Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antianginal drugs. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 1: A 42-year-old woman presents to the urgent care clinic with recurrent chest pain and pressure radiating to her jaw. ECG is obtained and shows ST-segment elevation, but her cardiac enzymes are repeatedly found to be within normal ranges. She has a heart rate of 82/min and a blood pressure of 128/76 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals regular heart sounds with no friction rub. Which of the following options is an acceptable treatment regimen for this patient’s suspected condition?
- A. Calcium channel blockers and nitrates (Correct Answer)
- B. Nitrates only
- C. Beta-blockers, nitrates and aspirin
- D. Aspirin and clopidogrel
- E. Aspirin, clopidogrel, beta-blockers, and nitrates
Antianginal drugs Explanation: **Calcium channel blockers and nitrates**
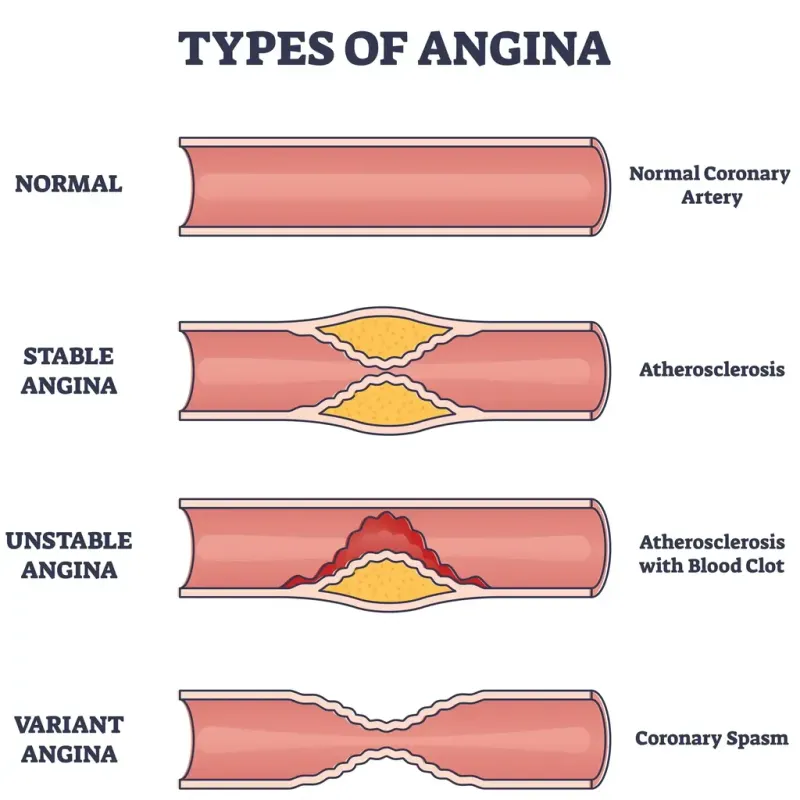
- This patient likely has **Prinzmetal's angina** (vasospastic angina), characterized by recurrent chest pain, ST-segment elevation on ECG, and normal cardiac enzymes, consistent with **coronary artery spasm**.
- **Calcium channel blockers** (e.g., diltiazem, amlodipine) and **nitrates** are the cornerstone of treatment, as they directly relax coronary arteries and prevent spasms.
*Nitrates only*
- While **nitrates** can alleviate acute symptoms of Prinzmetal's angina by vasodilation, they are generally **insufficient for long-term prevention** of recurrent spasms.
- **Calcium channel blockers** are crucial for sustained prophylaxis against vasospasm.
*Beta-blockers, nitrates and aspirin*
- **Beta-blockers** are generally **contraindicated** in Prinzmetal's angina as they can worsen **coronary artery spasm** by blocking beta-2 mediated vasodilation, leading to unopposed alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction.
- **Aspirin** is not the primary treatment for vasospastic angina, as the pain is due to spasm rather than thrombotic occlusion.
*Aspirin and clopidogrel*
- **Aspirin** and **clopidogrel** are **antiplatelet agents** primarily used to prevent thrombus formation in atherosclerotic coronary artery disease.
- They are not indicated as a first-line treatment for Prinzmetal's angina, where chest pain is due to **coronary vasospasm**, not platelet aggregation.
*Aspirin, clopidogrel, beta-blockers, and nitrates*
- This combination includes several treatments that are either **ineffective** or **harmful** for Prinzmetal's angina.
- **Beta-blockers** are contraindicated, and **antiplatelet agents** (aspirin, clopidogrel) are not primary treatments for vasospasm.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 2: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of episodic, pressure-like chest pain. The chest pain occurs when he is walking up stairs and improves with rest. He has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. His father died from a myocardial infarction at the age of 50 years. Current medications include hydrochlorothiazide and metformin. His pulse is 85/min, respirations are 12/min, and blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Cardiac examination shows normal heart sounds without any murmurs, rubs, or gallops. An ECG shows high amplitude of the S wave in lead V3. An exercise stress test is performed but stopped after 4 minutes because the patient experiences chest pain. An ECG obtained during the stress test shows sinus tachycardia and ST-segment depressions in leads V1–V4. Which of the following is the most appropriate long-term pharmacotherapy to reduce the frequency of symptoms in this patient?
- A. Metoprolol (Correct Answer)
- B. Clopidogrel
- C. Aspirin
- D. Nitroglycerin
- E. Isosorbide mononitrate
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***Metoprolol***
- **Beta-blockers** like metoprolol are first-line agents for **symptom relief** in stable angina by reducing myocardial oxygen demand.
- They decrease **heart rate**, **blood pressure**, and **myocardial contractility**, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of anginal episodes.
*Clopidogrel*
- **Clopidogrel** is an antiplatelet agent used primarily to prevent **thrombotic events** in patients with established cardiovascular disease or acute coronary syndromes.
- It does not directly reduce the frequency of anginal symptoms, but rather prevents progression to **myocardial infarction** or **stroke**.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is an antiplatelet medication used for **secondary prevention** of cardiovascular events by inhibiting platelet aggregation.
- While crucial for reducing cardiovascular risk, it does not directly alleviate the **frequency of anginal symptoms** themselves.
*Nitroglycerin*
- **Nitroglycerin** is a short-acting nitrate used to provide **immediate relief** of anginal pain during an acute episode.
- It is not a long-term pharmacotherapy for reducing the *frequency* of symptoms.
*Isosorbide mononitrate*
- **Isosorbide mononitrate** is a long-acting nitrate used to *prevent* angina, but it is typically a **second-line agent** after beta-blockers due to potential for **tolerance** and side effects.
- While it can reduce symptom frequency, beta-blockers are generally preferred as initial long-term therapy for symptom control.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is comparing the risk of adverse effects among various antiarrhythmic medications. One of the drugs being studied primarily acts by blocking the outward flow of K+ during myocyte repolarization. Further investigation shows that the use of this drug is associated with a lower rate of ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes when compared to similar drugs. Which of the following drugs is most likely being studied?
- A. Verapamil
- B. Procainamide
- C. Esmolol
- D. Amiodarone (Correct Answer)
- E. Sotalol
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***Amiodarone***
- Amiodarone is a **Class III antiarrhythmic drug** that primarily blocks **potassium channels**, thereby prolonging repolarization and the effective refractory period in cardiac myocytes.
- While it has properties of all four Vaughn-Williams classes, its dominant action as a potassium channel blocker makes it highly effective in preventing and treating various arrhythmias, including **ventricular tachycardia (VT)** and **ventricular fibrillation (VF)**, and it has a relatively lower risk of **torsades de pointes (TdP)** compared to other Class III drugs due to its broader ion channel effects.
*Verapamil*
- Verapamil is a **Class IV antiarrhythmic drug (non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker)** that primarily blocks **L-type calcium channels**, slowing conduction through the AV node.
- It is mainly used for **supraventricular tachycardias** and rate control in atrial fibrillation, not typically for ventricular arrhythmias like VT/VF.
*Procainamide*
- Procainamide is a **Class IA antiarrhythmic drug** that blocks **sodium channels** and also prolongs repolarization by blocking some potassium channels, but its primary effect is on sodium channels.
- Class IA drugs are known to **increase the QT interval** and carry a significant risk of **torsades de pointes**, making them less favorable for preventing VT/VF with adverse effect concerns.
*Esmolol*
- Esmolol is a **Class II antiarrhythmic drug (beta-blocker)** that primarily acts by **blocking beta-adrenergic receptors**, thereby reducing heart rate, contractility, and AV nodal conduction.
- While useful in some arrhythmias, its main mechanism is not potassium channel blockade, and it is not typically preferred for the direct prevention of VT/VF in situations with concerns about TdP.
*Sotalol*
- Sotalol is a **Class III antiarrhythmic drug** that primarily acts as a **potassium channel blocker**, prolonging the action potential duration and effective refractory period, and also has **beta-blocking properties**.
- While it blocks potassium channels, sotalol carries a **higher risk of torsades de pointes** compared to amiodarone, especially at higher doses and in patients with underlying heart conditions.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 4: A 55-year-old woman comes to the physician because of involuntary hand movements that improve with alcohol consumption. Physical examination shows bilateral hand tremors that worsen when the patient is asked to extend her arms out in front of her. The physician prescribes a medication that is associated with an increased risk of bronchospasms. This drug has which of the following immediate effects on the cardiovascular system?
Stroke volume | Heart rate | Peripheral vascular resistance
- A. ↓ ↓ ↓
- B. ↓ ↓ ↑ (Correct Answer)
- C. ↓ ↑ ↑
- D. ↑ ↑ ↑
- E. ↑ ↑ ↓
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***↓ ↓ ↑***
- This patient likely has **essential tremor**, which is characterized by **bilateral hand tremors** that improve with alcohol and worsen with intention (postural tremor). The prescribed medication is a **beta-blocker** (e.g., propranolol), which is associated with an increased risk of bronchospasms due to blocking **beta-2 receptors** in the airways.
- Beta-blockers **decrease heart rate** (negative chronotropic effect) and **stroke volume** (negative inotropic effect) by blocking beta-1 receptors in the heart, reducing cardiac output.
- **Peripheral vascular resistance increases** acutely due to: (1) **unopposed alpha-1 adrenergic tone** in blood vessels (loss of beta-2 mediated vasodilation), and (2) baroreceptor-mediated reflex vasoconstriction in response to decreased cardiac output. This helps maintain blood pressure despite reduced cardiac output.
*↓ ↓ ↓*
- While beta-blockers decrease **heart rate** and **stroke volume**, peripheral vascular resistance does not decrease acutely. A decrease in all three parameters would cause severe hypotension.
- The loss of beta-2 receptor-mediated vasodilation and baroreceptor reflexes lead to increased, not decreased, peripheral vascular resistance.
*↓ ↑ ↑*
- Beta-blockers **decrease heart rate** through beta-1 blockade, not increase it. This is their primary cardiac mechanism of action.
- An increase in heart rate would be expected with sympathomimetic drugs or anticholinergics, not beta-blockers.
*↑ ↑ ↑*
- This combination indicates increased cardiovascular activity, which is the opposite effect of **beta-blockers**.
- Beta-blockers reduce heart rate and stroke volume by blocking beta-1 receptors; they do not increase these parameters.
- This pattern would suggest sympathetic activation or administration of an adrenergic agonist.
*↑ ↑ ↓*
- Beta-blockers **decrease** (not increase) both heart rate and stroke volume through beta-1 receptor blockade.
- While decreased peripheral vascular resistance occurs with vasodilators, beta-blockers acutely **increase** PVR due to unopposed alpha-adrenergic tone.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 5: A 52-year-old man with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia comes to the physician because of a 10-month history of substernal chest pain on exertion that is relieved with rest. His pulse is 82/min and blood pressure is 145/82 mm Hg. He is prescribed a drug that acts by forming free radical nitric oxide. The patient is most likely to experience which of the following adverse effects as a result of this drug?
- A. Pulsating headaches (Correct Answer)
- B. Erectile dysfunction
- C. Hypertensive urgency
- D. Lower extremity edema
- E. Nonproductive cough
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***Pulsating headaches***
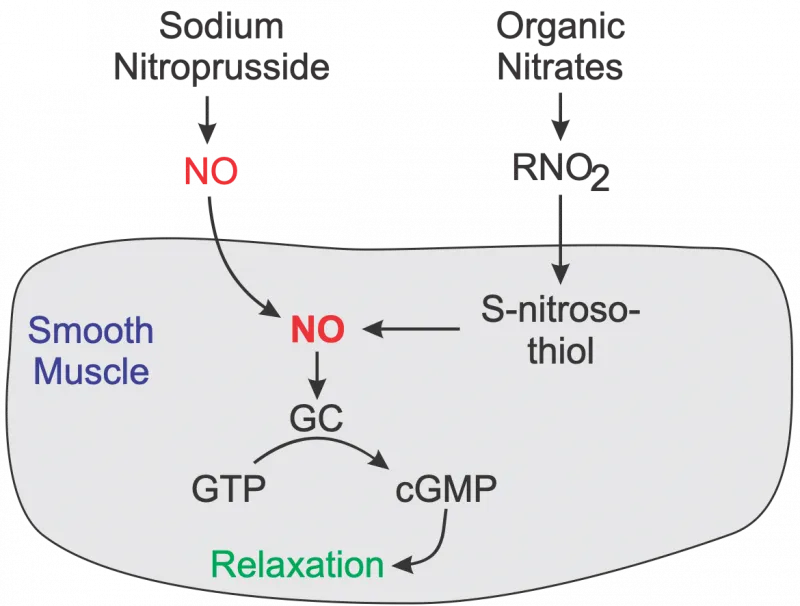
- The drug described is likely **nitroglycerin** or another **nitrate**, which acts by releasing **nitric oxide (NO)** to cause **vasodilation**.
- **Vasodilation** in the cerebral vasculature is a common side effect of nitrates and can lead to **pulsating headaches**.
*Erectile dysfunction*
- **Erectile dysfunction** is not a direct adverse effect of nitrates; in fact, nitrates can be used to treat it, though their use with PDE5 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- This condition is more commonly associated with the underlying cardiovascular disease rather than the medication used to treat angina.
*Hypertensive urgency*
- **Nitrates** cause **vasodilation** and typically **lower blood pressure**, making **hypotension** (not hypertension) a potential side effect.
- **Hypertensive urgency** would indicate a sudden, severe elevation in blood pressure, which is antithetical to the drug's mechanism of action.
*Lower extremity edema*
- **Lower extremity edema** is generally not a direct side effect of nitrates; it is more commonly associated with conditions like **heart failure**, certain **calcium channel blockers**, or **venous insufficiency**.
- While vasodilation can sometimes lead to fluid shifts, edema is not a prominent or expected adverse effect of this class of drugs.
*Nonproductive cough*
- A **nonproductive cough** is a common side effect of **ACE inhibitors** (e.g., lisinopril), which act on the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system**.
- This symptom is not associated with **nitrates** because their mechanism of action is primarily through nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation, unrelated to the respiratory irritation seen with ACE inhibitors.
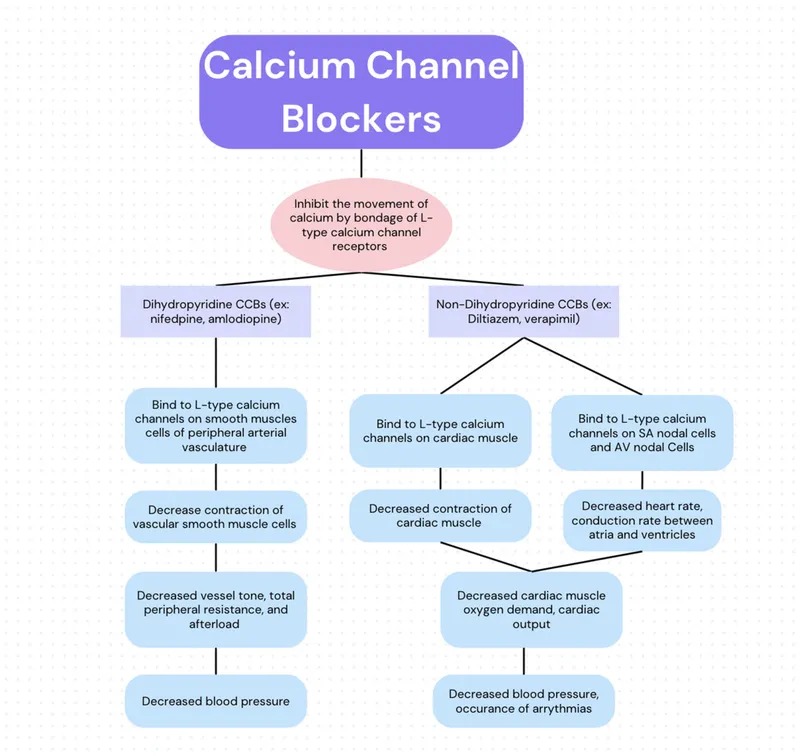
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 6: A 65-year-old male with a history of hypertension presents to his primary care physician complaining of multiple episodes of chest pain, palpitations, and syncope. Episodes have occurred twice daily for the last week, and he is asymptomatic between episodes. Electrocardiogram reveals a narrow-complex supraventricular tachycardia. He is treated with diltiazem. In addition to its effects on cardiac myocytes, on which of the following channels and tissues would diltiazem also block depolarization?
- A. L-type Ca channels in skeletal muscle
- B. T-type Ca channels in bone
- C. P-type Ca channels in Purkinje fibers
- D. N-type Ca channels in the peripheral nervous system
- E. L-type Ca channels in smooth muscle (Correct Answer)
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***L-type Ca channels in smooth muscle***
- **Diltiazem** is a **calcium channel blocker** that acts on **L-type calcium channels**, which are extensively found in both cardiac muscle and vascular **smooth muscle**.
- By blocking these channels in smooth muscle, diltiazem induces **vasodilation**, contributing to its use in hypertension, as seen in the patient's history.
*L-type Ca channels in skeletal muscle*
- While skeletal muscle does contain L-type calcium channels (also known as dihydropyridine receptors), their primary role is in **excitation-contraction coupling**, acting as voltage sensors rather than directly regulating calcium influx for contraction.
- **Skeletal muscle contraction** is primarily triggered by calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, not direct calcium influx through L-type channels, making them largely **insensitive to calcium channel blockers** like diltiazem at therapeutic doses.
*T-type Ca channels in bone*
- **T-type calcium channels** are found in various tissues, including neurons and cardiac pacemaker cells, but they are generally **not the primary target of diltiazem**, which preferentially binds to L-type channels.
- Furthermore, **bone tissue** is not known to have a significant physiological role mediated by T-type calcium channels that would be relevant to diltiazem's action or clinical effects.
*P-type Ca channels in Purkinje fibers*
- **Purkinje fibers** primarily rely on **L-type calcium channels** for phase 2 of their action potential and are sensitive to diltiazem, but **P-type calcium channels** are mainly found in neurons.
- P-type calcium channels are involved in **neurotransmitter release** at the presynaptic terminal, and diltiazem does not typically block these channels clinically.
*N-type Ca channels in the peripheral nervous system*
- **N-type calcium channels** are predominantly located in the **peripheral and central nervous systems**, where they are crucial for **neurotransmitter release** at nerve terminals.
- Diltiazem's primary mechanism of action is on **L-type calcium channels**, and it has **minimal to no clinically significant effect** on N-type calcium channels.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old male is started on nitrate therapy for treatment of stable angina. He experiences significant and immediate relief of his symptoms within minutes of starting therapy. Approximately 48 hours after initiating this new medication, he notes return of chest pain and pressure with exertion that no longer responds to continued nitrate use. Which of the following 24-hour dosing schedules would most likely explain this patient's response to nitrate treatment?
- A. PO regular-release isosorbide dinitrate taken at 8AM, noon, and 5PM
- B. Transdermal nitroglycerin patch placed upon awakening in the morning and removed at 7PM without replacement
- C. Transdermal nitroglycerin patch placed at 7AM then removed and replaced with another at 7PM (Correct Answer)
- D. Transdermal nitroglycerin patch placed at bedtime and removed at 7AM without replacement
- E. PO extended release isosorbide-5-mononitrate once daily at 8AM
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***Transdermal nitroglycerin patch placed at 7AM then removed and replaced with another at 7PM***
- This dosing schedule provides **continuous 24-hour nitrate exposure** with no nitrate-free interval, which leads to rapid development of **nitrate tolerance** within 48 hours.
- The patient experiences immediate relief initially, but by replacing one patch with another at 7PM, there is **no washout period**, causing complete loss of efficacy.
- To prevent tolerance, an **off-nitrate period of 10-14 hours daily** is essential to restore nitrate responsiveness.
*PO regular-release isosorbide dinitrate taken at 8AM, noon, and 5PM*
- This schedule provides **intermittent nitrate exposure** with a nitrate-free interval overnight (approximately 15 hours from 5PM to 8AM).
- This built-in washout period would **prevent rapid tolerance development** and maintain drug efficacy.
*Transdermal nitroglycerin patch placed upon awakening in the morning and removed at 7PM without replacement*
- This is the **recommended dosing strategy** that provides a 12-14 hour nitrate-free interval overnight.
- This schedule would **prevent tolerance** and maintain therapeutic efficacy, unlike what occurred in this patient.
*Transdermal nitroglycerin patch placed at bedtime and removed at 7AM without replacement*
- This schedule provides a **nitrate-free window during daytime hours**, which would prevent tolerance development.
- The rapid loss of efficacy in this patient indicates a schedule with **continuous nitrate presence**, not this regimen.
*PO extended release isosorbide-5-mononitrate once daily at 8AM*
- Extended-release mononitrate taken once daily typically provides coverage for **12-17 hours**, not full 24-hour exposure.
- While this could theoretically contribute to tolerance with prolonged use, it would not explain the **rapid tolerance within 48 hours** as definitively as continuous transdermal patching without any removal period.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 8: An 18-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because he suddenly collapsed while playing football. His parents mention that he had complained of dizziness while playing before, but never fainted in the middle of a game. On physical examination, the blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg, the respirations are 15/min, and the pulse is 110/min. The chest is clear, but a systolic ejection murmur is present. The remainder of the examination revealed no significant findings. An electrocardiogram is ordered, along with an echocardiogram. He is diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and the physician lists all the precautions he must follow. Which of the following drugs will be on the list of contraindicated substances?
- A. Βeta-blockers
- B. Dobutamine
- C. Nitrates (Correct Answer)
- D. Calcium channel blockers
- E. Potassium channel blockers
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***Nitrates***
- **Nitrates** cause **vasodilation**, which decreases **preload** and worsens **left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO)** in **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)**, potentially leading to syncope or sudden death.
- Reduced preload exacerbates the dynamic obstruction, causing a critical drop in cardiac output.
- **Commonly encountered substances** patients must avoid include nitroglycerin, isosorbide, and **phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors** (sildenafil, tadalafil) which potentiate nitrate effects.
- This is a critical counseling point for HCM patients in everyday life.
*Beta-blockers*
- **Beta-blockers** are **first-line treatment** for **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)** as they reduce heart rate, improve diastolic filling, and decrease contractility, thereby reducing **LVOTO**.
- They alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death in HCM.
*Dobutamine*
- **Dobutamine** is a **beta-1 adrenergic agonist** that increases contractility and heart rate, which would worsen **LVOTO** in HCM.
- While also contraindicated in HCM, dobutamine is only used in **controlled hospital settings** for stress testing or hemodynamic support, not a substance patients encounter in daily life.
- The question focuses on outpatient counseling about substances to avoid in everyday situations.
*Calcium channel blockers*
- **Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers** (verapamil, diltiazem) are used in **HCM management**, particularly in patients who cannot tolerate beta-blockers.
- They improve **diastolic function** and reduce **LVOTO** by decreasing contractility and heart rate.
- **Caution:** Dihydropyridines (nifedipine, amlodipine) can worsen obstruction and should be avoided.
*Potassium channel blockers*
- **Antiarrhythmics** like **amiodarone** (potassium channel blocker) are used in **HCM** patients for atrial or ventricular arrhythmias.
- Not contraindicated; therapeutically indicated for rhythm management.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying the effects of drugs on the cardiac action potential. Cardiomyocytes are infused with a pharmacological agent and incubated for 5 minutes, after which the action potential is registered on a graph in real time for 2 minutes. Following infusion of the pharmacological agent, the action potential demonstrates a decreased slope of phase 0 depolarization and reduced peak amplitude compared to baseline. These results are most likely caused by an agent that inhibits which of the following?
- A. Opening of voltage-gated sodium channels (Correct Answer)
- B. Opening of voltage-gated potassium channels
- C. Closure of voltage-gated potassium channels
- D. Closure of voltage-gated sodium channels
- E. Opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***Opening of voltage-gated sodium channels***
- The **upstroke (phase 0)** of the cardiac action potential, characterized by rapid depolarization, is primarily mediated by the fast influx of **sodium ions** through voltage-gated sodium channels.
- Inhibition of these channels would lead to a slower rate of depolarization, resulting in a **decreased slope** of phase 0 and a **reduced peak amplitude** of the action potential, as seen in the black line.
*Opening of voltage-gated potassium channels*
- The opening of voltage-gated potassium channels primarily contributes to **repolarization (phase 3)**, leading to an outward flow of potassium ions and a decrease in membrane potential.
- Inhibition of these channels would prolong repolarization and the **action potential duration**, which is not depicted as the primary change in the graph.
*Closure of voltage-gated potassium channels*
- An agent causing the closure of voltage-gated potassium channels would lead to a **slower efflux of potassium**, thus **prolonging repolarization** and the action potential duration.
- The graph shows a primary effect on depolarization (phase 0), not on the duration of repolarization.
*Closure of voltage-gated sodium channels*
- **Closure** of voltage-gated sodium channels is a normal part of the action potential cycle, contributing to the inactivation of sodium channels during the plateau phase.
- An agent that *promotes* closure would not cause the observed **slowed depolarization**, as the issue is with the initial opening or function of these channels.
*Opening of voltage-gated calcium channels*
- The opening of voltage-gated calcium channels primarily contributes to the **plateau phase (phase 2)** of the cardiac action potential, allowing a sustained influx of calcium ions.
- Inhibition of these channels would primarily affect the plateau phase duration, potentially **shortening it**, rather than significantly altering the initial upstroke.
Antianginal drugs US Medical PG Question 10: A group of investigators is studying a drug to treat refractory angina pectoris. This drug works by selectively inhibiting the late influx of sodium ions into cardiac myocytes. At high doses, the drug also partially inhibits the degradation of fatty acids. Which of the following is the most likely effect of this drug?
- A. Increased prolactin release
- B. Decreased uric acid excretion
- C. Decreased serum pH
- D. Increased oxygen efficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Decreased insulin release
Antianginal drugs Explanation: ***Increased oxygen efficiency***
- Inhibiting the **late sodium current** reduces intracellular calcium overload, preventing diastolic dysfunction and improving myocardial relaxation.
- Partial inhibition of **fatty acid degradation** shifts myocardial metabolism towards glucose utilization, which is more oxygen-efficient.
*Increased prolactin release*
- This drug does not act on **dopamine receptors**, which are typically involved in regulating prolactin release.
- **Ranolazine**, the drug described, has no known effect on the endocrine system, specifically prolactin.
*Decreased uric acid excretion*
- **Uric acid excretion** is primarily affected by renal handling, often influenced by diuretics or drugs that compete for renal transporters, which is not a mechanism of this drug.
- This drug does not interfere with the **organic anion transporters (OATs)** responsible for uric acid secretion.
*Decreased serum pH*
- Changes in **serum pH** are usually associated with severe metabolic or respiratory disturbances, which are not direct effects of a drug targeting cardiac ion channels and metabolism.
- The drug's mechanism of action does not directly produce **acidic byproducts** or inhibit acid-base regulatory systems.
*Decreased insulin release*
- Insulin release is primarily stimulated by **glucose** and modulated by various endocrine pathways, none of which are directly targeted by a drug that inhibits cardiac sodium channels and fatty acid oxidation.
- There is no evidence that this class of drugs affects **pancreatic beta-cell function**.
More Antianginal drugs US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.