Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Herpesvirus antivirals. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 1: A 57-year-old man comes to the emergency department because he has been having problems seeing over the last week. He says that he has been seeing specks in his vision and his vision also becomes blurry when he tries to focus on objects. He says that he cannot recall anything that may have precipitated this; however, he has been homeless for several months. His CD4+ cell count is 27 cells/mL so he is started on a new medication. Notably, this drug has the following properties when mixed with various proteins:
Drug alone - drug remains unphosphorylated
Drug and HSV proteins - drug remains unphosphorylated
Drug and CMV proteins - drug remains unphosphorylated
Drug and human proteins - drug is phosphorylated
Which of the following drugs is most consistent with this set of findings?
- A. Cidofovir (Correct Answer)
- B. Oseltamivir
- C. Ganciclovir
- D. Acyclovir
- E. Foscarnet
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Cidofovir***
- The patient's presentation with **seeing specks and blurry vision** (floaters) along with a **CD4+ count of 27 cells/mL** strongly suggests **CMV retinitis**, a common opportunistic infection in advanced HIV/AIDS.
- **Cidofovir** is a nucleotide analog that **does NOT require viral kinases for activation** - it remains unphosphorylated when mixed with HSV or CMV proteins, as stated in the question.
- However, cidofovir **DOES require phosphorylation by host cellular kinases** (specifically cellular kinases, not viral kinases) to become the active triphosphate form. This matches the drug property showing it **becomes phosphorylated with human proteins**.
- This unique activation mechanism (host-dependent, viral-independent) distinguishes it from other antivirals and matches the experimental findings described.
*Foscarnet*
- **Foscarnet** is also used for CMV retinitis and **does NOT require ANY phosphorylation** - neither viral nor host enzymes.
- It acts as a **pyrophosphate analog** that directly inhibits viral DNA polymerase without requiring activation.
- The drug properties show phosphorylation occurs with human proteins, which is **inconsistent with foscarnet** that remains unphosphorylated under all conditions.
*Ganciclovir*
- **Ganciclovir** requires phosphorylation by **viral kinase UL97 in CMV** (or thymidine kinase in HSV) for initial activation, followed by host kinases.
- The drug properties state it remains unphosphorylated with CMV proteins, which is **inconsistent with ganciclovir's mechanism**.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is primarily used for **HSV and VZV infections**, not CMV retinitis in AIDS patients.
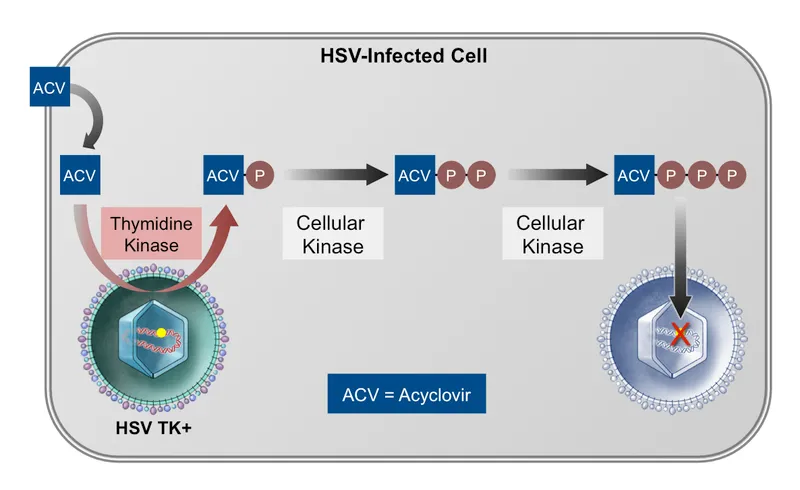
- It requires initial phosphorylation by **viral thymidine kinase** (HSV-TK), which contradicts the finding that it remains unphosphorylated with HSV proteins.
*Oseltamivir*
- **Oseltamivir** is a **neuraminidase inhibitor** used for **influenza treatment**.
- It has no role in CMV retinitis and does not act via phosphorylation-dependent DNA polymerase inhibition.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 2: A 40-year-old man presents with problems with his vision. He says he has been experiencing blurred vision and floaters in his left eye for the past few days. He denies any ocular pain, fever, or headaches. Past medical history is significant for HIV infection a few years ago, for which he is noncompliant with his antiretroviral medications and his most recent CD4 count was 100 cells/mm3. His temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F), the blood pressure is 110/89 mm Hg, the pulse rate is 70/min, and the respiratory rate is 14/min. Ocular exam reveals a decreased vision in the left eye, and a funduscopic examination is shown in the image. The patient is admitted and immediately started on intravenous ganciclovir. A few days after admission he is still complaining of blurry vision and floaters, so he is switched to a different medication. Inhibition of which of the following processes best describes the mechanism of action of the newly added medication?
- A. Protein synthesis
- B. Nucleic acid synthesis (Correct Answer)
- C. Progeny virus release
- D. Viral penetration into host cells
- E. Viral uncoating
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Nucleic acid synthesis***
- This patient likely has **cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis**, characterized by **blurred vision**, **floaters**, and **necrotizing retinitis** in an HIV-positive individual with a **low CD4 count (100 cells/mm3)**.
- The initial drug, **ganciclovir**, targets nucleic acid synthesis by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase. If ganciclovir fails, a common second-line agent like **foscarnet** or **cidofovir** is used, and both also inhibit viral **nucleic acid (DNA) synthesis** through different mechanisms (foscarnet directly inhibits DNA polymerase, cidofovir is a nucleotide analog).
*Protein synthesis*
- This mechanism is targeted by certain antibacterial and antifungal drugs, but not typically by antiviral medications used for CMV.
- Antiviral drugs generally target specific viral processes, distinct from host protein synthesis, to limit toxicity.
*Progeny virus release*
- This mechanism is primarily targeted by **neuraminidase inhibitors** (e.g., oseltamivir, zanamivir) used to treat influenza, which prevent the release of new viral particles from infected cells.
- It is not a common mechanism for CMV antivirals.
*Viral penetration into host cells*
- Medications that inhibit viral penetration or entry, such as **fusion inhibitors** (e.g., enfuvirtide for HIV) or **CCR5 antagonists** (e.g., maraviroc for HIV), prevent the virus from entering the host cell.
- These mechanisms are not relevant to the treatment of CMV retinitis.
*Viral uncoating*
- **Amantadine** and **rimantadine** are examples of antiviral drugs that inhibit **viral uncoating** by interfering with the M2 ion channel in influenza A.
- This mechanism is specific to influenza viruses and is not involved in the action of CMV antiviral medications.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 3: A 43-year-old man with HIV infection comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of progressive diarrhea and a 3-kg (6.6-lb) weight loss. During this period, he has had 3–4 episodes of watery stools daily, with multiple instances of blood in the stool. He is currently receiving antiretroviral therapy with zidovudine, lamivudine, and dolutegravir. Physical examination shows pallor and dry mucous membranes. A colonoscopy shows multiple linear ulcers. Polymerase chain reaction of a stool sample is positive for cytomegalovirus. Treatment with valganciclovir is begun. Adding this drug to his current medication regimen puts this patient at greatest risk for which of the following adverse effects?
- A. Hepatic steatosis
- B. Abnormal dreams
- C. Pancytopenia (Correct Answer)
- D. Orthostatic dysregulation
- E. Hyperglycemia
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Pancytopenia***
- **Valganciclovir** is a known cause of **bone marrow suppression**, leading to **pancytopenia** (low red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets).
- The patient is also on **zidovudine**, an antiretroviral that can cause **myelosuppression**, thus the combined use significantly increases the risk of pancytopenia.
*Hepatic steatosis*
- **Hepatic steatosis** (fatty liver) is a rare but known adverse effect of some nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), particularly older ones.
- While lamivudine is an NRTI, **valganciclovir** is not primarily associated with hepatic steatosis, and the combination does not specifically heighten this risk more than other options.
*Abnormal dreams*
- **Abnormal dreams** are a common side effect associated with certain antiretroviral drugs, particularly the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor **efavirenz**.
- This patient is on dolutegravir (an integrase inhibitor), zidovudine, and lamivudine, none of which are primarily known for causing abnormal dreams as a prominent side effect, and valganciclovir does not contribute to this.
*Orthostatic dysregulation*
- **Orthostatic dysregulation** (orthostatic hypotension) can be a side effect of various medications, but it is not a prominent adverse effect of either **valganciclovir** or the patient's current antiretroviral regimen.
- While dehydration from diarrhea can cause it, the medication itself does not directly increase this risk in particular.
*Hyperglycemia*
- **Hyperglycemia** can be a side effect of certain antiretroviral drugs, particularly some **protease inhibitors** and older NRTIs.
- However, the patient's current regimen (zidovudine, lamivudine, dolutegravir) and **valganciclovir** are not strongly associated with hyperglycemia as a primary adverse effect compared to other options.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 4: A 29-year-old female presents to her gynecologist complaining of a painful rash around her genitals. She has multiple sexual partners and uses condoms intermittently. Her last STD screen one year ago was negative. On examination, she has bilateral erosive vesicles on her labia majora and painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. She is started on an oral medication that requires a specific thymidine kinase for activation. Which of the following adverse effects is associated with this drug?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Deafness
- C. Renal failure (Correct Answer)
- D. Gingival hyperplasia
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Renal failure***
- The patient's symptoms (painful genital rash, erosive vesicles, inguinal lymphadenopathy) are highly suggestive of **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, likely genital herpes.
- The drug described is an antiviral agent like **acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir**, which require **viral thymidine kinase** for activation and are known to cause **renal impairment** (nephrotoxicity) as an adverse effect, especially with high doses or in dehydrated patients due to crystal nephropathy.
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common side effect of some antibiotics (e.g., tetracyclines, sulfonamides), diuretics (e.g., thiazides), and antifungals, but it is **not a prominent adverse effect of acyclovir or its derivatives**.
- While theoretical, it is not a clinically significant or frequently observed adverse effect associated with the class of antiviral drugs used for HSV.
*Deafness*
- **Ototoxicity**, leading to deafness or hearing loss, is a well-known adverse effect of certain classes of drugs, such as **aminoglycoside antibiotics** (e.g., gentamicin) and **loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide).
- It is **not an adverse effect** associated with antiviral medications like acyclovir.
*Gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** (overgrowth of gum tissue) is a recognized side effect of specific medications including **phenytoin** (an anticonvulsant), **cyclosporine** (an immunosuppressant), and **calcium channel blockers** (e.g., nifedipine, amlodipine).
- This adverse effect is **not associated with antiviral drugs** used to treat herpes simplex.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a serious adverse effect linked to various drugs like **amiodarone** (an antiarrhythmic), **bleomycin** (a chemotherapeutic agent), **methotrexate** (an immunosuppressant/chemotherapeutic), and **nitrofurantoin** (an antibiotic).
- **Antiviral medications for HSV** do not typically cause pulmonary fibrosis.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his friends in a confused state. He was doing fine 5 days ago when he started to complain of fever and flu-like symptoms. His fever was low-grade and associated with a headache. For the past 2 days, he has become increasingly irritable, confused, and was getting angry at trivial things. Past medical history is unremarkable. He is a college student and is physically active. He smokes cigarettes occasionally. He drinks alcohol socially. He is sexually active with his girlfriend and they use condoms inconsistently. Physical examination reveals: blood pressure 120/80 mm Hg, heart rate 108/min, respiratory rate 10/min, and temperature 37.4°C (99.4°F). He is confused and disoriented. Pupils are 3 mm in diameter and respond to light sluggishly. He is moving all his limbs spontaneously. His neck is supple. MRI of the brain is shown in the picture. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) reveals an opening pressure of 16 cm of H20, a total leukocyte count of 112/mm3 with 85% lymphocytes, the protein of 42 mg/dL, and glucose of 58 mg/dL. What is the best treatment for this condition?
- A. Intravenous immunoglobulin
- B. High-dose steroids
- C. Rituximab
- D. Acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- E. Ceftriaxone
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Acyclovir***
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **flu-like symptoms** followed by **irritability**, **confusion**, and **MRI findings** suggestive of temporal lobe involvement, along with **lymphocytic pleocytosis** in CSF, is highly indicative of **herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE)**.
- **Acyclovir** is the treatment of choice for HSE, as it is an antiviral drug effective against the **herpes simplex virus (HSV)**. Prompt administration significantly improves outcomes.
*Intravenous immunoglobulin*
- **Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)** is generally used for certain **immunodeficiencies** or **autoimmune conditions**, not for acute viral encephalitis like HSE.
- There is no evidence to support the use of IVIG as a primary treatment for HSV encephalitis.
*High-dose steroids*
- While steroids can reduce cerebral edema and inflammation, their routine use in **viral encephalitis** like HSE is **controversial** and not a first-line treatment.
- Steroids might be considered in specific cases of severe cerebral edema, but not as the primary antiviral therapy.
*Rituximab*
- **Rituximab** is a **monoclonal antibody** targeting **CD20-positive B cells**, primarily used in certain **lymphomas** and **autoimmune diseases** like **rheumatoid arthritis** or **multiple sclerosis**.
- It has no role in the treatment of acute viral encephalitis.
*Ceftriaxone*
- **Ceftriaxone** is a broad-spectrum **antibiotic** used to treat **bacterial meningitis** or other bacterial infections.
- It is ineffective against viral infections such as HSV encephalitis.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 6: A 61-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician complaining of left-sided facial pain that started yesterday. She describes the pain as stinging, burning, and constant. It does not worsen with jaw movement or chewing. Her past medical history includes hyperlipidemia and multiple sclerosis (MS), and she had chickenpox as a child but received a shingles vaccination last year. Medications include simvastatin and glatiramer acetate. The patient’s last MS flare was 5 weeks ago, at which time she received a prednisone burst with taper. At this visit, her temperature is 99.9 °F (37.7°C), blood pressure is 139/87 mmHg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 14/min. On exam, there is no rash or skin change on either side of the patient’s face. Gentle palpation of the left cheek and mandible produce significant pain, but there is full range of motion in the jaw. Which of the following medications is the most likely to prevent long-term persistence of this patient’s pain?
- A. Carbamazepine
- B. Topical corticosteroids
- C. Oral acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- D. Amitriptyline
- E. Gabapentin
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Oral acyclovir***
- The patient's symptoms (stinging, burning, constant facial pain, history of chickenpox, recent MS flare, and prednisone use) are highly suggestive of a **herpes zoster (shingles) reactivation**, despite prior vaccination. Early antiviral therapy, such as oral acyclovir, is crucial to reduce the duration and severity of the acute pain and, more importantly, to prevent **postherpetic neuralgia (PHN)**.
- Starting acyclovir within 72 hours of symptom onset significantly decreases the risk of developing long-term pain complications like PHN by inhibiting viral replication and reducing nerve damage.
*Carbamazepine*
- This medication is a first-line treatment for **trigeminal neuralgia**, characterized by brief, excruciating, shock-like pain triggered by specific stimuli, which differs from the patient's constant burning pain.
- While it can manage neuropathic pain, it does not address the underlying viral cause of herpes zoster and will not prevent PHN.
*Topical corticosteroids*
- Topical corticosteroids are primarily used to reduce **inflammation and itching** associated with skin rashes, such as those that may occur with herpes zoster.
- They do not possess antiviral properties and therefore will not *prevent* the long-term neurological complication of PHN.
*Amitriptyline*
- Amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, is a common treatment for **postherpetic neuralgia** once it has already developed, as well as other neuropathic pain conditions.
- However, it is not used to prevent the development of PHN in the acute phase of a herpes zoster infection; early antiviral treatment is the preventative strategy.
*Gabapentin*
- Gabapentin is an effective medication for established **neuropathic pain**, including postherpetic neuralgia.
- Similar to amitriptyline, gabapentin treats the *symptoms* of PHN once it is present but does not prevent its occurrence when used during the acute viral stage.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 7: A 56-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of progressively worsening shortness of breath and fever for 2 days. He also has a nonproductive cough. He does not have chest pain or headache. He has chronic myeloid leukemia and had a bone marrow transplant 3 months ago. His current medications include busulfan, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, and methylprednisolone. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F), pulse is 103/min, respirations are 26/min, and blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 93%. Pulmonary examination shows diffuse crackles. The spleen tip is palpated 4 cm below the left costal margin. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.3 g/dL
Leukocyte count 4,400/mm3
Platelet count 160,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 78 mg/dL
Creatinine 2.1 mg/dL
D-dimer 96 ng/mL (N < 250)
pp65 antigen positive
Galactomannan antigen negative
Urinalysis is normal. An x-ray of the chest shows diffuse bilateral interstitial infiltrates. An ECG shows sinus tachycardia. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Levofloxacin
- B. Ganciclovir (Correct Answer)
- C. Valganciclovir
- D. Azithromycin
- E. Acyclovir
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Ganciclovir***
- The patient's **positive pp65 antigen** confirms **cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection**, the most common viral infection in immunocompromised bone marrow transplant recipients.
- This patient has **severe, life-threatening CMV pneumonitis** evidenced by hypoxia (O2 sat 93%), tachypnea, and diffuse bilateral interstitial infiltrates.
- **Intravenous ganciclovir** is the **first-line treatment** for severe CMV disease due to its potent antiviral activity and reliable bioavailability in critically ill patients.
*Valganciclovir*
- **Valganciclovir** is an **oral prodrug of ganciclovir** with excellent bioavailability, but it is primarily reserved for **CMV prophylaxis** or **maintenance therapy** after initial IV treatment.
- In this patient with **acute, severe CMV pneumonitis** requiring urgent intervention (hypoxia, respiratory distress), **IV ganciclovir is strongly preferred** for faster, more reliable drug delivery and higher tissue concentrations.
*Levofloxacin*
- This **fluoroquinolone antibiotic** treats **bacterial infections**, not viral pathogens like CMV.
- The **positive pp65 antigen** specifically identifies CMV as the etiology, and negative galactomannan rules out invasive aspergillosis.
- While empiric antibacterial coverage might be considered in febrile neutropenic patients, the clear viral diagnosis directs therapy toward antivirals.
*Azithromycin*
- **Azithromycin** is a macrolide antibiotic effective against atypical bacteria (Mycoplasma, Chlamydophila) and some other bacterial pathogens.
- It has **no activity against CMV** and would not address the confirmed viral etiology.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is effective against **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** and **varicella-zoster virus (VZV)**, but has **poor activity against CMV** due to inadequate phosphorylation by CMV enzymes.
- The positive pp65 antigen specifically indicates CMV, for which ganciclovir (not acyclovir) is required.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 8: A 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of a sore throat and painful lesions in his mouth for the past few days. Six weeks ago, he underwent cardiac catheterization and stent implantation of the left anterior descending artery for treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Pharmacotherapy with aspirin and ticlopidine was started. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F). Oral examination shows several shallow ulcers on the buccal mucosa. Laboratory studies show:
Hematocrit 41.5%
Leukocyte count 1,050/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 35%
Platelet count 175,000/mm3
Which of the following drugs is most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
- A. Enoxaparin
- B. Aspirin
- C. Abciximab
- D. Apixaban
- E. Ticlopidine (Correct Answer)
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: **Ticlopidine**
* This patient presents with **neutropenia** (leukocyte count 1,050/mm3 with 35% segmented neutrophils) and **oral ulcers**, which signifies a severe adverse drug reaction.
* **Ticlopidine** is a P2Y12 inhibitor that carries a known risk of severe adverse effects, including **neutropenia** and **thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP).**
*Enoxaparin*
* Enoxaparin is a **low molecular weight heparin** used for anticoagulation.
* It is associated with **heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)**, but not typically neutropenia or oral ulcers.
*Aspirin*
* Aspirin is a **COX inhibitor** and an antiplatelet agent.
* Common side effects include **gastrointestinal upset** and bleeding, but it does not typically cause neutropenia or oral ulcers.
*Abciximab*
* Abciximab is a **glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor** used as an antiplatelet agent.
* Its primary adverse effect is **bleeding** and **thrombocytopenia**, but not neutropenia or oral ulcers.
*Apixaban*
* Apixaban is a **direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC)**, specifically a Factor Xa inhibitor.
* It is primarily associated with an increased risk of **bleeding** and does not typically cause neutropenia or oral ulcers.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 9: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of vomiting, abdominal pain, and blurry vision for the past hour. The parents report that the boy developed these symptoms after he accidentally ingested 2 tablets of his grandfather’s heart failure medication. On physical examination, the child is drowsy, and his pulse is 120/min and irregular. Digoxin toxicity is suspected. A blood sample is immediately sent for analysis and shows a serum digoxin level of 4 ng/mL (therapeutic range: 0.8–2 ng/mL). Which of the following electrolyte abnormalities is most likely to be present in the boy?
- A. Hypermagnesemia
- B. Hypokalemia
- C. Hypercalcemia
- D. Hyperkalemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypocalcemia
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***Hyperkalemia***
- **Digoxin** inhibits the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump**, leading to an increase in intracellular sodium and a decrease in intracellular potassium.
- The decreased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump results in reduced cellular uptake of potassium, causing **elevated extracellular potassium** levels.
*Hypermagnesemia*
- **Magnesium** is not directly affected by digoxin toxicity in a way that would lead to hypermagnesemia; in fact, hypomagnesemia can exacerbate digoxin toxicity.
- High magnesium levels are typically associated with renal failure or excessive intake of magnesium-containing antacids or laxatives.
*Hypokalemia*
- While hypokalemia can **predispose to digoxin toxicity** (by increasing digoxin binding to the Na+/K+-ATPase pump), acute digoxin overdose, as described here, often leads to **hyperkalemia** due to the direct inhibition of the pump's ability to drive potassium into cells.
- The classic association of hypokalemia with digoxin refers more to its role as a risk factor for toxicity, especially with diuretic use, rather than a direct consequence of acute overdose.
*Hypercalcemia*
- **Calcium** levels are not directly altered to hypercalcemia by digoxin toxicity.
- Digoxin's mechanism involves increasing intracellular calcium by promoting calcium influx and inhibiting its efflux via the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, but this typically does not manifest as measurable serum hypercalcemia.
*Hypocalcemia*
- Digoxin toxicity does not directly cause hypocalcemia.
- Digoxin actually leads to **increased intracellular calcium**, which is responsible for its positive inotropic effect, but this change is primarily intracellular and does not result in systemic hypocalcemia.
Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG Question 10: A 64-year-old woman presents to the clinic with a history of 3 fractures in the past year with the last one being last month. Her bone-density screening from last year reported a T-score of -3.1 and she was diagnosed with osteoporosis. She was advised to quit smoking and was asked to adapt to a healthy lifestyle to which she complied. She was also given calcium and vitamin D supplements. After a detailed discussion with the patient, the physician decides to start her on weekly alendronate. Which of the following statements best describes this patient’s new therapy?
- A. It should be stopped after 10 years due to the risk of esophageal cancer
- B. It is typically used as a second-line therapy for her condition after raloxifene
- C. It can cause hot flashes, flu-like symptoms, and peripheral edema
- D. It must be taken with the first meal of the day due to the significant risk of GI upset
- E. The patient must stay upright for at least 30 minutes after taking this medication (Correct Answer)
Herpesvirus antivirals Explanation: ***The patient must stay upright for at least 30 minutes after taking this medication***
- This instruction is crucial for **alendronate** (a bisphosphonate) to prevent **esophageal irritation** and potential esophagitis or ulcers.
- Alendronate must be taken with a full glass of plain water on an **empty stomach** at least 30-60 minutes before the first food, beverage, or other medication of the day, and the patient must remain upright.
*It should be stopped after 10 years due to the risk of esophageal cancer*
- The main concern with long-term bisphosphonate use (usually >5 years for oral agents) is the risk of **atypical femoral fractures** and **osteonecrosis of the jaw**, not esophageal cancer.
- While esophageal irritation is a known side effect, the risk of esophageal cancer is **not the primary reason** for treatment discontinuation after 10 years.
*It is typically used as a second-line therapy for her condition after raloxifene*
- **Alendronate** (an oral bisphosphonate) is considered a **first-line therapy** for postmenopausal osteoporosis, especially in patients with a history of fractures and low T-scores.
- **Raloxifene** is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) typically used when bisphosphonates are contraindicated or not tolerated, or there is a need to also treat breast cancer risk, and it is **less potent** in reducing non-vertebral fractures.
*It can cause hot flashes, flu-like symptoms, and peripheral edema*
- These side effects (hot flashes, flu-like symptoms, peripheral edema) are **not typically associated** with alendronate.
- **Hot flashes** are more common with estrogen-modulating drugs like raloxifene, while **flu-like symptoms** can occur with IV bisphosphonates (like zoledronic acid) or certain anabolic agents.
*It must be taken with the first meal of the day due to the significant risk of GI upset*
- This statement is incorrect; alendronate must be taken on an **empty stomach** (at least 30-60 minutes before the first food or drink) to ensure adequate absorption.
- Taking it with food or other beverages significantly **reduces its absorption**, making it less effective, and the risk of GI upset (specifically esophageal irritation) is why remaining upright and taking with water are stressed.
More Herpesvirus antivirals US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.