Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Influenza antivirals. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man comes to the emergency department with fever, nonproductive cough, and difficulty breathing. Three years ago, he underwent lung transplantation. A CT scan of the chest shows diffuse bilateral ground-glass opacities. Pathologic examination of a transbronchial lung biopsy specimen shows several large cells containing intranuclear inclusions with a clear halo. Treatment with ganciclovir fails to improve his symptoms. He is subsequently treated successfully with another medication. This drug does not require activation by viral kinases and also has known in-vitro activity against HIV and HBV. The patient was most likely treated with which of the following drugs?
- A. Lamivudine
- B. Foscarnet (Correct Answer)
- C. Elvitegravir
- D. Zanamivir
- E. Acyclovir
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Foscarnet***
- The patient presents with **cytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonitis** post-lung transplant, evidenced by **diffuse bilateral ground-glass opacities** and **intranuclear inclusions with a clear halo** on biopsy, and initial treatment with **ganciclovir failed**.
- **Foscarnet** is an alternative antiviral that does not require activation by viral kinases and is effective against viruses that develop **ganciclovir resistance** due to mutations in UL97 phosphotransferase, which activates ganciclovir. It also has known activity against **HIV** and **HBV**, fitting the description.
*Lamivudine*
- **Lamivudine** is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)** primarily used for **HIV** and **HBV** infections.
- It has **no activity against CMV** and would not be used to treat CMV pneumonitis, especially after ganciclovir failure.
*Elvitegravir*
- **Elvitegravir** is an **integrase inhibitor** used in combination therapy for **HIV infection**.
- It has **no activity against CMV** and would not be effective in treating CMV pneumonitis.
*Zanamivir*
- **Zanamivir** is a **neuraminidase inhibitor** used to treat and prevent **influenza A and B viruses**.
- It has **no activity against CMV** and is not indicated for the patient's condition.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is a guanosine analog primarily used to treat **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** and **varicella-zoster virus (VZV)** infections.
- It has **limited to no activity against CMV** at therapeutic doses and would not be effective in this case.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 2: A 59-year-old female presents to the emergency department after a fall. She reports severe pain in her right hip and an inability to move her right leg. Her past medical history is notable for osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and has never undergone surgery before. The patient was adopted, and her family history is unknown. She has never smoked and drinks alcohol socially. Her temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Her right leg is shortened, abducted, and externally rotated. A radiograph demonstrates a displaced femoral neck fracture. She is admitted and eventually brought to the operating room to undergo right hip arthroplasty. While undergoing induction anesthesia with inhaled sevoflurane, she develops severe muscle contractions. Her temperature is 103.4°F (39.7°C). A medication with which of the following mechanisms of action is indicated in the acute management of this patient’s condition?
- A. Ryanodine receptor antagonist (Correct Answer)
- B. Acetylcholine receptor agonist
- C. Serotonin 1B/1D agonist
- D. NMDA receptor antagonist
- E. GABA agonist
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Ryanodine receptor antagonist***
- The patient's presentation with **high fever**, **muscle rigidity**, and **tachycardia** shortly after induction with **sevoflurane** is highly suggestive of **malignant hyperthermia (MH)**.
- **Dantrolene**, a **ryanodine receptor antagonist**, is the specific treatment for MH, as it blocks the excessive release of **calcium** from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells.
*Acetylcholine receptor agonist*
- **Acetylcholine receptor agonists** (e.g., succinylcholine) stimulate muscle contraction and would worsen the muscle rigidity seen in malignant hyperthermia.
- These agents are often triggers for malignant hyperthermia when combined with volatile anesthetics.
*Serotonin 1B/1D agonist*
- **Serotonin 1B/1D agonists** (e.g., triptans) are primarily used in the acute treatment of migraines.
- They have no role in the management of malignant hyperthermia and would not address the underlying pathophysiology.
*NMDA receptor antagonist*
- **NMDA receptor antagonists** (e.g., ketamine) are dissociative anesthetics and analgesics.
- They do not directly affect the calcium release channels in skeletal muscle responsible for malignant hyperthermia.
*GABA agonist*
- **GABA agonists** (e.g., benzodiazepines, propofol) are central nervous system depressants used for sedation and anesthesia.
- While they can have muscle relaxant properties, they do not specifically target the **ryanodine receptor** pathway involved in malignant hyperthermia.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 3: A 68-year-old man comes to the physician because of headache, fatigue, and nonproductive cough for 1 week. He appears pale. Pulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show a hemoglobin concentration of 9.5 g/dL and an elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase concentration. A peripheral blood smear shows normal red blood cells that are clumped together. Results of cold agglutinin titer testing show a 4-fold elevation above normal. An x-ray of the chest shows diffuse, patchy infiltrates bilaterally. Treatment is begun with an antibiotic that is also used to promote gut motility. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase
- B. Inhibition of folic acid synthesis
- C. Free radical creation within bacterial cells
- D. Inhibition of transpeptidase cross-linking at the cell wall
- E. Inhibition of peptide translocation at the 50S ribosomal subunit (Correct Answer)
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Inhibition of peptide translocation at the 50S ribosomal subunit***
- This drug described is likely **erythromycin** or another **macrolide antibiotic**, which inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the **50S ribosomal subunit** and preventing translocation.
- Macrolides are used to treat **atypical pneumonia** caused by *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*, which is indicated by the patient's symptoms (headache, fatigue, nonproductive cough, bilateral patchy infiltrates) and **cold agglutinin disease**.
*Inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase*
- This is the mechanism of action of **rifampin**, which is primarily used for **tuberculosis** and **meningitis prophylaxis**, not for atypical pneumonia.
- Rifampin's side effects and spectrum of activity do not align with the implied clinical scenario, especially the gut motility promotion.
*Inhibition of folic acid synthesis*
- This is the mechanism for **sulfonamides** and **trimethoprim**, which are bacteriostatic and target different pathogens than those causing cold agglutinin positive pneumonia.
- These drugs are not known for promoting gut motility.
*Free radical creation within bacterial cells*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **metronidazole**, an antibiotic used for anaerobic bacterial and parasitic infections.
- Metronidazole does not fit the clinical context of atypical pneumonia with cold agglutinins, nor is it a macrolide that promotes gut motility.
*Inhibition of transpeptidase cross-linking at the cell wall*
- This describes the mechanism of **beta-lactam antibiotics** (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), which are ineffective against **atypical pneumonia** because *Mycoplasma* lacks a cell wall.
- Beta-lactams do not typically promote gut motility.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 4: A 43-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 45 minutes after his wife found him on the floor sweating profusely. On arrival, he is lethargic and unable to provide a history. He vomited multiple times on the way to the hospital. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 55/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 98/65 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 80%. Examination shows profuse diaphoresis and excessive salivation. He withdraws his extremities sluggishly to pain. The pupils are constricted and reactive. Scattered expiratory wheezing and rhonchi are heard throughout both lung fields. Cardiac examination shows no abnormalities. There are fine fasciculations in the lower extremities bilaterally. Muscle strength is reduced and deep tendon reflexes are 1+ bilaterally. His clothes are soaked with urine and feces. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the most appropriate initial pharmacotherapy?
- A. Non-selective α-adrenergic antagonism
- B. Competitive antagonism of mACh receptors (Correct Answer)
- C. Alkaloid emesis-induction
- D. Enteral binding
- E. Urine alkalization
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Competitive antagonism of mACh receptors***
- The patient's symptoms, including **profuse sweating, salivation, constricted pupils, wheezing, bradycardia, hypotension, fasciculations**, and incontinence, are classic signs of **cholinergic crisis** due to **organophosphate poisoning**.
- **Atropine**, a competitive antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine (mACh) receptors, is the primary initial pharmacotherapy for organophosphate poisoning, counteracting the excessive parasympathetic stimulation.
*Non-selective α-adrenergic antagonism*
- This mechanism would typically be used to treat conditions involving **excessive alpha-adrenergic activity**, such as a pheochromocytoma or severe hypertension.
- It would **worsen the hypotension** already present in this patient and does not address the underlying cholinergic overstimulation.
*Alkaloid emesis-induction*
- While vomiting occurred, inducing further emesis with an alkaloid is **contraindicated** in cases of organophosphate poisoning due to the risk of **aspiration pneumonitis** and the patient's altered mental status.
- Furthermore, modern management of poisoning rarely recommends routine emesis induction.
*Enteral binding*
- **Activated charcoal** acts by enteral binding to prevent absorption of toxins from the gastrointestinal tract.
- While it may be considered in some poisonings, the rapid onset of severe symptoms and the potential for aspiration in a lethargic patient makes **airway protection** and **antidote administration** the immediate priorities.
*Urine alkalization*
- Urine alkalization is a technique used to enhance the renal excretion of certain acidic drugs by increasing their ionization in the urine, preventing reabsorption.
- It is **not relevant** for the initial management of organophosphate poisoning, which primarily requires anticholinergic agents and cholinesterase reactivators.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 5: A 26-year-old nurse presents 12 hours after she accidentally stuck herself with a blood-contaminated needle. She reported the accident appropriately and now seeks post-exposure prophylaxis. She does not have any complaints at the moment of presentation. Her vital signs include: blood pressure 125/80 mm Hg, heart rate 71/min, respiratory rate 15/min, and temperature 36.5℃ (97.7℉). Physical examination is unremarkable. The nurse has prescribed a post-exposure prophylaxis regimen which includes tenofovir, emtricitabine, and raltegravir. How will tenofovir change the maximum reaction rate (Vm) and Michaelis constant (Km) of the viral reverse transcriptase?
- A. Vm will decrease, Km will increase
- B. Vm and Km will both decrease
- C. Vm will stay the same, Km will increase
- D. Vm and Km will both increase
- E. Vm will decrease, Km will stay the same (Correct Answer)
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Vm will decrease, Km will stay the same***
- **Tenofovir** is a **nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NtRTI)** that acts as a **competitive substrate analog**. Once phosphorylated to **tenofovir diphosphate**, it competes with natural deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) for incorporation into the viral DNA chain.
- Upon incorporation, tenofovir acts as a **chain terminator** because it lacks a 3'-hydroxyl group necessary for further DNA elongation. This **irreversibly inactivates** the enzyme-DNA complex, effectively reducing the **maximum reaction rate (Vm)** by decreasing the amount of functional enzyme available.
- Since tenofovir competes with natural nucleotides but doesn't affect the enzyme's affinity for its natural substrates, the **Michaelis constant (Km) remains unchanged**. The inhibition pattern shows characteristics of competitive inhibition with irreversible chain termination.
*Vm will decrease, Km will increase*
- This pattern is characteristic of a **mixed inhibitor**, where the inhibitor can bind to both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex, reducing Vm while also decreasing substrate affinity (increasing Km).
- While tenofovir does reduce Vm through chain termination, it does not significantly alter the enzyme's affinity for natural nucleotide substrates. Tenofovir diphosphate **competes directly** with dATP rather than binding to an allosteric site, so Km remains unchanged rather than increasing.
*Vm and Km will both decrease*
- This effect is typical of an **uncompetitive inhibitor**, which binds only to the **enzyme-substrate complex**. Uncompetitive inhibitors decrease both Vm and Km, implying increased apparent substrate affinity.
- Tenofovir does not function as an uncompetitive inhibitor. As a **nucleotide analog**, it competes for the active site and gets incorporated into DNA, causing chain termination. This mechanism does not involve preferential binding to the enzyme-substrate complex that would decrease Km.
*Vm will stay the same, Km will increase*
- This describes **pure reversible competitive inhibition**, where the inhibitor competes with substrate for the active site but can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration, leaving Vm unchanged.
- While tenofovir diphosphate does **compete with natural nucleotides**, it acts as a **suicide substrate** that causes irreversible chain termination once incorporated. This **permanently inactivates** the enzyme-DNA complex, reducing the pool of functional enzyme and thus decreasing Vm, distinguishing it from simple reversible competitive inhibition.
*Vm and Km will both increase*
- An increase in both Vm and Km is not a standard pattern for enzyme inhibition and would suggest **reduced substrate affinity** with paradoxically increased catalytic capacity, which is inconsistent with any inhibitory mechanism.
- This scenario contradicts the **intended therapeutic effect** of tenofovir, which is to inhibit HIV reverse transcriptase activity and prevent viral replication, not to enhance enzyme function.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 6: A 66-year-old woman with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is brought to the emergency department because of fever, body aches, malaise, and a dry cough. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years but quit smoking 1 year ago. She lives with her daughter and her granddaughter, who attends daycare. Her temperature is 38.1°C (101°F). Physical examination shows bilateral conjunctivitis, rhinorrhea, and erythematous tonsils without exudates. Further testing confirms infection with an enveloped orthomyxovirus. Administration of a drug with which of the following mechanisms of action is most appropriate?
- A. Inhibition of protease
- B. Inhibition of neuraminidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Inhibition of proton translocation
- D. Inhibition of nucleoside reverse transcriptase
- E. Inhibition of DNA polymerase
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Inhibition of neuraminidase***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, body aches, malaise, dry cough, conjunctivitis, rhinorrhea, erythematous tonsils), exposure history (daycare contact), and diagnosis of an **enveloped orthomyxovirus** strongly indicate **influenza**.
- **Neuraminidase inhibitors** (e.g., oseltamivir, zanamivir) prevent viral release from infected cells by cleaving sialic acid residues, effectively halting the spread of the virus.
*Inhibition of protease*
- **Protease inhibitors** are primarily used to treat **HIV infection**, preventing the cleavage of viral polyproteins into functional enzymes.
- This mechanism is not relevant for influenza virus, which utilizes different replication enzymes and strategies.
*Inhibition of proton translocation*
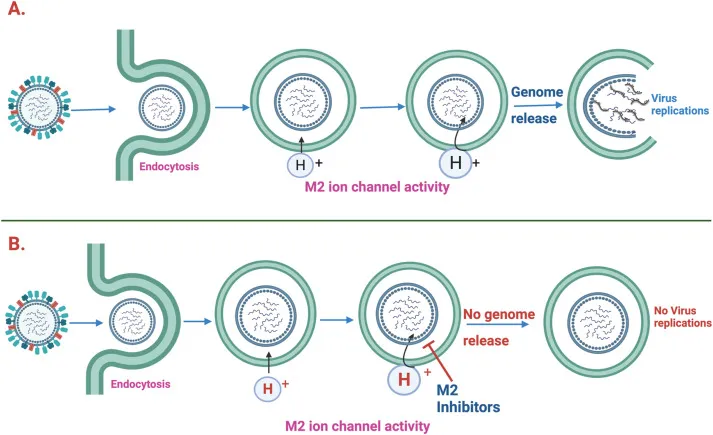
- **M2 inhibitors** (amantadine, rimantadine) act by blocking the viral M2 ion channel, which is essential for **viral uncoating** within the host cell.
- However, due to widespread resistance, especially among influenza A strains, these drugs are generally not recommended for routine use.
*Inhibition of nucleoside reverse transcriptase*
- **Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)** are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat **HIV infection** by inhibiting the reverse transcription of viral RNA into DNA.
- This mechanism is specific to retroviruses and has no role in the treatment of orthomyxovirus infections like influenza.
*Inhibition of DNA polymerase*
- **DNA polymerase inhibitors** (e.g., acyclovir, ganciclovir) are used to treat **herpesvirus infections** by interfering with viral DNA replication.
- Influenza is an RNA virus and does not rely on DNA polymerase for its replication cycle.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 7: A 49-year-old woman presents to her primary care doctor in late December with malaise. She reports worsening fatigue, myalgias, headache, and malaise that started 1 day ago. She works as a lunch lady at an elementary school. Her past medical history is notable for a distal radius fracture after a fall 2 years ago, but she is otherwise healthy and takes no medications. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She is married and has 3 adult children who are healthy. Her temperature is 102.9°F (39.4°C), blood pressure is 101/61 mmHg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 21/min. On exam, she appears lethargic and uncomfortable but is able to answer questions appropriately. Breath sounds are normal bilaterally. She is started on intravenous fluids and a pharmacologic agent for treatment. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of the drug being used to treat this patient?
- A. Neuraminidase inhibitor (Correct Answer)
- B. Reverse transcriptase inhibitor
- C. RNA-dependent polymerase inhibitor
- D. DNA polymerase inhibitor
- E. Protease inhibitor
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Neuraminidase inhibitor***
- The patient's symptoms (malaise, fatigue, myalgias, headache, fever) with rapid onset in **late December**, especially given her exposure to children in an elementary school, are highly suggestive of **influenza**.
- **Neuraminidase inhibitors** (e.g., oseltamivir, zanamivir) are the primary antiviral treatment for influenza, preventing the release of new viral particles from infected cells.
*Reverse transcriptase inhibitor*
- **Reverse transcriptase inhibitors** are primarily used in the treatment of **HIV infection**, which typically presents with a different constellation of symptoms and has a chronic rather than acute course.
- This class of drugs targets the enzyme **reverse transcriptase**, which is not central to the influenza virus replication cycle.
*RNA-dependent polymerase inhibitor*
- While **baloxavir marboxil** (an RNA polymerase inhibitor) is FDA-approved for influenza treatment, **neuraminidase inhibitors** remain the most commonly used first-line agents.
- In this clinical scenario without specific contraindications to neuraminidase inhibitors, oseltamivir or zanamivir would be the most likely agents prescribed.
*DNA polymerase inhibitor*
- **DNA polymerase inhibitors** are primarily used to treat **DNA viral infections** such as herpes viruses (e.g., acyclovir for HSV/VZV) or cytomegalovirus (e.g., ganciclovir).
- Influenza is an **RNA virus** and therefore does not have a DNA polymerase for replication.
*Protease inhibitor*
- **Protease inhibitors** are a class of antiviral drugs predominantly used in the treatment of **HIV** and **Hepatitis C virus** infections.
- Influenza viruses do not have a protease target that is typically inhibited by these drugs for therapeutic purposes.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 8: A 27-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his friends in a confused state. He was doing fine 5 days ago when he started to complain of fever and flu-like symptoms. His fever was low-grade and associated with a headache. For the past 2 days, he has become increasingly irritable, confused, and was getting angry at trivial things. Past medical history is unremarkable. He is a college student and is physically active. He smokes cigarettes occasionally. He drinks alcohol socially. He is sexually active with his girlfriend and they use condoms inconsistently. Physical examination reveals: blood pressure 120/80 mm Hg, heart rate 108/min, respiratory rate 10/min, and temperature 37.4°C (99.4°F). He is confused and disoriented. Pupils are 3 mm in diameter and respond to light sluggishly. He is moving all his limbs spontaneously. His neck is supple. MRI of the brain is shown in the picture. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) reveals an opening pressure of 16 cm of H20, a total leukocyte count of 112/mm3 with 85% lymphocytes, the protein of 42 mg/dL, and glucose of 58 mg/dL. What is the best treatment for this condition?
- A. Intravenous immunoglobulin
- B. High-dose steroids
- C. Rituximab
- D. Acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- E. Ceftriaxone
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Acyclovir***
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **flu-like symptoms** followed by **irritability**, **confusion**, and **MRI findings** suggestive of temporal lobe involvement, along with **lymphocytic pleocytosis** in CSF, is highly indicative of **herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE)**.
- **Acyclovir** is the treatment of choice for HSE, as it is an antiviral drug effective against the **herpes simplex virus (HSV)**. Prompt administration significantly improves outcomes.
*Intravenous immunoglobulin*
- **Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)** is generally used for certain **immunodeficiencies** or **autoimmune conditions**, not for acute viral encephalitis like HSE.
- There is no evidence to support the use of IVIG as a primary treatment for HSV encephalitis.
*High-dose steroids*
- While steroids can reduce cerebral edema and inflammation, their routine use in **viral encephalitis** like HSE is **controversial** and not a first-line treatment.
- Steroids might be considered in specific cases of severe cerebral edema, but not as the primary antiviral therapy.
*Rituximab*
- **Rituximab** is a **monoclonal antibody** targeting **CD20-positive B cells**, primarily used in certain **lymphomas** and **autoimmune diseases** like **rheumatoid arthritis** or **multiple sclerosis**.
- It has no role in the treatment of acute viral encephalitis.
*Ceftriaxone*
- **Ceftriaxone** is a broad-spectrum **antibiotic** used to treat **bacterial meningitis** or other bacterial infections.
- It is ineffective against viral infections such as HSV encephalitis.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 9: A 22-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a fever and a sore throat. He has had these symptoms for the past 2 weeks and has felt progressively more fatigued. His temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 120/68 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for tonsillar exudates, posterior cervical lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management for this patient?
- A. No further workup needed
- B. Rapid strep test
- C. Amoxicillin
- D. Oseltamivir
- E. Monospot test (Correct Answer)
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Monospot test***
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **sore throat**, **tonsillar exudates**, **posterior cervical lymphadenopathy**, and **splenomegaly** for 2 weeks is highly suggestive of **infectious mononucleosis**.
- A **Monospot test** (heterophile antibody test) is the most appropriate initial diagnostic step to confirm the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis.
*No further workup needed*
- This is incorrect because the patient has a constellation of symptoms and physical findings suggestive of a specific condition that warrants **diagnostic confirmation** for appropriate management and to rule out other possible causes.
- Without further workup, the underlying condition remains undiagnosed, potentially leading to **mismanagement** or delayed treatment of complications.
*Rapid strep test*
- While a **sore throat** with exudates can suggest streptococcal pharyngitis, the presence of **splenomegaly** and **posterior cervical lymphadenopathy** in this age group makes infectious mononucleosis a more likely diagnosis.
- A rapid strep test might be negative and would not explain the splenomegaly or prolonged symptoms, potentially delaying the correct diagnosis.
*Amoxicillin*
- Administering **amoxicillin** to a patient with infectious mononucleosis can cause a **characteristic maculopapular rash**, which is often mistaken for an allergic reaction.
- Additionally, infectious mononucleosis is caused by a **virus (EBV)**, so antibiotics like amoxicillin are ineffective and not indicated for treatment unless a co-occurring bacterial infection is confirmed.
*Oseltamivir*
- **Oseltamivir** is an antiviral medication specifically used for the treatment of **influenza**.
- This patient's symptoms are not typical for influenza, and the duration of illness (2 weeks) along with specific physical findings like splenomegaly point away from influenza and towards infectious mononucleosis.
Influenza antivirals US Medical PG Question 10: A 53-year-old woman comes to the physician in February because of a 1-day history of fever, chills, headache, and dry cough. She also reports malaise and generalized muscle aches. She works as a teacher at a local high school, where there was recently an outbreak of influenza. She has a history of intermittent asthma, for which she takes albuterol as needed. She declined the influenza vaccine offered in the fall because her sister told her that a friend developed a flulike illness after receiving the vaccine. She is worried about possibly becoming ill and cannot afford to miss work. Her temperature is 37.9°C (100.3°F), heart rate is 58/min, and her respirations are 12/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Her hemoglobin concentration is 14.5 g/dL, leukocyte count is 9,400/mm3, and platelet count is 280,000/mm3. In addition to analgesia, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Inactivated influenza vaccine
- B. Amantadine
- C. Live attenuated influenza vaccine
- D. Oseltamivir (Correct Answer)
- E. Supportive therapy only
Influenza antivirals Explanation: ***Oseltamivir***
- This patient presents with classic symptoms of **influenza** (fever, chills, headache, dry cough, malaise, myalgias) during an outbreak, making **antiviral therapy** like oseltamivir appropriate.
- She is at risk for complications due to her history of **asthma**, and early treatment (within 48 hours of symptom onset) can reduce illness severity and duration.
*Inactivated influenza vaccine*
- An **inactivated influenza vaccine** is a **preventive measure** and is not effective as a treatment once symptoms have already begun.
- Vaccination in the past fall would have been appropriate, but it will not help resolve her current acute illness.
*Amantadine*
- **Amantadine** is an older antiviral agent active only against **influenza A**, and its use is limited due to widespread **resistance**.
- It is generally not recommended for routine influenza treatment due to its narrow spectrum and resistance profile.
*Live attenuated influenza vaccine*
- The **live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV)** is a **preventive measure** indicated for healthy individuals aged 2-49 years and is contraindicated in individuals with **asthma**.
- Like the inactivated vaccine, it is not used for treating active influenza infection.
*Supportive therapy only*
- While supportive care (analgesia, hydration) is important, relying solely on it is not the most appropriate step given the patient's **risk factors** (asthma) and the availability of effective antiviral treatment.
- Early antiviral therapy can reduce serious complications in at-risk individuals.
More Influenza antivirals US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.