HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 1 week after being admitted to the hospital for oral candidiasis and esophagitis. His CD4+ T lymphocyte count is 180 cells/μL. An HIV antibody test is positive. Genotypic resistance assay shows the virus to be susceptible to all antiretroviral therapy regimens and therapy with dolutegravir, tenofovir, and emtricitabine is initiated. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings would be most likely on follow-up evaluation 3 months later?
$$$ CD4 +/CD8 ratio %%% HIV RNA %%% HIV antibody test $$$
- A. ↓ ↓ negative
- B. ↑ ↑ negative
- C. ↓ ↑ negative
- D. ↑ ↓ positive (Correct Answer)
- E. ↓ ↑ positive
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***↑ ↓ positive***
- With effective **antiretroviral therapy (ART)**, the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would increase as **CD4+ T cell counts rise** and **CD8+ T cell counts decrease**.
- **HIV RNA (viral load)** would significantly decrease (ideally to undetectable levels) due to the suppression of viral replication, but HIV antibodies would remain positive indefinitely.
*↓ ↓ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** and **HIV RNA** (viral load) along with a negative **HIV antibody test** is inconsistent with successful ART.
- A negative HIV antibody test would mean the patient was never infected, which contradicts the initial positive result and symptoms.
*↑ ↑ negative*
- An increase in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** is expected with ART, but an increase in **HIV RNA** (viral load) indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is impossible after a confirmed positive result, regardless of treatment success.
*↓ ↑ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would suggest worsening immune function, while an increase in **HIV RNA** indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is not possible once a patient has developed antibodies to HIV.
*↓ ↑ positive*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would indicate immune decline, contrary to the expected improvement with effective ART.
- An increase in **HIV RNA (viral load)** would signify treatment failure, even if HIV antibodies remain positive.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 2: A 25-year-old sexually active male presents to an internal medicine physician for a routine health check up after having several unprotected sexual encounters. After appropriate testing the physician discusses with the patient that he is HIV+ and must be started on anti-retroviral treatment. Which of the following medications prescribed acts on the gp41 subunit of the HIV envelope glycoprotein?
- A. Zidovudine
- B. Saquinavir
- C. Enfuvirtide (Correct Answer)
- D. Amantadine
- E. Rimantadine
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***Enfuvirtide***
- **Enfuvirtide** is a **fusion inhibitor** that binds specifically to the **gp41 subunit** of the HIV envelope glycoprotein.
- By binding to gp41, Enfuvirtide prevents the **fusion of the viral and host cell membranes**, thereby blocking viral entry and replication.
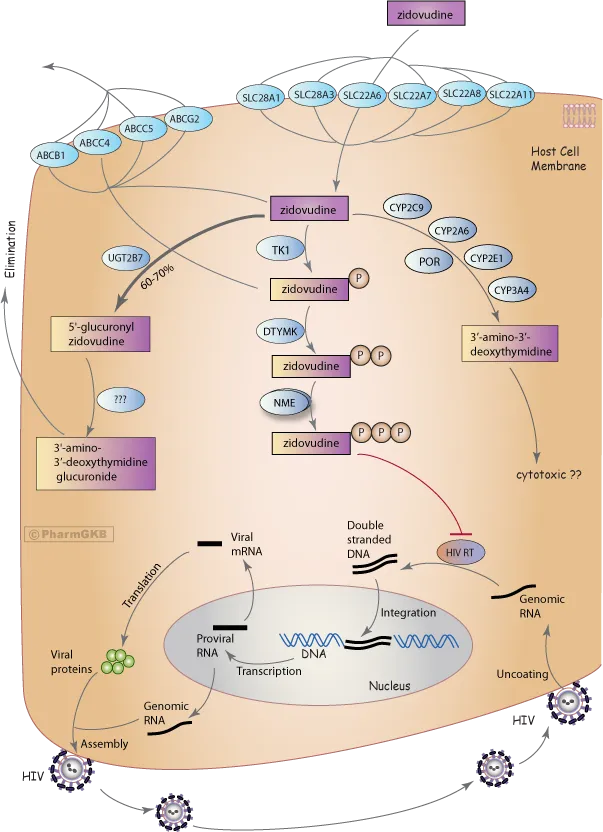
*Zidovudine*
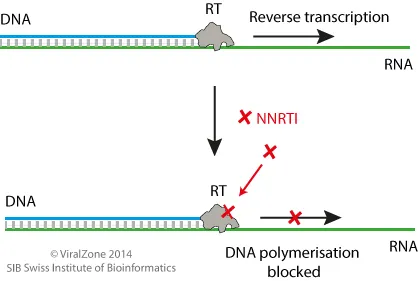
- **Zidovudine** is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)**.
- It works by inhibiting the enzyme **reverse transcriptase**, which is responsible for converting viral RNA into DNA.
*Saquinavir*
- **Saquinavir** is a **protease inhibitor (PI)**.
- This drug works by inhibiting the **HIV protease enzyme**, which is crucial for cleaving viral polyproteins into functional proteins required for viral assembly and maturation.
*Amantadine*
- **Amantadine** is an **antiviral agent** primarily used to treat **influenza A**.
- It works by interfering with the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, thus inhibiting viral uncoating.
*Rimantadine*
- **Rimantadine** is another **antiviral agent** used for **influenza A treatment and prophylaxis**.
- Similar to amantadine, it targets the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, preventing the uncoating step necessary for viral replication.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 3: A 43-year-old man with HIV infection comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of progressive diarrhea and a 3-kg (6.6-lb) weight loss. During this period, he has had 3–4 episodes of watery stools daily, with multiple instances of blood in the stool. He is currently receiving antiretroviral therapy with zidovudine, lamivudine, and dolutegravir. Physical examination shows pallor and dry mucous membranes. A colonoscopy shows multiple linear ulcers. Polymerase chain reaction of a stool sample is positive for cytomegalovirus. Treatment with valganciclovir is begun. Adding this drug to his current medication regimen puts this patient at greatest risk for which of the following adverse effects?
- A. Hepatic steatosis
- B. Abnormal dreams
- C. Pancytopenia (Correct Answer)
- D. Orthostatic dysregulation
- E. Hyperglycemia
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***Pancytopenia***
- **Valganciclovir** is a known cause of **bone marrow suppression**, leading to **pancytopenia** (low red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets).
- The patient is also on **zidovudine**, an antiretroviral that can cause **myelosuppression**, thus the combined use significantly increases the risk of pancytopenia.
*Hepatic steatosis*
- **Hepatic steatosis** (fatty liver) is a rare but known adverse effect of some nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), particularly older ones.
- While lamivudine is an NRTI, **valganciclovir** is not primarily associated with hepatic steatosis, and the combination does not specifically heighten this risk more than other options.
*Abnormal dreams*
- **Abnormal dreams** are a common side effect associated with certain antiretroviral drugs, particularly the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor **efavirenz**.
- This patient is on dolutegravir (an integrase inhibitor), zidovudine, and lamivudine, none of which are primarily known for causing abnormal dreams as a prominent side effect, and valganciclovir does not contribute to this.
*Orthostatic dysregulation*
- **Orthostatic dysregulation** (orthostatic hypotension) can be a side effect of various medications, but it is not a prominent adverse effect of either **valganciclovir** or the patient's current antiretroviral regimen.
- While dehydration from diarrhea can cause it, the medication itself does not directly increase this risk in particular.
*Hyperglycemia*
- **Hyperglycemia** can be a side effect of certain antiretroviral drugs, particularly some **protease inhibitors** and older NRTIs.
- However, the patient's current regimen (zidovudine, lamivudine, dolutegravir) and **valganciclovir** are not strongly associated with hyperglycemia as a primary adverse effect compared to other options.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 4: A 49-year-old woman presents to her primary care doctor in late December with malaise. She reports worsening fatigue, myalgias, headache, and malaise that started 1 day ago. She works as a lunch lady at an elementary school. Her past medical history is notable for a distal radius fracture after a fall 2 years ago, but she is otherwise healthy and takes no medications. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She is married and has 3 adult children who are healthy. Her temperature is 102.9°F (39.4°C), blood pressure is 101/61 mmHg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 21/min. On exam, she appears lethargic and uncomfortable but is able to answer questions appropriately. Breath sounds are normal bilaterally. She is started on intravenous fluids and a pharmacologic agent for treatment. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of the drug being used to treat this patient?
- A. Neuraminidase inhibitor (Correct Answer)
- B. Reverse transcriptase inhibitor
- C. RNA-dependent polymerase inhibitor
- D. DNA polymerase inhibitor
- E. Protease inhibitor
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***Neuraminidase inhibitor***
- The patient's symptoms (malaise, fatigue, myalgias, headache, fever) with rapid onset in **late December**, especially given her exposure to children in an elementary school, are highly suggestive of **influenza**.
- **Neuraminidase inhibitors** (e.g., oseltamivir, zanamivir) are the primary antiviral treatment for influenza, preventing the release of new viral particles from infected cells.
*Reverse transcriptase inhibitor*
- **Reverse transcriptase inhibitors** are primarily used in the treatment of **HIV infection**, which typically presents with a different constellation of symptoms and has a chronic rather than acute course.
- This class of drugs targets the enzyme **reverse transcriptase**, which is not central to the influenza virus replication cycle.
*RNA-dependent polymerase inhibitor*
- While **baloxavir marboxil** (an RNA polymerase inhibitor) is FDA-approved for influenza treatment, **neuraminidase inhibitors** remain the most commonly used first-line agents.
- In this clinical scenario without specific contraindications to neuraminidase inhibitors, oseltamivir or zanamivir would be the most likely agents prescribed.
*DNA polymerase inhibitor*
- **DNA polymerase inhibitors** are primarily used to treat **DNA viral infections** such as herpes viruses (e.g., acyclovir for HSV/VZV) or cytomegalovirus (e.g., ganciclovir).
- Influenza is an **RNA virus** and therefore does not have a DNA polymerase for replication.
*Protease inhibitor*
- **Protease inhibitors** are a class of antiviral drugs predominantly used in the treatment of **HIV** and **Hepatitis C virus** infections.
- Influenza viruses do not have a protease target that is typically inhibited by these drugs for therapeutic purposes.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 5: A 44-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. Eight months ago, he was diagnosed with HIV infection and combined antiretroviral treatment was begun. He feels well. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. Current medications include lamivudine, zidovudine, atazanavir, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.2 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume 102 μm3
Leukocyte count 2,600/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 38%
Lymphocytes 54%
Platelet count 150,000/mm3
Serum
Folate normal
Lactate 6.0 mEq/L (N = 0.5–2.2)
Arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows:
pH 7.34
pCO2 55 mm Hg
pO2 99 mmHg
HCO3- 14 mEq/L
The drug most likely responsible for this patient's current laboratory findings belongs to which of the following classes of drugs?
- A. Entry inhibitor
- B. Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor
- C. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (Correct Answer)
- D. Integrase inhibitor
- E. Protease inhibitor
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor***
- The patient presents with **macrocytic anemia** (Hgb 11.2, MCV 102), **leukopenia** (2600), **lactic acidosis** (lactate 6.0, pH 7.34, HCO3- 14, pCO2 55), and is on a regimen including **zidovudine** and **lamivudine**.
- **Zidovudine** (AZT), a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), is well-known for causing **myelosuppression** (anemia, leukopenia) and **mitochondrial toxicity**, which can lead to lactic acidosis due to impaired oxidative phosphorylation.
*Entry inhibitor*
- Entry inhibitors like **enfuvirtide** and **maraviroc** block HIV from entering CD4+ cells; side effects are mainly injection site reactions or hepatotoxicity.
- They are not associated with macrocytic anemia, leukopenia, or lactic acidosis.
*Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor*
- **Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)**, listed as a current medication, is a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor that can cause **bone marrow suppression** mimicking folate deficiency.
- However, the patient's folate levels are normal, and the significant lactic acidosis points away from TMP-SMX as the primary cause of all findings.
*Integrase inhibitor*
- Integrase inhibitors like **raltegravir** or **dolutegravir** prevent the integration of viral DNA into the host genome.
- Their primary side effects are typically gastrointestinal (nausea, diarrhea), headache, or insomnia, and they do not cause macrocytic anemia, leukopenia, or lactic acidosis.
*Protease inhibitor*
- **Atazanavir**, a protease inhibitor from the patient's regimen, can cause **hyperbilirubinemia** and **lipodystrophy** but is not directly linked to the bone marrow suppression and severe lactic acidosis seen here.
- Other protease inhibitors can cause metabolic complications, but not this specific constellation of hematologic and metabolic abnormalities.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 6: A 29-year-old female presents to her gynecologist complaining of a painful rash around her genitals. She has multiple sexual partners and uses condoms intermittently. Her last STD screen one year ago was negative. On examination, she has bilateral erosive vesicles on her labia majora and painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. She is started on an oral medication that requires a specific thymidine kinase for activation. Which of the following adverse effects is associated with this drug?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Deafness
- C. Renal failure (Correct Answer)
- D. Gingival hyperplasia
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***Renal failure***
- The patient's symptoms (painful genital rash, erosive vesicles, inguinal lymphadenopathy) are highly suggestive of **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, likely genital herpes.
- The drug described is an antiviral agent like **acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir**, which require **viral thymidine kinase** for activation and are known to cause **renal impairment** (nephrotoxicity) as an adverse effect, especially with high doses or in dehydrated patients due to crystal nephropathy.
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common side effect of some antibiotics (e.g., tetracyclines, sulfonamides), diuretics (e.g., thiazides), and antifungals, but it is **not a prominent adverse effect of acyclovir or its derivatives**.
- While theoretical, it is not a clinically significant or frequently observed adverse effect associated with the class of antiviral drugs used for HSV.
*Deafness*
- **Ototoxicity**, leading to deafness or hearing loss, is a well-known adverse effect of certain classes of drugs, such as **aminoglycoside antibiotics** (e.g., gentamicin) and **loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide).
- It is **not an adverse effect** associated with antiviral medications like acyclovir.
*Gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** (overgrowth of gum tissue) is a recognized side effect of specific medications including **phenytoin** (an anticonvulsant), **cyclosporine** (an immunosuppressant), and **calcium channel blockers** (e.g., nifedipine, amlodipine).
- This adverse effect is **not associated with antiviral drugs** used to treat herpes simplex.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a serious adverse effect linked to various drugs like **amiodarone** (an antiarrhythmic), **bleomycin** (a chemotherapeutic agent), **methotrexate** (an immunosuppressant/chemotherapeutic), and **nitrofurantoin** (an antibiotic).
- **Antiviral medications for HSV** do not typically cause pulmonary fibrosis.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 7: A 63-year-old HIV-positive man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. Four years ago, he was diagnosed with HIV and was started on cART therapy. He tells the physician that he has been having difficulty adhering to his medication regimen. He has been unemployed for the past couple of years and relies on unemployment benefits to cover the costs of daily living. His father died of lymphoma at the age of 60 years. He wants more information about his risk of developing DLBCL. Which of the following is the greatest risk factor for the development of DLBCL in HIV-positive patients?
- A. Poor adherence to cART (Correct Answer)
- B. Income below $30,000 per year
- C. Male sex
- D. Positive family history of cancer
- E. Age over 55 years
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: **Poor adherence to cART**
- **Poor adherence** to cART leads to **uncontrolled HIV replication** and persistent **immunosuppression**, which significantly increases the risk of developing **DLBCL**.
- **Immune dysregulation** caused by HIV directly contributes to a higher incidence of **AIDS-defining malignancies**, including DLBCL.
*Income below $30,000 per year*
- While **socioeconomic factors** can impact access to care and medication adherence, low income itself is not a direct biological risk factor for DLBCL.
- Its influence is secondary to its effect on adherence and overall health status, rather than a primary risk factor for the malignancy.
*Positive family history of cancer*
- Although a family history of cancer can increase the risk for some malignancies, it is generally **not a significant risk factor** for **HIV-associated DLBCL**.
- The primary drivers of HIV-associated DLBCL are linked to HIV-induced immunodeficiency, not specific inherited genetic predispositions for lymphoma.
*Age over 55 years*
- While the incidence of many cancers increases with **age**, for **HIV-associated DLBCL**, age is less prominent than the degree of **immunodeficiency** caused by HIV.
- The stronger prognostic factor remains the state of the immune system, particularly a **low CD4 count**, which is often exacerbated by poor cART adherence.
*Male sex*
- While there are minor differences in cancer incidence between sexes, **male sex** is not a primary or significant independent risk factor for **HIV-associated DLBCL**.
- The risk is predominantly driven by factors related to HIV infection itself and the resulting immune dysfunction.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 8: A group of investigators discovers a novel monomeric enzyme that cleaves glutamate-valine bonds in a bacterial exotoxin. The substrate binding site of the enzyme is rich in aspartate. A sample of the enzyme is added to two serum samples containing the bacterial exotoxin. One sample is assigned a test condition while the other is maintained as the control. The averaged results of several trials comparing Vmax and Km between control serum and test serum are shown.
Vmax (μmol/min) Km (mM)
Control serum 13.2 81.2
Test serum 28.8 80.9
Which of the following conditions in the test serum would best explain these findings?
- A. Presence of a reversible competitive inhibitor
- B. Increased exotoxin concentration
- C. Increased enzyme concentration (Correct Answer)
- D. Presence of an irreversible competitive inhibitor
- E. Increased serum pH
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***Increased enzyme concentration***
- An increase in enzyme concentration directly leads to a higher **Vmax** because there are more active sites available to convert substrate into product.
- The **Km** (substrate concentration at half Vmax) remains unchanged as the enzyme's affinity for the substrate is not altered, only the total number of enzyme molecules.
*Presence of a reversible competitive inhibitor*
- A **competitive inhibitor** would increase the **apparent Km** (making it seem like the enzyme has lower affinity for the substrate) because it competes with the substrate for the active site.
- The **Vmax** would remain unchanged, as a sufficiently high substrate concentration can overcome the inhibition.
*Increased exotoxin concentration*
- Increasing the substrate (**exotoxin**) concentration within the range where the enzyme is not saturated would increase the reaction rate up to **Vmax**, but it would not change the intrinsic **Vmax** or **Km** of the enzyme.
- If the enzyme is already saturated, increasing substrate concentration further will not affect the rate.
*Presence of an irreversible competitive inhibitor*
- An **irreversible inhibitor** permanently binds to the enzyme, effectively reducing the concentration of functional enzyme.
- This would lead to a decrease in **Vmax** because fewer enzyme molecules are available for catalysis.
- Note: True competitive inhibitors are reversible; this option tests understanding that irreversible inhibition reduces functional enzyme concentration and thus Vmax.
*Increased serum pH*
- Changing the **pH** away from the enzyme's optimal pH would typically lead to a decrease in enzyme activity, thereby reducing the **Vmax** and potentially altering the **Km** due to changes in enzyme conformation.
- The observed increase in **Vmax** and unchanged **Km** do not align with a deviation from optimal pH.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 9: A physician scientist is looking for a more efficient way to treat HIV. Patients infected with HIV mount a humoral immune response by producing antibodies against the HIV envelope proteins. These antibodies are the same antibodies detected by the ELISA and western blot assays used to diagnose the disease. The physician scientist is trying to generate a new, more potent antibody against the same HIV envelope proteins targeted by the natural humoral immune response. Of the following proteins, which is the most likely target of the antibody he is designing?
- A. p24
- B. CXCR4
- C. CCR5
- D. p17
- E. gp120 (Correct Answer)
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***gp120***
- **gp120** is an **envelope glycoprotein** on the surface of HIV, responsible for binding to CD4 receptors on host cells.
- Antibodies against **gp120** are generated during natural infection and are detected by diagnostic assays, making it a primary target for therapeutic antibody development.
*p24*
- **p24** is a **capsid protein** of HIV, forming the conical core of the virus, but it is not an envelope protein.
- While antibodies against **p24** are produced during infection and are detectable, it's an internal protein, not exposed on the viral surface for direct neutralization.
*CXCR4*
- **CXCR4** is a **chemokine co-receptor** found on the surface of host cells (e.g., T-lymphocytes), used by some HIV strains (T-tropic) for entry.
- It is a host cell protein, not an HIV viral protein, so it would not be a target for antibodies aiming to directly neutralize the virus.
*CCR5*
- **CCR5** is another **chemokine co-receptor** on host cells (e.g., macrophages, T-lymphocytes) used by other HIV strains (M-tropic) for viral entry.
- Similar to CXCR4, it is a host cell protein, not an HIV envelope protein, and therefore not a direct target for neutralizing antibodies against the virus itself.
*p17*
- **p17** is an HIV **matrix protein** located just beneath the viral envelope, playing a role in viral assembly and budding.
- Similar to p24, it is an internal structural protein, not an external envelope protein, making it less accessible for neutralizing antibodies.
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG Question 10: A 37-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of progressive breast enlargement. Two years ago, he was diagnosed with HIV infection and started treatment with antiretroviral medications. Examination shows a soft, non-tender, ill-defined swelling at the nape of the neck. The cheeks appear hollowed. Serum studies show increased total cholesterol and LDL concentration. Which of the following medications is the most likely cause of these findings?
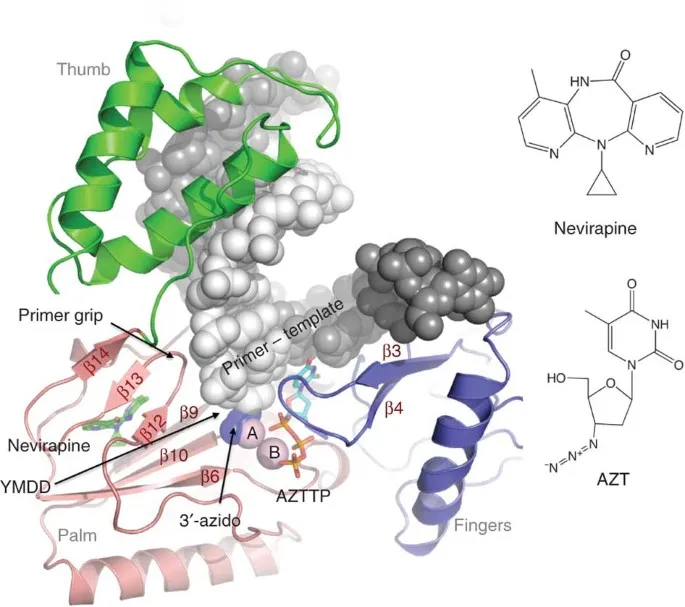
- A. Nevirapine
- B. Indinavir (Correct Answer)
- C. Enfuvirtide
- D. Abacavir
- E. Raltegravir
HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors Explanation: ***Indinavir***
- This patient presents with signs of **lipodystrophy**, specifically **lipoaccumulation** (breast enlargement, "buffalo hump" at the nape of the neck) and **lipoatrophy** (hollow cheeks), along with **dyslipidemia**.
- **Protease inhibitors (PIs)**, such as indinavir, are well-known to cause these metabolic complications, including **lipodystrophy** and **hyperlipidemia**, in patients with HIV.
*Nevirapine*
- Nevirapine is a **non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI)**.
- While NNRTIs can be associated with some metabolic side effects, they are less commonly implicated in severe **lipodystrophy** and **dyslipidemia** compared to protease inhibitors.
*Enfuvirtide*
- Enfuvirtide is a **fusion inhibitor** and generally has a favorable metabolic profile.
- It is not typically associated with **lipodystrophy** or significant **dyslipidemia**.
*Abacavir*
- Abacavir is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)**.
- While some NRTIs (especially stavudine and zidovudine) were strongly linked to lipoatrophy, abacavir is much less likely to cause this severe form of **lipodystrophy** or **hyperlipidemia**.
*Raltegravir*
- Raltegravir is an **integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)**.
- INSTIs are increasingly used due to their generally good metabolic profile and are not a common cause of **lipodystrophy** or **dyslipidemia**.
More HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.