Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 1: An 87-year-old male nursing home resident is currently undergoing antibiotic therapy for the treatment of a decubitus ulcer. One week into the treatment course, he experiences several episodes of watery diarrhea. Subsequent sigmoidoscopy demonstrates the presence of diffuse yellow plaques on the mucosa of the sigmoid colon. Which of the following is the best choice of treatment for this patient?
- A. Intravenous vancomycin
- B. Intravenous gentamicin
- C. Oral metronidazole (Correct Answer)
- D. Oral trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
- E. Oral morphine
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Oral metronidazole***
- The patient's presentation with **watery diarrhea** and **yellow plaques (pseudomembranes) on sigmoidoscopy** after antibiotic therapy is classic for **Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI)**.
- Among the options provided, **oral metronidazole** is the best choice as it achieves therapeutic concentrations in the colonic lumen and has activity against C. difficile.
- Current **IDSA guidelines** recommend oral **vancomycin or fidaxomicin** as first-line therapy for CDI; however, metronidazole remains an acceptable alternative, particularly in resource-limited settings or when first-line agents are unavailable.
- Metronidazole has good **colonic penetration** when administered orally and is effective against anaerobic bacteria including C. difficile.
*Intravenous vancomycin*
- While **vancomycin** is highly effective against C. difficile, it **must be administered orally** to treat CDI because IV vancomycin does not achieve adequate concentrations in the gut lumen.
- Intravenous vancomycin is excreted primarily by the kidneys and does not reach the colonic mucosa in therapeutic amounts.
- IV vancomycin is appropriate for systemic infections like **MRSA bacteremia or endocarditis**, but not for intestinal infections like CDI.
*Intravenous gentamicin*
- **Gentamicin** is an aminoglycoside antibiotic effective against **gram-negative bacteria** but has **no activity against C. difficile**, which is a gram-positive anaerobic bacillus.
- Aminoglycosides carry significant risks of **nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity**, making them inappropriate for this clinical scenario.
- Use of gentamicin would not address the underlying CDI and could worsen outcomes.
*Oral trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole*
- **Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole** is a broad-spectrum antibiotic effective for various infections (UTIs, Pneumocystis, etc.) but has **no significant activity against C. difficile**.
- Continued antibiotic use with agents ineffective against C. difficile could further disrupt normal gut flora and potentially **worsen the CDI**.
*Oral morphine*
- **Morphine** is an opioid analgesic with **no antibacterial properties** and therefore cannot treat bacterial infections like CDI.
- Opioids can actually **slow gastrointestinal motility**, which may worsen outcomes in CDI by prolonging exposure to toxins.
- While it might provide symptomatic relief of abdominal discomfort, it does not address the underlying infection and is contraindicated in infectious diarrhea.
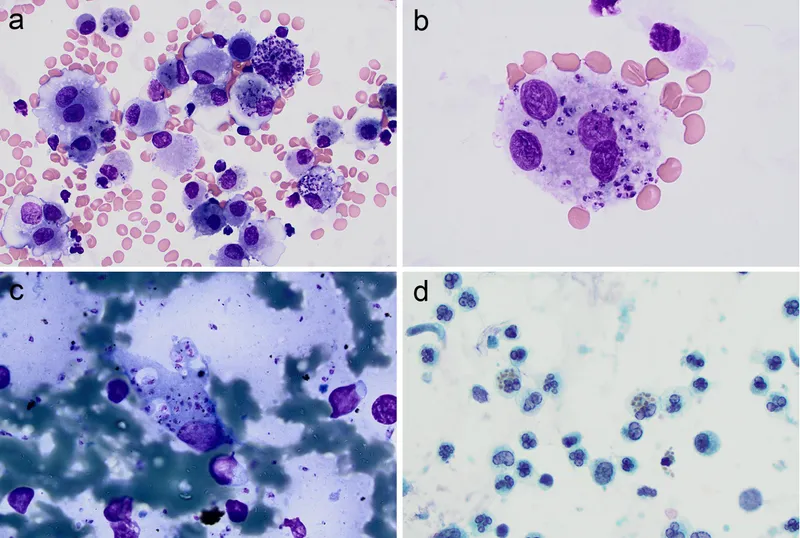
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 4-week history of irritability, diarrhea, and a 2.2-kg (5-lb) weight loss that was preceded by a dry cough. The family returned from a vacation to Indonesia 2 months ago. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Abdominal examination shows mild tenderness with no guarding or rebound and increased bowel sounds. Her leukocyte count is 9,200/mm3 with 20% eosinophils. A photomicrograph of a wet stool mount is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Diethylcarbamazine
- B. Metronidazole
- C. Albendazole (Correct Answer)
- D. Praziquantel
- E. Doxycycline
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Albendazole***
- The image shows a **hookworm egg**, characterized by its thin shell and developing larva inside; clinical features like **eosinophilia**, diarrhea, weight loss, and travel to an endemic area (Indonesia) are consistent with hookworm infection.
- **Albendazole** is the drug of choice for treating hookworm infections and other intestinal nematode infections.
*Diethylcarbamazine*
- This drug is primarily used for treating **lymphatic filariasis** (e.g., Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi) and **Loiasis** (African eye worm).
- It is not effective against hookworm infections.
*Metronidazole*
- **Metronidazole** is an antimicrobial agent effective against certain parasitic infections like **Giardia**, **Entamoeba histolytica**, and bacterial vaginosis.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of hookworm infections.
*Praziquantel*
- **Praziquantel** is an anthelminthic drug primarily used to treat infections caused by **flukes** (e.g., Schistosoma species) and **tapeworms** (e.g., Taenia species).
- It is not effective against hookworm infections.
*Doxycycline*
- **Doxycycline** is a tetracycline antibiotic with broad-spectrum activity against various bacterial infections and is also used in the treatment of some parasitic infections like **malaria prophylaxis** and **filariasis** (due to activity against Wolbachia endosymbionts).
- It is not a primary treatment for hookworm infections.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 3: You are seeing a patient in clinic who recently started treatment for active tuberculosis. The patient is currently being treated with rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. The patient is not used to taking medicines and is very concerned about side effects. Specifically regarding the carbohydrate polymerization inhibiting medication, which of the following is a known side effect?
- A. Vision loss (Correct Answer)
- B. Paresthesias of the hands and feet
- C. Cutaneous flushing
- D. Arthralgias
- E. Elevated liver enzymes
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Vision loss***
- The "carbohydrate polymerization inhibiting medication" refers to **ethambutol**, which inhibits **arabinosyl transferase** (involved in mycobacterial cell wall arabinogalactan synthesis)
- **Ethambutol** causes **optic neuritis**, leading to **decreased visual acuity**, **red-green color blindness**, and potentially **irreversible vision loss**
- **Regular ophthalmologic monitoring** is essential during ethambutol therapy
*Paresthesias of the hands and feet*
- This describes **peripheral neuropathy** caused by **isoniazid**
- Isoniazid interferes with **pyridoxine (vitamin B6) metabolism**, leading to neurotoxicity
- Risk factors include malnutrition, diabetes, alcoholism, and pregnancy
- Prevented by **pyridoxine supplementation**
*Cutaneous flushing*
- Not a characteristic side effect of first-line anti-tuberculosis medications
- More commonly associated with niacin or certain allergic/vasodilatory reactions
*Arthralgias*
- Classic side effect of **pyrazinamide**, often affecting small joints
- Caused by **pyrazinamide-induced hyperuricemia** (inhibits renal uric acid excretion)
- May require dose adjustment or discontinuation if severe
*Elevated liver enzymes*
- **Hepatotoxicity** can occur with **rifampin**, **isoniazid**, and **pyrazinamide**
- Requires regular monitoring of liver function tests during TB treatment
- Most common serious adverse effect of combination TB therapy
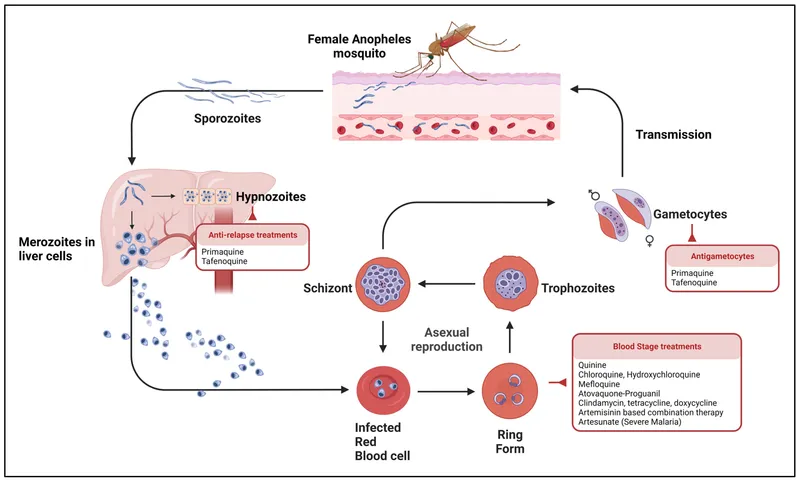
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old male traveler in Thailand experiences fever, headache, and excessive sweating every 48 hours. Peripheral blood smear shows trophozoites and schizonts indicative of Plasmodia infection. The patient is given chloroquine and primaquine. Primaquine targets which of the following Plasmodia forms:
- A. Schizont
- B. Hypnozoite (Correct Answer)
- C. Trophozoite
- D. Merozoite
- E. Sporozoite
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Hypnozoite***
- **Primaquine** is a **radical cure** for malaria caused by *Plasmodium vivax* and *Plasmodium ovale* because it targets the dormant **hypnozoite** forms in the liver.
- The presence of **hypnozoites** leads to relapses, as they can reactivate and re-initiate the erythrocytic cycle.
*Schizont*
- **Schizonts** are merozoite-producing forms in red blood cells (**erythrocytic schizonts**) or liver cells (**hepatic schizonts**).
- While chloroquine targets **erythrocytic schizonts**, primaquine's primary unique action is against the dormant liver stages.
*Trophozoite*
- **Trophozoites** are the feeding and growing stages of the parasite within red blood cells, which mature into schizonts.
- **Chloroquine** is highly effective against **erythrocytic trophozoites** and schizonts, resolving acute malarial symptoms.
*Merozoite*
- **Merozoites** are released from ruptured schizonts and infect new red blood cells during the erythrocytic cycle.
- No specific antimalarial drug solely targets **merozoites** as a primary form; they are an infective stage for red blood cells.
*Sporozoite*
- **Sporozoites** are the forms injected by infected mosquitoes, which then travel to the liver and infect hepatocytes.
- While some drugs like atovaquone have activity against sporozoites, primaquine is specifically indicated for destroying the **hypnozoite** stage, preventing relapses.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 5: A 24-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 4-hour history of headaches, nausea, and vomiting. During this time, she has also had recurrent dizziness and palpitations. The symptoms started while she was at a friend's birthday party, where she had one beer. One week ago, the patient was diagnosed with a genitourinary infection and started on antimicrobial therapy. She has no history of major medical illness. Her pulse is 106/min and blood pressure is 102/73 mm Hg. Physical examination shows facial flushing and profuse sweating. The patient is most likely experiencing adverse effects caused by treatment for an infection with which of the following pathogens?
- A. Candida albicans
- B. Chlamydia trachomatis
- C. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- D. Herpes simplex virus
- E. Trichomonas vaginalis (Correct Answer)
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Trichomonas vaginalis***
- The patient's symptoms (headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, palpitations, facial flushing, sweating) after consuming alcohol while on antimicrobial therapy for a genitourinary infection are characteristic of a **disulfiram-like reaction**.
- **Metronidazole**, a common treatment for *Trichomonas vaginalis* infection, is known to cause a disulfiram-like reaction when combined with alcohol, due to inhibition of **acetaldehyde dehydrogenase**.
*Candida albicans*
- Genitourinary infections with *Candida albicans* (e.g., vulvovaginal candidiasis) are typically treated with **antifungal medications** like fluconazole, which do not cause disulfiram-like reactions with alcohol.
- While symptoms like headache can occur with some antifungals, the constellation of flushing, palpitations, and nausea after a single beer strongly points away from this pathogen.
*Chlamydia trachomatis*
- *Chlamydia trachomatis* is commonly treated with **azithromycin** or **doxycycline**, neither of which are associated with disulfiram-like reactions to alcohol.
- The patient's symptoms are specific to alcohol interaction with certain antimicrobials, not typical side effects of these antibiotics.
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae*
- Infections with *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* are usually treated with **ceftriaxone** (often with azithromycin), which also do not cause disulfiram-like reactions.
- The clinical presentation after alcohol consumption is inconsistent with the typical adverse effects of these treatments.
*Herpes simplex virus*
- Genitourinary infections caused by herpes simplex virus are treated with **antiviral medications** such as acyclovir or valacyclovir.
- These antiviral drugs do not cause disulfiram-like reactions when ingested with alcohol.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 6: A 31-year-old woman presents to your office with one week of recurrent fevers. The highest temperature she recorded was 101°F (38.3°C). She recently returned from a trip to Nigeria to visit family and recalls a painful bite on her right forearm at that time. Her medical history is significant for two malarial infections as a child. She is not taking any medications. On physical examination, her temperature is 102.2°F (39°C), blood pressure is 122/80 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, respirations are 18/min, and pulse oximetry is 99% on room air. She has bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy and a visible, enlarged, mobile posterior cervical node. Cardiopulmonary and abdominal examinations are unremarkable. She has an erythematous induration on her right forearm. The most likely cause of this patient's symptoms can be treated with which of the following medications?
- A. Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine
- B. Atovaquone and azithromycin
- C. Primaquine
- D. Chloroquine
- E. Fexinidazole (Correct Answer)
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Fexinidazole***
- This patient's symptoms (recurrent fevers, cervical lymphadenopathy, erythematous induration after a trip to Nigeria with a painful bite) are highly suggestive of **African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)**.
- **Fexinidazole** is an oral nitroimidazole derivative approved for treating both first and second-stage human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) caused by *Trypanosoma brucei gambiense*.
*Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine*
- This combination is primarily used to treat **toxoplasmosis**, an infection caused by the parasite *Toxoplasma gondii*.
- While it can cause fever and lymphadenopathy, the travel history to Nigeria and a "painful bite" are not typical for toxoplasmosis transmission.
*Atovaquone and azithromycin*
- This combination is utilized for treating **Babesiosis**, a tick-borne parasitic infection.
- While Babesiosis can cause fever and fatigue, the characteristic erythematous induration and prominent lymphadenopathy point away from this diagnosis.
*Primaquine*
- **Primaquine** is an antimalarial drug specifically used for the **radical cure of *Plasmodium vivax*** and ***Plasmodium ovale*** malaria, targeting the hypnozoite liver stages.
- Although the patient has a history of malaria and a travel history to an endemic area, the current presentation with distinct lymphadenopathy and skin lesion points away from a straightforward malarial relapse or new infection primarily requiring primaquine as the sole treatment.
*Chloroquine*
- **Chloroquine** is an antimalarial drug, but its use is limited primarily to areas where **chloroquine-sensitive *Plasmodium falciparum*** strains are prevalent.
- While the patient traveled to Nigeria, a region where malaria is endemic, the specific constellation of symptoms, including the bite and lymphadenopathy, is less characteristic of typical malaria than of trypanosomiasis.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old student arrives to student health for persistent diarrhea. She states that for the past 2 months she has had foul-smelling diarrhea and abdominal cramping. She also reports increased bloating, flatulence, and an unintentional 4 lb weight loss. Prior to 2 months ago, she had never felt these symptoms before. She denies other extra-gastrointestinal symptoms. The patient is an avid hiker and says her symptoms have caused her to miss recent camping trips. The patient has tried to add more fiber to her diet without relief. She feels her symptoms worsen with milk or cheese. Her medical history is insignificant and she takes no medications. She drinks whiskey socially, but denies smoking tobacco or using any illicit drugs. She is sexually active with her boyfriend of 2 years. She went to Mexico 6 months ago and her last multi-day backpacking trek was about 3 months ago in Vermont. Physical examination is unremarkable. A stool sample is negative for fecal occult blood. Which of the following is an associated adverse effect of the most likely treatment given to manage the patient’s symptoms?
- A. Tendon rupture
- B. QT prolongation
- C. Photosensitivity
- D. Disulfiram-like reaction (Correct Answer)
- E. Osteoporosis
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Disulfiram-like reaction***
- The patient's symptoms (foul-smelling diarrhea, bloating, flatulence, weight loss after hiking) are highly suggestive of **Giardiasis**, which is commonly treated with **metronidazole**.
- **Metronidazole** is known to cause a **disulfiram-like reaction** when consumed with alcohol, as it inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase, leading to an accumulation of acetaldehyde.
*Tendon rupture*
- **Tendon rupture** is a well-known adverse effect associated with **fluoroquinolone antibiotics** (e.g., ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin).
- Fluoroquinolones are not the first-line treatment for Giardiasis, and there is no indication for their use in this patient's presentation.
*QT prolongation*
- **QT prolongation** is a potential adverse effect of several medications, including some **macrolide antibiotics** (e.g., azithromycin), certain **antifungals**, and **antiarrhythmics**.
- While some medications used for parasitic infections might rarely cause this, it's not a primary or common side effect of metronidazole.
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** reactions are commonly associated with certain **antibiotics** (e.g., tetracyclines, sulfonamides), **diuretics**, and **NSAIDs**.
- This adverse effect is not typically linked to metronidazole.
*Osteoporosis*
- **Osteoporosis** is a long-term skeletal condition often linked to chronic corticosteroid use, hormonal imbalances, or certain chronic diseases.
- It is not an acute or common adverse effect of anti-parasitic medications like metronidazole.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 8: An experimental drug, ES 62, is being studied. It prohibits the growth of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It is highly lipid-soluble. The experimental design is dependent on a certain plasma concentration of the drug. The target plasma concentration is 100 mmol/dL. Which of the following factors is most important for calculating the appropriate loading dose?
- A. Volume of distribution (Correct Answer)
- B. Half-life of the drug
- C. Therapeutic index
- D. Clearance of the drug
- E. Rate of administration
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: **Volume of distribution**
- The **loading dose** is primarily determined by the desired **plasma concentration** and the **volume of distribution (Vd)**, as it reflects how extensively a drug is distributed in the body.
- The formula for loading dose is: Loading Dose = (Target Plasma Concentration × Vd).
*Half-life of the drug*
- The **half-life** is crucial for determining the **dosing interval** and the time it takes to reach **steady-state concentrations**, not the initial loading dose.
- It reflects the rate at which the drug is eliminated from the body.
*Therapeutic index*
- The **therapeutic index** is a measure of a drug's relative safety, indicating the ratio between the **toxic dose** and the **effective dose**.
- While important for drug safety, it does not directly determine the magnitude of the loading dose itself.
*Clearance of the drug*
- **Clearance** is the rate at which the drug is removed from the body and is a primary determinant of the **maintenance dose** required to sustain a desired plasma concentration.
- It does not directly calculate the initial loading dose needed to achieve an immediate target concentration.
*Rate of administration*
- The **rate of administration** (e.g., infusion rate) primarily influences how quickly the drug reaches its target concentration, but not the total quantity of drug needed for the initial loading dose.
- It affects the kinetics of how the loading dose achieves the target concentration, rather than defining the dose amount.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old man presents for a routine checkup. Past medical history is remarkable for stage 1 systemic hypertension and hepatitis A infection diagnosed 10 years ago. He takes aspirin, rosuvastatin, enalapril daily, and a magnesium supplement every once in a while. He is planning to visit Ecuador for a week-long vacation and is concerned about malaria prophylaxis before his travel. The physician advised taking 1 primaquine pill every day while he is there and for 7 consecutive days after leaving Ecuador. On the third day of his trip, the patient develops an acute onset headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, and fingertips and toes turning blue. His blood pressure is 135/80 mm Hg, heart rate is 94/min, respiratory rate is 22/min, temperature is 36.9℃ (98.4℉), and blood oxygen saturation is 97% in room air. While drawing blood for his laboratory workup, the nurse notes that his blood has a chocolate brown color. Which of the following statements best describes the etiology of this patient’s most likely condition?
- A. The patient’s condition is due to consumption of water polluted with nitrates.
- B. The patient had pre-existing liver damage caused by viral hepatitis.
- C. This condition resulted from primaquine overdose.
- D. It is a type B adverse drug reaction. (Correct Answer)
- E. The condition developed because of his concomitant use of primaquine and magnesium supplement.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***It is a type B adverse drug reaction.***
- The patient's symptoms (headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, cyanosis, chocolate brown blood) are consistent with **methemoglobinemia**, which is a known idiosyncratic reaction to **primaquine**. Type B adverse drug reactions are **unpredictable** and not dose-dependent, representing an individual's unique response to a drug.
- This reaction likely stems from an underlying **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**, making him susceptible to oxidative stress induced by primaquine, leading to methemoglobin formation. The occurrence of symptoms early in the course of medication (3rd day) also supports an idiosyncratic reaction rather than a typical dose-related effect.
*The patient’s condition is due to consumption of water polluted with nitrates.*
- While **nitrate poisoning** can cause methemoglobinemia, the patient’s symptoms appeared shortly after starting primaquine for malaria prophylaxis, making drug-induced methemoglobinemia a more direct and probable cause in this clinical context.
- Exposure to nitrate-polluted water is unlikely to cause a sudden onset of such severe symptoms within 3 days of arrival, especially considering he is taking a known oxidizing agent (primaquine).
*The patient had pre-existing liver damage caused by viral hepatitis.*
- Although **liver dysfunction** can alter drug metabolism, hepatitis A is an acute infection that does not typically cause chronic liver damage leading to altered drug metabolism for primaquine in the long term, especially 10 years after diagnosis.
- The primary risk factor for primaquine-induced methemoglobinemia is G6PD deficiency, not liver damage, which affects red blood cell susceptibility to oxidative stress.
*This condition resulted from primaquine overdose.*
- The prescribed dose of primaquine (one pill daily) is standard for malaria prophylaxis, and there is no indication the patient took more than prescribed. This reaction is likely due to an **idiosyncratic response** rather than an excessive dose.
- Methemoglobinemia from primaquine is often seen in individuals with **G6PD deficiency** even at therapeutic doses, making it an unpredictable Type B adverse reaction rather than a direct dose-dependent toxicity.
*The condition developed because of his concomitant use of primaquine and magnesium supplement.*
- There is no known direct significant **drug interaction** between primaquine and magnesium supplements that would lead to methemoglobinemia.
- The underlying cause of methemoglobinemia with primaquine is typically due to its **oxidative properties** in susceptible individuals (e.g., G6PD deficiency), not an interaction with magnesium.
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old male with diffuse large B cell lymphoma is treated with a chemotherapy regimen including 6-mercaptopurine. Administration of which of the following agents would increase this patient’s risk for mercaptopurine toxicity?
- A. Allopurinol (Correct Answer)
- B. Mesna
- C. Leucovorin
- D. Dexrazoxane
- E. Amifostine
Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) Explanation: ***Allopurinol***
- **Allopurinol** inhibits **xanthine oxidase**, an enzyme responsible for metabolizing **6-mercaptopurine (6-MP)** into inactive metabolites.
- Concurrent administration significantly increases **6-MP levels**, leading to enhanced myelotoxicity and other severe adverse effects.
*Mesna*
- **Mesna** (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate) is a uroprotectant used to prevent **hemorrhagic cystitis** caused by oxazaphosphorine chemotherapy agents like **ifosfamide** and **cyclophosphamide**.
- It does not interact with the metabolism of **6-mercaptopurine**.
*Leucovorin*
- **Leucovorin** (folinic acid) is a rescue agent for **methotrexate toxicity** and enhances the efficacy of **5-fluorouracil**.
- It does not have a direct interaction with the metabolism or toxicity of **6-mercaptopurine**.
*Dexrazoxane*
- **Dexrazoxane** is a cardioprotective agent used to prevent **doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity**.
- It does not interact with the metabolic pathways of **6-mercaptopurine**.
*Amifostine*
- **Amifostine** is a cytoprotective agent that reduces the toxicity of **cisplatin** and **radiation therapy** to normal tissues, particularly the kidneys and salivary glands.
- It is not involved in the metabolism or potentiation of **6-mercaptopurine toxicity**.
More Antiparasitic drugs (antiprotozoals) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.