Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Positive inotropic agents. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 1: An 82-year-old male with congestive heart failure experiences rapid decompensation of his condition, manifesting as worsening dyspnea, edema, and increased fatigue. Labs reveal an increase in his serum creatinine from baseline. As part of the management of this acute change, the patient is given IV dobutamine to alleviate his symptoms. Which of the following effects occur as a result of this therapy?
- A. Decreased cardiac contractility
- B. Decreased heart rate
- C. Increased myocardial oxygen consumption (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased systemic vascular resistance due to systemic vasoconstriction
- E. Slowed atrioventricular conduction velocities
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Increased myocardial oxygen consumption***
- Dobutamine is a **beta-1 adrenergic agonist** that increases **myocardial contractility** and **heart rate**.
- This enhanced cardiac workload directly leads to an **increased demand for oxygen** by the heart muscle.
*Decreased cardiac contractility*
- Dobutamine is primarily used in heart failure to **increase cardiac contractility** (positive inotropic effect), thus improving cardiac output.
- Decreased contractility would worsen the patient's condition, which is contrary to the therapeutic goal of dobutamine.
*Decreased heart rate*
- Dobutamine, through its beta-1 agonism, typically causes an **increase in heart rate**, not a decrease.
- A decreased heart rate would further compromise cardiac output in a decompensated heart failure patient.
*Increased systemic vascular resistance due to systemic vasoconstriction*
- Dobutamine has a relatively weak effect on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, and its primary action is to cause **vasodilation**, which tends to **decrease systemic vascular resistance**.
- While other inotropes like norepinephrine can cause vasoconstriction, dobutamine's effect on SVR is generally minimal or mildly vasodilatory, which helps to reduce afterload.
*Slowed atrioventricular conduction velocities*
- Beta-1 agonists like dobutamine generally tend to **increase atrioventricular (AV) conduction velocity** and can even precipitate arrhythmias.
- Slowed AV conduction is characteristic of drugs like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers, which would be contraindicated in this setting.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 2: A 65-year-old male with a history of CHF presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath, lower leg edema, and fatigue. He is diagnosed with acute decompensated congestive heart failure, was admitted to the CCU, and treated with a medication that targets beta-1 adrenergic receptors preferentially over beta-2 adrenergic receptors. The prescribing physician explained that this medication would only be used temporarily as its efficacy decreases within 2-3 days due to receptor downregulation. Which of the following was prescribed?
- A. Epinephrine
- B. Norepinephrine
- C. Milrinone
- D. Isoproterenol
- E. Dobutamine (Correct Answer)
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Dobutamine***
- **Dobutamine** is a beta-1 adrenergic agonist preferentially acting on beta-1 receptors in the heart, increasing contractility and heart rate during acute decompensated heart failure.
- Its efficacy reduces over time due to **receptor downregulation**, making it effective for only short-term use, typically less than 72 hours.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is a non-selective adrenergic agonist acting on both alpha and beta receptors, causing vasoconstriction and bronchodilation in addition to cardiac stimulation.
- It is typically used in emergency situations like **cardiac arrest** and **anaphylaxis**, not primarily for acute CHF exacerbation in this manner.
*Norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** primarily acts on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing significant vasoconstriction, and has some beta-1 agonistic effects.
- It is mainly used as a **vasopressor** in septic shock or severe hypotension to increase systemic vascular resistance, rather than directly improving cardiac output in decompensated CHF.
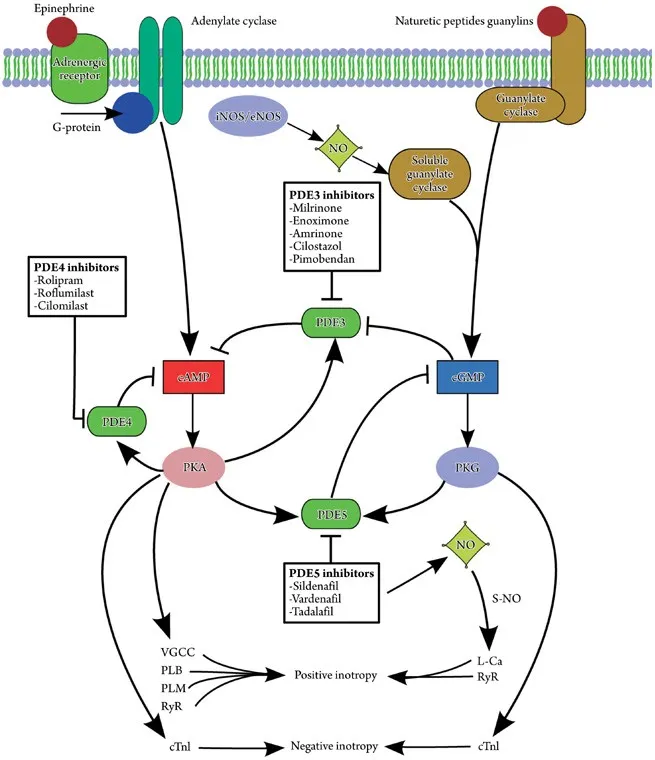
*Milrinone*
- **Milrinone** is a phosphodiesterase-3 inhibitor, increasing intracellular cAMP levels and leading to positive inotropy and vasodilation.
- While used in acute heart failure, its mechanism is distinct from adrenergic agonists, and its efficacy is not limited by a rapid receptor downregulation mechanism as described.
*Isoproterenol*
- **Isoproterenol** is a non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist, stimulating both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, leading to increased heart rate and contractility, as well as bronchodilation and vasodilation.
- Due to its strong chronotropic effects and potential for severe arrhythmias and hypotension, it is rarely used in CHF and is primarily reserved for conditions like **bradycardia** or **torsades de pointes**.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old man is admitted to the intensive care unit with confusion and severe dyspnea at rest which started 3 hours ago. The symptoms worsen when the patient lies down and improve in the sitting position. The patient has a history of cocaine abuse. The patient's blood pressure is 75/50 mm Hg, the heart rate is 95/min, the respiratory rate is 22/min, the temperature is 36.5℃ (97.7℉), and the SpO2 is 89% on room air. On physical examination, there is peripheral cyanosis with pallor, coldness of the extremities, diaphoresis, and marked peripheral veins distension. Lung auscultation reveals bilateral absence of the lung sounds over the lower lobes and widespread rales over the other lung fields. On cardiac auscultation, there is a protodiastolic gallop and S2 accentuation best heard in the second intercostal space at the left sternal border. Abdominal palpation shows signs of intraperitoneal fluid accumulation and hepatomegaly. Considering the low cardiac output, milrinone is administered as an inotropic agent. What is the most likely side effect which can result from administration of milrinone?
- A. Asystole
- B. Third grade AV-blockade
- C. Ventricular arrhythmias (Correct Answer)
- D. Supraventricular arrhythmia
- E. QT-prolongation
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Ventricular arrhythmias***
- **Milrinone** is a positive inotropic agent and vasodilator used in severe heart failure; it **increases cardiac contractility** and **reduces afterload**.
- Its mechanism of action, phosphodiesterase (PDE-3) inhibition, can increase intracellular cAMP in cardiomyocytes, raising the risk of **ventricular arrhythmias**, particularly in patients with pre-existing heart conditions or electrolyte imbalances.
*Asystole*
- While milrinone can have significant cardiovascular effects, **asystole** (complete cessation of electrical and mechanical activity of the heart) is not a common or direct side effect.
- Asystole is typically associated with conditions like severe myocardial ischemia, advanced conduction system disease, or terminal stages of shock.
*Third grade AV-blockade*
- **Third-degree AV block** involves complete dissociation between atrial and ventricular electrical activity.
- Milrinone's primary action is to increase contractility and vasodilation; it does not directly interfere with the **AV node conduction** in a way that would commonly cause complete heart block.
*Supraventricular arrhythmia*
- While milrinone can cause various rhythm disturbances due to increased **cAMP levels** and myocardial excitability, **supraventricular arrhythmias** (like atrial fibrillation or flutter) are less commonly reported as a primary side effect compared to ventricular arrhythmias.
- The direct effect on ventricular excitability is more pronounced.
*QT-prolongation*
- **QT prolongation** can lead to torsades de pointes and other ventricular arrhythmias, but milrinone itself is not typically listed as a drug that directly causes significant QT prolongation.
- Medications that block **potassium channels** are more commonly associated with this side effect.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 4: A 77-year-old man with refractory shock has been under treatment in an intensive care unit for last 7 days. Despite the best possible management by the team of physicians and intensivists, he fails to show improvement. After discussion with his relatives and obtaining informed consent from them, the team administers to him a novel drug, an adrenergic agonist that produces positive chronotropic effects and inotropic effects and stimulates the release of renin from the kidneys. The drug does not have any other adrenergic effects. Which of the following second messengers is most likely to be responsible for the actions of the novel drug?
- A. Calcium ion
- B. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) (Correct Answer)
- C. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
- D. Diacylglycerol (DAG)
- E. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3)
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: **Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)**
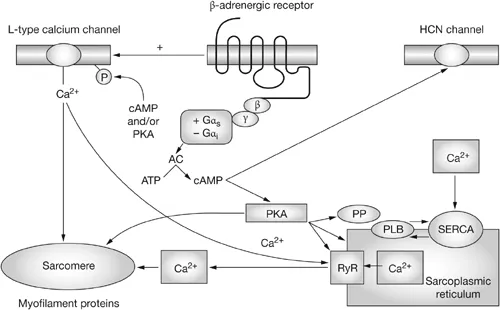
- The drug described is an **adrenergic agonist** with **positive chronotropic** and **inotropic effects**, and it stimulates **renin release**. These actions are characteristic of **beta-1 (β1) adrenergic receptor** activation.
- Activation of β1 receptors is coupled to **G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)** that activate **adenylyl cyclase**, leading to an increase in intracellular **cAMP**, which acts as the second messenger.
*Calcium ion*
- While **calcium ions** are crucial for cardiac contractility and renin release, they are often directly modulated downstream by events initiated by second messengers like **cAMP** or **IP3/DAG**, rather than being the primary direct second messenger for β1-adrenergic stimulation.
- For example, increased cAMP in cardiac cells leads to **phosphorylation of L-type calcium channels**, increasing calcium influx, but cAMP itself is the direct initiating second messenger.
*Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)*
- **cGMP** is typically associated with pathways activated by **nitric oxide** and **natriuretic peptides**, leading to vasodilation and smooth muscle relaxation, which are not the primary effects described for this drug.
- Drugs that activate **guanylyl cyclase** to increase cGMP would generally have opposite effects to the cardiotonic and renin-releasing actions mentioned.
*Diacylglycerol (DAG)*
- **DAG** is a second messenger produced along with **IP3** by the activation of **phospholipase C**, typically initiated by **alpha-1 (α1) adrenergic receptors** or other Gq-coupled GPCRs.
- α1 adrenergic activation causes **vasoconstriction** and other effects, which are distinct from the positive chronotropic and inotropic actions of a β1 agonist.
*Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3)*
- **IP3** is generated alongside **DAG** through the activation of **phospholipase C**, following the binding of agonists to **Gq-coupled receptors** like the α1 adrenergic receptor.
- Its primary role is to trigger the release of **calcium from intracellular stores**, which, while important for muscle contraction, is not the direct second messenger pathway for the described β1-adrenergic actions.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 5: An 82-year-old male with a history of congestive heart failure presented with new-onset atrial fibrillation. He was initially started on carvedilol, but he now requires an additional agent for rate control. He is started on a medicine and is warned by his physician of the following potential side effects associated with this therapy: nausea, vomiting, confusion, blurry yellow vision, electrolyte abnormalities, and potentially fatal arrhythmia. Which of the following is most likely to increase this patient's susceptibility to the toxic effects associated with this medication?
- A. Hyperkalemia
- B. Elevated AST and ALT
- C. Increased GFR with normal creatinine
- D. Hypokalemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Hyponatremia
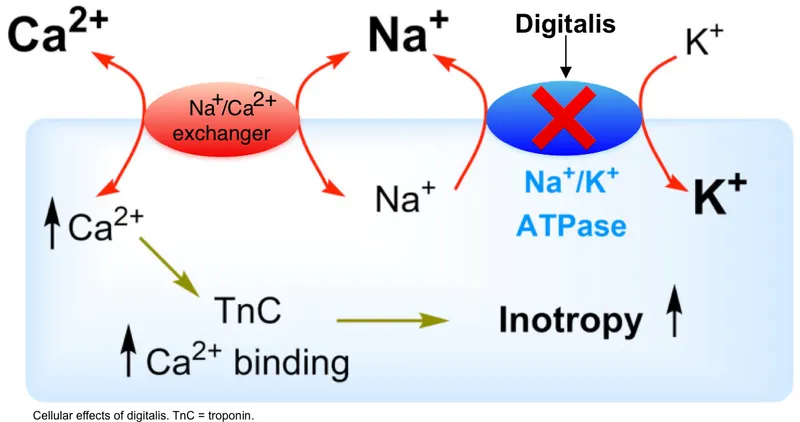
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Hypokalemia***
- The symptoms described (nausea, vomiting, confusion, blurry yellow vision, potentially fatal arrhythmias) are classic for **digoxin toxicity**.
- **Hypokalemia** increases the binding of digoxin to the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump**, exacerbating its effects and increasing the risk of toxicity.
*Hyperkalemia*
- **Hyperkalemia** actually **inhibits** digoxin binding to the Na+/K+-ATPase pump.
- This can reduce the therapeutic efficacy and the toxic effects of digoxin.
*Elevated AST and ALT*
- Elevated AST and ALT indicate **liver dysfunction**, which can affect the metabolism of certain drugs.
- However, digoxin is primarily eliminated by the **kidneys**, so liver enzyme abnormalities are not a primary risk factor for digoxin toxicity.
*Increased GFR with normal creatinine*
- An increased **Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)** would lead to more rapid renal clearance of digoxin.
- This would **decrease** the risk of digoxin accumulation and toxicity, rather than increase it.
*Hyponatremia*
- While electrolyte imbalances can be associated with cardiac conditions, **hyponatremia** itself does not directly increase the susceptibility to digoxin toxicity.
- The most critical electrolyte imbalance for digoxin toxicity is **hypokalemia**.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 6: A previously healthy 52-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of chest pain on exertion. She takes no medications. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Cardiac stress ECG shows inducible ST-segment depressions in the precordial leads that coincide with the patient's report of chest pain and resolve upon cessation of exercise. Pharmacotherapy with verapamil is initiated. This drug is most likely to have which of the following sets of effects?
$$$ End-diastolic volume (EDV) %%% Blood pressure (BP) %%% Contractility %%% Heart rate (HR) $$$
- A. No change no change no change no change
- B. ↓ ↓ no change ↑
- C. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↑
- D. ↓ ↓ ↓ no change
- E. ↑ ↓ ↓ ↓ (Correct Answer)
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***↑ ↓ ↓ ↓***
- **Verapamil**, a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker**, reduces **cardiac contractility**, leading to decreased **heart rate** and **blood pressure**, while increasing **end-diastolic volume**.
- Its therapeutic effect in **exertional angina** is primarily due to reduced myocardial oxygen demand, achieved by decreasing **heart rate**, **contractility** (both leading to reduced work of heart), and **afterload** (due to vasodilation which decreases blood pressure).
*No change no change no change no change*
- This option is incorrect because verapamil has significant **pharmacological effects** on the cardiovascular system.
- Verapamil is prescribed to treat the patient's symptoms, implying a need for **hemodynamic changes**, not stasis.
*↓ ↓ no change ↑*
- Verapamil typically **decreases heart rate** due to its action on the sinoatrial (SA) node, making an increase unlikely.
- While it decreases **blood pressure** and **contractility**, the absence of an effect on heart rate and an increase in heart rate are inconsistent with verapamil's known pharmacology.
*↓ ↓ ↓ ↑*
- This option incorrectly suggests an **increase in heart rate**, whereas verapamil is known to cause a dose-dependent **decrease in heart rate**.
- The other parameters (decreased EDV, BP, contractility) are also not fully aligned with verapamil's effects; EDV tends to increase due to better filling time and reduced contractility.
*↓ ↓ ↓ no change*
- This option suggests a **decrease in EDV**, which is generally incorrect; verapamil tends to allow for **increased ventricular filling** due to a reduced heart rate and prolonged diastole.
- The absence of a change in heart rate is also incorrect, as verapamil is a known **negative chronotropic agent**.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 7: A 78-year-old male comes to the physician’s office for a routine check-up. He complains of increased lower extremity swelling, inability to climb the one flight of stairs in his home, and waking up in the middle of the night 2-3 times gasping for breath. He has had to increase the number of pillows on which he sleeps at night. These symptoms started 9 months ago and have been progressing. The doctor starts him on a medication regimen, one of which changes his Starling curve from A to B as shown in the Figure. Which of the following medications is most consistent with this mechanism of action?
- A. Aspirin
- B. Furosemide
- C. Digoxin (Correct Answer)
- D. Metoprolol
- E. Hydrochlorothiazide
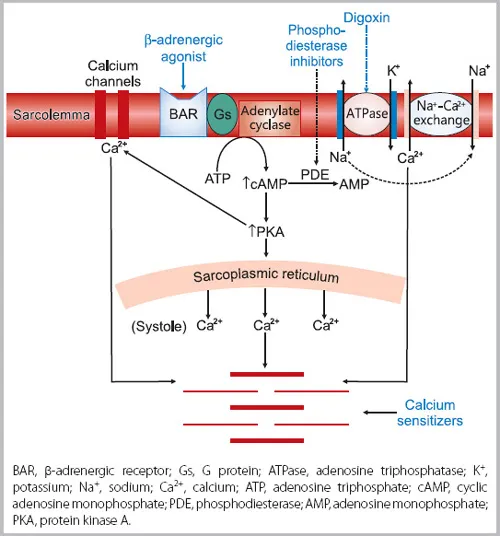
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Digoxin***
- The patient's symptoms (lower extremity swelling, dyspnea on exertion, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea) are highly suggestive of **congestive heart failure (CHF)**.
- The Starling curve shifts from **A to B** with the medication, indicating an increase in stroke volume for a given left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, which is characteristic of an **inotropic effect**.
- **Digoxin** is a positive inotropic agent that increases cardiac contractility by inhibiting Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase, leading to increased intracellular calcium.
*Aspirin*
- Aspirin is an antiplatelet agent used for cardiovascular disease prevention, but it does not directly alter the Starling curve in the manner shown by improving cardiac contractility.
- It would not improve the symptoms of heart failure by increasing stroke volume.
*Furosemide*
- Furosemide is a loop diuretic that reduces preload (LV end-diastolic pressure) but does not directly improve cardiac contractility.
- On the Starling curve, a diuretic would shift the operating point to the left, not upward as shown from A to B.
*Metoprolol*
- Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that reduces heart rate and myocardial oxygen demand and can improve mortality in CHF, but it is a **negative inotrope**, reducing contractility acutely.
- It would not cause an immediate upward shift in the Starling curve representing increased stroke volume.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic that reduces preload by increasing sodium and water excretion, similar to furosemide but less potent.
- It would cause a leftward shift on the Starling curve, not an upward shift indicating improved contractility.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 8: A 63-year-old woman presents with dyspnea on exertion. She reports that she used to work in her garden without any symptoms, but recently she started to note dyspnea and fatigue after working for 20–30 minutes. She has type 2 diabetes mellitus diagnosed 2 years ago but she does not take any medications preferring natural remedies. She also has arterial hypertension and takes torsemide 20 mg daily. The weight is 88 kg and the height is 164 cm. The vital signs include: blood pressure is 140/85 mm Hg, heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, and the temperature is 36.6℃ (97.9℉). Physical examination is remarkable for increased adiposity, pitting pedal edema, and present S3. Echocardiography shows a left ventricular ejection fraction of 51%. The combination of which of the following medications would be a proper addition to the patient’s therapy?
- A. Metoprolol and indapamide
- B. Enalapril and bisoprolol (Correct Answer)
- C. Spironolactone and fosinopril
- D. Indapamide and amlodipine
- E. Valsartan and spironolactone
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Enalapril and bisoprolol***
- This patient presents with **heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)**, characterized by symptoms of heart failure (dyspnea, fatigue, edema, S3 sound) with an LVEF >50%. She also has **uncontrolled hypertension** (BP 140/85) and a **heart rate of 90/min**.
- **Important:** Unlike HFrEF, **ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers have NOT demonstrated mortality benefit in HFpEF** (CHARM-Preserved, PEP-CHF trials). However, they remain important for **blood pressure control** and **symptom management** in patients with HFpEF and comorbid hypertension.
- **Enalapril** (ACE inhibitor) helps control blood pressure through reduction of preload and afterload. **Bisoprolol** (beta-blocker) provides **heart rate control** (patient's HR is 90/min) and further blood pressure reduction. Both medications address her inadequately controlled hypertension while managing symptoms.
- **Note:** Current guidelines emphasize SGLT2 inhibitors as first-line therapy for HFpEF (not offered here), along with diuretics for volume management (patient is already on torsemide) and aggressive treatment of comorbidities like hypertension and diabetes.
*Metoprolol and indapamide*
- Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that could help with rate and blood pressure control. However, **indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic** that is redundant since the patient is already on **torsemide** (a loop diuretic) for volume management.
- This combination lacks an **ACE inhibitor or ARB** for optimal blood pressure control and neurohormonal modulation, which is important even in HFpEF for managing hypertension and its consequences.
*Spironolactone and fosinopril*
- **Spironolactone** (mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist) showed modest benefit in reducing HF hospitalizations in the TOPCAT trial for HFpEF. **Fosinopril** is an ACE inhibitor appropriate for blood pressure control.
- However, the patient has a **heart rate of 90/min**, indicating need for **rate control** which neither spironolactone nor fosinopril provides. A **beta-blocker would be more appropriate** to address both rate control and blood pressure.
- Additionally, while spironolactone has some evidence in HFpEF, the combination with an ACE inhibitor **without rate control** is suboptimal for this patient's presentation.
*Indapamide and amlodipine*
- **Indapamide** (thiazide-like diuretic) is **redundant** since the patient is already on torsemide. **Amlodipine** (calcium channel blocker) is effective for hypertension but can cause **peripheral edema**, which this patient already has (pitting pedal edema).
- **Calcium channel blockers are not recommended in heart failure** due to lack of mortality benefit and potential to worsen fluid retention. This combination does not address the underlying HFpEF pathophysiology or provide optimal symptom management.
*Valsartan and spironolactone*
- **Valsartan** (ARB) is appropriate for blood pressure control and is an alternative to ACE inhibitors. **Spironolactone** has modest evidence for reducing hospitalizations in HFpEF (TOPCAT trial).
- However, similar to the fosinopril/spironolactone combination, this lacks a **beta-blocker for heart rate control** (patient's HR is 90/min). Rate control is important for optimizing diastolic filling time in HFpEF and controlling blood pressure.
- While this combination has theoretical benefits, **enalapril and bisoprolol** better addresses both blood pressure control and rate control simultaneously.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old male is hospitalized for acute heart failure. The patient has a 20-year history of alcoholism and was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2) 5 years ago. Physical examination reveals ascites and engorged paraumbilical veins as well as 3+ pitting edema around both ankles. Liver function tests show elevations in gamma glutamyl transferase and aspartate transaminase (AST). Of the following medication, which most likely contributed to this patient's presentation?
- A. Glargine
- B. Pramlintide
- C. Pioglitazone (Correct Answer)
- D. Glipizide
- E. Metformin
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Pioglitazone***
- **Pioglitazone**, a thiazolidinedione, is known to cause **fluid retention** and can exacerbate or precipitate **congestive heart failure**.
- The patient's presentation with **ascites**, **pitting edema**, and **acute heart failure** is consistent with the adverse effects of this medication, especially in a patient with risk factors like alcoholism.
*Glargine*
- **Glargine** is a **long-acting insulin** analog primarily used to control blood glucose levels in diabetes.
- It does not typically cause **fluid retention** or worsen **heart failure** directly, making it an unlikely contributor to these specific symptoms.
*Pramlintide*
- **Pramlintide** is an **amylin analog** used to improve glycemic control by slowing gastric emptying and suppressing glucagon secretion.
- It is not associated with **fluid retention** or the exacerbation of **heart failure**.
*Glipizide*
- **Glipizide** is a **sulfonylurea** that stimulates insulin release from pancreatic beta cells.
- While it can cause hypoglycemia, it does not typically contribute to **fluid retention** or worsen **heart failure**.
*Metformin*
- **Metformin** is a **biguanide** that reduces hepatic glucose production and increases insulin sensitivity.
- It is generally considered **cardioprotective** and does not cause **fluid retention** or exacerbate **heart failure**.
Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG Question 10: A 39-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of fatigue, decreased sexual desire, and difficulty achieving an erection. He has no past medical history except for a traumatic brain injury he sustained in a motor vehicle accident 4 months ago. At that time, neuroimaging studies showed no abnormalities. Physical examination shows bilateral gynecomastia and a thin white nipple discharge. Decreased production of which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's current condition?
- A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- B. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
- C. Luteinizing hormone
- D. Growth hormone
- E. Dopamine (Correct Answer)
Positive inotropic agents Explanation: ***Dopamine***
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, decreased sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, gynecomastia, galactorrhea) following a **traumatic brain injury (TBI)** are indicative of **hypopituitarism**, specifically affecting dopamine's inhibitory control over prolactin.
- **Dopamine** is produced in the hypothalamus and tonically inhibits **prolactin secretion** from the anterior pituitary; a decrease in dopamine can lead to elevated prolactin, causing the observed symptoms.
*Gonadotropin-releasing hormone*
- While TBI can cause **hypogonadism** due to GnRH deficiency, this would primarily lead to decreased LH/FSH and subsequent low testosterone, causing sexual dysfunction but not necessarily **galactorrhea** or **gynecomastia**.
- Decreased GnRH would result in low levels of LH and FSH, but the direct cause of gynecomastia and nipple discharge in this case is likely **hyperprolactinemia**.
*Thyrotropin-releasing hormone*
- TRH stimulates TSH release; a deficiency would lead to **central hypothyroidism** (fatigue, cold intolerance, weight gain), but it does not directly explain **gynecomastia** or **galactorrhea**.
- While TRH can stimulate prolactin secretion, a primary TRH deficiency would more prominently feature symptoms of hypothyroidism, which are not mentioned as the primary concern.
*Luteinizing hormone*
- A decrease in LH would lead to **decreased testosterone production** and symptoms like low sexual desire and erectile dysfunction. However, it does not directly cause **galactorrhea** or **gynecomastia** as seen in this patient.
- LH primarily acts on Leydig cells to produce testosterone; while low testosterone can cause gynecomastia, the nipple discharge points more strongly to **hyperprolactinemia**.
*Growth hormone*
- Growth hormone deficiency in adults can cause fatigue, decreased muscle mass, and central obesity but is not typically associated with **gynecomastia** or **galactorrhea**.
- A decrease in GH does not explain the breast-related symptoms observed in this patient.
More Positive inotropic agents US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.