Antivirals

On this page
🦠 The Antiviral Arsenal: Molecular Warfare Against Viral Invaders
Viruses hijack your cells' machinery to replicate, but antivirals strike back at precise molecular targets across the viral lifecycle-from blocking entry to sabotaging replication enzymes. You'll master how each drug class exploits viral vulnerabilities, recognize resistance patterns that threaten efficacy, and apply evidence-based algorithms to optimize therapy across HIV, hepatitis, influenza, and herpes infections. This lesson transforms abstract mechanisms into clinical decision-making power, equipping you to select the right weapon against each viral invader.
📌 Remember: VIRAL TARGETS - Viral entry, Integration, Replication, Assembly, Lysis - Transcription, Attachment, Release, Genome synthesis, Enzymes, Translation, Synthesis
Modern antiviral therapy operates on 5 fundamental principles: viral specificity (>1000-fold selectivity), resistance prevention (combination therapy), pharmacokinetic optimization (>90% bioavailability), toxicity minimization (<5% severe adverse events), and therapeutic monitoring (drug levels ±20% target range).
- Viral Entry Inhibitors
- CCR5 antagonists: maraviroc blocks HIV coreceptor binding
- Fusion inhibitors: enfuvirtide prevents membrane fusion (36-amino acid peptide)
- Efficacy: >90% viral suppression in treatment-experienced patients
- Resistance barrier: high (multiple mutations required)
- Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analogs
- Chain terminators: zidovudine, tenofovir, sofosbuvir
- Incorporation rate: 10-100x higher than natural nucleotides
- Selectivity mechanism: viral polymerases lack 3'-5' exonuclease activity
- Resistance development: weeks to months with monotherapy
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Combination antiviral therapy reduces resistance development by >95% compared to monotherapy, with genetic barrier requiring ≥3 simultaneous mutations for viral escape.
| Drug Class | Viral Target | Selectivity Index | Resistance Barrier | Clinical Efficacy | Monitoring Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRTIs | Reverse transcriptase | >100:1 | Moderate | 85-95% suppression | Mitochondrial toxicity |
| NNRTIs | RT allosteric site | >500:1 | Low | 90-98% suppression | Hepatotoxicity |
| Protease inhibitors | Viral protease | >1000:1 | High | 95-99% suppression | Drug interactions |
| Integrase inhibitors | Viral integrase | >200:1 | High | 95-98% suppression | CNS effects |
| Entry inhibitors | Viral receptors | >50:1 | Very high | 85-95% suppression | Tropism testing |
The evolution from single-agent therapy (zidovudine monotherapy, 1987) to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART, 1996) revolutionized viral treatment paradigms. Modern regimens achieve undetectable viral loads (<50 copies/mL) in >95% of treatment-naive patients within 24 weeks, transforming HIV from fatal disease to chronic manageable condition.
Connect these foundational principles through viral lifecycle targeting to understand how specific drug classes exploit unique vulnerabilities in viral replication machinery.
🦠 The Antiviral Arsenal: Molecular Warfare Against Viral Invaders
⚔️ Viral Lifecycle Warfare: Precision Strike Points
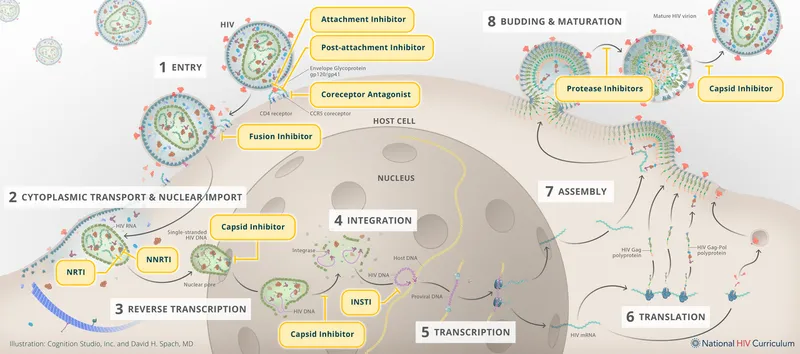
Understanding viral replication mechanisms reveals 7 critical intervention points: attachment (seconds), entry (2-5 minutes), uncoating (5-15 minutes), replication (30-60 minutes), assembly (60-120 minutes), maturation (2-4 hours), and release (4-8 hours). Each step presents unique therapeutic opportunities with distinct resistance profiles.
📌 Remember: REPLICATION STEPS - Attachment, Entry, Reverse transcription, Integration, Transcription, Assembly, Maturation, Release - "A ERITAMR" (A Eritrean Army Marches Rapidly)
- Early Replication Targets (0-30 minutes)
- Attachment inhibitors: ibalizumab (CD4 receptor blocker)
- Entry inhibitors: maraviroc (CCR5 antagonist, >90% R5-tropic virus suppression)
- Mechanism: conformational change in CCR5 coreceptor
- Resistance: rare (requires viral tropism switch to CXCR4)
- Fusion inhibitors: enfuvirtide (gp41 peptide, 36 amino acids)
- Injection site reactions: >95% of patients
- Efficacy: 1.7 log₁₀ viral load reduction
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Viral tropism testing is mandatory before maraviroc initiation-15-20% of HIV strains use CXCR4 coreceptor, rendering CCR5 antagonists ineffective.
- Mid-Replication Targets (30-120 minutes)
- Reverse transcriptase inhibitors: tenofovir, efavirenz, rilpivirine
- Integration inhibitors: dolutegravir, bictegravir, cabotegravir
- Genetic barrier: ≥3 mutations required for significant resistance
- CNS penetration: CSF:plasma ratio 0.1-0.2
- Efficacy: >95% viral suppression at 48 weeks
| Replication Phase | Time Window | Drug Classes | Resistance Rate | Genetic Barrier | Clinical Success |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attachment/Entry | 0-5 min | Entry inhibitors | <5% | Very high | 85-95% |
| Reverse transcription | 5-30 min | NRTIs, NNRTIs | 10-40% | Low-moderate | 90-95% |
| Integration | 30-60 min | INSTIs | <5% | High | 95-98% |
| Assembly/Maturation | 60-240 min | Protease inhibitors | 5-15% | High | 95-99% |
| Release | 4-8 hours | Budding inhibitors | Variable | Unknown | Experimental |
Late replication targeting focuses on viral maturation: protease inhibitors prevent gag-pol polyprotein cleavage, producing non-infectious viral particles. Modern boosted protease inhibitors achieve trough concentrations >10x the IC₉₀, maintaining efficacy despite moderate resistance mutations.
Connect viral lifecycle understanding through drug mechanism specificity to master how molecular targets determine therapeutic success and resistance patterns.
⚔️ Viral Lifecycle Warfare: Precision Strike Points
🎯 Mechanism Mastery: Molecular Precision Targeting
Antiviral selectivity operates through 4 fundamental mechanisms: enzyme specificity (viral vs host polymerases), metabolic activation (viral kinases preferentially phosphorylate prodrugs), structural mimicry (nucleoside analogs lack 3'-OH groups), and allosteric inhibition (viral-specific binding sites).
📌 Remember: SELECTIVITY MECHANISMS - Enzyme specificity, Metabolic activation, Structural mimicry, Allosteric binding - "Every Mechanism Stops Attacks"
- Nucleoside Analog Mechanisms
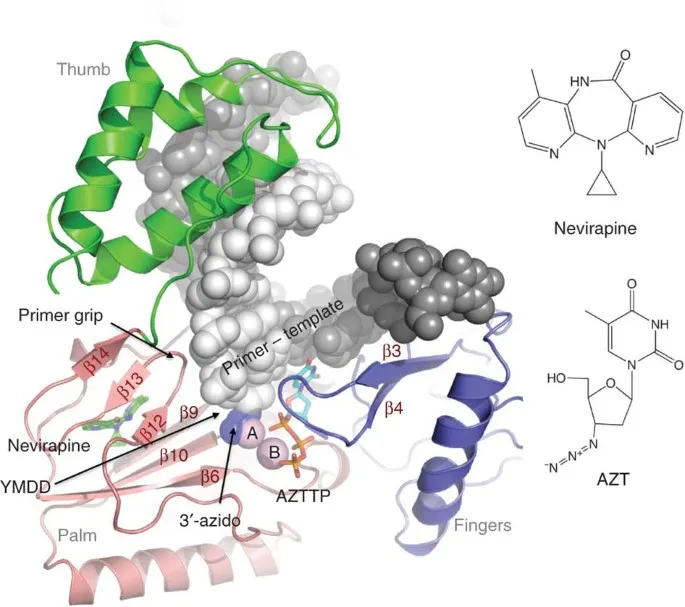
- Zidovudine (AZT): 3'-azido group prevents chain elongation
- Phosphorylation: thymidine kinase converts to active triphosphate
- Selectivity: 100x higher affinity for HIV RT vs human DNA polymerase
- Resistance: M184V, K65R mutations reduce incorporation >10-fold
- Tenofovir: acyclic nucleotide analog bypasses first phosphorylation
- Bioavailability: 25% (tenofovir disoproxil), >90% (tenofovir alafenamide)
- Intracellular half-life: >60 hours (allows once-daily dosing)
- Zidovudine (AZT): 3'-azido group prevents chain elongation
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Tenofovir alafenamide achieves 90% lower plasma concentrations than tenofovir disoproxil while maintaining equivalent efficacy, reducing nephrotoxicity risk by >70% through targeted lymphoid tissue delivery.
- Non-Nucleoside Mechanisms
- Efavirenz: binds allosteric site 12Å from active site
- Conformational change: "butterfly effect" distorts polymerase geometry
- Resistance: single mutations (K103N, Y181C) cause >100-fold resistance
- CNS penetration: CSF:plasma ratio 0.69 (highest among NNRTIs)
- Rilpivirine: higher genetic barrier requires ≥2 mutations
- Binding affinity: 13x tighter than efavirenz
- Food requirement: >500 calories increases absorption 40%
- Efavirenz: binds allosteric site 12Å from active site
| Mechanism Type | Drug Examples | Selectivity Index | Resistance Mutations | Genetic Barrier | Half-life |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chain termination | Zidovudine, Tenofovir | >100:1 | M184V, K65R | Moderate | 1-17 hours |
| Allosteric inhibition | Efavirenz, Rilpivirine | >500:1 | K103N, Y181C | Low-moderate | 40-50 hours |
| Competitive inhibition | Raltegravir, Dolutegravir | >200:1 | Q148H, N155H | High | 7-15 hours |
| Peptide mimicry | Enfuvirtide | >50:1 | gp41 mutations | Very high | 3.8 hours |
| Receptor antagonism | Maraviroc | >50:1 | Tropism switch | Very high | 14-18 hours |
Protease inhibitor mechanisms exploit viral-specific cleavage sites: HIV protease recognizes specific amino acid sequences in gag-pol polyprotein. Modern protease inhibitors achieve picomolar binding affinities (Kd <1 nM) through transition state mimicry, explaining their high genetic barriers requiring ≥4-6 mutations for clinical resistance.
Connect mechanism understanding through resistance pattern recognition to predict therapeutic outcomes and optimize drug selection strategies.
🎯 Mechanism Mastery: Molecular Precision Targeting
🔍 Resistance Pattern Recognition: Viral Escape Strategies
Viral resistance develops through 3 primary mechanisms: point mutations (single nucleotide changes), insertions/deletions (frameshift mutations), and recombination events (genetic reassortment). Understanding resistance patterns enables predictive therapy selection and resistance prevention strategies.
📌 Remember: RESISTANCE PATTERNS - Point mutations, Amino acid substitutions, Transmitted resistance, Treatment failure, Emergence kinetics, Recombination, Natural polymorphisms, Selection pressure - "PATTERNS"
- NRTI Resistance Patterns
- M184V mutation: >100-fold resistance to emtricitabine/lamivudine
- Emergence: 2-4 weeks with monotherapy
- Cross-resistance: none to other NRTIs
- Fitness cost: reduces viral replication by 40-60%
- K65R mutation: multidrug resistance to tenofovir, abacavir, didanosine
- Selection pressure: tenofovir monotherapy >12 weeks
- Phenotype: 2-4 fold resistance to multiple NRTIs
- Clinical impact: limits NRTI backbone options
- M184V mutation: >100-fold resistance to emtricitabine/lamivudine
⭐ Clinical Pearl: M184V mutation paradoxically improves treatment outcomes when present-it reduces viral fitness and resensitizes virus to zidovudine, explaining why lamivudine is often continued despite resistance.
- NNRTI Resistance Patterns
- K103N mutation: >100-fold resistance to efavirenz, nevirapine
- Prevalence: 5-15% in treatment-naive patients (transmitted resistance)
- Cross-resistance: complete within first-generation NNRTIs
- Salvage options: rilpivirine (reduced activity), doravirine (maintains activity)
- Y181C mutation: moderate resistance to multiple NNRTIs
- Phenotype: 10-50 fold resistance depending on drug
- Combination with K103N: >1000-fold resistance
- K103N mutation: >100-fold resistance to efavirenz, nevirapine
| Resistance Mutation | Drug Class | Fold Resistance | Emergence Time | Cross-Resistance | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M184V | NRTI | >100x | 2-4 weeks | FTC/3TC only | Backbone change |
| K65R | NRTI | 2-4x | 8-12 weeks | TDF/ABC/ddI | Multi-NRTI |
| K103N | NNRTI | >100x | 1-2 weeks | EFV/NVP | Class resistance |
| Q148H | INSTI | 10-50x | 12-24 weeks | RAL/EVG | Salvage needed |
| I50V | PI | 5-10x | 8-16 weeks | ATV specific | Switch PI |
- Integrase Inhibitor Resistance
- Q148H + G140S: major resistance pathway for raltegravir/elvitegravir
- Phenotype: >50-fold resistance to first-generation INSTIs
- Dolutegravir activity: maintained (requires additional mutations)
- Emergence: rare (<5% at 5 years) due to high genetic barrier
- R263K mutation: dolutegravir-specific resistance pathway
- Clinical significance: minimal (requires multiple additional mutations)
- Fitness cost: significant reduction in viral replication capacity
- Q148H + G140S: major resistance pathway for raltegravir/elvitegravir
Transmitted resistance affects 10-15% of newly diagnosed patients, with NNRTI resistance most common (8-12%), followed by NRTI resistance (6-8%), and PI resistance (3-5%). Integrase inhibitor resistance remains <2% due to recent introduction and high genetic barriers.
Connect resistance pattern recognition through therapeutic optimization strategies to master salvage regimen design and resistance prevention protocols.
🔍 Resistance Pattern Recognition: Viral Escape Strategies
⚖️ Therapeutic Optimization: Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithms
📌 Remember: OPTIMIZATION FACTORS - Resistance profile, Efficacy data, Genotype results, Interactions, Monitoring, Emergence risk, New options, Tolerance - "REGIMENT"
- First-Line Regimen Selection
- Integrase inhibitor-based: dolutegravir + tenofovir/emtricitabine
- Efficacy: >95% viral suppression at 48 weeks
- Resistance barrier: high (requires ≥3 mutations)
- Pill burden: 1-2 tablets daily
- Drug interactions: minimal (no CYP3A4 induction/inhibition)
- Alternative backbones: tenofovir alafenamide vs tenofovir disoproxil
- TAF advantages: 90% lower plasma exposure, reduced nephrotoxicity
- TDF advantages: lower cost, extensive safety data
- Bone density: TAF superior (1-2% less bone loss)
- Integrase inhibitor-based: dolutegravir + tenofovir/emtricitabine
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Single-tablet regimens improve adherence by 15-25% compared to multi-pill combinations, with bictegravir/tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine achieving >98% viral suppression in treatment-naive patients.
- Salvage Therapy Algorithms
- Resistance-guided selection: ≥2 fully active agents required
- Genotypic sensitivity score: ≥3 predicts >90% success rate
- Phenotypic testing: recommended for complex resistance patterns
- Novel agents: ibalizumab, fostemsavir for multidrug resistance
- Boosted protease inhibitor backbone: darunavir/ritonavir
- Genetic barrier: ≥6-8 mutations for significant resistance
- Efficacy: 85-90% suppression in treatment-experienced patients
- Monitoring: drug levels if malabsorption suspected
- Resistance-guided selection: ≥2 fully active agents required
| Clinical Scenario | Recommended Regimen | Success Rate | Monitoring Frequency | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment-naive | DTG + TAF/FTC | >95% | Week 4, 12, 24 | Resistance testing |
| NNRTI resistance | DTG + 2 NRTIs | >90% | Week 8, 16, 24 | Cross-resistance |
| Multi-class resistance | DRV/r + 2 active | 85-90% | Week 4, 8, 12 | Expert consultation |
| Virologic failure | Genotype-guided | 80-95% | Week 2, 4, 8 | Adherence support |
| Drug intolerance | Class substitution | >90% | Week 4, 12 | Interaction review |
- Special Population Considerations
- Pregnancy: dolutegravir + zidovudine/lamivudine
- Neural tube defect risk: 0.3% (population baseline 0.1%)
- Viral suppression: >95% prevents perinatal transmission
- Monitoring: monthly viral loads in third trimester
- Renal impairment: dose adjustments for tenofovir, emtricitabine
- CrCl 30-49 mL/min: tenofovir every 48 hours
- CrCl <30 mL/min: avoid tenofovir, use abacavir/lamivudine
- Hemodialysis: post-dialysis dosing for renally eliminated drugs
- Pregnancy: dolutegravir + zidovudine/lamivudine
Therapeutic drug monitoring becomes critical for protease inhibitors and entry inhibitors-ritonavir-boosted regimens require trough level monitoring when malabsorption, drug interactions, or treatment failure suspected. Target darunavir trough levels: >550 ng/mL (treatment-naive), >2400 ng/mL (treatment-experienced with resistance).
Connect therapeutic optimization through advanced integration strategies to master complex resistance scenarios and emerging antiviral technologies.
⚖️ Therapeutic Optimization: Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithms
🔗 Advanced Integration: Multi-System Antiviral Strategies
Advanced antiviral integration requires understanding cross-system interactions: hepatitis B/HIV coinfection (tenofovir dual activity), hepatitis C/HIV coinfection (drug-drug interactions), CMV/HIV interactions (immune reconstitution), and influenza prophylaxis in immunocompromised patients.
📌 Remember: INTEGRATION SYSTEMS - HIV combinations, Hepatitis coinfections, Immune reconstitution, Interactions management, Resistance cross-patterns, Emergency protocols, Special populations - "HHI HIRES"
- HIV/Hepatitis B Coinfection Management
- Dual-active agents: tenofovir + emtricitabine treat both viruses
- HBV suppression: >95% achieve undetectable HBV DNA
- HIV efficacy: maintained with integrase inhibitor third agent
- Resistance prevention: never use tenofovir/emtricitabine alone for HBV
- Monitoring: HBV DNA, HBsAg, ALT every 3-6 months
- HBV flare risk: discontinuing anti-HBV agents causes ALT elevation
- Flare incidence: 20-30% within 12 weeks of discontinuation
- Severity: ALT >10x ULN in 5-10% of cases
- Prevention: never stop tenofovir/emtricitabine without HBV-active replacement
- Dual-active agents: tenofovir + emtricitabine treat both viruses
⭐ Clinical Pearl: HBV/HIV coinfection accelerates liver fibrosis progression by 3-5 years compared to HBV monoinfection, making dual viral suppression critical for preventing cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- HIV/Hepatitis C Coinfection Strategies
- Direct-acting antivirals: sofosbuvir/velpatasvir with HIV regimens
- Drug interactions: minimal with integrase inhibitors
- Contraindications: efavirenz reduces sofosbuvir levels >50%
- Cure rates: >95% in HIV-coinfected patients (similar to monoinfection)
- Timing: treat HCV first (shorter duration, fewer interactions)
- Immune reconstitution: CD4+ recovery improves HCV treatment response
- Optimal CD4 count: >200 cells/μL for maximum DAA efficacy
- SVR rates: 98% (CD4 >200) vs 92% (CD4 <200)
- Direct-acting antivirals: sofosbuvir/velpatasvir with HIV regimens
| Coinfection Type | Preferred Regimen | Drug Interactions | Monitoring Parameters | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV/HBV | TDF/FTC + DTG | Minimal | HBV DNA, ALT | Never stop anti-HBV |
| HIV/HCV | SOF/VEL + DTG | Avoid EFV | HCV RNA, SVR12 | Treat HCV first |
| HIV/CMV | GCV + ART | ZDV antagonism | CMV PCR, retinal exam | IRIS risk |
| HIV/HSV | ACV + ART | Minimal | Clinical lesions | Suppressive therapy |
| HIV/Influenza | Oseltamivir + ART | None significant | Clinical response | Extended duration |
- Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS)
- CMV-IRIS: occurs in 10-15% of patients starting ART
- Timeline: 2-8 weeks after ART initiation
- Manifestations: worsening retinitis, vitritis, uveitis
- Management: continue ART + anti-CMV, add corticosteroids
- Prevention: screen for CMV before ART in CD4 <50 cells/μL
- HBV-IRIS: hepatitis flare during immune recovery
- Incidence: 5-10% in HBV-coinfected patients
- Timing: 4-12 weeks after ART initiation
- Severity: ALT >5x baseline, bilirubin elevation
- CMV-IRIS: occurs in 10-15% of patients starting ART
Resistance cross-patterns between viral families create therapeutic challenges: tenofovir resistance (K65R) affects both HIV and HBV, while lamivudine resistance (M184V in HIV, rtM204V in HBV) shows similar patterns. Understanding these cross-resistance mechanisms guides sequential therapy planning and resistance prevention strategies.
Connect advanced integration concepts through clinical mastery frameworks to develop expertise in complex antiviral scenarios and emerging therapeutic approaches.
🔗 Advanced Integration: Multi-System Antiviral Strategies
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Antiviral Expertise
📌 Remember: MASTERY ESSENTIALS - Resistance recognition, Adherence optimization, Pharmacology mastery, Interaction management, Dosing precision, Failure prevention, IRIS recognition, Regimen selection, Emergency protocols - "RAPID FIRE"
Essential Clinical Thresholds:
- Viral suppression: <50 copies/mL (HIV), <20 IU/mL (HBV), undetectable (HCV)
- Treatment failure: >200 copies/mL on 2 occasions ≥2 weeks apart
- Resistance testing: viral load >500 copies/mL (genotype), >1000 copies/mL (phenotype)
- Drug level monitoring: trough levels for protease inhibitors when indicated
- Adherence threshold: >95% required for viral suppression and resistance prevention
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "The 48-week rule"->95% of treatment-naive patients achieve viral suppression by week 48 with modern regimens; failure suggests resistance, adherence issues, or drug interactions.
- Rapid Resistance Recognition
- Single mutations: K103N (NNRTI), M184V (NRTI), I50V (PI-specific)
- Multi-drug patterns: K65R + M184V (NRTI backbone failure)
- Class resistance: Q148H + G140S (INSTI resistance pathway)
- Transmitted resistance: 5-15% prevalence in treatment-naive patients
| Clinical Scenario | Immediate Action | Timeline | Success Predictor | Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virologic failure | Resistance testing | Within 1 week | ≥2 active agents | Week 2, 4, 8 |
| Drug intolerance | Class substitution | Within 48 hours | Maintained potency | Week 4, 12 |
| Drug interactions | Regimen modification | Same day | Interaction resolution | Drug levels |
| Adherence failure | Regimen simplification | Within 1 week | Pill burden reduction | Weekly initially |
| Pregnancy | Safety optimization | Within 24 hours | Viral suppression | Monthly VL |
Emergency Antiviral Protocols:
- Occupational exposure: start PEP within 72 hours (preferably <2 hours)
- Perinatal transmission: zidovudine within 6-12 hours of birth
- Severe influenza: oseltamivir within 48 hours of symptom onset
- CMV retinitis: immediate ganciclovir to prevent blindness
- HSV encephalitis: acyclovir within 24 hours for optimal outcomes
Advanced Monitoring Framework:
- Viral kinetics: first-phase decline (1-2 weeks), second-phase decline (4-12 weeks)
- Resistance emergence: weeks (NNRTI) vs months (INSTI) vs years (boosted PI)
- Drug interactions: CYP3A4 substrates require dose adjustments or alternative agents
- Toxicity monitoring: renal function (tenofovir), bone density (tenofovir), CNS effects (efavirenz, dolutegravir)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "Viral load blips" (50-200 copies/mL) occur in 15-20% of suppressed patients and rarely indicate resistance-continue current regimen and recheck in 4 weeks unless adherence concerns exist.
Cutting-Edge Developments:
- Long-acting injectables: cabotegravir + rilpivirine every 8 weeks
- Broadly neutralizing antibodies: ibalizumab for multidrug-resistant HIV
- Capsid inhibitors: lenacapavir with 6-month dosing potential
- Cure research: "shock and kill" strategies, gene editing approaches
This clinical mastery arsenal transforms complex antiviral scenarios into systematic, evidence-based management protocols, enabling rapid decision-making and optimal patient outcomes across diverse clinical presentations.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Antiviral Expertise
Practice Questions: Antivirals
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 32-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 1 week after being admitted to the hospital for oral candidiasis and esophagitis. His CD4+ T lymphocyte count is 180 cells/μL. An HIV antibody test is positive. Genotypic resistance assay shows the virus to be susceptible to all antiretroviral therapy regimens and therapy with dolutegravir, tenofovir, and emtricitabine is initiated. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings would be most likely on follow-up evaluation 3 months later? $$$ CD4 +/CD8 ratio %%% HIV RNA %%% HIV antibody test $$$













