's additional alpha-blocking activity makes hypotension more distinguishing.
*Bronchospasm*
- Both carvedilol and propranolol are **non-selective beta-blockers** (blocking both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors) and can cause **bronchospasm** by blocking beta-2 receptors in the bronchi.
- Therefore, this adverse effect is common to both and not more likely with carvedilol specifically in comparison to propranolol.
*Hyperkalemia*
- Neither carvedilol nor propranolol is directly associated with causing **hyperkalemia** as a primary adverse effect.
- Beta-blockers can sometimes lead to minor shifts in potassium, but it's not a common or more significant side effect compared to others listed.
*Hyperglycemia*
- **Non-selective beta-blockers** like propranolol can impair the recovery from **hypoglycemia** and mask its symptoms.
- While beta-blockers can have some metabolic effects, **hyperglycemia** is not a generally recognized or more prominent adverse effect of carvedilol compared to propranolol.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 8: A 75-year-old male arrives by ambulance to the emergency room severely confused. His vitals are T 40 C, HR 120 bpm, BP 80/55 mmHg, RR 25. His wife explains that he injured himself about a week ago while cooking, and several days later his finger became infected, oozing with pus. He ignored her warning to see a doctor and even refused after he developed fever, chills, and severe fatigue yesterday. After being seen by the emergency physician, he was given antibiotics and IV fluids. Following initial resuscitation with IV fluids, he remains hypotensive. The ED physicians place a central venous catheter and begin infusing norepinephrine. Which of the following receptors are activated by norepinephrine?
- A. Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1, Beta 2
- B. Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Alpha 2
- D. Alpha 1, Beta 1, Dopamine 1
- E. Alpha 1, Beta 1
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1***
- **Norepinephrine** primarily activates **alpha-1** (peripheral vasoconstriction), **alpha-2** (presynaptic inhibition and some vasoconstriction), and **beta-1** (increased heart rate and contractility) adrenergic receptors.
- These are the **primary receptors** responsible for norepinephrine's clinical effects: vasoconstriction (alpha-1, alpha-2) and positive inotropic/chronotropic effects (beta-1).
- This receptor profile makes norepinephrine an ideal **vasopressor** in septic shock, as seen in this patient.
*Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1, Beta 2*
- While **norepinephrine** does activate alpha-1, alpha-2, and beta-1 receptors, it has **negligible affinity for beta-2 receptors**.
- **Epinephrine** (not norepinephrine) is the catecholamine with significant **beta-2 activity**, causing bronchodilation and vasodilation in skeletal muscle.
- Including beta-2 is a common mistake when confusing norepinephrine with epinephrine.
*Alpha 2*
- This option is far too incomplete as **norepinephrine** has significant action on **alpha-1** and **beta-1** receptors, which are crucial for its vasoconstrictive and inotropic effects.
- Activating only alpha-2 receptors would primarily lead to presynaptic inhibition and limited vasoconstriction, not the broad cardiovascular support required in septic shock.
*Alpha 1, Beta 1, Dopamine 1*
- While **norepinephrine** does activate **alpha-1** and **beta-1** receptors, it does **not** activate **dopamine 1 (D1) receptors**.
- Only **dopamine** itself or specific **dopamine agonists** stimulate D1 receptors, leading to renal and mesenteric vasodilation.
- This option incorrectly attributes dopaminergic activity to norepinephrine.
*Alpha 1, Beta 1*
- This option correctly identifies two of the main receptors activated by **norepinephrine**: alpha-1 (vasoconstriction) and beta-1 (positive inotropy and chronotropy).
- However, it **omits alpha-2 receptors**, which norepinephrine also activates, contributing to both presynaptic feedback inhibition and additional vasoconstriction.
- While not completely wrong, this is an incomplete answer.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 9: Match the following:
Column A:
a. Beta 1
b. Beta 2
c. Beta 3
Column B:
1. Mirabegron
2. Betaxolol
3. Salbutamol
- A. a-2, b-3 ,c-1 (Correct Answer)
- B. a-2, b-1, c-3
- C. a-3, b-2, c-1
- D. a-3, b-1, c-2
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***a-2, b-3, c-1***
- This pairing correctly matches **Betaxolol** with **Beta 1 selective** antagonism, **Salbutamol** with **Beta 2 selective** agonism, and **Mirabegron** with **Beta 3 selective** agonism.
- **Betaxolol** is a beta-1 selective adrenergic receptor antagonist, primarily used in ophthalmology to reduce intraocular pressure and as an antihypertensive. **Salbutamol** is a selective beta-2 adrenergic agonist used as a bronchodilator in asthma and COPD, causing relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle. **Mirabegron** is a selective beta-3 adrenergic agonist used to treat overactive bladder by relaxing the detrusor muscle.
*a-2, b-1, c-3*
- This option incorrectly assigns **Mirabegron** to Beta 2. Mirabegron is a **Beta 3 selective agonist**.
- It also incorrectly assigns **Salbutamol** to Beta 3. Salbutamol is a **Beta 2 selective agonist**.
*a-3, b-2, c-1*
- This option incorrectly assigns **Salbutamol** to Beta 1. Salbutamol is a **Beta 2 selective agonist**.
- It also incorrectly assigns **Betaxolol** to Beta 2. Betaxolol is a **Beta 1 selective antagonist**.
*a-3, b-1, c-2*
- This option incorrectly assigns **Salbutamol** to Beta 1 and **Betaxolol** to Beta 3.
- **Salbutamol** is a Beta 2 selective agonist, and **Betaxolol** is a Beta 1 selective antagonist.
Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG Question 10: A high-throughput screen to identify new sympathomimetic compounds was developed such that a transgenic line of cells was created that contained the alpha-1 (red), alpha-2 (yellow), beta-1 (green) and beta-2 (blue) receptors. When each of the receptors was activated a different fluorescent protein was expressed and new compounds with different properties could be identified by the fluorescence that they induced. Compound 7583 selectively induced the expression of the blue fluorescent protein. Which of the following known sympathomimetic medications if administered would similarly result in expression of only the blue fluorescent protein?
- A. Albuterol (Correct Answer)
- B. Fenoldopam
- C. Epinephrine
- D. Isoproterenol
- E. Midodrine
Alpha-adrenergic agonists Explanation: ***Albuterol***
- The blue fluorescent protein is expressed upon activation of the **beta-2 receptor**. Albuterol is a **selective beta-2 adrenergic agonist**.
- Its primary clinical use is as a **bronchodilator** in asthma and COPD, acting by relaxing bronchial smooth muscle via beta-2 receptor activation.
*Fenoldopam*
- Fenoldopam is a **D1 dopamine receptor agonist** used as a rapid-acting vasodilator.
- It has **no significant direct activity** at adrenergic alpha or beta receptors.
*Epinephrine*
- Epinephrine is a **non-selective adrenergic agonist** that activates alpha-1, alpha-2, beta-1, and beta-2 receptors.
- It would induce the expression of **all four fluorescent proteins** (red, yellow, green, and blue).
*Isoproterenol*
- Isoproterenol is a **non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist**, activating both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors.
- It would induce the expression of **green and blue fluorescent proteins**, but not exclusively blue.
*Midodrine*
- Midodrine is a **selective alpha-1 adrenergic agonist** and would induce the expression of the **red fluorescent protein**.
- It is primarily used to treat **orthostatic hypotension** by causing vasoconstriction.
More Alpha-adrenergic agonists US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.