Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cardiac glycosides. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 1: An experimental infusable drug, X729, is currently being studied to determine its pharmacokinetics. The drug was found to have a half life of 1.5 hours and is eliminated by first order kinetics. What is the minimum number of hours required to reach a steady state concentration of >90%?
- A. 6 (Correct Answer)
- B. 3
- C. 7.5
- D. 1.5
- E. 4.5
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***6***
- For a drug eliminated by **first-order kinetics**, approximately **4 to 5 half-lives** are required to reach **steady-state concentration**.
- To reach >90% of steady-state, at least **4 half-lives** are needed, where **93.75%** of the steady state is achieved.
- The time taken would be **4 half-lives × 1.5 hours/half-life = 6 hours**, making this the **minimum time** to exceed 90%.
*3*
- This represents only **2 half-lives** (2 × 1.5 hours = 3 hours), which would achieve roughly **75%** of the steady-state concentration.
- This is insufficient to reach >90% of the steady-state concentration.
*7.5*
- This time point represents **5 half-lives** (5 × 1.5 hours = 7.5 hours), which would achieve approximately **97%** of the steady-state concentration.
- While this does exceed 90%, the question asks for the **minimum** number of hours required, and 90% is already exceeded at 6 hours (4 half-lives).
*1.5*
- This is only **1 half-life**, which would achieve approximately **50%** of the steady-state concentration.
- This is far too early to reach a >90% steady-state concentration.
*4.5*
- This represents **3 half-lives** (3 × 1.5 hours = 4.5 hours), achieving approximately **87.5%** of the steady-state concentration.
- While close to 90%, it does not quite reach "greater than 90%".
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old male with a history of congestive heart failure and hypertension comes to you with the chief complaint of new-onset cough as well as increased serum potassium in the setting of a new medication. Which of the following medications is most likely responsible for these findings?
- A. Lisinopril (Correct Answer)
- B. Metoprolol
- C. Furosemide
- D. Amiodarone
- E. Digoxin
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Lisinopril***
- **Lisinopril** is an ACE inhibitor, which can cause a **persistent dry cough** due to the accumulation of bradykinin.
- ACE inhibitors can also cause **hyperkalemia** by inhibiting aldosterone secretion, which normally promotes potassium excretion.
*Metoprolol*
- **Metoprolol** is a beta-blocker that primarily decreases heart rate and blood pressure; it is not typically associated with cough or hyperkalemia.
- While it can be used in CHF, its common side effects include bradycardia and fatigue, not the described symptoms.
*Furosemide*
- **Furosemide** is a loop diuretic that promotes potassium excretion, leading to **hypokalemia**, not hyperkalemia.
- It does not typically cause cough; instead, it can help reduce fluid accumulation in the lungs associated with CHF.
*Amiodarone*
- **Amiodarone** is an antiarrhythmic drug known for several significant side effects, including **pulmonary fibrosis** (which can cause cough) and thyroid dysfunction.
- However, it does not typically cause hyperkalemia; instead, it can cause changes in electrolyte levels, but not the specific combination seen here.
*Digoxin*
- **Digoxin** is a cardiac glycoside used to increase cardiac contractility and slow heart rate in heart failure and arrhythmias.
- It does not typically cause cough or hyperkalemia; its toxicity is often associated with nausea, visual disturbances, and arrhythmias.
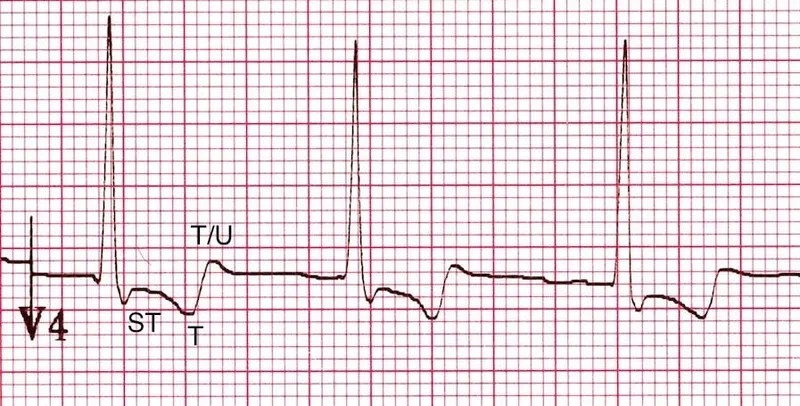
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 3: A 53-year-old man with obesity and heart disease presents to your outpatient clinic with complaints of orthopnea, significant dyspnea on minimal exertion, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. He says that his old doctor gave him "some pills" that he takes in varying amounts every morning. Physical exam is significant for a severely displaced point of maximal impulse, bilateral rales in the lower lung fields, an S3 gallop, and hepatomegaly. You decide to perform an EKG (shown in figure A). Suddenly, his rhythm changes to ventricular tachycardia followed by ventricular fibrillation, and he syncopizes and expires despite resuscitative efforts. High levels of which medication are most likely responsible?
- A. Propranolol
- B. Amiodarone
- C. Lidocaine
- D. Verapamil
- E. Digoxin (Correct Answer)
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Digoxin***
- The patient's presentation with **heart failure** symptoms (dyspnea, orthopnea, rales, S3 gallop, hepatomegaly) and erratic self-dosing of "some pills" strongly suggests **digoxin toxicity**.
- **Gastrointestinal symptoms** (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) are common initial signs of digoxin toxicity, and the progression to **ventricular tachycardia** and **ventricular fibrillation** is consistent with severe digitalis-induced arrhythmia.
*Propranolol*
- This is a **beta-blocker** primarily used for hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias.
- While overdose can cause bradycardia, hypotension, and heart block, it typically does not lead to **ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation** as seen in this case.
*Amiodarone*
- This is a **Class III antiarrhythmic** medication with a long half-life, used for various tachyarrhythmias.
- Though it can cause many side effects, including proarrhythmia, it is less likely to present with the classic **GI symptoms** and rapid progression to fatal ventricular arrhythmias seen here, especially in the context of erratic self-dosing and underlying heart failure.
*Lidocaine*
- This is a **Class IB antiarrhythmic** primarily used for ventricular arrhythmias, especially post-myocardial infarction.
- Toxicity typically manifests as **neurological symptoms** (drowsiness, confusion, seizures) and sometimes hypotension or bradycardia, not the wide range of GI and lethal cardiac arrhythmias described.
*Verapamil*
- This is a **calcium channel blocker** used for hypertension, angina, and supraventricular tachycardias.
- Overdose primarily causes **bradycardia, hypotension, and atrioventricular block**, but it is generally not associated with the pronounced GI symptoms or directly triggering ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation like digoxin toxicity.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 4: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of vomiting, abdominal pain, and blurry vision for the past hour. The parents report that the boy developed these symptoms after he accidentally ingested 2 tablets of his grandfather’s heart failure medication. On physical examination, the child is drowsy, and his pulse is 120/min and irregular. Digoxin toxicity is suspected. A blood sample is immediately sent for analysis and shows a serum digoxin level of 4 ng/mL (therapeutic range: 0.8–2 ng/mL). Which of the following electrolyte abnormalities is most likely to be present in the boy?
- A. Hypermagnesemia
- B. Hypokalemia
- C. Hypercalcemia
- D. Hyperkalemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypocalcemia
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Hyperkalemia***
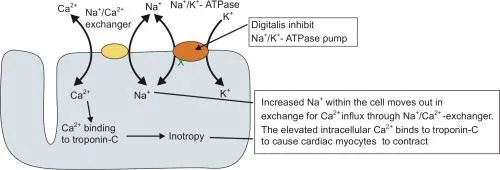
- **Digoxin** inhibits the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump**, leading to an increase in intracellular sodium and a decrease in intracellular potassium.
- The decreased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump results in reduced cellular uptake of potassium, causing **elevated extracellular potassium** levels.
*Hypermagnesemia*
- **Magnesium** is not directly affected by digoxin toxicity in a way that would lead to hypermagnesemia; in fact, hypomagnesemia can exacerbate digoxin toxicity.
- High magnesium levels are typically associated with renal failure or excessive intake of magnesium-containing antacids or laxatives.
*Hypokalemia*
- While hypokalemia can **predispose to digoxin toxicity** (by increasing digoxin binding to the Na+/K+-ATPase pump), acute digoxin overdose, as described here, often leads to **hyperkalemia** due to the direct inhibition of the pump's ability to drive potassium into cells.
- The classic association of hypokalemia with digoxin refers more to its role as a risk factor for toxicity, especially with diuretic use, rather than a direct consequence of acute overdose.
*Hypercalcemia*
- **Calcium** levels are not directly altered to hypercalcemia by digoxin toxicity.
- Digoxin's mechanism involves increasing intracellular calcium by promoting calcium influx and inhibiting its efflux via the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, but this typically does not manifest as measurable serum hypercalcemia.
*Hypocalcemia*
- Digoxin toxicity does not directly cause hypocalcemia.
- Digoxin actually leads to **increased intracellular calcium**, which is responsible for its positive inotropic effect, but this change is primarily intracellular and does not result in systemic hypocalcemia.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 5: A scientist is studying the excretion of a novel toxin X by the kidney in order to understand the dynamics of this new substance. He discovers that this new toxin X has a clearance that is half that of inulin in a particular patient. This patient's filtration fraction is 20% and his para-aminohippuric acid (PAH) dynamics are as follows:
Urine volume: 100 mL/min
Urine PAH concentration: 30 mg/mL
Plasma PAH concentration: 5 mg/mL
Given these findings, what is the clearance of the novel toxin X?
- A. 1,500 mL/min
- B. 600 mL/min
- C. 300 mL/min
- D. 60 mL/min (Correct Answer)
- E. 120 mL/min
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***60 ml/min***
- First, calculate the **renal plasma flow (RPF)** using PAH clearance: RPF = (Urine PAH conc. × Urine vol.) / Plasma PAH conc. = (30 mg/mL × 100 mL/min) / 5 mg/mL = 600 mL/min.
- Next, calculate the **glomerular filtration rate (GFR)**, which is the clearance of inulin. GFR = RPF × Filtration Fraction = 600 mL/min × 0.20 = 120 mL/min. Toxin X clearance is half of inulin clearance, so 120 mL/min / 2 = **60 mL/min**.
*1,500 ml/min*
- This value is likely obtained if an incorrect formula or conversion was made, possibly by misinterpreting the units or the relationship between GFR, RPF, and filtration fraction.
- It significantly overestimates the clearance for a substance that is cleared at half the rate of inulin.
*600 ml/min*
- This value represents the **renal plasma flow (RPF)**, calculated using the PAH clearance data.
- It does not account for the filtration fraction or the fact that toxin X clearance is half of inulin clearance (GFR).
*300 ml/min*
- This value would be obtained if the renal plasma flow (RPF) was incorrectly halved, or if an intermediate calculation was misinterpreted as the final answer.
- It does not align with the given filtration fraction and the relationship between toxin X and inulin clearance.
*120 ml/min*
- This value represents the **glomerular filtration rate (GFR)**, which is equal to the clearance of inulin (RPF × Filtration Fraction = 600 mL/min × 0.20 = 120 mL/min).
- The question states that the clearance of toxin X is **half** that of inulin, so this is an intermediate step, not the final answer.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 6: A 63-year-old man with a history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation is brought into the emergency room and found to have a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Ibutilide is discontinued and the patient is switched to another drug that also prolongs the QT interval but is associated with a decreased risk of torsades de pointes. Which drug was most likely administered in this patient?
- A. Esmolol
- B. Digoxin
- C. Sotalol
- D. Amiodarone (Correct Answer)
- E. Quinidine
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Amiodarone***
- **Amiodarone** prolongs the **QT interval** but has a lower risk of **torsades de pointes** compared to other **Class III antiarrhythmics** due to its mixed ion channel blocking properties and consistent action potential prolongation.
- It's a broad-spectrum **antiarrhythmic drug** effective for both **atrial** and **ventricular arrhythmias**, making it a good choice for someone with a history of **atrial fibrillation** presenting with **ventricular tachyarrhythmia**.
*Esmolol*
- **Esmolol** is a **beta-blocker** that does not prolong the **QT interval**; it is used to slow heart rate and can be used for rhythm control but not by **QT prolongation**.
- Its primary action is on **beta-1 receptors**, reducing **myocardial contractility** and **heart rate**, primarily used for acute control of **tachyarrhythmias** or **hypertensive emergencies**.
*Digoxin*
- **Digoxin** is a **cardiac glycoside** that does not prolong the **QT interval**; it primarily works by inhibiting the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump** and increasing **vagal tone**.
- It is used to control **ventricular rate** in **atrial fibrillation** and to manage **heart failure**, but it is not an **antiarrhythmic** in the sense of directly terminating **ventricular tachyarrhythmias** by affecting **QT prolongation**.
*Sotalol*
- **Sotalol** is a **beta-blocker** with **Class III antiarrhythmic properties** that prolongs the **QT interval** and has a significant **dose-related risk of torsades de pointes**, particularly at higher doses.
- While it's effective for both **ventricular** and **supraventricular arrhythmias**, its risk of **TdP** is a major concern, making **amiodarone** a safer alternative when **TdP risk** is to be minimized.
*Quinidine*
- **Quinidine** is a **Class IA antiarrhythmic** that significantly prolongs the **QT interval** and is known for a high risk of causing **torsades de pointes**.
- It primarily blocks **fast sodium channels** and also **potassium channels**, contributing to its **proarrhythmic effects** and making it a less favored option when **TdP risk** needs to be decreased.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 7: A 25-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 12 hours after ingesting 30 tablets of an unknown drug in a suicide attempt. The tablets belonged to her father, who has a chronic heart condition. She has had nausea and vomiting. She also reports blurring and yellowing of her vision. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 51/min, and blood pressure is 108/71 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows diffuse tenderness with no guarding or rebound. Bowel sounds are normal. An ECG shows prolonged PR-intervals and flattened T-waves. Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following electrolyte abnormalities?
- A. Increased serum K+ (Correct Answer)
- B. Decreased serum K+
- C. Decreased serum Na+
- D. Increased serum Na+
- E. Increased serum Ca2+
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Increased serum K+***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **digoxin toxicity**, including **nausea, vomiting, blurry and yellow vision, bradycardia**, and ECG changes like **prolonged PR interval** and **flattened T-waves**.
- **Digoxin inhibits the Na+/K+-ATPase pump**, leading to an increase in extracellular potassium as potassium cannot enter the cells.
*Decreased serum K+*
- While hypokalemia can exacerbate digoxin toxicity by increasing digoxin binding to the Na+/K+-ATPase, digoxin overdose itself typically causes **hyperkalemia** due to its direct effect on the pump.
- ECG changes like **flattened T-waves** can be seen in hypokalemia, but the overall clinical picture, especially the history of overdose and bradycardia, points more strongly to digoxin toxicity with hyperkalemia.
*Decreased serum Na+*
- **Hyponatremia** is not a characteristic feature of acute digoxin overdose.
- Digoxin primarily affects potassium and calcium channels, with less direct impact on sodium levels, unless related to fluid status changes which are not indicated here.
*Increased serum Na+*
- **Hypernatremia** is not typically associated with digoxin toxicity.
- Digoxin's mechanism of action does not directly lead to increased serum sodium; rather, it primarily inhibits the Na+/K+-ATPase.
*Increased serum Ca2+*
- Digoxin **increases intracellular calcium** by inhibiting the Na+/K+-ATPase, which indirectly leads to increased Na+/Ca2+ exchanger activity.
- However, this primarily affects intracellular levels and **does not typically result in increased serum calcium**.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 8: A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of a 4-hour history of abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and confusion. His wife reports that he had blurry vision on the way to the hospital. Two weeks ago, he lost his job and since then has been extremely worried about their financial situation and future. He has congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation well controlled with combination medical therapy. His temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F), pulse is 57/min and irregular, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 118/63 mm Hg. The patient is oriented only to person. Serum studies show:
Na+ 138 mEq/L
Cl− 100 mEq/L
K+ 5.3 mEq/L
HCO3− 25 mEq/L
Blood urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
An ECG shows premature ventricular beats. The drug most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms has which of the following mechanisms of action?
- A. Blockade of aldosterone receptors
- B. Blockade of beta-adrenergic receptors
- C. Inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibition of Na+-K+-2Cl--cotransporters
- E. Inhibition of funny channels
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase***
- The patient's symptoms (confusion, blurry vision, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, arrhythmia, hyperkalemia) are classic for **digoxin toxicity**, which occurs due to the inhibition of the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump**.
- Inhibition of this pump leads to increased intracellular calcium, enhancing cardiac contractility but also causing hyperexcitability and arrhythmias like **premature ventricular beats**.
*Blockade of aldosterone receptors*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **aldosterone antagonists** (e.g., spironolactone, eplerenone) which are often used in heart failure.
- While they can cause hyperkalemia, they typically do not cause the constellation of neurological (confusion, blurry vision) and gastrointestinal symptoms seen in this patient.
*Blockade of beta-adrenergic receptors*
- This is the mechanism of **beta-blockers** (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol), also commonly used in heart failure and atrial fibrillation.
- Symptoms of beta-blocker overdose usually include bradycardia, hypotension, and bronchospasm, but not the prominent GI or blurry vision symptoms seen here.
*Inhibition of Na+-K+-2Cl--cotransporters*
- This mechanism belongs to **loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide), often used in congestive heart failure.
- Loop diuretics primarily cause electrolyte imbalances such as hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia, and volume depletion, which does not match the patient's presentation of hyperkalemia and specific digoxin toxicity symptoms.
*Inhibition of funny channels*
- This is the mechanism of action of **ivabradine**, a selective inhibitor of the I_f current in the sinoatrial node, used to reduce heart rate in heart failure.
- While it can cause bradycardia, it is not associated with the severe GI distress, neurological symptoms, or hyperkalemia observed in this patient.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 9: A 58-year-old woman with New York Heart Association Class III heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and bipolar disorder presents to the urgent care center with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, double vision, and describes seeing green/yellow outlines around objects. Her current medications include ramipril, bisoprolol, spironolactone, digoxin, amiodarone, and lithium. Of the following, which medication is most likely responsible for her symptoms?
- A. Lithium
- B. Amiodarone
- C. Digoxin (Correct Answer)
- D. Bisoprolol
- E. Spironolactone
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Digoxin***
- The patient's symptoms, including **nausea**, **vomiting**, **abdominal pain**, **double vision**, and seeing **green/yellow outlines** around objects, are classic signs of **digoxin toxicity**.
- This is particularly concerning given her Class III heart failure and atrial fibrillation for which digoxin is often prescribed, and the presence of other medications like amiodarone, which can increase digoxin levels.
*Lithium*
- **Lithium toxicity** typically presents with neurological symptoms such as **tremor**, **sedation**, **ataxia**, and seizures, as well as gastrointestinal upset.
- While gastrointestinal symptoms can occur, the **visual disturbances** (double vision, green/yellow outlines) are not characteristic of lithium toxicity.
*Amiodarone*
- **Amiodarone side effects** can include **pulmonary fibrosis**, **thyroid dysfunction**, **corneal deposits** (halo vision), and liver toxicity.
- Although visual halos can occur, the specific description of green/yellow outlines and generalized GI distress points away from amiodarone as the primary cause here.
*Bisoprolol*
- **Bisoprolol**, a beta-blocker, can cause **bradycardia**, **hypotension**, **fatigue**, and **dizziness**.
- It does not typically cause the severe gastrointestinal symptoms or the specific visual disturbances described by the patient.
*Spironolactone*
- **Spironolactone**, an aldosterone antagonist, can cause **hyperkalemia**, **gynecomastia**, and gastrointestinal upset such as nausea.
- However, it does not cause the specific visual changes or the constellation of symptoms prominent in this case.
Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG Question 10: An investigator is studying the effects of drugs on the cardiac action potential. Cardiomyocytes are infused with a pharmacological agent and incubated for 5 minutes, after which the action potential is registered on a graph in real time for 2 minutes. Following infusion of the pharmacological agent, the action potential demonstrates a decreased slope of phase 0 depolarization and reduced peak amplitude compared to baseline. These results are most likely caused by an agent that inhibits which of the following?
- A. Opening of voltage-gated sodium channels (Correct Answer)
- B. Opening of voltage-gated potassium channels
- C. Closure of voltage-gated potassium channels
- D. Closure of voltage-gated sodium channels
- E. Opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
Cardiac glycosides Explanation: ***Opening of voltage-gated sodium channels***
- The **upstroke (phase 0)** of the cardiac action potential, characterized by rapid depolarization, is primarily mediated by the fast influx of **sodium ions** through voltage-gated sodium channels.
- Inhibition of these channels would lead to a slower rate of depolarization, resulting in a **decreased slope** of phase 0 and a **reduced peak amplitude** of the action potential, as seen in the black line.
*Opening of voltage-gated potassium channels*
- The opening of voltage-gated potassium channels primarily contributes to **repolarization (phase 3)**, leading to an outward flow of potassium ions and a decrease in membrane potential.
- Inhibition of these channels would prolong repolarization and the **action potential duration**, which is not depicted as the primary change in the graph.
*Closure of voltage-gated potassium channels*
- An agent causing the closure of voltage-gated potassium channels would lead to a **slower efflux of potassium**, thus **prolonging repolarization** and the action potential duration.
- The graph shows a primary effect on depolarization (phase 0), not on the duration of repolarization.
*Closure of voltage-gated sodium channels*
- **Closure** of voltage-gated sodium channels is a normal part of the action potential cycle, contributing to the inactivation of sodium channels during the plateau phase.
- An agent that *promotes* closure would not cause the observed **slowed depolarization**, as the issue is with the initial opening or function of these channels.
*Opening of voltage-gated calcium channels*
- The opening of voltage-gated calcium channels primarily contributes to the **plateau phase (phase 2)** of the cardiac action potential, allowing a sustained influx of calcium ions.
- Inhibition of these channels would primarily affect the plateau phase duration, potentially **shortening it**, rather than significantly altering the initial upstroke.
More Cardiac glycosides US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.