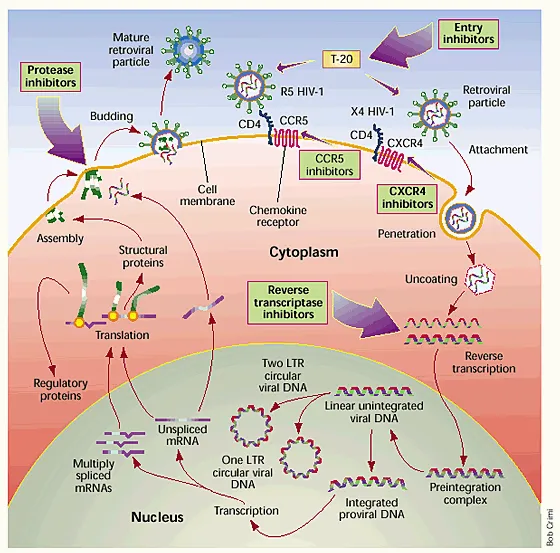
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for HIV entry inhibitors. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 1: An HIV-positive 48-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 3-month history of recurrent, painful mouth ulcers. This time, the pain is so severe that the patient cannot eat. He has a history of a seizure disorder but currently does not take any medications. He appears very ill. His temperature is 39.0°C (102.2°F). Physical examination shows numerous vesicular ulcerations on the lips and sloughing of the gums, buccal mucosa, and hard palate. Genetic analysis of the pathogen isolated from the lesions shows a mutation in a gene encoding viral phosphotransferases. Which of the following drugs is the most appropriate treatment?
- A. Acyclovir
- B. Famciclovir
- C. Cidofovir
- D. Ganciclovir
- E. Foscarnet (Correct Answer)
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***Foscarnet***
- The presence of **recurrent, painful vesicular ulcerations** in an HIV-positive patient, especially with **gingivostomatitis-like symptoms** (sloughing gums, buccal mucosa), points to a severe **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, likely resistant to nucleoside analogues given the **phosphotransferase mutation**.
- **Foscarnet** is a pyrophosphate analog that directly inhibits viral DNA polymerase without requiring phosphorylation by viral thymidine kinase, making it effective against **acyclovir-resistant HSV** strains, which often develop resistance via mutations in viral phosphotransferases or thymidine kinase.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is a nucleoside analog that requires phosphorylation by viral thymidine kinase (a phosphotransferase) to become active.
- A **mutation in viral phosphotransferases** would render the virus resistant to acyclovir, making it an ineffective treatment.
*Famciclovir*
- **Famciclovir** is a prodrug of penciclovir, which is also a nucleoside analog that requires phosphorylation by viral thymidine kinase for activation.
- Similar to acyclovir, a **mutation in viral phosphotransferases** would lead to resistance and make famciclovir ineffective.
*Cidofovir*
- **Cidofovir** is a nucleotide analog that does not require phosphorylation by viral enzymes for its initial activation.
- While it can be effective against some resistant strains, **foscarnet is generally preferred** for severe, resistant HSV infections as cidofovir is primarily used for **CMV retinitis** and is associated with significant nephrotoxicity.
*Ganciclovir*
- **Ganciclovir** is a nucleoside analog primarily used for **CMV infections**, and it also requires phosphorylation by viral kinases for activation.
- It is not the first-line treatment for HSV, and the **phosphotransferase mutation** would likely confer resistance to ganciclovir as well.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 2: You are seeing a patient in clinic who recently started treatment for active tuberculosis. The patient is currently being treated with rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. The patient is not used to taking medicines and is very concerned about side effects. Specifically regarding the carbohydrate polymerization inhibiting medication, which of the following is a known side effect?
- A. Vision loss (Correct Answer)
- B. Paresthesias of the hands and feet
- C. Cutaneous flushing
- D. Arthralgias
- E. Elevated liver enzymes
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***Vision loss***
- The "carbohydrate polymerization inhibiting medication" refers to **ethambutol**, which inhibits **arabinosyl transferase** (involved in mycobacterial cell wall arabinogalactan synthesis)
- **Ethambutol** causes **optic neuritis**, leading to **decreased visual acuity**, **red-green color blindness**, and potentially **irreversible vision loss**
- **Regular ophthalmologic monitoring** is essential during ethambutol therapy
*Paresthesias of the hands and feet*
- This describes **peripheral neuropathy** caused by **isoniazid**
- Isoniazid interferes with **pyridoxine (vitamin B6) metabolism**, leading to neurotoxicity
- Risk factors include malnutrition, diabetes, alcoholism, and pregnancy
- Prevented by **pyridoxine supplementation**
*Cutaneous flushing*
- Not a characteristic side effect of first-line anti-tuberculosis medications
- More commonly associated with niacin or certain allergic/vasodilatory reactions
*Arthralgias*
- Classic side effect of **pyrazinamide**, often affecting small joints
- Caused by **pyrazinamide-induced hyperuricemia** (inhibits renal uric acid excretion)
- May require dose adjustment or discontinuation if severe
*Elevated liver enzymes*
- **Hepatotoxicity** can occur with **rifampin**, **isoniazid**, and **pyrazinamide**
- Requires regular monitoring of liver function tests during TB treatment
- Most common serious adverse effect of combination TB therapy
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 3: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 4: A 49-year-old homeless man comes to the emergency department because of fatigue, cough, and worsening shortness of breath for 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with HIV-infection 25 years ago but has never had any symptoms. He has always refused to take antiretroviral medication. Pulmonary examination shows diffuse crackles over bilateral lower lung fields. An x-ray of the chest shows diffuse, symmetrical interstitial infiltrates. His serum level of beta-d-glucan is elevated. Further testing shows a heterozygous mutation that prevents entry of HIV into macrophages. Which of the following proteins is most likely affected by the mutation in this patient?
- A. ICAM-1
- B. Gp120
- C. CD4
- D. P antigen
- E. CCR5 (Correct Answer)
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***CCR5***
- The mutation preventing HIV entry into **macrophages** points to an issue with a coreceptor, most commonly **CCR5**, which is crucial for macrophage-tropic HIV strains.
- A **heterozygous mutation** in CCR5 (CCR5-Δ32) can confer partial resistance to HIV-1 infection, explaining why the patient has been asymptomatic for 25 years despite refusing antiretroviral therapy.
- This is a well-documented host genetic factor that slows HIV disease progression.
*ICAM-1*
- **ICAM-1 (Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1)** is involved in cell adhesion and immune cell trafficking, but not directly in HIV entry into macrophages.
- Mutations in ICAM-1 would not specifically prevent HIV entry, nor would it explain the long-term asymptomatic status in an HIV-positive individual.
*Gp120*
- **Gp120** is an HIV envelope glycoprotein that binds to the **CD4 receptor** and a coreceptor (CCR5 or CXCR4) on host cells.
- While gp120 is essential for HIV entry, it is a **viral protein**; the question asks about a mutation in a **host protein** that prevents viral entry.
*CD4*
- **CD4** is the primary receptor for HIV on T cells and macrophages, essential for viral entry.
- However, a **heterozygous CD4 mutation** would not provide meaningful protection against HIV, as one functional copy would be sufficient for viral entry.
- In contrast, heterozygous **CCR5-Δ32** mutation provides documented partial resistance, making CCR5 the better answer given this patient's 25-year asymptomatic course.
*P antigen*
- **P antigen** typically refers to a red blood cell antigen and is not involved in HIV entry into macrophages.
- There is no known direct association between P antigen and HIV susceptibility or disease progression.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old pregnant woman presents to an obstetrician at 35 weeks gestation reporting that she noted the presence of a mucus plug in her vaginal discharge this morning. The obstetrician performs an examination and confirms that she is in labor. She was diagnosed with HIV infection 1 year ago. Her current antiretroviral therapy includes abacavir, lamivudine, and nevirapine. Her last HIV RNA level was 2,000 copies/mL 3 weeks ago. Which of the following anti-retroviral drugs should be administered intravenously to the woman during labor?
- A. Enfuvirtide
- B. Nevirapine
- C. Abacavir
- D. Rilpivirine
- E. Zidovudine (Correct Answer)
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***Zidovudine***
- Intravenous **zidovudine** is recommended during labor for HIV-positive pregnant women, especially when the viral load is **>1000 copies/mL**, to reduce the risk of **mother-to-child transmission (MTCT)**.
- This intervention significantly lowers the viral load in the maternal blood and reduces fetal exposure to the virus during delivery.
*Enfuvirtide*
- **Enfuvirtide** is a **fusion inhibitor** administered subcutaneously, not intravenously, and is reserved for treatment-experienced patients with multi-drug resistant HIV.
- It is not a standard recommendation for intrapartum prophylaxis against MTCT.
*Nevirapine*
- **Nevirapine** is an **NNRTI** that is typically given orally, and while it has been used for MTCT prophylaxis, intravenous administration is not standard for intrapartum use.
- The woman is already on oral nevirapine as part of her ART regimen.
*Abacavir*
- **Abacavir** is an **NRTI** given orally and is part of the patient's current ART regimen.
- It is not administered intravenously for intrapartum MTCT prophylaxis.
*Rilpivirine*
- **Rilpivirine** is an **NNRTI** that is taken orally and is not indicated for intravenous administration during labor to prevent MTCT.
- Its use is limited by potential drug interactions and efficacy in patients with high viral loads.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 6: A physician scientist is looking for a more efficient way to treat HIV. Patients infected with HIV mount a humoral immune response by producing antibodies against the HIV envelope proteins. These antibodies are the same antibodies detected by the ELISA and western blot assays used to diagnose the disease. The physician scientist is trying to generate a new, more potent antibody against the same HIV envelope proteins targeted by the natural humoral immune response. Of the following proteins, which is the most likely target of the antibody he is designing?
- A. p24
- B. CXCR4
- C. CCR5
- D. p17
- E. gp120 (Correct Answer)
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***gp120***
- **gp120** is an **envelope glycoprotein** on the surface of HIV, responsible for binding to CD4 receptors on host cells.
- Antibodies against **gp120** are generated during natural infection and are detected by diagnostic assays, making it a primary target for therapeutic antibody development.
*p24*
- **p24** is a **capsid protein** of HIV, forming the conical core of the virus, but it is not an envelope protein.
- While antibodies against **p24** are produced during infection and are detectable, it's an internal protein, not exposed on the viral surface for direct neutralization.
*CXCR4*
- **CXCR4** is a **chemokine co-receptor** found on the surface of host cells (e.g., T-lymphocytes), used by some HIV strains (T-tropic) for entry.
- It is a host cell protein, not an HIV viral protein, so it would not be a target for antibodies aiming to directly neutralize the virus.
*CCR5*
- **CCR5** is another **chemokine co-receptor** on host cells (e.g., macrophages, T-lymphocytes) used by other HIV strains (M-tropic) for viral entry.
- Similar to CXCR4, it is a host cell protein, not an HIV envelope protein, and therefore not a direct target for neutralizing antibodies against the virus itself.
*p17*
- **p17** is an HIV **matrix protein** located just beneath the viral envelope, playing a role in viral assembly and budding.
- Similar to p24, it is an internal structural protein, not an external envelope protein, making it less accessible for neutralizing antibodies.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 7: An 11-year-old boy with HIV and esophageal candidiasis is being treated with caspofungin. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Pore formation in cell membranes
- B. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis
- C. Inhibition of 1,3-Beta-glucan synthase (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase
- E. Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***Inhibition of 1,3-Beta-glucan synthase***
- **Caspofungin** is an **echinocandin** antifungal agent that works by inhibiting **1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase**.
- This enzyme is crucial for the synthesis of **glucan**, a vital component of the **fungal cell wall**, leading to cell wall disruption and fungal cell death.
*Pore formation in cell membranes*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B**.
- These drugs bind to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, forming pores that lead to leakage of cellular contents.
*Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis*
- This is the mechanism of action for **azole antifungals** (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole) and **allylamines** (e.g., terbinafine).
- Azoles inhibit **14-alpha-demethylase**, an enzyme involved in converting lanosterol to ergosterol, while allylamines inhibit **squalene epoxidase**.
*Inhibition of squalene epoxidase*
- This is the specific mechanism for **allylamine antifungals** like **terbinafine**.
- Inhibition of **squalene epoxidase** prevents the synthesis of **ergosterol**, primarily used for superficial fungal infections.
*Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **flucytosine**, an antifungal pro-drug.
- Flucytosine is converted to **5-fluorouracil** within fungal cells, which then inhibits fungal DNA and RNA synthesis.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 8: A student health coordinator plans on leading a campus-wide HIV screening program that will be free for the entire undergraduate student body. The goal is to capture as many correct HIV diagnoses as possible with the fewest false positives. The coordinator consults with the hospital to see which tests are available to use for this program. Test A has a sensitivity of 0.92 and a specificity of 0.99. Test B has a sensitivity of 0.95 and a specificity of 0.96. Test C has a sensitivity of 0.98 and a specificity of 0.93. Which of the following testing schemes should the coordinator pursue?
- A. Test A on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive
- B. Test A on the entire student body followed by Test C on those who are positive
- C. Test C on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive
- D. Test C on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive (Correct Answer)
- E. Test B on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***Test C on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive***
- To "capture as many correct HIV diagnoses as possible" (maximize true positives), the initial screening test should have the **highest sensitivity**. Test C has the highest sensitivity (0.98).
- To "capture as few false positives as possible" (maximize true negatives and confirm diagnoses), the confirmatory test should have the **highest specificity**. Test A has the highest specificity (0.99).
*Test A on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive*
- Starting with Test A (sensitivity 0.92) would miss more true positive cases than starting with Test C (sensitivity 0.98), failing the goal of **capturing as many cases as possible**.
- Following with Test B (specificity 0.96) would result in more false positives than following with Test A (specificity 0.99).
*Test A on the entire student body followed by Test C on those who are positive*
- This scheme would miss many true positive cases initially due to Test A's lower sensitivity compared to Test C.
- Following with Test C would introduce more false positives than necessary, as it has a lower specificity (0.93) than Test A (0.99).
*Test C on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive*
- While Test C is a good initial screen for its high sensitivity, following it with Test B (specificity 0.96) is less optimal than Test A (specificity 0.99) for minimizing false positives in the confirmation step.
- This combination would therefore yield more false positives in the confirmatory stage than using Test A.
*Test B on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive*
- Test B has a sensitivity of 0.95, which is lower than Test C's sensitivity of 0.98, meaning it would miss more true positive cases at the initial screening stage.
- While Test A provides excellent specificity for confirmation, the initial screening step is suboptimal for the goal of capturing as many diagnoses as possible.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old female presents to her gynecologist complaining of a painful rash around her genitals. She has multiple sexual partners and uses condoms intermittently. Her last STD screen one year ago was negative. On examination, she has bilateral erosive vesicles on her labia majora and painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. She is started on an oral medication that requires a specific thymidine kinase for activation. Which of the following adverse effects is associated with this drug?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Deafness
- C. Renal failure (Correct Answer)
- D. Gingival hyperplasia
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: ***Renal failure***
- The patient's symptoms (painful genital rash, erosive vesicles, inguinal lymphadenopathy) are highly suggestive of **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, likely genital herpes.
- The drug described is an antiviral agent like **acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir**, which require **viral thymidine kinase** for activation and are known to cause **renal impairment** (nephrotoxicity) as an adverse effect, especially with high doses or in dehydrated patients due to crystal nephropathy.
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common side effect of some antibiotics (e.g., tetracyclines, sulfonamides), diuretics (e.g., thiazides), and antifungals, but it is **not a prominent adverse effect of acyclovir or its derivatives**.
- While theoretical, it is not a clinically significant or frequently observed adverse effect associated with the class of antiviral drugs used for HSV.
*Deafness*
- **Ototoxicity**, leading to deafness or hearing loss, is a well-known adverse effect of certain classes of drugs, such as **aminoglycoside antibiotics** (e.g., gentamicin) and **loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide).
- It is **not an adverse effect** associated with antiviral medications like acyclovir.
*Gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** (overgrowth of gum tissue) is a recognized side effect of specific medications including **phenytoin** (an anticonvulsant), **cyclosporine** (an immunosuppressant), and **calcium channel blockers** (e.g., nifedipine, amlodipine).
- This adverse effect is **not associated with antiviral drugs** used to treat herpes simplex.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a serious adverse effect linked to various drugs like **amiodarone** (an antiarrhythmic), **bleomycin** (a chemotherapeutic agent), **methotrexate** (an immunosuppressant/chemotherapeutic), and **nitrofurantoin** (an antibiotic).
- **Antiviral medications for HSV** do not typically cause pulmonary fibrosis.
HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG Question 10: A 63-year-old HIV-positive man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. Four years ago, he was diagnosed with HIV and was started on cART therapy. He tells the physician that he has been having difficulty adhering to his medication regimen. He has been unemployed for the past couple of years and relies on unemployment benefits to cover the costs of daily living. His father died of lymphoma at the age of 60 years. He wants more information about his risk of developing DLBCL. Which of the following is the greatest risk factor for the development of DLBCL in HIV-positive patients?
- A. Poor adherence to cART (Correct Answer)
- B. Income below $30,000 per year
- C. Male sex
- D. Positive family history of cancer
- E. Age over 55 years
HIV entry inhibitors Explanation: **Poor adherence to cART**
- **Poor adherence** to cART leads to **uncontrolled HIV replication** and persistent **immunosuppression**, which significantly increases the risk of developing **DLBCL**.
- **Immune dysregulation** caused by HIV directly contributes to a higher incidence of **AIDS-defining malignancies**, including DLBCL.
*Income below $30,000 per year*
- While **socioeconomic factors** can impact access to care and medication adherence, low income itself is not a direct biological risk factor for DLBCL.
- Its influence is secondary to its effect on adherence and overall health status, rather than a primary risk factor for the malignancy.
*Positive family history of cancer*
- Although a family history of cancer can increase the risk for some malignancies, it is generally **not a significant risk factor** for **HIV-associated DLBCL**.
- The primary drivers of HIV-associated DLBCL are linked to HIV-induced immunodeficiency, not specific inherited genetic predispositions for lymphoma.
*Age over 55 years*
- While the incidence of many cancers increases with **age**, for **HIV-associated DLBCL**, age is less prominent than the degree of **immunodeficiency** caused by HIV.
- The stronger prognostic factor remains the state of the immune system, particularly a **low CD4 count**, which is often exacerbated by poor cART adherence.
*Male sex*
- While there are minor differences in cancer incidence between sexes, **male sex** is not a primary or significant independent risk factor for **HIV-associated DLBCL**.
- The risk is predominantly driven by factors related to HIV infection itself and the resulting immune dysfunction.
More HIV entry inhibitors US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.