Antimicrobials

On this page
🎯 Antimicrobial Arsenal: The Precision Medicine Battlefield
Antimicrobials represent humanity's most powerful weapon against infectious disease, yet their misuse threatens to render them obsolete within our lifetime. You'll master how these agents exploit microbial vulnerabilities at the molecular level, develop systematic frameworks for selecting the right drug for each pathogen, and recognize resistance patterns before they compromise patient outcomes. This lesson transforms antimicrobial therapy from memorization into strategic clinical reasoning, equipping you to prescribe with precision while safeguarding these irreplaceable tools for future generations.
📌 Remember: CAMPFIRE - Coverage, Allergies, Metabolism, Penetration, Formulation, Interactions, Resistance, Economics guide every antimicrobial decision
The antimicrobial landscape encompasses 150+ distinct agents across 12 major classes, each with unique spectra, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Beta-lactams dominate with 40% of all prescriptions, while fluoroquinolones account for 15% and macrolides 12%. Understanding this therapeutic hierarchy enables strategic selection based on infection severity, pathogen likelihood, and resistance probability.
| Drug Class | Mechanism | Spectrum | Resistance Rate | Cost Index | Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | Cell wall synthesis | Gram+ primarily | 25-30% S. aureus | $ | First-line strep |
| Cephalosporins | Cell wall synthesis | Broad spectrum | 15-20% E. coli | $ | Surgical prophylaxis |
| Fluoroquinolones | DNA gyrase | Broad spectrum | 30-35% E. coli | $$ | UTI, respiratory |
| Macrolides | Protein synthesis | Atypicals, Gram+ | 20-25% S. pneumo | $ | Atypical pneumonia |
| Aminoglycosides | Protein synthesis | Gram- primarily | 10-15% overall | $ | Severe sepsis |
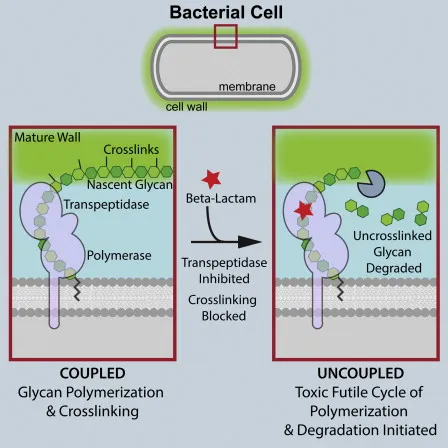
- Bactericidal agents achieve ≥3-log reduction in bacterial counts within 24 hours
- Beta-lactams: 99.9% kill rate at 4x MIC
- Fluoroquinolones: 99.99% kill rate at 8x MIC
- Aminoglycosides: 99.9% kill rate at 10x MIC
- Bacteriostatic agents maintain stable bacterial counts
- Macrolides: Growth inhibition at 2x MIC
- Tetracyclines: 50% growth reduction at 1x MIC
- Chloramphenicol: 90% protein synthesis inhibition
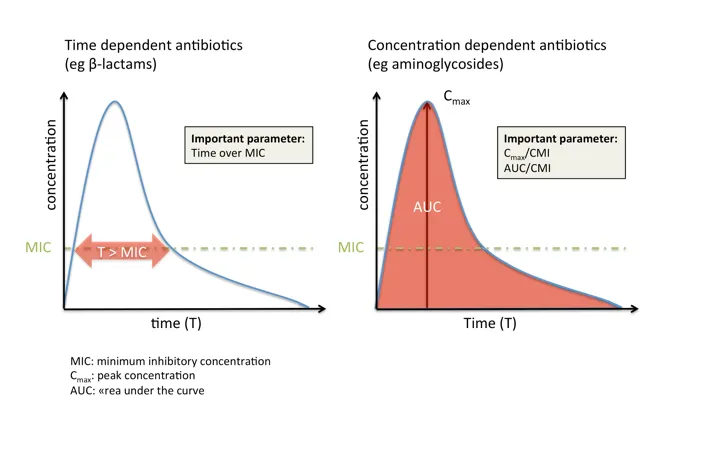
💡 Master This: Time-dependent killing (beta-lactams) requires 40-50% time above MIC, while concentration-dependent killing (fluoroquinolones) needs Cmax/MIC ratio >10 for optimal outcomes
The foundation of antimicrobial mastery rests on understanding that every clinical decision integrates pathogen probability, host factors, and drug characteristics. This systematic approach transforms empiric therapy from educated guessing into evidence-based precision, setting the stage for exploring the intricate mechanisms that govern antimicrobial action.
🎯 Antimicrobial Arsenal: The Precision Medicine Battlefield
⚙️ Mechanism Mastery: The Cellular Warfare Arsenal
📌 Remember: CRISP - Cell wall, Ribosome, Intermediates, Synthesis (DNA), Permeability define the five major antimicrobial targets
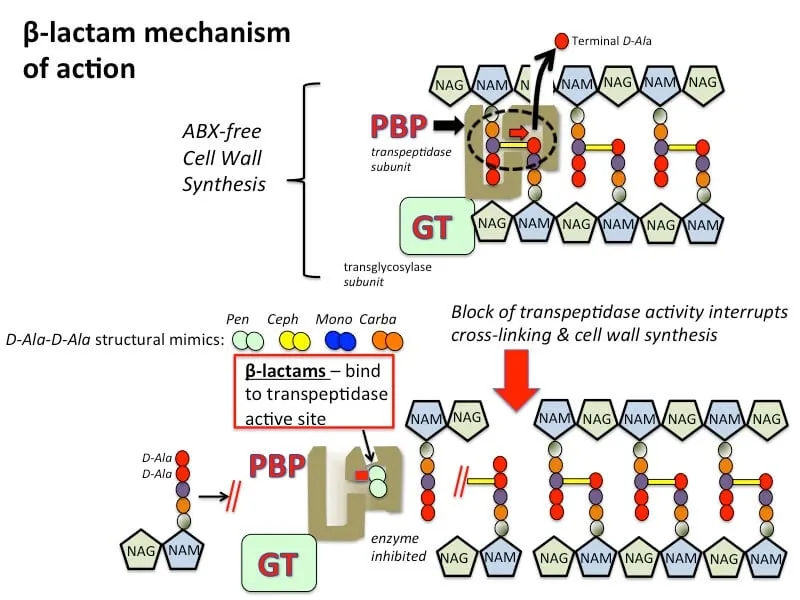
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibition represents the most clinically successful antimicrobial strategy, accounting for 60% of all prescriptions. Beta-lactams bind irreversibly to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), preventing cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains and causing osmotic lysis.
- Penicillins target PBP2 and PBP3 primarily
- Natural penicillins: MIC <0.1 mcg/mL against S. pyogenes
- Antistaphylococcal penicillins: MIC 0.5-2 mcg/mL against MSSA
- Extended-spectrum: MIC 2-8 mcg/mL against Enterobacteriaceae
- Cephalosporins demonstrate generation-specific PBP affinity
- 1st generation: High PBP1 affinity, Gram+ focus
- 3rd generation: Enhanced PBP3 binding, Gram- coverage
- 4th generation: Dual PBP targeting, broad spectrum
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Beta-lactam resistance occurs through three mechanisms-beta-lactamase production (70% of resistance), PBP modification (20%), and efflux pumps (10%)
| Mechanism | Target | Killing Type | Time to Effect | Resistance Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell wall inhibition | PBPs | Bactericidal | 2-4 hours | 15-30% |
| Protein synthesis (30S) | Ribosome | Bactericidal | 1-2 hours | 5-15% |
| Protein synthesis (50S) | Ribosome | Bacteriostatic | 4-6 hours | 10-25% |
| DNA synthesis | Gyrase/Topoisomerase | Bactericidal | 1-3 hours | 20-35% |
| Folate synthesis | DHFR/DHPS | Bacteriostatic | 6-12 hours | 25-40% |
- Aminoglycosides bind 16S rRNA in the 30S subunit
- Cause misreading of mRNA with >95% error rate
- Require oxygen-dependent transport for cellular entry
- Achieve concentration-dependent killing with Cmax/MIC >10
- Macrolides bind 23S rRNA in the 50S subunit
- Block peptide exit tunnel with reversible binding
- Demonstrate tissue concentrations 10-50x serum levels
- Show post-antibiotic effect lasting 2-4 hours
💡 Master This: Ribosomal binding specificity explains why aminoglycosides require aerobic conditions (oxygen-dependent transport) while macrolides work in anaerobic environments (passive diffusion)
DNA Synthesis Disruption through topoisomerase inhibition creates double-strand breaks that trigger bacterial death pathways. Fluoroquinolones demonstrate concentration-dependent killing with mutant prevention windows that minimize resistance development when Cmax/MIC ratios exceed 12.
Understanding these mechanistic principles enables prediction of clinical outcomes, resistance patterns, and optimal dosing strategies, forming the foundation for systematic antimicrobial selection in complex clinical scenarios.
⚙️ Mechanism Mastery: The Cellular Warfare Arsenal
🎯 Clinical Decision Architecture: The Systematic Selection Framework
📌 Remember: SITE-BUGS - Source, Immunocompromised, Timing, Epidemiology determines Bug likelihood, Underlying conditions, Gram stain, Severity guide empiric selection
Source-Based Selection leverages epidemiological data to predict pathogen likelihood with mathematical precision. Each infection site demonstrates characteristic microbiology that guides initial therapy before culture results.
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia
- S. pneumoniae: 35-40% of cases, MIC ≤2 mcg/mL for penicillin
- Atypicals (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia): 15-20%, require macrolide/fluoroquinolone
- H. influenzae: 10-15%, beta-lactamase positive in 30%
- Urinary Tract Infections
- E. coli: 75-85% uncomplicated UTI, fluoroquinolone resistance 25-30%
- Klebsiella: 5-10%, ESBL production in 15-20%
- Enterococcus: 5-15% complicated UTI, ampicillin resistance 20%
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Local antibiograms provide institution-specific resistance patterns-use >30 isolates for statistical validity and update annually for clinical relevance
| Infection Site | Primary Pathogens | First-Line Therapy | Resistance Concerns | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAP (outpatient) | S. pneumo, atypicals | Amoxicillin + macrolide | Pneumococcal resistance 15% | 5-7 days |
| UTI (uncomplicated) | E. coli, Klebsiella | Nitrofurantoin | Fluoroquinolone resistance 25% | 5 days |
| SSTI (cellulitis) | S. pyogenes, S. aureus | Cephalexin | MRSA prevalence 10-15% | 7-10 days |
| IAI (complicated) | Enterobacteriaceae, anaerobes | Piperacillin-tazobactam | ESBL production 15-20% | 7-14 days |
| Sepsis (unknown) | Broad spectrum | Ceftriaxone + vancomycin | Multi-drug resistance 20% | Variable |
- Mild Infections (outpatient management)
- Oral bioavailability >80%: Fluoroquinolones, linezolid, clindamycin
- Single-agent therapy appropriate for immunocompetent hosts
- Narrow spectrum preferred to minimize collateral damage
- Severe Infections (hospitalization required)
- IV therapy ensures predictable levels and rapid onset
- Broader spectrum covers resistant pathogens with 15-20% probability
- Combination therapy for synergy or resistance prevention
💡 Master This: Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic optimization requires time above MIC >40% for beta-lactams and AUC/MIC >125 for fluoroquinolones to achieve bacteriological cure rates >90%
Host Factor Integration modifies antimicrobial selection based on patient-specific variables that affect drug disposition, toxicity risk, and treatment response. These factors can alter cure rates by 20-30% when not properly considered.
- Renal Impairment (CrCl <50 mL/min)
- Dose reduction required for 60% of antimicrobials
- Avoid nephrotoxic agents: Aminoglycosides, vancomycin high-dose
- Preferred agents: Beta-lactams with hepatic elimination
- Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh B/C)
- Avoid hepatotoxic agents: Isoniazid, ketoconazole, high-dose acetaminophen
- Dose reduction for hepatically metabolized drugs
- Monitor levels for narrow therapeutic index agents
This systematic framework enables evidence-based selection that optimizes clinical outcomes while minimizing resistance development and adverse effects, preparing clinicians for the complex comparative analysis required in challenging clinical scenarios.
🎯 Clinical Decision Architecture: The Systematic Selection Framework
🔍 Resistance Pattern Recognition: The Molecular Detective Framework
📌 Remember: BETA-PUMP - Beta-lactamase, Efflux, Target modification, Altered permeability, Pump overexpression, Uptake reduction, Metabolic bypass, Plasmid transfer describe resistance mechanisms
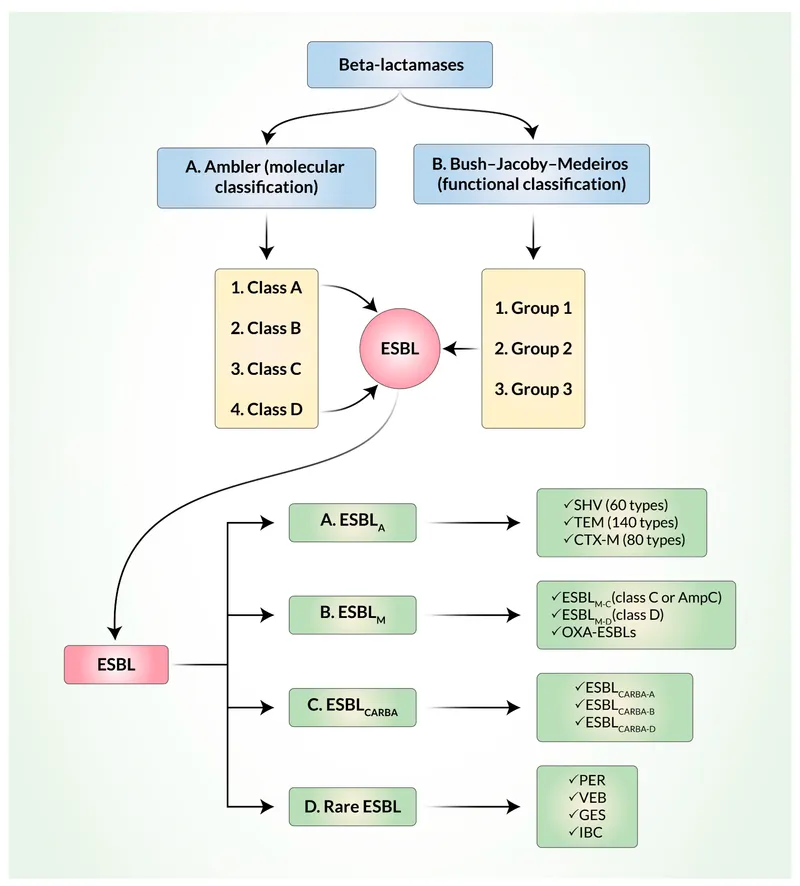
Beta-lactamase Production represents the most common resistance mechanism, affecting >70% of clinical isolates in many institutions. These enzymes demonstrate class-specific substrate preferences and inhibitor susceptibility patterns that guide therapeutic selection.
- Class A Beta-lactamases (TEM, SHV, CTX-M)
- TEM-1: Hydrolyzes penicillins and early cephalosporins
- ESBL variants: Extend spectrum to 3rd generation cephalosporins
- Inhibitor susceptibility: Clavulanate, sulbactam, tazobactam
- Class B Metallo-beta-lactamases (NDM, VIM, IMP)
- Carbapenem hydrolysis: MIC >8 mcg/mL for meropenem
- Zinc-dependent: EDTA inhibition in laboratory testing
- No inhibitor available: Requires alternative drug classes
| Resistance Mechanism | Frequency | Affected Drugs | Clinical Impact | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-lactamase (Class A) | 60-70% | Penicillins, cephalosporins | Moderate | Nitrocefin test |
| ESBL production | 15-25% | 3rd gen cephalosporins | High | Double-disk synergy |
| Carbapenemase (Class B) | 5-10% | Carbapenems | Critical | Modified Hodge test |
| Efflux pumps | 20-30% | Fluoroquinolones | Moderate | Efflux inhibitor assay |
| Target modification | 10-20% | Macrolides, lincosamides | Variable | Molecular testing |
Efflux Pump Overexpression creates multidrug resistance by actively removing antimicrobials from bacterial cells. These pumps demonstrate substrate specificity and energy requirements that influence resistance patterns and therapeutic options.
- AcrAB-TolC (Enterobacteriaceae)
- Fluoroquinolone efflux: MIC increases 8-32 fold
- Beta-lactam efflux: Variable effect depending on pump expression
- Inhibitor development: Phenylalanine-arginine beta-naphthylamide (PAβN)
- MexAB-OprM (P. aeruginosa)
- Broad substrate range: Fluoroquinolones, beta-lactams, chloramphenicol
- Constitutive expression: 10-15% of clinical isolates
- Clinical significance: Treatment failure with standard dosing
💡 Master This: Pump-mediated resistance often affects multiple drug classes simultaneously-look for parallel resistance patterns in fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, and chloramphenicol
Target Modification alters antimicrobial binding sites through point mutations or enzymatic modification, reducing drug affinity and therapeutic efficacy. These modifications often demonstrate stepwise accumulation that progressively increases MIC values.
- Fluoroquinolone Resistance (gyrA, parC mutations)
- Single mutation: MIC increase 4-8 fold
- Double mutation: MIC increase 16-64 fold
- Clinical breakpoint: MIC >4 mcg/mL for ciprofloxacin
- Macrolide Resistance (23S rRNA methylation)
- Erm methylases: High-level resistance to all macrolides
- Cross-resistance: Lincosamides and streptogramin B
- Inducible expression: Clindamycin testing requires D-test
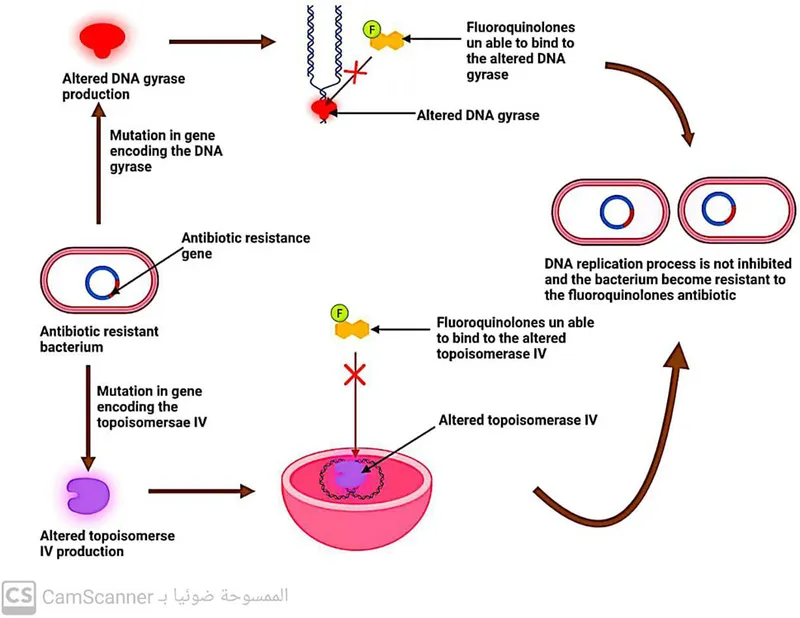
Epidemiological Surveillance reveals resistance trends that guide empiric therapy and infection control measures. National surveillance programs provide annual resistance data with statistical significance for clinical decision-making.
Understanding resistance patterns enables proactive therapeutic strategies that maintain clinical efficacy while minimizing resistance selection pressure, setting the foundation for evidence-based treatment algorithms that optimize patient outcomes.
🔍 Resistance Pattern Recognition: The Molecular Detective Framework
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm Mastery: The Evidence-Based Decision Engine
📌 Remember: STREAM - Source control, Timing, Resistance patterns, Escalation/de-escalation, Adverse effects, Monitoring guide treatment optimization
Empiric Therapy Optimization requires rapid initiation within 1 hour for sepsis and 3 hours for severe infections. Delayed therapy increases mortality by 7.6% per hour in septic shock, making systematic selection critical for patient survival.
- Sepsis Management (qSOFA ≥2 or SIRS criteria)
- Blood cultures before antibiotics (>90% compliance target)
- Broad-spectrum coverage: Piperacillin-tazobactam or carbapenem
- MRSA coverage: Vancomycin if risk factors present
- Antifungal therapy: Candidemia risk >10% in ICU patients
- Pneumonia Algorithms (CAP vs HAP/VAP)
- CAP severity: CURB-65 score guides inpatient vs outpatient
- HAP/VAP: Onset timing determines resistance probability
- Atypical coverage: Required for severe CAP (ICU admission)
| Clinical Syndrome | Empiric Therapy | Duration | De-escalation Trigger | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncomplicated UTI | Nitrofurantoin 100mg BID | 5 days | Culture sensitivity | 95% |
| Severe CAP | Ceftriaxone + azithromycin | 7-10 days | Clinical improvement | 90% |
| HAP/VAP | Piperacillin-tazobactam | 7-8 days | Negative cultures | 85% |
| Complicated IAI | Ertapenem | 7-14 days | Source control + cultures | 88% |
| Septic shock | Meropenem + vancomycin | Variable | Pathogen identification | 75% |
De-escalation Strategies optimize spectrum narrowing based on culture results, clinical response, and biomarker trends. Successful de-escalation occurs in 60-70% of cases when systematic protocols are followed.
- Culture-Directed Therapy
- Pathogen identification: Switch to narrow spectrum within 48-72 hours
- Susceptibility testing: MIC values guide optimal agent selection
- Combination therapy: Discontinue when synergy not required
- Clinical Response Monitoring
- Fever resolution: Expected within 72 hours for most infections
- Biomarker trends: CRP reduction >50% indicates therapeutic response
- Organ function: Improvement supports therapy continuation
💡 Master This: Antibiotic duration should be pathogen-specific-S. aureus bacteremia requires minimum 14 days, while uncomplicated gram-negative bacteremia needs only 7-10 days
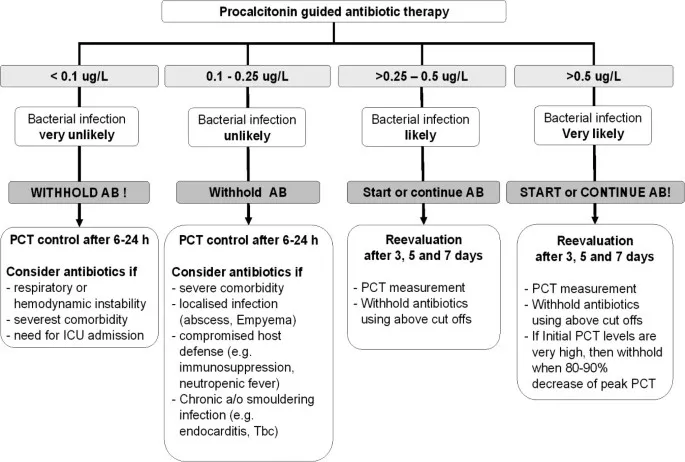
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring ensures optimal exposure for concentration-dependent and narrow therapeutic index antimicrobials. TDM-guided dosing improves cure rates by 15-20% and reduces toxicity by 30-40%.
- Vancomycin Monitoring
- Target trough: 15-20 mcg/mL for serious infections
- AUC/MIC target: >400 for optimal efficacy
- Nephrotoxicity risk: Trough >20 mcg/mL increases risk 3-fold
- Aminoglycoside Monitoring
- Peak levels: 5-10 mcg/mL for gentamicin/tobramycin
- Trough levels: <2 mcg/mL to minimize toxicity
- Extended-interval dosing: Single daily dose with 24-48 hour intervals
Combination Therapy Indications include severe sepsis, resistant pathogens, and specific synergistic combinations. Inappropriate combination therapy increases costs by 40-60% without clinical benefit.
- Synergistic Combinations
- Beta-lactam + aminoglycoside: Enterococcal endocarditis
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole: Pneumocystis pneumonia
- Rifampin combinations: Staphylococcal prosthetic infections
- Empiric Combinations
- Anti-MRSA + anti-Pseudomonas: Severe HAP/VAP
- Antifungal + antibacterial: Neutropenic fever
- Duration limitation: 48-72 hours until cultures available
These evidence-based algorithms provide systematic frameworks for complex clinical decisions, ensuring optimal outcomes while minimizing resistance development and adverse effects, preparing clinicians for advanced integration of antimicrobial stewardship principles.
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm Mastery: The Evidence-Based Decision Engine
🔗 Stewardship Integration: The Resistance Prevention Ecosystem
📌 Remember: IMPROVE - Indication review, Monitoring parameters, Prophylaxis optimization, Route conversion, Optimization dosing, Verification cultures, Education programs drive stewardship success
Core Stewardship Interventions target high-impact opportunities where systematic changes produce measurable improvements in antimicrobial use and resistance patterns. These interventions demonstrate return on investment of $3-7 for every $1 invested.
- Prospective Audit and Feedback
- Daily review of broad-spectrum antimicrobials
- Pharmacist-physician collaboration with >95% acceptance rates
- Intervention documentation with outcome tracking
- Cost savings: $200,000-500,000 annually per 300-bed hospital
- Preauthorization Programs
- Restricted antimicrobials: Carbapenems, anti-MRSA agents, antifungals
- Approval criteria: Evidence-based indications with clinical justification
- Response time: <2 hours for urgent requests
- Compliance rates: >90% with appropriate use criteria
| Intervention Type | Target Drugs | Reduction Achieved | Implementation Time | Sustainability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prospective audit | Broad-spectrum | 20-30% use reduction | 3-6 months | High |
| Preauthorization | Restricted agents | 40-50% use reduction | 6-12 months | Moderate |
| Clinical pathways | Syndrome-specific | 15-25% duration reduction | 6-9 months | High |
| Rapid diagnostics | Culture-dependent | 1-2 day duration reduction | 3-6 months | High |
| Education programs | All antimicrobials | 10-15% inappropriate use | 12-18 months | Variable |
Diagnostic Stewardship optimizes test utilization and result interpretation to guide antimicrobial decisions. Inappropriate testing leads to false-positive results in 5-10% of cases, driving unnecessary antimicrobial use.
- Blood Culture Optimization
- Appropriate indications: Fever + SIRS criteria or clinical suspicion
- Contamination rates: Target <3% through proper technique
- Volume requirements: 20-30 mL total for optimal sensitivity
- Timing considerations: Before antimicrobials when clinically feasible
- Molecular Diagnostics Integration
- Syndromic panels: Respiratory, GI, CNS pathogen detection
- Resistance gene detection: mecA, vanA/B, carbapenemase genes
- Turnaround time: 1-6 hours vs 24-72 hours for culture
- Clinical impact: Therapy modification in 60-80% of cases
💡 Master This: Biomarker-guided therapy using procalcitonin and C-reactive protein reduces antibiotic duration by 2-3 days and mortality by 10-15% in respiratory tract infections
Antimicrobial Cycling and Heterogeneity Strategies manage selective pressure to prevent resistance emergence. Cycling programs rotate antimicrobial classes every 3-6 months, while heterogeneity promotes simultaneous use of different classes.
- Cycling Implementation
- Class rotation: Fluoroquinolones → Beta-lactams → Carbapenems
- Duration: 3-6 month cycles with resistance monitoring
- Compliance: >80% adherence required for effectiveness
- Outcomes: Variable results depending on baseline resistance
- Heterogeneity Approaches
- Unit-based diversity: Different ICUs use different protocols
- Patient-level mixing: Random assignment to equivalent regimens
- Theoretical advantage: Reduced selective pressure per antimicrobial class
Outpatient Stewardship addresses 80% of antimicrobial prescriptions through clinical decision support, patient education, and provider feedback. Inappropriate outpatient prescribing accounts for 30-50% of antimicrobial use.
- Acute Respiratory Infections
- Viral etiology: >90% of upper respiratory infections
- Antibiotic prescribing: Reduced from 80% to 20% with stewardship
- Patient satisfaction: Maintained with appropriate education
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria: No treatment except pregnancy
- Duration optimization: 3-5 days for uncomplicated cystitis
- Fluoroquinolone restriction: Reserve for complicated infections
Economic Impact Assessment demonstrates stewardship value through cost reduction, length of stay decrease, and resistance prevention. Comprehensive programs achieve net savings of $500,000-2,000,000 annually.
This integrated approach creates sustainable antimicrobial use patterns that preserve therapeutic options for future generations while optimizing current patient outcomes, establishing the foundation for rapid clinical mastery tools.
🔗 Stewardship Integration: The Resistance Prevention Ecosystem
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Rapid-Fire Reference System
📌 Remember: MASTER-ID - Mechanism knowledge, Allergy assessment, Spectrum matching, Toxicity awareness, Efficacy optimization, Resistance prevention, Interaction screening, Duration optimization
Essential Clinical Thresholds provide quantitative benchmarks for therapeutic decision-making. These evidence-based cutpoints guide drug selection, dosing optimization, and monitoring requirements with mathematical precision.
- Pharmacokinetic Targets
- Beta-lactams: Time above MIC >40-50% for bactericidal effect
- Fluoroquinolones: AUC/MIC >125 and Cmax/MIC >10
- Vancomycin: AUC/MIC >400 for serious infections
- Aminoglycosides: Cmax/MIC >8-10 for optimal killing
- Resistance Breakpoints
- MRSA prevalence >10-15%: Empiric anti-MRSA therapy
- ESBL rate >20%: Avoid 3rd generation cephalosporins
- Fluoroquinolone resistance >25%: Alternative agents preferred
- Carbapenem resistance >5%: Combination therapy consideration
| Clinical Scenario | Key Threshold | Therapeutic Implication | Monitoring Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe sepsis | qSOFA ≥2 | Broad-spectrum within 1 hour | Lactate clearance |
| MRSA risk | Prevalence >15% | Empiric vancomycin | Trough levels |
| Renal impairment | CrCl <50 mL/min | Dose adjustment required | Serum creatinine |
| C. diff risk | Prior antibiotics | Avoid fluoroquinolones | Stool testing |
| Neutropenia | ANC <500 | Empiric broad-spectrum | Daily CBC |
Rapid Resistance Recognition enables real-time therapeutic adjustments based on phenotypic patterns and molecular markers. Pattern recognition prevents clinical failures and guides alternative therapy.
- Beta-lactamase Patterns
- AmpC production: Ceftazidime susceptible, ceftriaxone resistant
- ESBL production: Ceftazidime resistant, clavulanate synergy
- Carbapenemase: Meropenem resistant, colistin susceptible
- Efflux Pump Indicators
- Parallel resistance: Fluoroquinolones + tetracyclines + chloramphenicol
- MIC elevation: 4-32 fold increase across multiple classes
- Pump inhibitor effect: MIC reduction with efflux blockers
💡 Master This: "SPACE" organisms (Serratia, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Citrobacter, Enterobacter) have inducible AmpC-avoid 3rd generation cephalosporins for serious infections
Dosing Optimization Algorithms ensure therapeutic efficacy while minimizing toxicity through patient-specific calculations and real-time adjustments. Precision dosing improves cure rates by 15-20%.
- Renal Dose Adjustments
- CrCl 30-50 mL/min: 50-75% of normal dose
- CrCl 10-30 mL/min: 25-50% of normal dose
- CrCl <10 mL/min: 10-25% of normal dose or alternative agent
- Hepatic Dose Modifications
- Child-Pugh A: Normal dosing for most agents
- Child-Pugh B: 50-75% dose reduction for hepatically metabolized
- Child-Pugh C: Avoid hepatotoxic agents, consider alternatives
Clinical Decision Shortcuts provide systematic approaches for common scenarios that achieve optimal outcomes through evidence-based protocols. These mental models accelerate clinical reasoning and reduce errors.
- The "SNAP" Assessment (Severity, Neutropenia, Allergies, Pathogens)
- Severity: Mild = oral, Moderate = IV, Severe = broad-spectrum
- Neutropenia: ANC <500 = anti-Pseudomonas coverage
- Allergies: True penicillin allergy = avoid all beta-lactams
- Pathogens: Local resistance patterns guide empiric selection
- The "STOP" Criteria (Source control, Targeted therapy, Optimization, Prevention)
- Source control: Drainage, debridement, device removal
- Targeted therapy: Culture-directed within 48-72 hours
- Optimization: PK/PD targets and TDM when indicated
- Prevention: Duration limits and resistance monitoring
This comprehensive mastery framework transforms antimicrobial complexity into systematic clinical excellence, enabling rapid decision-making that optimizes patient outcomes while preserving antimicrobial effectiveness for future therapeutic challenges.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Rapid-Fire Reference System
Practice Questions: Antimicrobials
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 64-year-old woman with a past medical history of poorly managed diabetes presents to the emergency department with nausea and vomiting. Her symptoms started yesterday and have been progressively worsening. She is unable to eat given her symptoms. Her temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 115/68 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for left-sided costovertebral angle tenderness, and urinalysis demonstrates bacteriuria and pyuria. The patient is admitted to the hospital and started on IV ceftriaxone. On day 3 of her hospital stay she is afebrile, able to eat and drink, and feels better. Which of the following antibiotic regimens should be started or continued as an outpatient upon discharge?













