Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antiviral prophylaxis strategies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 1: For which of the following patients would you recommend prophylaxis against mycobacterium avium-intracellulare?
- A. 30-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 20 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL (Correct Answer)
- B. 22-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 750 cells/microliter and a viral load of 500,000 copies/mL
- C. 45-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 250 cells/microliter and a viral load of 100,000 copies/mL
- D. 50-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 150 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL
- E. 36-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 75 cells/microliter and an undetectable viral load
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***30-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 20 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL***
- Prophylaxis against **Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)** is recommended for HIV-positive individuals with a **CD4 count below 50 cells/µL** to prevent disseminated MAC infection.
- While an undetectable viral load suggests effective antiretroviral therapy (ART) in general, the extremely low CD4 count indicates severe immunosuppression, making prophylaxis crucial.
*36-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 75 cells/microliter and an undetectable viral load*
- The **CD4 count of 75 cells/µL** is above the threshold of 50 cells/µL for MAC prophylaxis, even though it's still low.
- An **undetectable viral load** indicates successful ART, which generally helps improve immune function over time, albeit slowly in this CD4 range.
*22-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 750 cells/microliter and a viral load of 500,000 copies/mL*
- A **CD4 count of 750 cells/µL** is well above the threshold for MAC prophylaxis, indicating relatively preserved immune function.
- Although the **viral load is very high**, suggesting uncontrolled HIV replication, the immune system is currently strong enough to ward off MAC.
*45-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 250 cells/microliter and a viral load of 100,000 copies/mL*
- A **CD4 count of 250 cells/µL** is above the threshold for MAC prophylaxis, which is 50 cells/µL.
- While the **high viral load** implies an increased risk for opportunistic infections over time, other specific prophylaxes (e.g., PCP if <200) would be considered earlier.
*50-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 150 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL*
- A **CD4 count of 150 cells/µL** is above the threshold for MAC prophylaxis (50 cells/µL).
- An **undetectable viral load** is a positive sign of ART efficacy, but this patient would still require prophylaxis for **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP)**, as her CD4 count is below 200 cells/µL.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 2: A 65-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a rash. He states that for the past several days he has felt burning and itching around his eye. Yesterday, he noticed that a rash had formed. Review of systems is notable for mild diarrhea for the past week. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes, asthma, seasonal allergies, and hypertension. He is not currently taking any medications. Physical exam is notable for a vesicular rash surrounding the orbit. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- B. Removal of gluten containing products from the diet
- C. Topical steroids
- D. Topical mupirocin
- E. Oral steroids
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Acyclovir***
- The patient's symptoms of **burning, itching**, and a **vesicular rash around the orbit** are highly suggestive of **herpes zoster ophthalmicus**, a reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (shingles).
- **Antiviral medications** like acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir are the mainstay of treatment and should be initiated promptly (within 72 hours of rash onset) to reduce the severity and duration of the rash, prevent new lesions, and decrease the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia and ocular complications.
*Removal of gluten-containing products from the diet*
- This intervention is appropriate for **dermatitis herpetiformis**, an intensely pruritic, vesicular rash associated with **celiac disease**.
- While the patient has mild diarrhea, his rash distribution and the characteristic burning/itching are inconsistent with dermatitis herpetiformis, and there is no evidence of underlying celiac disease.
*Topical steroids*
- Topical steroids are used for various inflammatory skin conditions but are **contraindicated** in viral infections like herpes zoster, especially around the eye, as they can worsen ocular involvement and viral replication.
- They would not address the underlying viral etiology and could delay healing or increase complications.
*Topical mupirocin*
- **Mupirocin is an antibiotic** used for bacterial skin infections, such as impetigo or secondary bacterial infections of skin lesions.
- The primary rash described is viral (vesicular), and there is no mention of signs of bacterial superinfection, such as pustules, purulent discharge, or increasing redness and warmth.
*Oral steroids*
- Oral steroids might be considered for severe cases of post-herpetic neuralgia or to reduce inflammation in specific circumstances, but they are generally **not recommended as primary therapy** for acute herpes zoster due to limited evidence of benefit and potential for adverse effects.
- They also do not treat the underlying viral cause and can potentially suppress the immune system, which is generally undesirable in a viral infection.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 3: A thymidine kinase-deficient varicella-zoster virus strain has been isolated at a retirement home. Many of the elderly had been infected with this strain and are experiencing shingles. Which of the following would be the best antiviral agent to treat this population?
- A. Famciclovir
- B. Ganciclovir
- C. Cidofovir (Correct Answer)
- D. Amantadine
- E. Acyclovir
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Cidofovir***
- This is the best choice because **cidofovir** does not require **thymidine kinase** for its activation; it is phosphorylated by cellular kinases.
- Since the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) strain is **thymidine kinase-deficient**, drugs dependent on this enzyme (like acyclovir, famciclovir, ganciclovir) would be ineffective.
*Famciclovir*
- This is a prodrug that is converted to **penciclovir**, which requires **viral thymidine kinase** for its initial phosphorylation.
- Due to the VZV strain's **thymidine kinase deficiency**, famciclovir would not be effectively activated and thus not offer therapeutic benefit.
*Ganciclovir*
- Similar to acyclovir, ganciclovir requires **phosphorylation by viral thymidine kinase** (or phosphotransferase in CMV) for its antiviral activity.
- The **thymidine kinase-deficient VZV** would render ganciclovir ineffective against this specific resistant strain.
*Amantadine*
- **Amantadine** is an antiviral agent specifically used for **influenza A virus** and has no activity against VZV.
- Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the M2 proton channel of influenza A, which is not relevant for herpesviruses.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is a nucleoside analog that requires **viral thymidine kinase** for its initial phosphorylation and subsequent activation.
- A **thymidine kinase-deficient VZV** strain would be resistant to acyclovir, making it an ineffective treatment.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 39 weeks' gestation, is admitted to the hospital in active labor. She currently has contractions occurring every 3–5 minutes. For the past 3 days, she has had burning pain in the vulvar area associated with intense itching. Her pregnancy has been uneventful. She has a history of genital herpes at the age of 16, which was treated with acyclovir. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Genital examination shows grouped vesicles on an erythematous base over the vulvar region. Pelvic examination shows rupture of membranes and that the cervix is 3 cm dilated. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Tocolytic therapy until lesions are crusted
- B. Oral acyclovir therapy and vaginal delivery
- C. Topical acyclovir and vaginal delivery
- D. Oral acyclovir therapy and cesarean delivery (Correct Answer)
- E. Topical acyclovir and cesarean delivery
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Oral acyclovir therapy and cesarean delivery***
- The presence of **active genital herpes lesions** at the time of labor poses a high risk of **neonatal herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection** during vaginal delivery, which can be severe or fatal for the neonate.
- **Acyclovir therapy** aims to reduce viral shedding and transmission, but given the active lesions and rupture of membranes, a **cesarean delivery** is indicated to prevent vertical transmission to the newborn.
*Tocolytic therapy until lesions are crusted*
- **Tocolytic therapy** is used to inhibit uterine contractions and delay labor, but it is not indicated for managing active herpes lesions in a term pregnancy as it would only delay an inevitable delivery.
- Waiting for lesions to crust would prolong labor unnecessarily and still carry a risk of transmission, especially with ruptured membranes.
*Oral acyclovir therapy and vaginal delivery*
- While **oral acyclovir** can help suppress viral shedding, a **vaginal delivery** is contraindicated when active genital herpes lesions are present at the onset of labor due to the significant risk of **neonatal HSV infection**.
- Ruptured membranes further increase the risk of ascending infection and direct contact during passage through the birth canal.
*Topical acyclovir and vaginal delivery*
- **Topical acyclovir** is generally less effective than oral antivirals in suppressing systemic viral replication and does not adequately prevent viral shedding from active lesions during labor.
- A **vaginal delivery** would still expose the neonate to the virus, making this an inappropriate choice given the high risk of neonatal herpes.
*Topical acyclovir and cesarean delivery*
- While a **cesarean delivery** is the correct mode of delivery in this scenario, **topical acyclovir** is not the optimal antiviral treatment for active genital herpes during labor.
- **Oral acyclovir** provides better systemic viral suppression and is the preferred antiviral agent in such cases, though the urgency of active lesions still necessitates a cesarean.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 5: A 53-year-old woman comes to the physician in February because of a 1-day history of fever, chills, headache, and dry cough. She also reports malaise and generalized muscle aches. She works as a teacher at a local high school, where there was recently an outbreak of influenza. She has a history of intermittent asthma, for which she takes albuterol as needed. She declined the influenza vaccine offered in the fall because her sister told her that a friend developed a flulike illness after receiving the vaccine. She is worried about possibly becoming ill and cannot afford to miss work. Her temperature is 37.9°C (100.3°F), heart rate is 58/min, and her respirations are 12/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Her hemoglobin concentration is 14.5 g/dL, leukocyte count is 9,400/mm3, and platelet count is 280,000/mm3. In addition to analgesia, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Inactivated influenza vaccine
- B. Amantadine
- C. Live attenuated influenza vaccine
- D. Oseltamivir (Correct Answer)
- E. Supportive therapy only
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Oseltamivir***
- This patient presents with classic symptoms of **influenza** (fever, chills, headache, dry cough, malaise, myalgias) during an outbreak, making **antiviral therapy** like oseltamivir appropriate.
- She is at risk for complications due to her history of **asthma**, and early treatment (within 48 hours of symptom onset) can reduce illness severity and duration.
*Inactivated influenza vaccine*
- An **inactivated influenza vaccine** is a **preventive measure** and is not effective as a treatment once symptoms have already begun.
- Vaccination in the past fall would have been appropriate, but it will not help resolve her current acute illness.
*Amantadine*
- **Amantadine** is an older antiviral agent active only against **influenza A**, and its use is limited due to widespread **resistance**.
- It is generally not recommended for routine influenza treatment due to its narrow spectrum and resistance profile.
*Live attenuated influenza vaccine*
- The **live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV)** is a **preventive measure** indicated for healthy individuals aged 2-49 years and is contraindicated in individuals with **asthma**.
- Like the inactivated vaccine, it is not used for treating active influenza infection.
*Supportive therapy only*
- While supportive care (analgesia, hydration) is important, relying solely on it is not the most appropriate step given the patient's **risk factors** (asthma) and the availability of effective antiviral treatment.
- Early antiviral therapy can reduce serious complications in at-risk individuals.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 6: A 2-month-old girl is admitted to the hospital because of a 1-day history of fever and difficulty breathing. She has also had nasal congestion for 2 days. She was born at 28 weeks' gestation and weighed 1105 g (2 lb 7 oz); she currently weighs 2118 g (4 lb 11 oz). Her neonatal course was complicated by respiratory distress syndrome. She required supplemental oxygen for 36 days following birth. She was diagnosed with bronchopulmonary dysplasia 3 weeks ago. The infant missed an appointment with the pediatrician 2 weeks ago. Her only medication is vitamin D drops. She appears lethargic. Her temperature is 38.6°C (101.4°F), pulse is 160/min, respirations are 55/min, and blood pressure is 80/45 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 87%. Physical examination shows moderate subcostal retractions. Wheezing is heard on auscultation of the chest. Her hemoglobin concentration is 10.5 g/dL, leukocyte count is 13,000/mm3, and platelet count is 345,000/mm3. Mechanic ventilatory support is initiated. After 4 days in the pediatric intensive care unit, the patient dies. Administration of which of the following is most likely to have prevented this patient's outcome?
- A. Ceftriaxone
- B. Ribavirin
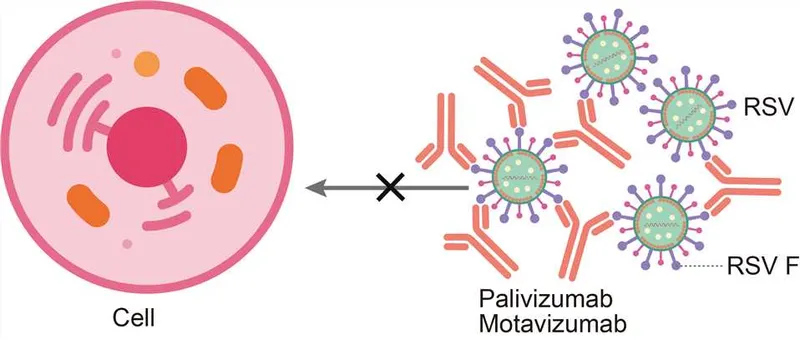
- C. Palivizumab (Correct Answer)
- D. Respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin
- E. Postnatal glucocorticoid
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Palivizumab***
* This premature infant with a history of **bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)** is at extremely high risk for severe **respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)** infection, which can be fatal.
* **Palivizumab** is a monoclonal antibody specifically designed to prevent severe RSV disease in high-risk infants, and its administration would have been crucial here.
*Ceftriaxone*
* **Ceftriaxone** is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections, but the primary pathogen in this case is highly likely to be viral (RSV) given the symptoms and rapid deterioration despite supportive care.
* While bacterial superinfection is possible, **antibiotics** are not the primary preventative measure for the initial viral illness that led to this outcome.
*Ribavirin*
* **Ribavirin** is an antiviral medication used in some severe RSV cases, but it is typically reserved for hospitalized patients with severe disease, not for routine prophylaxis in high-risk infants.
* Its use is controversial, and it is not considered a primary preventative measure to achieve the outcome of preventing this patient's death.
*Respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin*
* **RSV immune globulin** (RespiGam) was an older prophylactic agent for RSV, but it has been largely replaced by **palivizumab** due to palivizumab's superior efficacy, easier administration (intramuscular vs. intravenous), and fewer side effects.
* While it aimed to provide passive immunity, it is not the current standard or most effective preventative intervention.
*Postnatal glucocorticoid*
* **Postnatal glucocorticoids** like dexamethasone are sometimes used in premature infants with BPD to reduce inflammation and dependence on ventilator support.
* However, administering glucocorticoids does not directly prevent severe RSV infection, which was the overwhelming cause of the patient's acute deterioration and death in this scenario.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old female medical student presents to occupational health after sustaining a needlestick injury. She reports that she was drawing blood from an HIV-positive patient when she stuck herself percutaneously while capping the needle. She immediately washed the puncture wound with betadine. The medical student has a negative HIV serology from the beginning of medical school two years ago. She is monogamous with one male partner and denies any intravenous drug use. The source patient was recently diagnosed with HIV, and has a CD4 count of 550 cells/µL. His most recent viral load is 1,800,000 copies/mL, and he was started on HAART three days ago.
Which of the following is the best next step to manage the female medical student’s exposure?
- A. Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if positive
- B. Perform genotype testing on source patient and initiate antiretroviral therapy tailored to results
- C. Immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy
- D. Draw her repeat HIV serology and immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy (Correct Answer)
- E. Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if negative
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Draw her repeat HIV serology and immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy***
- This approach ensures that baseline **HIV status** is established while simultaneously providing **post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)** as quickly as possible. Time is critical for PEP efficacy.
- The patient has a high-risk exposure (percutaneous injury, high viral load source) warranting immediate initiation of a **three-drug antiretroviral regimen** to prevent seroconversion.
*Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if positive*
- Waiting for serology results before initiating therapy would delay PEP, significantly reducing its effectiveness in potentially preventing **HIV transmission**.
- If the student is already HIV-positive from a prior undisclosed exposure, PEP for a new exposure is not the primary concern; rather, she would need full **HIV treatment**. However, the immediate concern after an exposure is always prevention.
*Immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy*
- While immediate initiation of PEP is correct, it is still crucial to obtain a **baseline HIV serology** for the exposed individual.
- This baseline allows for clear documentation of the pre-exposure HIV status, which is vital for any future testing and counseling following the exposure.
*Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if negative*
- Waiting for serology results to return before starting PEP is incorrect as this would significantly delay the initiation of therapy.
- The critical window for effective PEP is within hours of exposure, ideally within 72 hours.
*Perform genotype testing on source patient and initiate antiretroviral therapy tailored to results*
- While **genotype testing** on the source patient provides valuable information about drug resistance, it should not delay the immediate initiation of **empiric PEP** for the exposed individual.
- PEP must be started as soon as possible, and the regimen can be adjusted later if the genotype results indicate resistance to the initial drugs.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old woman G1P0 presents at 38 weeks of gestation for a standard prenatal visit. She endorses occasional mild lower back pain but otherwise remains asymptomatic. Her past medical history is significant for HIV for which she is treated with azidothymidine (AZT). Her vital signs and physical exam are unremarkable. Her current HIV viral titer level is 1,400 copies. If she were to go into labor today, what would be the next and most important step for the prevention of vertical HIV transmission to the newborn?
- A. Urge the patient to have a cesarean section delivery (Correct Answer)
- B. Add nevirapine to the patient’s AZT
- C. Treat the newborn with AZT following delivery
- D. Increase AZT dose
- E. Avoid breastfeeding
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Urge the patient to have a cesarean section delivery***
- A **high viral load** (>1000 copies/mL) at 38 weeks gestation is an indication for a **scheduled cesarean section** to reduce the risk of vertical HIV transmission.
- This approach minimizes the infant's exposure to maternal blood and genital secretions during vaginal delivery.
*Add nevirapine to the patient’s AZT*
- While adding a second antiretroviral (ARV) medication is generally beneficial in HIV treatment, a single dose of **nevirapine** given to the mother in labor is typically used when **highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)** has not been given prenatally or with unknown viral load status.
- The primary intervention for a known high viral load near term is delivery mode modification.
*Treat the newborn with AZT following delivery*
- This is a standard and essential component of **post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)** for all infants born to HIV-positive mothers, regardless of maternal viral load or delivery route.
- However, it is a post-delivery intervention and not the **next and most important step** for prevention *at the time of labor* with a high viral load.
*Increase AZT dose*
- Increasing the dose of a single ARV medication like **AZT** alone is unlikely to rapidly suppress a viral load of 1,400 copies/mL sufficiently to mitigate transmission risks during labor, and could lead to toxicity.
- Achieving viral suppression before labor is crucial, and if not achieved, a C-section is indicated.
*Avoid breastfeeding*
- **Avoiding breastfeeding** is a critical recommendation for HIV-positive mothers in developed countries to prevent **postnatal vertical transmission**.
- While important for overall prevention, it addresses transmission after birth and is not the immediate and most important step to prevent transmission *at the onset of labor* when a high viral load is present.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 9: A 61-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician complaining of left-sided facial pain that started yesterday. She describes the pain as stinging, burning, and constant. It does not worsen with jaw movement or chewing. Her past medical history includes hyperlipidemia and multiple sclerosis (MS), and she had chickenpox as a child but received a shingles vaccination last year. Medications include simvastatin and glatiramer acetate. The patient’s last MS flare was 5 weeks ago, at which time she received a prednisone burst with taper. At this visit, her temperature is 99.9 °F (37.7°C), blood pressure is 139/87 mmHg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 14/min. On exam, there is no rash or skin change on either side of the patient’s face. Gentle palpation of the left cheek and mandible produce significant pain, but there is full range of motion in the jaw. Which of the following medications is the most likely to prevent long-term persistence of this patient’s pain?
- A. Carbamazepine
- B. Topical corticosteroids
- C. Oral acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- D. Amitriptyline
- E. Gabapentin
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Oral acyclovir***
- The patient's symptoms (stinging, burning, constant facial pain, history of chickenpox, recent MS flare, and prednisone use) are highly suggestive of a **herpes zoster (shingles) reactivation**, despite prior vaccination. Early antiviral therapy, such as oral acyclovir, is crucial to reduce the duration and severity of the acute pain and, more importantly, to prevent **postherpetic neuralgia (PHN)**.
- Starting acyclovir within 72 hours of symptom onset significantly decreases the risk of developing long-term pain complications like PHN by inhibiting viral replication and reducing nerve damage.
*Carbamazepine*
- This medication is a first-line treatment for **trigeminal neuralgia**, characterized by brief, excruciating, shock-like pain triggered by specific stimuli, which differs from the patient's constant burning pain.
- While it can manage neuropathic pain, it does not address the underlying viral cause of herpes zoster and will not prevent PHN.
*Topical corticosteroids*
- Topical corticosteroids are primarily used to reduce **inflammation and itching** associated with skin rashes, such as those that may occur with herpes zoster.
- They do not possess antiviral properties and therefore will not *prevent* the long-term neurological complication of PHN.
*Amitriptyline*
- Amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, is a common treatment for **postherpetic neuralgia** once it has already developed, as well as other neuropathic pain conditions.
- However, it is not used to prevent the development of PHN in the acute phase of a herpes zoster infection; early antiviral treatment is the preventative strategy.
*Gabapentin*
- Gabapentin is an effective medication for established **neuropathic pain**, including postherpetic neuralgia.
- Similar to amitriptyline, gabapentin treats the *symptoms* of PHN once it is present but does not prevent its occurrence when used during the acute viral stage.
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old man presents with jaw discomfort and the inability to open his mouth fully for about 3 days. About a week ago, he says he cut himself while preparing a chicken dinner but did not seek medical assistance. Five days after the original injury, he started noticing jaw discomfort and an inability to open his mouth completely. He has no history of a serious illness or allergies and takes no medications. The patient says he had received his primary tetanus series in childhood, and that his last booster was more than 10 years ago. His blood pressure is 125/70 mm Hg and temperature is 36.9℃ (98.5°F). On physical examination, the patient is unable to open his jaw wider than 2.5 cm. Head and neck examinations are otherwise unremarkable. There is a 5 cm linear shallow laceration with some granulation tissue on the right index finger without necrosis, erythema, or pus. After wound care and initiation of metronidazole, which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. DTaP
- B. Td
- C. Tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG) (Correct Answer)
- D. No further treatment is required
- E. Tdap
Antiviral prophylaxis strategies Explanation: ***Tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG)***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **tetanus**, including **trismus** (lockjaw) and a recent puncture wound. TIG provides **passive immunity** with pre-formed antibodies that can neutralize circulating tetanus toxin, which is crucial for immediate treatment.
- Given that his last tetanus booster was more than 10 years ago and he is symptomatic, immediate TIG is necessary to combat the toxin already produced by *Clostridium tetani*.
- **Note**: A tetanus toxoid vaccine (Td or Tdap) should also be administered at a different site to provide active immunity, but TIG is the **priority** intervention for neutralizing existing toxin in a symptomatic patient.
*DTaP*
- **DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis)** is administered to **children younger than 7 years old**. This patient is 25 years old.
- While it provides **active immunity**, its effect is not immediate and would not address the acute, life-threatening toxin effects already present in a symptomatic patient.
*Td*
- **Td (tetanus and diphtheria)** is a booster vaccine providing **active immunity** suitable for adults.
- Like DTaP, it confers active immunity, which takes time to develop and would not provide immediate protection against the existing tetanus toxin in a symptomatic patient. However, Td should be administered alongside TIG at a different site as part of complete management.
*No further treatment is required*
- This patient is clearly symptomatic with **trismus** after a puncture wound and an outdated tetanus vaccination, indicating an active **tetanus infection**.
- Without immediate intervention, tetanus can lead to severe muscle spasms, respiratory failure, and death, so further treatment is urgently required.
*Tdap*
- **Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, acellular pertussis)** is an adult-formulation booster vaccine, primarily given to adolescents and adults, especially during pregnancy or when in contact with infants.
- It provides **active immunity**, which is not effective in neutralizing the immediate effects of existing tetanus toxin in a symptomatic patient. However, Tdap should be administered alongside TIG at a different site as part of complete management.
More Antiviral prophylaxis strategies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.