Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Hepatitis B antivirals. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 1: A 25-year-old sexually active male presents to an internal medicine physician for a routine health check up after having several unprotected sexual encounters. After appropriate testing the physician discusses with the patient that he is HIV+ and must be started on anti-retroviral treatment. Which of the following medications prescribed acts on the gp41 subunit of the HIV envelope glycoprotein?
- A. Zidovudine
- B. Saquinavir
- C. Enfuvirtide (Correct Answer)
- D. Amantadine
- E. Rimantadine
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Enfuvirtide***
- **Enfuvirtide** is a **fusion inhibitor** that binds specifically to the **gp41 subunit** of the HIV envelope glycoprotein.
- By binding to gp41, Enfuvirtide prevents the **fusion of the viral and host cell membranes**, thereby blocking viral entry and replication.
*Zidovudine*
- **Zidovudine** is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)**.
- It works by inhibiting the enzyme **reverse transcriptase**, which is responsible for converting viral RNA into DNA.
*Saquinavir*
- **Saquinavir** is a **protease inhibitor (PI)**.
- This drug works by inhibiting the **HIV protease enzyme**, which is crucial for cleaving viral polyproteins into functional proteins required for viral assembly and maturation.
*Amantadine*
- **Amantadine** is an **antiviral agent** primarily used to treat **influenza A**.
- It works by interfering with the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, thus inhibiting viral uncoating.
*Rimantadine*
- **Rimantadine** is another **antiviral agent** used for **influenza A treatment and prophylaxis**.
- Similar to amantadine, it targets the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, preventing the uncoating step necessary for viral replication.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 2: A 30-year-old woman presents with generalized fatigue, joint pain, and decreased appetite. She says that symptoms onset a year ago and have not improved. The patient’s husband says he has recently noticed that her eyes and skin are yellowish. The patient denies any history of smoking or alcohol use, but she admits to using different kinds of intravenous illicit drugs during her college years. The patient is afebrile and vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination is unremarkable, except for moderate scleral icterus. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of a blood sample is positive for a viral infection that reveals a positive-sense RNA virus, that is small, enveloped, and single-stranded. The patient is started on a drug that resembles a purine RNA nucleotide. She agrees not to get pregnant before or during the use of this medication. Which of the following is the drug that was most likely given to this patient?
- A. Sofosbuvir
- B. Cidofovir
- C. Ribavirin (Correct Answer)
- D. Simeprevir
- E. Interferon-alpha
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Ribavirin***
- The patient's history of **intravenous drug use**, fatigue, joint pain, decreased appetite, and **scleral icterus** are highly suggestive of **chronic Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection**. The description of the virus as a **small, enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus** confirms HCV. The patient is started on a drug that resembles a **purine RNA nucleotide** and is instructed not to get pregnant, which is characteristic of Ribavirin.
- **Ribavirin** is a **guanosine analog** that interferes with viral RNA synthesis and is known to be **teratogenic**, necessitating strict contraception during and after treatment.
*Sofosbuvir*
- While **Sofosbuvir** is used to treat Hepatitis C and is a **nucleotide analog** (specifically a uridine analog), it is a **prodrug** that mimics a uridine nucleotide, not a purine, and it is **not associated with the severe teratogenicity** that requires a two-contraception rule like Ribavirin.
- Sofosbuvir is a **direct-acting antiviral (DAA)** that inhibits the HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, but the description of a purine RNA nucleotide points away from this drug.
*Cidofovir*
- **Cidofovir** is a **cytosine nucleotide analog** primarily used to treat **cytomegalovirus (CMV)** retinitis in HIV/AIDS patients.
- It works by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase, and it is **not used for Hepatitis C infection**.
*Simeprevir*
- **Simeprevir** is an **HCV protease inhibitor**, not a nucleotide analog. It specifically targets the **NS3/4A protease** of the Hepatitis C virus.
- Although it is an effective DAA for HCV, its mechanism of action and class are different from the described "purine RNA nucleotide."
*Interferon-alpha*
- **Interferon-alpha** was historically used to treat Hepatitis C, but it is a **cytokine** that modulates the immune response, not a nucleoside/nucleotide analog.
- Its use has largely been replaced by more effective and better-tolerated direct-acting antivirals due to significant side effects and lower efficacy.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 3: A 39-year-old male presents to the emergency department with fever, jaundice, and abdominal pain. The patient is a known intravenous drug-user. Serologic testing reveals an ALT of 1040 units/L, AST of 810 units/L, and titer evidence of infection with an enveloped, negative sense, single-stranded, closed circular RNA virus. Which of the following infections must also be present in this patient for him to develop his current disease?
- A. Hepatitis C virus
- B. Hepatitis B virus (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatitis A virus
- D. Hepatitis D virus
- E. Hepatitis E virus
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: **Hepatitis B virus**
- Hepatitis D virus is a **defective RNA virus** that requires co-infection with the **Hepatitis B virus** for its replication and expression.
- The description of the virus as an **enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded, closed circular RNA virus** specifically matches the characteristics of Hepatitis D virus (HDV).
*Hepatitis C virus*
- Although Hepatitis C virus (HCV) can cause similar symptoms and is common among intravenous drug users, it is a **positive-sense RNA virus** and does not require co-infection with another hepatitis virus.
- HCV infection does not fit the specific viral description provided in the question.
*Hepatitis A virus*
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is an **unenveloped, positive-sense RNA virus** typically transmitted via the fecal-oral route, and it does not require co-infection with another virus.
- Its viral characteristics and transmission route do not match the clinical scenario.
*Hepatitis D virus*
- Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is described in the question as the infecting agent (enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded, closed circular RNA virus). However, it is a **defective virus** and requires **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** for its replication.
- Therefore, while HDV is the direct cause of the current disease, HBV must also be present for HDV to establish infection.
*Hepatitis E virus*
- Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is an **unenveloped, positive-sense RNA virus** mainly transmitted via the fecal-oral route, similar to HAV.
- It does not require co-infection with another virus and its viral characteristics do not match the description.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 4: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician for a pre-employment examination. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. A screening blood test is performed in which peptides are added to the sample to stimulate in vitro production of interferon-gamma, which is then measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. This test is most likely to be helpful in diagnosing infection with which of the following pathogens?
- A. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Staphylococcus aureus
- C. Human immunodeficiency virus
- D. Hepatitis B virus
- E. Legionella pneumophila
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Mycobacterium tuberculosis***
- The described test, an **interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)**, specifically measures immune response to *Mycobacterium tuberculosis* antigens.
- IGRAs are used to diagnose **latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)** by detecting T-cell mediated immunity to the bacteria.
*Staphylococcus aureus*
- This bacterium causes a variety of infections, but its diagnosis primarily relies on **bacterial culture** and **antigen detection**, not interferon-gamma release assays.
- *Staphylococcus aureus* is a common **bacterial pathogen** with different diagnostic approaches.
*Human immunodeficiency virus*
- **HIV infection** is diagnosed by detecting anti-HIV antibodies, HIV RNA, or p24 antigen through tests like **ELISA** and **Western blot**, not IGRA.
- The virus primarily targets **CD4+ T cells**, leading to immunodeficiency.
*Hepatitis B virus*
- **HBV infection** is diagnosed by detecting viral **antigens (HBsAg, HBeAg)** and **antibodies (anti-HBs, anti-HBc)** in the blood.
- It is a **DNA virus** causing hepatitis.
*Legionella pneumophila*
- **Legionnaire's disease**, caused by *Legionella pneumophila*, is typically diagnosed via **urine antigen testing**, **sputum culture**, or **PCR**.
- This bacterium is primarily associated with **respiratory tract infections**.
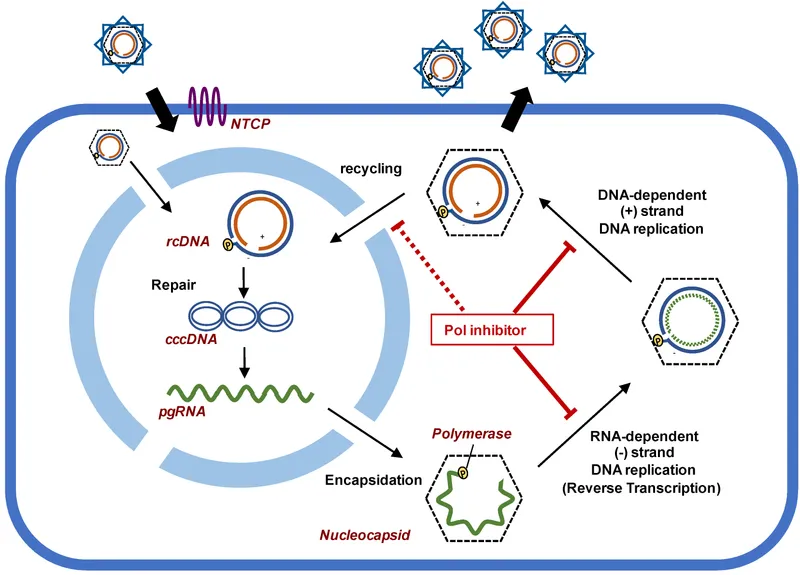
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old woman who recently emigrated from Brazil comes to the physician because of fever, fatigue, decreased appetite, and mild abdominal discomfort. She has not seen a physician in several years and her immunization status is unknown. She drinks 2 alcoholic beverages on the weekends and does not use illicit drugs. She is sexually active with several male partners and uses condoms inconsistently. Her temperature is 38°C (99.8°F). Physical examination shows right upper quadrant tenderness and scleral icterus. Serology confirms acute infection with a virus that has partially double-stranded, circular DNA. Which of the following is most likely involved in the replication cycle of this virus?
- A. Adhesion of virus to host ICAM-1 receptor
- B. Cleavage of gp160 to form envelope glycoprotein
- C. Bacterial translation of viral DNA
- D. Transcription of viral DNA to RNA in the cytoplasm
- E. Reverse transcription of viral RNA to DNA (Correct Answer)
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Reverse transcription of viral RNA to DNA***
- The description of a virus with **partially double-stranded, circular DNA** that causes acute infection with fever, fatigue, and **scleral icterus** points to **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)**.
- HBV is a **hepadnavirus** with a unique replication strategy: despite being a DNA virus, it replicates through an **RNA intermediate** (pregenomic RNA).
- The virus uses **reverse transcriptase** to synthesize DNA from this RNA template within the nucleocapsid—making it the only DNA virus that uses reverse transcription in its replication cycle.
*Adhesion of virus to host ICAM-1 receptor*
- The **intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) receptor** is primarily used by viruses like **rhinovirus** for entry into host cells, which is not characteristic of HBV.
- HBV primarily uses the **sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP)** as its entry receptor on hepatocytes.
*Cleavage of gp160 to form envelope glycoprotein*
- **gp160** is a precursor protein of the **HIV envelope glycoprotein**, which is cleaved into gp120 and gp41, essential for HIV entry.
- This process is specific to **retroviruses** like HIV and is not involved in HBV replication.
*Bacterial translation of viral DNA*
- Viruses, including HBV, replicate within **eukaryotic host cells** and utilize the host cell's machinery for replication, transcription, and translation.
- **Bacterial translation** is irrelevant to viral replication in human hosts.
*Transcription of viral DNA to RNA in the cytoplasm*
- While transcription of viral DNA to RNA does occur in HBV, it primarily takes place in the **nucleus** of the host hepatocyte, not the cytoplasm.
- The resulting pregenomic RNA is then exported to the cytoplasm for **reverse transcription** within newly assembled nucleocapsids.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 6: A 52-year-old woman comes to the physician because of abdominal discomfort, anorexia, and mild fatigue. She has systemic lupus erythematosus and takes hydroxychloroquine. She does not drink alcohol or use illicit drugs. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Alanine aminotransferase 455 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase 205 U/L
Hepatitis B surface antigen positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody negative
Hepatitis B envelope antigen positive
Hepatitis B core antigen IgG antibody positive
Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
- A. Acyclovir
- B. Tenofovir (Correct Answer)
- C. Pegylated interferon-alpha
- D. Dolutegravir
- E. Sofosbuvir
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Tenofovir***
- This patient has **chronic active hepatitis B infection**, as indicated by **positive HBsAg**, **HBeAg**, and elevated liver enzymes. Antiviral therapy with **tenofovir** is highly effective and appropriate to suppress viral replication.
- The coexistence of **Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)** and **hydroxychloroquine** use increases the importance of managing HBV, as immunosuppression can lead to viral reactivation; tenofovir effectively targets the virus without significant interactions.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat infections caused by **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** and **varicella-zoster virus (VZV)**.
- It has **no efficacy** against hepatitis B virus (HBV) and therefore would not be appropriate for this patient's condition.
*Pegylated interferon-alpha*
- **Pegylated interferon-alpha** is an immunomodulatory agent used to treat chronic hepatitis B and C; however, it has a **less favorable side effect profile** and is often reserved for patients who cannot tolerate or respond to nucleoside/nucleotide analogs.
- The patient's underlying **SLE** could be **exacerbated by interferon**, making tenofovir a safer and more appropriate first-line choice given its better tolerability and potent antiviral effect.
*Dolutegravir*
- **Dolutegravir** is an **integrase inhibitor** used in the treatment of **HIV infection**.
- It has **no antiviral activity** against the hepatitis B virus and is therefore not indicated for this patient's condition.
*Sofosbuvir*
- **Sofosbuvir** is a direct-acting antiviral agent primarily used to treat **chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection**.
- It is **not effective** against hepatitis B virus (HBV) and would not be the correct treatment for this patient.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old nurse presents 12 hours after she accidentally stuck herself with a blood-contaminated needle. She reported the accident appropriately and now seeks post-exposure prophylaxis. She does not have any complaints at the moment of presentation. Her vital signs include: blood pressure 125/80 mm Hg, heart rate 71/min, respiratory rate 15/min, and temperature 36.5℃ (97.7℉). Physical examination is unremarkable. The nurse has prescribed a post-exposure prophylaxis regimen which includes tenofovir, emtricitabine, and raltegravir. How will tenofovir change the maximum reaction rate (Vm) and Michaelis constant (Km) of the viral reverse transcriptase?
- A. Vm will decrease, Km will increase
- B. Vm and Km will both decrease
- C. Vm will stay the same, Km will increase
- D. Vm and Km will both increase
- E. Vm will decrease, Km will stay the same (Correct Answer)
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Vm will decrease, Km will stay the same***
- **Tenofovir** is a **nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NtRTI)** that acts as a **competitive substrate analog**. Once phosphorylated to **tenofovir diphosphate**, it competes with natural deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) for incorporation into the viral DNA chain.
- Upon incorporation, tenofovir acts as a **chain terminator** because it lacks a 3'-hydroxyl group necessary for further DNA elongation. This **irreversibly inactivates** the enzyme-DNA complex, effectively reducing the **maximum reaction rate (Vm)** by decreasing the amount of functional enzyme available.
- Since tenofovir competes with natural nucleotides but doesn't affect the enzyme's affinity for its natural substrates, the **Michaelis constant (Km) remains unchanged**. The inhibition pattern shows characteristics of competitive inhibition with irreversible chain termination.
*Vm will decrease, Km will increase*
- This pattern is characteristic of a **mixed inhibitor**, where the inhibitor can bind to both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex, reducing Vm while also decreasing substrate affinity (increasing Km).
- While tenofovir does reduce Vm through chain termination, it does not significantly alter the enzyme's affinity for natural nucleotide substrates. Tenofovir diphosphate **competes directly** with dATP rather than binding to an allosteric site, so Km remains unchanged rather than increasing.
*Vm and Km will both decrease*
- This effect is typical of an **uncompetitive inhibitor**, which binds only to the **enzyme-substrate complex**. Uncompetitive inhibitors decrease both Vm and Km, implying increased apparent substrate affinity.
- Tenofovir does not function as an uncompetitive inhibitor. As a **nucleotide analog**, it competes for the active site and gets incorporated into DNA, causing chain termination. This mechanism does not involve preferential binding to the enzyme-substrate complex that would decrease Km.
*Vm will stay the same, Km will increase*
- This describes **pure reversible competitive inhibition**, where the inhibitor competes with substrate for the active site but can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration, leaving Vm unchanged.
- While tenofovir diphosphate does **compete with natural nucleotides**, it acts as a **suicide substrate** that causes irreversible chain termination once incorporated. This **permanently inactivates** the enzyme-DNA complex, reducing the pool of functional enzyme and thus decreasing Vm, distinguishing it from simple reversible competitive inhibition.
*Vm and Km will both increase*
- An increase in both Vm and Km is not a standard pattern for enzyme inhibition and would suggest **reduced substrate affinity** with paradoxically increased catalytic capacity, which is inconsistent with any inhibitory mechanism.
- This scenario contradicts the **intended therapeutic effect** of tenofovir, which is to inhibit HIV reverse transcriptase activity and prevent viral replication, not to enhance enzyme function.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 8: A 20-year-old man who is a biology major presents to his physician for a simple check-up. He is informed that he hasn't received a hepatitis B vaccine. When the first injection is applied, the medical professional informs him that he will need to come back 2 more times on assigned days, since the vaccine is given in 3 doses. Which of the following antibodies is produced first in the college student as a result of the first vaccination?
- A. IgE
- B. IgG
- C. IgM (Correct Answer)
- D. IgD
- E. IgA
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***IgM***
- Upon initial exposure to an antigen (like in the first vaccine dose), **IgM antibodies** are the first class to be produced and secreted by plasma cells.
- This **primary immune response** is characterized by a rapid, but short-lived, **IgM** peak.
*IgE*
- **IgE antibodies** are primarily involved in **allergic reactions** and defense against parasites, not the initial response to vaccination.
- Their production is typically triggered by exposure to specific allergens or parasites and mediated by Th2 helper T cells.
*IgG*
- **IgG antibodies** are the most abundant class in serum and are produced later in the primary response and predominantly during the **secondary immune response**.
- They provide **long-term immunity** and can cross the placenta, but are not the first antibody produced after initial antigen exposure.
*IgD*
- **IgD antibodies** are mainly found on the surface of **naive B cells** and act as B-cell receptors, playing a role in B-cell activation.
- They are not secreted in significant amounts into the serum and thus are not the first circulating antibody produced after vaccination.
*IgA*
- **IgA antibodies** are primarily found in **mucosal secretions** (e.g., saliva, tears, breast milk, gastrointestinal fluid) and play a key role in mucosal immunity.
- They are not the first antibody produced systemically in response to an initial vaccine exposure.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 9: A 45-year-old man presents for follow-up to monitor his chronic hepatitis C treatment. The patient was infected with hepatitis C genotype 1, one year ago. He has been managed on a combination of pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin, but a sustained viral response has not been achieved. Past medical history is significant for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease for the last 5 years. Which of the following, if added to the patient’s current treatment regimen, would most likely benefit this patient?
- A. Emtricitabine
- B. Entecavir
- C. Simeprevir (Correct Answer)
- D. Tenofovir
- E. Telbivudine
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Simeprevir***
- Simeprevir is a **first-generation direct-acting antiviral (DAA)**, specifically a **protease inhibitor (NS3/4A inhibitor)**, highly effective against **HCV genotype 1**.
- Adding simeprevir to a regimen of **pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin** significantly increases the likelihood of achieving a **sustained virologic response** for patients who previously failed interferon-based therapy.
- **Note:** While this triple therapy approach was standard practice historically, current guidelines (as of 2024-2025) favor **interferon-free DAA combination regimens** (such as sofosbuvir/ledipasvir or glecaprevir/pibrentasvir) as first-line treatment for HCV genotype 1. However, among the options provided, simeprevir remains the only appropriate HCV-specific antiviral agent.
*Emtricitabine*
- This is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)** primarily used in the treatment of **HIV infection** and sometimes for hepatitis B.
- It has **no significant role** in the treatment of **hepatitis C viral infection**.
*Entecavir*
- Entecavir is an **antiviral agent** specifically used for the treatment of **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It has **no established efficacy** against the **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
*Tenofovir*
- Tenofovir is a **nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor** primarily used for treating **HIV infection** and **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It is **not effective** against **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
*Telbivudine*
- Telbivudine is an **oral antiviral agent** indicated specifically for the treatment of **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It does **not have antiviral activity** against the **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his friends in a confused state. He was doing fine 5 days ago when he started to complain of fever and flu-like symptoms. His fever was low-grade and associated with a headache. For the past 2 days, he has become increasingly irritable, confused, and was getting angry at trivial things. Past medical history is unremarkable. He is a college student and is physically active. He smokes cigarettes occasionally. He drinks alcohol socially. He is sexually active with his girlfriend and they use condoms inconsistently. Physical examination reveals: blood pressure 120/80 mm Hg, heart rate 108/min, respiratory rate 10/min, and temperature 37.4°C (99.4°F). He is confused and disoriented. Pupils are 3 mm in diameter and respond to light sluggishly. He is moving all his limbs spontaneously. His neck is supple. MRI of the brain is shown in the picture. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) reveals an opening pressure of 16 cm of H20, a total leukocyte count of 112/mm3 with 85% lymphocytes, the protein of 42 mg/dL, and glucose of 58 mg/dL. What is the best treatment for this condition?
- A. Intravenous immunoglobulin
- B. High-dose steroids
- C. Rituximab
- D. Acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- E. Ceftriaxone
Hepatitis B antivirals Explanation: ***Acyclovir***
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **flu-like symptoms** followed by **irritability**, **confusion**, and **MRI findings** suggestive of temporal lobe involvement, along with **lymphocytic pleocytosis** in CSF, is highly indicative of **herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE)**.
- **Acyclovir** is the treatment of choice for HSE, as it is an antiviral drug effective against the **herpes simplex virus (HSV)**. Prompt administration significantly improves outcomes.
*Intravenous immunoglobulin*
- **Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)** is generally used for certain **immunodeficiencies** or **autoimmune conditions**, not for acute viral encephalitis like HSE.
- There is no evidence to support the use of IVIG as a primary treatment for HSV encephalitis.
*High-dose steroids*
- While steroids can reduce cerebral edema and inflammation, their routine use in **viral encephalitis** like HSE is **controversial** and not a first-line treatment.
- Steroids might be considered in specific cases of severe cerebral edema, but not as the primary antiviral therapy.
*Rituximab*
- **Rituximab** is a **monoclonal antibody** targeting **CD20-positive B cells**, primarily used in certain **lymphomas** and **autoimmune diseases** like **rheumatoid arthritis** or **multiple sclerosis**.
- It has no role in the treatment of acute viral encephalitis.
*Ceftriaxone*
- **Ceftriaxone** is a broad-spectrum **antibiotic** used to treat **bacterial meningitis** or other bacterial infections.
- It is ineffective against viral infections such as HSV encephalitis.
More Hepatitis B antivirals US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.